"OKI" is a drug that has anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and analgesic effects. Available in different forms:
- granules (used to prepare a solution to be taken orally);
- suppositories (candles) for children;
- suppositories (candles) for adults;
- solution (applied externally).
In all cases, the active ingredient is ketoprofen in the form of lysine salt. The drug is dispensed without a prescription, with the exception of granules. Storage conditions are standard - room temperature (no more than 25 degrees), moderate humidity, no access to children. The general shelf life is 2 years for solution, 3 years for suppositories for children, 5 years for suppositories for adults and 3 years for granules.
Solution "OKI": indications for use
The drug is indicated for use by adults and children over 7 years of age. Adults use medications to treat certain joint diseases associated with inflammatory processes:
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- spondyloarthritis;
- osteoarthritis;
- gouty type arthritis;
- inflammation in the area of periarticular tissue.
For children, the drug is indicated to relieve inflammatory processes that manifest themselves against the background of:
- otitis;
- diseases of bones, joints;
- postoperative complications.
The solution is also used for gargling in the treatment of such pathologies;
- pharyngitis;
- stomatitis;
- chronic periodontal disease;
- tonsillitis;
- gingivitis;
- angina;
- glossitis;
- laryngitis.
Less commonly, the product is used during dental interventions. In this case, “OKI” is used as an anesthetic drug.
Why do you need a mouth rinse?
Mouthwash is an additional oral care product and does not replace toothpaste. Using a mouthwash slows down the formation of plaque and freshens breath.
Why else do you need a rinse aid?
- For the treatment of gum disease
to reduce inflammation and bleeding. - To protect sensitive enamel
: the rinse envelops it with a biofilm, which acts as a shield. - For antibacterial treatment
of the entire mucous membrane: this is important after surgical interventions and tooth extraction. - For the treatment and relief of symptoms of dry mouth
, xerostomia. - whitening or fluoridation
procedures , or the effect of a whitening or remineralizing paste. - To eliminate volatile sulfur compounds - the causes of unpleasant odors
.
Contraindications
In some cases, the use of all forms of the drug is excluded:
- increased sensitivity to individual components;
- Aspirin asthma;
- gastrointestinal ulcers in the acute stage;
- ulcerative colitis;
- Crohn's disease;
- blood clotting problems, including hemophilia;
- chronic kidney disease;
- diverticulitis;
- pregnancy (last stage);
- lactation period;
- children under 6 years of age (for using candles - children under 18 years of age).
In some cases, there is no strict prohibition on taking the drug. Patients with the following disorders can use it with caution:
- anemia;
- severe dehydration;
- swelling;
- sepsis;
- liver failure;
- increased bilirubin content;
- diabetes;
- chronic heart disease;
- blood diseases;
- high blood pressure.
Additional restrictions on taking suppositories and granules (with caution):
- bad habits (drinking alcohol, smoking);
- liver cirrhosis due to alcoholism;
- elderly patients;
- pregnancy (trimester 1 and 2).
Side effects from rinsing "OKI"
The use of a rinse solution, as a rule, does not cause side effects, since the liquid does not penetrate inside or enters in small quantities. Allergic reactions are rarely possible.
If the solution is used internally, as well as taking suppositories, the following side effects are possible:
- abdominal pain;
- dyspnea;
- diarrhea;
- ulcers of the gastrointestinal tract;
- stomatitis;
- increased bilirubin concentration;
- dizziness;
- unexplained mood changes;
- increased nervous excitability;
- conjunctivitis;
- itching, rashes;
- hives;
- discomfort when urinating;
- swelling;
- cystitis;
- vasculitis;
- increased blood pressure;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- chest pain;
- anaphylactic shock;
- swelling of the pharynx.
Solution "OKI": instructions for use
To treat joint diseases, prepare a solution and take it orally. The instructions are simple:
- Take 1 sachet.
- Dissolve the contents in half a glass of water.
- Visually divide the volume into 3 parts and drink 3 times a day while eating.
Adults take the full dosage, children take half the dose. It is advisable for elderly patients to consult a doctor; the dose may be adjusted downward.
Types of throat antiseptics
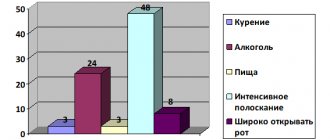
The most common diseases that a person can suffer from are caused by viruses. The main symptom by which one can judge the development of the disease is a sore throat.
In infections caused by viruses, mucus may accumulate in the throat and on the surface of the tonsils. You can also cure a sore throat at home. Let's look at the most effective methods.
We will not consider potent substances like antibiotics, which will naturally help relieve a sore throat, but will cause significant harm to the body as a whole.
Depending on the disease (pharyngitis, laryngitis, tonsillitis, etc.), different drugs and antiseptics are used, which are aimed at destroying certain microbes. Antiseptics come in the form of tablets, gargling solutions, throat sprays, absorbent lozenges, and solutions for treating tonsils.
- Lugol. Available in the form of a spray and solution for treating tonsils. Very effective for infectious diseases. Thanks to the iodine contained in the composition, which has a bactericidal effect, pathogenic microorganisms are destroyed. Glycerin also has a protective effect and relieves painful burning at the site of inflammation. Indications for the use of Lugol are diseases such as ARVI, influenza, tonsillitis, tonsillitis, etc.
When using the spray, you should irrigate your throat 4-6 times a day. The main thing is not to use it often so as not to cause a burn.
To apply the solution, cotton swabs are required. It should be moistened in the solution and treated the sore part of the throat. You should not eat or drink water for 30-40 minutes for the medicine to work better. You can repeat the procedure every 3 hours. Details about the use of Lugol: https://med-gorlo.ru/preparaty-i-lekarstva/lyugol-dlya-gorla.html.
- Rotokan. Herbal solution is sold in every pharmacy. There will be something for everyone. At the first discomfort in the throat, 1 tsp. Dilute rotokana in a glass of warm water and gargle with this liquid for a sore throat 2-3 times a day. The only drawback to using this solution is that it contains alcohol, which causes a dry throat. But this happens if you rinse too often.
- Among the rinses, the most effective are: hydrogen peroxide, miramistin, furatsilin, soda solution, propolis tincture.
- A good antiseptic lozenge is Lysobact. Despite the expensive price, they are worth it. After them you should not eat for 2 hours. They destroy all microbes in the oral cavity. Also, as a bonus, it neutralizes mouth odor. It relieves itching and dryness well. Strengthens local immunity.
- Among the folk remedies for rinsing are: herbs from sage, calendula, chamomile.
- Today, there are many antimicrobial and antiseptic drugs in the form of sprays for sore throat and sore throat: Hexoral, Miramistin, Strepsils, Septoletotal, Tantumverde, etc. They are very convenient to use, especially for treating children who do not know how to gargle. You should irrigate a sore throat 3-4 times a day.
- Chlorophyllipt. Contains eucalyptus leaves. It fights germs and sore throat well.
If you have severe pain in the throat and if the medications do not provide any improvement, you should visit a doctor! Because the disease is not as important as its consequences!
All about diseases and treatment of the throat on the website https://med-gorlo.ru/.
Instructions for use of candles
Suppositories are also used to treat joint diseases. They are administered rectally; the quantity and frequency of administration depends on the patient’s age:
- Children under 12 years old - 1 suppository with a dosage of the active substance of 60 mg 1 or 2 times a day.
- Children over 12, but under 18 years old - the same with an increase in the total amount up to 3 times in essence.
- Adults – 1 suppository 2 or 3 times a day.
- Elderly patients - 1 suppository 1 or 2 times a day.
Attention!
The duration of the course of treatment is determined by the doctor. Children and adolescents can take suppositories for no more than 5 days in a row.
Rules for using rinse aid
- Before use, carefully study the composition and instructions
: some liquids require dilution with water. - Rinse your mouth after brushing your teeth
- in this case, the active substances will linger on the teeth. - Recommended rinse time: 10–30 seconds
. - 10–15 ml of product
is the volume for one rinse for an adult,
5 ml
for a child or teenager. - Strain the solution
through your teeth several times to cleanse your entire oral cavity. - For the solution to work, do not drink or eat
.
"OKI" for rinsing: instructions
A ready-made solution is used to treat sore throat, stomatitis and other diseases of the oral cavity. With its help, 2 rinses are done per day, and 10 ml should be used once, which corresponds to 5 injections. You should proceed like this:
- Pour water up to half the volume into the glass supplied with the preparation.
- Inject exactly 10 ml of solution.
- Mix, put on the dispenser.
- Give 5 consecutive injections into the throat (for teenagers - a maximum of 3 injections).
- Repeat the procedure in the evening.
What types of mouth rinses can there be?
For self-hygiene, solutions with antibacterial, antiseptic, mineralizing, anti-inflammatory, and antifungal effects can be used. It is better to use a rinse selected by your dentist or hygienist, taking into account the condition of your teeth and gums.
Mineralizing. The basis of the solution is sodium fluoride or olafur. This is a mineral component that can penetrate the enamel structure and strengthen it. After rinsing, a protective film is formed on the surface of the teeth. It lasts for several hours, “saturating” the enamel with minerals. The use of such rinses reduces the risk of caries and reduces the sensitivity of enamel.
Antiseptic. The main component may be chlorhexidine, triclosan, or benzydamine in low concentrations. The solution destroys bacteria, protects against gum disease, slows down the formation of tartar, and improves the condition of gingivitis and some other diseases. After tooth extraction, rinsing with antiseptic solutions may be prescribed to reduce the risk of inflammation or dry socket formation. Rinse aids with an antiseptic effect are used as prescribed by the attending physician. They are usually used as part of complex therapy in the treatment of periodontitis, gingivitis and other inflammatory diseases. You cannot use them for too long: this is dangerous due to dysbacteriosis of the oral cavity, dry mucous membranes, and the appearance of halitosis.
Health-improving. They are made from extracts or decoctions of herbs, using essential oils. The effect is mild, supportive or preventive (not pronounced enough if treatment of existing diseases is needed). Such rinses can contain extracts of chamomile, myrrh, sage, eucalyptus, sea buckthorn, hawthorn, essential oil of geranium and other plants. Their effect is anti-inflammatory, restorative, restoring local immunity. Such products are used as a means of daily hygiene. Even with long-term use they do not cause side effects.
Alcohol based. They are classified as antiseptic, used as prescribed by a doctor, the ethanol content can be up to 27%. Effective for halitosis and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity. They cannot be used by minors, people for whom alcohol is contraindicated, or drivers (after rinsing, the breath may contain alcohol vapor, and this is recorded during testing with a breathalyzer).
Some rinses are used as prescribed by a doctor for specific diseases or conditions. They may include:
- diphenhydramine - for a local allergic reaction;
- xylocaine or lidocaine - anesthetic effect (temporarily removes sensitivity);
- nystatin, betamethasone, stomatidine - for aphthous stomatitis and other acute inflammations;
- benzydamine is a pain reliever.
special instructions
Taking OKI in the form of a rinse solution does not affect the ability to drive a car or operate machinery, since it does not reduce reaction and performance. However, when taking the drug orally, as well as suppositories, inhibition is possible, so it is better to refrain from such activities.
If during the course of "OKI" the patient becomes infected with an infection, he may not have the corresponding symptoms for some time, since the drug masks them.
If the patient has persistent dysfunction of the liver and kidneys, the dosage of ketoprofen should be reduced. There is also a risk of an asthma attack. In such cases, taking the medicine is allowed only in consultation with the doctor. If a woman is planning a pregnancy, it is better for her to refrain from using OKI orally and use alternative drugs.
Cons of mouthwashes
- For the mouthwash to work
, you need to rinse your mouth not for 10 seconds, as most people do, but for 30–40 seconds. At first it’s not easy: out of habit, the facial muscles quickly get tired. But with daily rinsing, they become trained. - Mouthwashes should not be swallowed
, even those that say they are harmless on the packaging. Most products contain ethanol. It effectively fights bacteria, but if accidentally swallowed it can cause dysbacteriosis. In addition, within 10-15 minutes after rinsing, the alcohol test gives a positive result: take this into account if you drive a car. - Cheap rinses eliminate symptoms
, not causes, as they consist of water and herbal infusions or green tea. They simply dull bad breath, but do not eliminate the cause of its occurrence. - Some rinses contain synthetic dyes
(CI 42090, CI 19140, CI 17200), preservatives and foaming agents that cause dry mucous membranes and can even stain the enamel. - Rinses containing chlorhexidine can cause inflammation
and dryness of the mucous membranes. Such drugs are contraindicated for children. - Rinses containing the foaming agent Sodium Lauryl Sulfate (SLS) also cause dry mucous membranes
and neutralize the effect of chlorhexidine.