From this article you will learn:
- treatment of gums for inflammation - drugs, regimens,
- means for strengthening gums,
- best ointment for teething gums.
The article was written by a dentist with more than 19 years of experience.
In this article, we will conduct a detailed analysis of which gel for gum disease will be most effective, and which of them can also be used to relieve teething symptoms. It should be noted that it is advisable to treat gums only with drugs in the form of gels, because they have the property of being well fixed to the moist mucous membrane of the oral cavity.
But fat-based products, for example, ointment for gums against inflammation, are pointless to use for two reasons. Firstly, the active components from such a fatty base practically do not penetrate the mucous membranes. And secondly, fatty substances adhere very poorly to moist mucous membranes, and therefore, immediately after application, the ointment is quickly swallowed with saliva.
Gel for gums for inflammation -
Preparations for the treatment of gum inflammation in the form of gels are best combined with antiseptic rinses. Then you will be able to carry out an almost complete professional course of anti-inflammatory therapy, which a dentist would prescribe for you. In this article we will tell you in detail how you should use dental gel for gums (including in combination with rinsing your mouth with antiseptics). But you must understand that without removing tartar from a dentist, the effect of such therapy will not be very long-lasting.
Gel and ointment for gums - application diagram
The standard course of anti-inflammatory therapy for gingivitis and periodontitis takes 10 days.
This course should include - 1) antiseptic rinses, 2) gel applications on the gums, 3) anti-inflammatory toothpaste. Usually 10 days is enough if you went to the dentist and had dental plaque removed. Remember that it is supra- and subgingival dental plaque (consisting of pathogenic bacteria) that causes gum inflammation. Therefore, the most important thing you can do before starting a course of gum gel applications is to go for ultrasonic teeth cleaning. If you use the gel for gum inflammation without removing plaque, then such anti-inflammatory therapy will only have a short-term effect. Carrying out a course of antiseptic rinses and gel applications on the gums is quite simple, using our recommendations. Let us remind you that the author of the article is a dentist with 20 years of experience, of which at least 10 years were devoted to periodontal treatment (treatment of gum inflammation, open curettage and flap operations).
Anti-inflammatory therapy regimen –
Gum treatment is carried out 2 times a day (morning and evening). It looks like this: first you have breakfast, then you need to brush your teeth and after oral hygiene, perform an antiseptic rinse. You need to rinse your mouth with chlorhexidine for 1 minute, but if you use “Parodontocid mouthwash” with anti-inflammatory components, then you can do it for 2-3 minutes (after rinsing your mouth, do not rinse your mouth with water under any circumstances).
If you rinsed your mouth with chlorhexidine, then the gel can be applied to the gums immediately, but if you rinsed your mouth with periodonticide, it is better after 5-10 minutes. This is due to the fact that after rinsing with chlorhexidine, a layer of chlorhexidine bigluconate is formed on the teeth and gums, which cannot be washed off by saliva, which will be effective for up to 7 hours. And after rinsing with periodonticide, such a layer does not form, but after spitting the solution in the oral cavity, its high residual concentration still remains for some time (and you need to give it time to act on the gums).
Next, we proceed to applying the gel to the gums -
The gel should be applied to the marginal gum around the necks of the teeth and interdental (gingival) papillae. The gel should be applied to the gums - both from the front surface of the teeth and from the side of the tongue/palate. It would be optimal if you dry the gums with a dry gauze pad before applying the gel, because in this case, the gel will adhere better to the mucous membrane. Next, there are 2 options for applying the gel.
Firstly, you simply squeeze out portions of the gel onto your finger and apply them to the gums around the necks of the teeth. Or the second option - you first rub a small portion of the gel into the gum, and then re-apply another portion of the gel onto it and leave it alone (without massaging). During the application of the gel, as well as after treatment, you will produce saliva - no need to accumulate it or spit it out. Behave as usual, swallowing a portion of saliva, as it happens in normal life (swallowing part of the gel is absolutely harmless).
Next, it is very important - you should not rinse your mouth or eat food for several hours (it is advisable not to even drink for at least 30 minutes). The second session of applying the gel to the gums is carried out in the evening - according to the same scheme, i.e. after eating and oral hygiene, after which it is already carried out - first rinsing the mouth with an antiseptic, and it all ends with applying the gel to the gums. And so on for 10 days.
Important: in parallel, there must be very good proper oral hygiene, which should include not only toothbrush and toothpaste, but also, ideally, dental floss. If teeth are brushed irregularly or poorly, there will still be a lot of microbial plaque on them, and there will also be food residues in the interdental spaces. And in this case, treatment will be ineffective. For the rules of oral hygiene, see the link below, but if you are not ready for such rules, gum inflammation will be your constant companion.
→ How to brush your teeth properly
Drugs for the treatment of stomatitis
How to treat stomatitis in adults and children?
In the pharmacy you can find a huge number of drugs that help in the fight against stomatitis, the cause of its occurrence and symptoms.
Most of them are sold without a prescription, so anyone can purchase the drug. In the treatment of stomatitis, an integrated approach is used: it is necessary to influence the cause of the disease, as well as alleviate the severity of symptoms.
Painkillers
If the ulcers interfere with eating and talking, or cause great discomfort for the patient, it is considered advisable to prescribe painkillers for topical use. These include:
- Anestezin is available in tablet form for grinding into powder. It has a local analgesic effect on the mucous membrane in the affected area.
- Hexoral is an effective tablet for resorption in the mouth, helping in the fight against ulcerative lesions of the mucous membrane. They have a double result - the drug has an antibacterial and anesthetic effect.
- Lidocaine Asept is available in the form of a spray, which is convenient for topical use. The drug contains lidocaine and chlorhexidine: they provide a disinfecting and analgesic effect. This spray is preferable for ulcerative stomatitis.
- Lidochlor - this gel relieves pain and has an antibacterial effect on the oral mucosa, relieves inflammation.
Herbal remedies - a decoction of chamomile, calendula, sage, also have some antiseptic properties and have a calming effect on the mucous membrane. They help relieve inflammation and relieve swelling of the affected mucosa.
Antiseptics and anti-inflammatory drugs
These drugs are the basis for the treatment of stomatitis. They are produced in the form of tablets for resorption in the oral cavity, in the form of sprays for irrigation of the mucous membranes, ointments, gels, etc.
- Kamistad - contains chamomile, which provides relief from inflammation and a calming effect. Lidocaine has an analgesic effect on the affected mucous membrane.
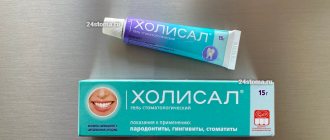
- Cholisal is available in gel form. Has an excellent anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effect.
- Stomatidine (hexetidine) is an antiseptic drug widely used in dental practice.
- Cametone – contains essential oils, has an antimicrobial and local anesthetic effect. Sold in pharmacy chains in the form of an aerosol or spray.
Ingalipt and Hexoral sprays are also used for topical use for stomatitis. They prevent the spread of infection in the oral cavity and speed up the onset of recovery.
Special products for the treatment of stomatitis in adults
Depending on the cause of the development of stomatitis - a fungus, a virus or a bacterium, specific medications are selected.
Acyclovir, Zovirax are used to combat herpetic stomatitis; in some cases, it is advisable to use interferons. When treating fungal stomatitis, the doctor may prescribe Mycozon, Levorin, nystatin ointment, etc. Bacterial stomatitis requires the prescription of antibiotics, taking into account the sensitivity of microorganisms.
Drugs that enhance regeneration
In this case, drugs that accelerate the healing process of damaged mucous membranes can help.
- Solcoseryl - this medicine is often used in the practice of a dentist. Available in the form of a paste, which must be applied to the lesions. Solcoseryl helps improve trophic processes and accelerates tissue regeneration;
- Sea buckthorn oil is an excellent natural remedy; it helps accelerate the healing of mouth ulcers;
- Vinylin is an antiseptic balm. The principle of action is to envelop the ulcers and heal them more quickly;
- Proposol spray - the effect of the drug is based on propolis.
In the case of an allergic form of pathology, the first step in treatment is the identification and exclusion of the allergen. Some people may experience an allergic reaction after getting braces or dentures, or when using a new drug. Since ulcers in this form of stomatitis are a symptom of the body’s reaction to an allergen, it is the allergy that must be eliminated first. Antihistamines are used for this purpose. You can take them in the form of tablets or applications to the mucous membrane.
There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Anti-inflammatory toothpastes –
There are very good toothpastes with anti-inflammatory components that can quickly reduce the symptoms of inflammation, relieve bleeding and swelling of the gums. Such pastes can be an excellent addition to the course of anti-inflammatory therapy, which we described above. But there is one subtlety with the choice of toothpastes. Scientific studies (source) have shown that chlorhexidine can be inactivated by sodium lauryl sulfate, which is part of toothpastes.
The fact is that after brushing your teeth with paste and rinsing your mouth with water, a thin layer of surfactants and copolymers (including sodium lauryl sulfate) still remains on the teeth and mucous membrane. And because We prescribe mouth rinses with chlorhexidine - immediately after oral hygiene in the morning or evening, then the presence of sodium lauryl sulfate in toothpaste quite significantly reduces the antimicrobial activity of chlorhexidine (especially if you decide to use its lowest 0.05% concentration).
Important: studies have shown that after brushing your teeth with a paste containing sodium lauryl sulfate, ideally 2 hours should pass (at least 30 minutes, but this is not enough) so that this does not affect the antimicrobial effect of chlorhexidine. Therefore, if you are going to use chlorhexidine as a mouth rinse, we recommend buying toothpaste without sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS). Here we can recommend you anti-inflammatory toothpastes or “President”, which do not contain sodium lauryl sulfate.
Read more about all the best toothpastes for strengthening gums at the link below. → Rating of toothpastes for gum inflammation
An example of an excellent paste without lauryl sulfate (SLS) -
Types of ointments
The main difference between drugs of this form lies in their composition - it is the properties of the main component that determine the ability of the drug to destroy one or several different pathogens. Based on this principle, four types of ointments have been developed against different types of this disease:
- for the treatment of herpes stomatitis resulting from damage to the body by a virus;
- against aphthous stomatitis associated with poor oral hygiene (considered the most common form of the disease);
- for the treatment of candidal stomatitis, which is often found in children and has another common name - “thrush”;
- universal drugs suitable for eliminating all types of stomatitis.
However, to decide what to apply to a child’s stomatitis, knowing only the main effect of the main component is not enough. Therefore, to choose the right ointment, you need to familiarize yourself with the most popular ones.
Holisal
Cholisal is a universal ointment suitable for the treatment of all types of stomatitis, including fungal. It is capable of providing local analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects. Prescribed primarily for children over 1 year of age.
- Ingredients: Cetalkonium chloride and Choline salicylate.
- Application : apply 2-3 times a day after meals, as well as at night. To treat a child, squeeze 5 mm of ointment onto a clean finger and rub it into the affected areas of the oral cavity.
- Contraindications : intolerance to salicylates and other components. Not recommended for treating children under 1 year of age.
Oxolinic ointment
A drug based on oxoline (0.25%) is an effective remedy for getting rid of stomatitis caused by herpes viruses, influenza and adenoviruses. It is especially often prescribed to neutralize this disease in a child.
- Composition : Oxolin.
- Application : a certain amount of ointment is rubbed into the affected areas of the oral cavity 2-3 times a day.
- Contraindications : oxolin-containing products are prohibited for use in the presence of any drug allergies.
Bonafton
This drug has an antiviral effect and is intended to combat stomatitis caused by the Herpes simplex virus and adenoviruses.
- Ingredients : Bromonaphthoquinone.
- Application : a small amount of the product should be applied to the affected areas 3-4 times a day and left for a maximum of 5-10 minutes.
- Contraindications: the drug is contraindicated for use if the child has a hypersensitivity to its components.
Acyclovir ointment
It is one of the drugs prescribed for the treatment of herpetic stomatitis in a child.
- Composition : thymidine nucleoside analogue of synthetic origin.
- Application : acyclovir ointment should be rubbed into the surface of the affected areas every 4 hours. The duration of treatment is determined by the pediatrician individually.
- Contraindications : the presence of individual intolerance to the constituent ingredients.
Tebrofen ointment
It has antiviral properties and is prescribed to combat stomatitis caused by various types of viruses.
- Composition: Tetrabromotetrahydroxydiphenyl.
- Application : a certain amount of 2% ointment is applied to the inflamed areas 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 1 week.
- Contraindications: increased sensitivity to the components of the ointment.