The sadly familiar toothache is actually not even a toothache at all - strictly speaking, there is nothing to hurt in the tooth itself, since it consists of hard tissues and enamel minerals. This is why caries
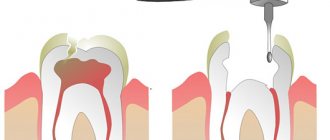
, and often
pulpitis
can go unnoticed for so long - until the destruction becomes serious, the tooth simply does not give any pain signals. The pain we experience actually comes from the nerve, or more precisely, from the pulp. So, when we say that a tooth hurts, it actually hurts the nerve in the tooth.
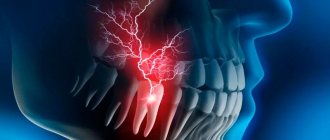
Pulp
- this is a bundle of neurovascular fibers, soft tissue that serves as a layer between the crown of the tooth and its root. The nerves located in it react to hot and cold, and nutrients and minerals enter the tooth through the vessels. However, when the destruction of the enamel affects the pulp, the nerves become inflamed and the tooth begins to hurt. This is pulpitis - inflammation of the pulp.
In case of pulpitis, it is too late to save the pulp and nerve, and therefore they are removed - this is a common procedure that completely anesthetizes the tooth and prevents the infection from spreading further to neighboring teeth. However, a tooth deprived of pulp becomes “dead”: it is deprived of nutrition, its tissues become thinner, and the color of the enamel darkens. This is unfortunately a side effect of nerve removal.
Features of the structure of the root system
Human teeth have a purely individual structure, so the root system of the same element may differ from person to person, including the number of canals in it and their branches. The structure of the roots is directly related to the immediate purpose of the tooth:
- incisors of the upper and lower jaws - help to bite off food,
- canines and premolars - perform the primary chewing function,
- molars - take on the main chewing load and help crush solid food as thoroughly as possible.
The photo shows teeth with roots.
The last ones in the row, sixes and sevens, and sometimes eights, require more nutrients to remain strong and wear-resistant throughout a person’s life. Therefore, premolars and molars usually have a developed canal system. But before we move on to a more detailed consideration of the structural features of the root system, let’s look at what a tooth actually consists of.
What is a human tooth made of?
The visible part or crown is covered with a layer of enamel - the strongest tissue in the human body. Beneath it is dentin, and then the walls of the pulp chamber. The pulp (nerve) is a neurovascular bundle that smoothly passes into the root canals. At the very end of the root there is a small apical opening - nerve endings, vessels and capillaries pass through it.
The photo shows the structure of the tooth
Thus, if for some reason the pulp becomes inflamed, the pathological process spreads very quickly through the canals. Essentially, these are communicating vessels, so if one of the passages is missed during treatment and filling, the inflammatory process will continue to develop and ultimately lead to the need to completely remove the diseased element.
Can three-channel pulpitis go away on its own?
Pulpitis of a three-canal tooth, of course, will not go away from lack of treatment and will become chronic. The nerve will die under the influence of microbes, the pain will go away, and the patient will deceptively think that the problem is solved. But this will turn out to be a temporary calm before the storm. The nerve will decompose inside the tooth, there will be even more microbes, inflammation will affect the surrounding tissues, and ultimately it will all end in the formation of a cyst. It will be very difficult to save such a tooth from removal. Treatment of pulpitis of a 3-canal tooth should be immediate.
Differences in the structure of incisors, canines and molars on the upper and lower jaws - table
As mentioned above, the number of channels is largely determined by the range of the element. The essence is the same: the very last chewing teeth bear the maximum chewing load, so they must be strong and resilient, and for this they need abundant nutrition - this is provided by a developed internal system. The table below shows average data on the number of passages in the tooth roots in the upper and lower jaws.
| Tooth | Number of channels | |
| Fangs | upper | 1 |
| lower | 2 | |
| Incisors | upper | 1 |
| lower | 1-2 | |
| Premolars | upper | usually 2, but sometimes from 1 to 3 |
| lower | first – 1-2, second – 1 | |
| Molars | top first | 3 or 4 |
| second | 3, less often 4 | |
| third | 5 | |
| lower first | usually 3, but can be from 4 to 5 | |
| second | usually 3, but sometimes 4 | |
| third | 3 | |
On the upper jaw
The teeth on the upper jaw have their own structural characteristics, and therefore they are somewhat different from their antagonists on the lower jaw. Here are the main distinguishing features:
- second molars (sixes) most often have three canal passages, but in some cases there are 4,
- premolars usually have 2 canals, although in some situations their number can vary from 1 to 3.
The photo shows the teeth of the upper jaw.
It should be noted that the roots on the upper jaw usually have a more complex and branched structure. Therefore, upper molars are more difficult to treat, which explains the higher percentage of complications due to incompletely healed cavities.
On the lower jaw
The structure of the upper and lower jaws is different, which is partly due to the peculiarities in the distribution of chewing load. In the lower teeth, as a rule, there are fewer canals, but here much depends on the individual anatomical parameters of the jaw apparatus. Therefore, the patient must undergo an X-ray examination, and with the image in hand, the doctor will be able to begin treatment directly.
The following are the features in the internal structure of the incisors, canines and molars of the lower jaw:
- in the first molars (sixes) there can be from 2 to 4 moves - there is no exact number to focus on,
- the lower second premolar (five) most often has one canal, although in approximately 10% of cases specialists find two canals at once1,
- the first premolar usually has only one root, but in about a third of cases there are 2,
- Eights are the most unpredictable - the exact number of roots located inside can only be determined using radiography. As a rule, there are no more than 3 of them, but often during treatment specialists identify additional cavities. This is one of the reasons why wisdom teeth are difficult to treat therapeutically.
The photo shows the teeth of the lower jaw.
Regardless of the type and stage of the disease, competent dental treatment necessarily involves a preliminary x-ray diagnosis. Otherwise, any wrong move by the doctor can easily lead to serious complications.
Eights - third molars
A wisdom tooth usually has a complex and intricate root system - this is the only element in which the number of roots can reach 5. But this is extremely rare, and more often the figure eight has from 3 to 4 roots, while the lower third molar may not have any. more than 3.
The photo shows wisdom teeth
We are talking about a rudiment that we inherited from our ancient ancestors. Now we do not need to carefully crush very tough foods, such as raw meat. Therefore, there was no longer any urgent need for the figure eight, and due to the reduction in the size of the jaws, there was practically no free space left for it.
Because of this, the tooth almost always erupts with problems, since it initially begins to grow in the wrong position and often half remains under the gum - retention and dystopia. All this significantly complicates the treatment of pathological processes that are localized in this area. Therefore, most often the eight has to be deleted.
What crowns to put
A crown is a cap-shaped structure that is placed on a previously prepared tooth. What does prepared mean? Before prosthetics, the tooth must be cured and the necessary shape created to secure the crown. This restoration method allows you to preserve the part of the tooth that remains intact and not cause harm to neighboring teeth. Restoring a badly damaged tooth with a filling is ineffective: while chewing hard food, it can crack, and along with it, the walls of the tooth can break off. The crown protects the tooth from further destruction and mechanical impact.
Several types of crowns are used to replace the sixth tooth:
- metal;
- metal-ceramic;
- from zirconium dioxide.
In rare cases, ceramic crowns are placed on chewing teeth.
However, we do not recommend doing this, since such crowns are very fragile and may not withstand heavy loads. Crowns differ in appearance and characteristics Table 1. Types of crowns
| Type of crown | Appearance | Advantages | Flaws |
| Metal | Strong and durable, do not require heavy turning, inexpensive | Poor aesthetics, gives a metallic taste in the mouth | |
| Metal-ceramic | Durable, since the frame is made of metal, more aesthetically pleasing than metal crowns | Requires strong grinding, the metal edge can show through the gum and can stand out against the background of natural teeth | |
| From zirconium dioxide | Highly aesthetic (impossible to distinguish from natural teeth), very durable, color retaining, hypoallergenic | They are more expensive than metal-ceramic crowns and are not suitable for restoring teeth in the smile area | |
| Ceramic | Maximum aesthetic (impossible to distinguish from natural teeth), retain color, hypoallergenic | Not suitable for restoring chewing teeth |
When choosing a material for a crown, the following conditions are taken into account:
- how damaged the tooth is;
- how important is aesthetics;
- how strong are the walls of the teeth;
- budget and patient wishes.
Based on the answers to each item listed, the doctor develops a treatment program.
Types of root canals
As noted above, the internal structure of each individual element has its own individual characteristics. But there is also a classification that makes it possible to group various options for the structure of dental canals into several categories:
- for one root there is one passage and one apical foramen,
- the root has several branches that connect closer to the apical foramen,
- two branched passages with one mouth and two apical openings,
- in one root, the cavities are connected and separated several times,
- three canals emerge from the same orifice but approach three different apical foramina.
The internal structure of each individual tooth has its own individual characteristics.
The number of roots and canals may be the same, but more often their number differs. In this case, cavities of various types may be present in one chewing premolar or molar.
Promotions of the DentBerg clinic
Treatment of caries “All inclusive”
Treatment of caries with placement of a heliocomposite filling at the DentBerg clinic at a fixed price.
6,500 5,500 rub. More details
the promotion is valid until 12/31/2021
10% discount on dental treatment for pensioners
Get a 10% discount on dental treatment at the DentBerg clinic.
More details
the promotion is valid until 12/31/2021
Features of the structure of the root system in children
Each baby tooth has one nerve, just like the molars. In addition, they have a similar root system structure. In pathological processes, temporary elements are also opened, processed and filled, but the tactics largely depend on how long ago they erupted and how much time is left before the bite changes. Thus, the roots of baby teeth are usually filled with a special paste, which dissolves as the root system dissolves.
The process of root formation in permanent incisors, canines and molars takes about three years. If the root system is still at the stage of its development, special compounds are chosen for filling it - pastes with a high concentration of fluorine and calcium.
The photo shows the process of resorption of the roots of baby teeth
When inflammation begins - diseases and treatment
The internal structures of the tooth can become inflamed as a result of rapid development, caries, pulpitis or periodontitis. To determine the exact cause of the problem and the stage of development of the pathology, the patient must undergo an x-ray examination. The standard treatment regimen is as follows:
- the doctor removes an old filling or opens a carious cavity to open access to the insides of the teeth,
- if the nerve is still there, it is removed using a special instrument - depulpation is performed,
- Next, the doctor carefully cleans the canals and treats the walls with an antiseptic,
- fills the canals and fixes the filling on top. When treating periodontitis, to ensure the elimination of inflammatory processes, it is usually necessary to apply medication and install a temporary filling - and this procedure will have to be completed more than once.
“My root canals were cured in just 2 visits. It’s a pity, of course, that the nerve had to be removed. They say the tooth can darken. But the treatment was quite quick and easy, and there were no problems afterwards. I heard that sometimes people go for several months to clean out the roots, but at my second appointment they gave me a permanent filling. By the way, it was the first time they filled with gutta-percha, and it still has the same smell!”
KirillMigo, from correspondence on the forum www.32top.ru
The photo shows a treatment regimen for periodontitis.
The treatment regimen described above is a universal scenario that can be changed depending on the type, shape and stage of the pathological process. But the essence remains the same: it is important that all passages are thoroughly cleaned and sealed. Otherwise, relapses of inflammatory processes are possible, and then the risk of complete tooth loss will increase significantly.
Complex cases
Double-canal teeth can be arranged non-standardly, have excessively narrow or curved canals. It also often happens that treatment has already been carried out, but the results were unsatisfactory. All this leads to serious problems.
If a broken pin is stuck in the tooth canal, or if the intervention was unsuccessful, then most clinics will recommend removal. However, we are ready to correct the situation. Our dentists have experience in dealing with the consequences of colleagues’ mistakes. Moreover, assistance is provided as delicately as possible. And the tooth is saved!
The Dentberg Clinic is a fusion of experienced professionals and advanced equipment. This allows us to successfully provide assistance in a variety of situations. Contact us!
Why do we need to know the structural features of roots?
X-ray diagnostics and computed tomography in particular allow us to carefully study the root system and at the same time identify the narrowest and most intricate branches. And if the length of the canal is determined instrumentally, then the exact number of internal passages will be clearly visible on the x-ray image. Information regarding their cross-country ability is also extremely important:
- curvature up to 25 degrees – tool processing available,
- within the range from 25 to 50 degrees – the cavity is considered impassable,
- from 50 degrees - it is impossible to carry out instrumental treatment, but if the corner is in close proximity to the mouth, a specialist can try to improve patency.
An X-ray examination allows you to examine the canals and roots of the teeth.
Due to severe narrowing or even overgrowth as a result of an advanced pathological process, the doctor may not find the canal at all. Among other reasons for this situation, experts in the field of endodontics identify age-related changes and previous medical errors.
The complex anatomy of teeth makes endodontic treatment a complex and risky undertaking. But with the advent of modern technologies in the arsenal of specialists, the likelihood of medical errors has noticeably decreased. We are talking about treatment under a microscope, when during work the doctor has a clear picture of what is happening in real time before his eyes. The use of optics can significantly reduce the risk of poor-quality filling or root perforation, which means that treatment can be carried out efficiently and without complications
- Dmitrienko CB, Krayushkin A.I. Anatomy of human teeth, 2003.
Prices
| Consultation | |
| Initial dental consultation and treatment plan | 500 rub. |
| Tooth canal treatment | |
| Endodontic treatment of a single-canal tooth | 4,500 rub. |
| Endodontic treatment of a two-canal tooth | 6,700 rub. |
| Endodontic treatment of a three-canal tooth | 8,000 rub. |
| Endodontic treatment, fourth channel | 1,500 rub. |
| Unsealing one channel | 1,700 rub. |
| Removing a foreign body from the canal | 1,500 rub. |
| Mechanical and medicinal treatment of 1 channel | 700 rub. |
| In-canal whitening | 1,500 rub. |
| Temporary filling of 1 canal "Colosept" (USA) | 1,500 rub. |
| Root canal obturation | 1,200 rub. |
| Diagnostics | |
| X-ray (sight) image of teeth | 400 rub. |
| Panoramic photograph of teeth (orthopantomogram) | 1,000 rub. |
| Anesthesia | |
| Infiltration anesthesia | 500 rub. |
| Conduction anesthesia | 600 rub. |