Tonsillitis is an infectious disease in which inflammation of the tonsils (glands) occurs. This disease affects both adults and children aged 2 years and older. Tonsillitis in a child most often occurs between the ages of five and ten years, and inflammation can recur several times a year.
The acute form of the disease is nothing more than the well-known sore throat. A person who has suffered from a sore throat at least once, during which he experienced severe pain in the throat, will not confuse it with any other diagnosis. Sore throat is an insidious disease that can cause serious complications in related organs and even lead to disability. What effective measures should be taken in the treatment of inflammation of the tonsils to avoid complications? We will talk about this in detail in our article.
Tonsils on guard
The tonsils (or tonsils) are located on both sides of the throat. All bacteria and viruses that enter the body through the mouth are encountered first. Externally, the tonsils have a porous structure; this structure helps them “examine” all the substances that enter the body and decide what to do with them. In the thickness of the palatine tonsils there are special depressions - lacunae, and the convoluted channels in the thickness of the tonsils are called crypts; they are difficult to see in a photo or with the naked eye. There are also target cells that act as “traps” for microorganisms. When it comes into contact with them, the tonsil decides whether to fight them or not, whether they will cause harm to a person or whether they will be harmless.
When a person is healthy and his tonsils are strong, when any infection enters the body, they begin to actively produce white blood cells to fight the infectious pathogen. But when inflammation affects the tonsils themselves, they lose their protective function and themselves become a source of infection. Pathogenic viruses and bacteria settle firmly in the gaps. What function can inflamed tonsils perform? None! As a result, the tonsils fall out of the body's general defense system and there is a high chance of developing chronic tonsillitis in children.
Causes of candidiasis
The main cause of candidiasis in children is a yeast fungus of the genus Candida, present in the human microflora. But to activate it and increase the number of microorganisms, a number of factors are required:
- weakened immune system;
- frequent viral and colds;
- thyroid diseases;
- diabetes;
- hypovitaminosis;
- taking hormonal drugs or antibiotics for a long time;
- chronic diseases;
- HIV infection;
- intestinal dysbiosis.
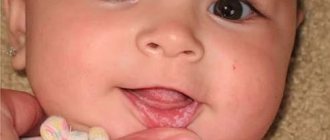
The disease often occurs in premature infants and weakened children. If the mother's birth canal has been affected by candida, the baby, passing through it, becomes infected. The risk of developing candidiasis in such a newborn is much higher.
Causes of tonsillitis
As a rule, the cause of the disease is bacteria and viruses (usually streptococcus). Typically, infection occurs through airborne droplets, especially when children are in large groups (kindergarten, school, various clubs and sports sections). If the causative agent of the disease is bacteria, you can become infected through dishes, a handshake, or through the patient’s personal items (towel, spoon). A child only needs to play with the toys of another sick child to become infected. Alas, acute tonsillitis is a highly contagious disease; and it is very easy to become infected with it.
Another cause of the disease is microorganisms that constantly live on the mucous membranes. This is the norm. A healthy body controls their amount and does not allow them to be exceeded. But as soon as the immune system weakens, the number of pathogenic microorganisms begins to increase: and in essence it turns out that the body infects itself. That is, the development of inflammation can occur with prolonged exposure to unfavorable factors on the child’s body that cause a decrease in immunity: dry indoor air, cigarette smoke, polluted air in big cities, etc.
Treatment of candidiasis
The goal of treatment for candidiasis in children is to eliminate symptoms and prevent further proliferation of fungi in order to reduce their number. General recommendations for strengthening the baby’s body are as follows:
- reduce the consumption of sweet, salty and flour foods, which create a favorable environment for the growth of candida;
- take vitamin complexes, including folic and ascorbic acids, probiotics to normalize microflora;
- give the child drugs to strengthen the immune system;
- For newborns on artificial nutrition, switch to medicinal mixtures containing probiotics and vitamins.
If candidiasis has affected the oral cavity, treatment of the mucous membrane with antifungal agents is prescribed:
- a solution of baking soda, fucorcin or brilliant green;
- Miramistin (antiseptic);
- Clotrimazole (antifungal ointment);
- Nizoral, Pimafucin (antimycotic medications);
- spray for sore throat, stomatitis.
It is recommended to lubricate nails infected with fungus with iodine, antifungal ointments Clotrimazole, Decamine, Mikoseptin and varnishes. If the vagina is affected in girls, antifungal suppositories are recommended. You should not select medications yourself. It is better to consult a doctor and get examined. Self-medication can only worsen the baby’s condition. If thrush, despite the measures taken, does not go away, you may need to consult an immunologist, because This condition is usually associated with weak immunity.
Symptoms of the disease in children
The first symptoms in children suffering from acute tonsillitis appear already on the first to third days after infection, among them:
- high body temperature (with fever, the temperature may rise to 40°C);
- severe pain in the throat, it is very difficult and painful for the child to swallow;
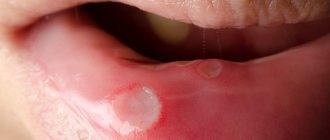
- the tonsils increase in size and turn red; pustules may be noticeable on them;
- headache;
- sick children lose their appetite;
- weakness, lethargy;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- gastrointestinal tract disorders are possible;
- bad breath.
In children with chronic tonsillitis, the symptoms are not as pronounced. The body temperature remains at the subfebrile level for a long time (37-37.5°C). The tonsils become loose - a sign that they have lost their protective function.
Causes
Primary pharyngitis is associated with exposure to the pharyngeal mucosa of infectious agents. The disease can be provoked by intestinal and general infections, inflammation of the upper respiratory tract. In some cases, the cause is burns of the throat mucosa, foreign objects in the throat, or damage to the throat during surgery. The most common causative agents of pharyngitis are the following pathogenic microorganisms:
- influenza viruses, herpes, parainfluenza, cytomegalovirus, enteroviruses, adenoviruses, rhinoviruses;
- bacteria such as staphylococci, meningococci, streptococci, Haemophilus influenzae and diphtheria bacillus, corynebacteria, moraxella, diplococci;
- fungi, intracellular agents (chlamydia, mycoplasma).
Pharyngitis of viral etiology is observed in 70% of cases, bacterial and other ones account for 30%. Its acute form is associated with pathologies such as infectious mononucleosis, measles, scarlet fever, and ARVI. The chronic type of pharyngitis is more often diagnosed in patients with the following inflammatory diseases of the oropharynx:
- adenoiditis;
- sinusitis;
- stomatitis;
- rhinitis;
- chronic tonsillitis;
- sore throat;
- caries.
Risk factors for the development of pharyngitis include local or general hypothermia. There is a high probability of inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa as a result of exposure to spicy food, tobacco smoke, dusty or cold air. Patients who have the following are also at risk:
- weakening of local immunity;
- removal of the palatine tonsils, after which atrophic changes in the pharyngeal mucosa are observed;
- gastroesophageal reflux, which causes stomach contents to flow into the throat;
- posterior rhinitis, in which mucus flows down the throat when blowing the nose;
- difficulty breathing through the nose, causing unpurified cold air to be inhaled through the mouth;
- allergies due to histamine reaching the mucous membrane of the throat.
Types and forms
Bacteria and viruses enter the mucous membrane of the pharynx from other areas of inflammation. For this reason, pharyngobronchitis, pharyngolaryngitis, nasopharyngitis and pharyngotonsillitis in children are diagnosed more often than the isolated form of pharyngitis. Depending on the nature of the course, the disease can be of the following types:
- Spicy. Inflammation continues for 2 weeks. The symptoms of the disease are pronounced. Pain and sore throat and dry cough are more common. The cause may be infectious and inflammatory processes in the trachea or nasopharynx.
- Chronic. It lasts for more than six months with frequent exacerbations.
Taking into account the area of inflammation, the disease is divided into 2 more types: widespread - the entire back surface of the pharynx is affected, limited - inflammation is observed only on the lateral ridges. Depending on the location, chronic pharyngitis in children can be presented in the following forms:
- catarrhal (only the mucous membrane of the throat is affected);
- granulosa (inflammation is located deeper in the lymphoid follicles);
- atrophic (accompanied by drying out of inflamed tissues).
Symptoms
Pharyngitis in a child is accompanied by pain when swallowing, dryness, rawness and sore throat. Against this background, a shallow cough is observed, and hoarseness appears. When examining the throat, the following signs can be noted:
- redness of the wall of the pharynx, soft palate and velopharyngeal arches;
- a granular throat in a child with protruding, inflamed follicles;
- hyperemia and swelling of the uvula, lateral ridges of the pharynx.
The temperature of a child with pharyngitis can be normal or low-grade (37 degrees). It rises higher if the disease develops against the background of viral diseases. Then the little patient experiences fever, headache and swelling of the submandibular lymph nodes. The following symptoms indicate a chronic course of the disease:
- obsessive cough;
- sensation of a foreign body in the throat;
- loose mucous membrane of the throat.
Depending on the form and nature of the disease, very different, subjective symptoms may be observed. The main ones are the following:
- With a fungal form (pharyngomycosis). There are erosions and cracks in the corners of the mouth (jams), a cheesy coating on the back wall of the pharynx, and enlarged lymph nodes in the neck.
- In the atrophic form. Thinning, pallor and dryness of the mucous membrane of the throat are diagnosed. It contains hard-to-remove dried crusts.
- In chronic hyperplastic form. The child may complain of a dry and sore throat. Thick mucus accumulates on the pharyngeal mucosa, which can cause vomiting. Against this background, hyperplasia of the throat epithelium can be noted.
Acute pharyngitis
It has a clear clinical picture. The child complains that it hurts to swallow, itching, dryness and sore throat. The increase in temperature is insignificant - up to 37-38 degrees. If the illness occurs against the background of a cold, then all its characteristic symptoms will appear, including cough, runny nose, and conjunctivitis. With an “empty throat”, the pain in the throat intensifies - this is a characteristic symptom.
In children, hypertrophied inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa is observed. Large and medium-sized granulations form on it, which cause pain. Characteristic symptoms of the acute form are the following:
- child's refusal to eat;
- irradiation of pain in the ear and lower jaw;
- pinpoint hemorrhages in the hard palate;
- pain and enlargement of regional nodes;
- drowsiness, apathy.
Chronic
A distinctive sign of the chronic form of the disease is a false cough, in which sputum is not produced. It is celebrated mainly at night. Mucus accumulates on the back wall of the throat, which the child constantly swallows reflexively. When examining the throat, you may notice its redness and graininess. Purulent plaque is observed only with a bacterial etiology of the disease. Other distinctive features are presented in the list:
- slight increase in temperature in the morning;
- dry throat, which causes you to constantly swallow;
- hoarseness of voice;
- feeling of stuffiness in the upper part of the throat;
- malaise.
Pharyngitis in infants
The disease is much more severe in infants. Since they cannot say what bothers them, the parents themselves have to identify the disease. In infants, general symptoms predominate, expressed by signs from the following list:
- poor sleep, anxiety;
- periodic coughing;
- tearfulness and moodiness;
- temperature 39 degrees;
- regurgitation after feeding;
- loss of appetite;
- salivation - salivation;
- dysphagia – a disorder of swallowing;
- severe fever;
- rash on the body;
- dyspepsia;
- runny nose.
Complications
Most complications of the disease occur due to improper treatment. The infection spreads throughout the body, primarily affecting the respiratory tract, although inflammation can also affect the membranes of the brain. The list of complications of pharyngitis includes the following serious diseases: Otitis, Tonsillitis, Sinusitis, Rhinitis, Conjunctivitis, Meningitis.
Treatment of pharyngitis in children
Treatment of this disease in childhood is often limited to local treatment. It consists of inhalation and rinsing. Young children who cannot rinse their mouths are recommended to drink plenty of fluids and drip irrigation of the mucous membranes with antiseptics. If the child already knows how to dissolve tablets, then he is prescribed lozenges with analgesic, antibacterial and softening effects.
To prevent pharyngitis from getting worse in children, it is necessary to take measures to treat the underlying disease: caries, tonsils, adenoids, intestinal dysbiosis, colds, rhinitis, sinusitis, etc. Taking into account the etiology of inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa, systemic therapy with the following drugs is prescribed:
- antibiotics - for bacterial infections;
- antiviral – for viral infections;
- antimycotics – for fungal infections;
- antihistamines - for allergies.
Antibacterial agents can also be used topically, for example, such as Bioparox, Grammidin or Orasept. Regardless of the chosen regimen, treatment should be aimed at achieving the following goals:
- normalization of temperature - it is recommended to take antipyretic drugs, for example, children's Paracetamol or Cefecol;
- reduction of pain and discomfort in the throat - inhalations, rinsing, warm, generous drinks are indicated;
- ensuring complete rest - bed rest is prescribed;
- elimination of nasal congestion - it is necessary to instill vasoconstrictor drops into the nostrils;
- strengthening the immune system - for this purpose, Grippferon or Derinat is instilled into the nose.
Treatment of pharyngitis in children at home
If the child has no complications or high fever, the doctor may allow treatment at home. An important criterion for recovery in this case is compliance with bed rest during the acute period - until the temperature drops to normal values. Parents must follow the following rules:
- give the baby only warm food;
- exclude spicy foods that irritate the throat mucosa;
- regularly ventilate the patient’s room;
- carry out wet cleaning and humidify the air daily;
- limit the patient's vocal load.
You can give drink not only warm water, but also milk with honey or soda. If the temperature has subsided, then hot foot baths are allowed. To gargle, use decoctions of chamomile, oak bark, and calendula.
To eliminate unpleasant symptoms in the throat, inhalations are indicated. It is better to carry them out using a nebulizer. The recommended frequency of the procedure is 1-4 times per day. Borjomi mineral water, Furacilin solution or saline solution are suitable for inhalation. The latter can be diluted with tincture of calendula or propolis in a ratio of 20:1.
Prevention
An important condition for the prevention of this disease in childhood is routine vaccination. Maintaining proper nutrition and taking vitamins will help prevent any inflammation of the respiratory tract. The child needs to be provided with regular daily exposure to fresh air. The list of preventive measures includes the following:
- hardening;
- limiting contact with sick people;
- ventilation of the home and regular wet cleaning;
- promptly treat colds, rhinitis, sinusitis, adenoiditis;
- Avoid child contact with tobacco smoke and dust.
Bibliography:
Diseases of the ear, nose and throat Luchikhin L.A. /2010
Pediatric otorhinolaryngology. Volume 1, Chistyakova V.R./2005
All about ENT diseases. Pechkareva A.V./2013
Otorhinolaryngologist L.V. Ledova
Complications
It may seem that acute tonsillitis is a completely harmless disease. “Sore throat, fever - what’s wrong with that? A common manifestation of infection,” you say. But let us remember the nature of the disease. Its causative agent, streptococcus, can cause serious consequences.
Complications after tonsillitis can be divided into local (they are localized and noticeable in a certain area) and general (when changes affect the whole body).
Local ones include:
- paratonsillar and parapharyngeal abscess;
- mediastinitis (when a purulent infection descends into the heart sac);
- bleeding from the tonsils, provided that there were ulcers on their surface;
- otitis and eustacheitis (ENT organs are directly connected to each other, so an infection from the throat can easily migrate to the middle ear cavity, the auditory tube and cause an inflammatory process there);
- swelling of the larynx (with this condition, asphyxia develops. This condition is very dangerous, even fatal. A characteristic sign is a bluish tint of the skin against the background of severe suffocation);
- phlegmon and abscesses (purulent inflammation).
Common complications include diseases of the heart, kidneys, joints (rheumatism), tonsil intoxication and sepsis. In order to avoid dangerous consequences for the child’s body, it is very important to promptly begin the fight against tonsillitis under the supervision of a qualified otolaryngologist.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
How to cure tonsillitis in a child
Treatment methods for sore throat depend on the nature of the pathogen: for bacterial sore throat, the doctor will prescribe effective antibiotics (the drugs Augmentin, Amoxiclav, Erythromycin are more often prescribed), for sore throats of a viral and fungal nature - anti-inflammatory and antifungal drugs, respectively. The name of the drug, its dosage and the duration of its use can only be determined by an ENT doctor. Excessive parental independence can interfere with the effective treatment of acute or chronic tonsillitis.
If a child's temperature rises above 38°C, an antipyretic based on ibuprofen or paracetamol should be given. Due to blood thinning and the risk of bleeding, aspirin is strictly contraindicated in children.
It is necessary to adhere to strict bed rest and a gentle diet. Eating and drinking should not cause additional strain on the throat. It’s better to make do with warm soups, broths and purees for the first time. Oral antiseptic sprays, special lozenges and tablets (for example, Faringosept) are perfect for relieving a sore throat.
Chronic tonsillitis in a child: treatment methods
This disease is diagnosed in children if inflammation of the tonsils occurs more than twice a year. In case of chronic disease, the tonsils themselves become a source of infection. The immune system weakens, and the child is often exposed to illness.
Chronic tonsillitis should be treated by an experienced otolaryngologist. Some ENT doctors recommend removing the tonsils immediately. But you need to remember, by removing the tonsils, you lose the body’s natural defenses against bacteria and viruses forever!
At the ENT Clinic of Doctor Zaitsev, we treat chronic tonsillitis, and we resort to removal of the tonsils only in the most extreme cases, when conservative treatment methods have been completely exhausted.
The procedures for ultrasonic medicinal irrigation of the tonsils using the “Tonsillor” apparatus (it can be seen in the photo) have a good therapeutic effect. Our clinic also has a unique vacuum attachment for this device, which has no analogues in other medical institutions. This attachment is painless, safe and can be used to treat children starting from school age.
Literature
- T.I. Garashchenko. Sore throats in children and their systemic antibacterial therapy. Consilium Medicum. Pediatrics. (Add.) 2008; 02: 14-20.
- E. I. Krasnova, N. I. Khokhlova. Differential diagnosis and treatment tactics for acute tonsillitis (angina) at the present stage. Attending physician No. 11/2018; Page numbers in the issue: 58-63.
- Clinical recommendations (treatment protocol) for providing medical care to children with tonsillitis (acute streptococcal tonsillitis), FSBI NIIDI FMBA of Russia, 2015.
- Tatochenko V.K.. Once again about antipyretics. Issues of modern pediatrics. Volume 6 No. 2 2007, p. 128-130.
- Instructions for the drug HEXORAL® SOLUTION.
- Instructions for the drug HEXORAL® in AEROSOL form.
- Instructions for the drug HEXORAL® TABS.
- Instructions for the drug HEXORAL® TABS CLASSIC.
- Instructions for the drug HEXORAL® TABS EXTRA.
Up to contents
Prevention of tonsillitis
To reduce the risk of developing the disease, you need to devote time to preventing this disease and strengthening the immune system. It is necessary to accustom children to hardening procedures. Hardening will bring positive results if you do it gradually, and at the same time consistently and regularly.
It is important to eat healthy and varied, eat foods rich in vitamins and avoid seasonings that irritate the throat. You also need to remember the relationship between the ENT organs and the surrounding tissue. Therefore, it is extremely necessary to promptly treat dental diseases and any inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx and larynx.
From an early age, children should be taught sanitary standards: washing hands, washing fruits, covering their mouths when coughing with a handkerchief or napkin. During periods of epidemics, it is advisable to avoid places with large crowds of people.
Following these simple measures will help avoid inflammation and the unpleasant consequences of this disease.
Diagnosis of candidiasis
A pediatrician usually has no problems diagnosing thrush on the oral mucosa.
This is a common disease with characteristic symptoms, so an experienced specialist can easily identify it. In particularly difficult cases, when diagnosing a sore throat, sputum analysis may be required to identify the pathogen. The situation is more complicated with the diagnosis of candidiasis on the genital mucosa. In this case, you will have to take a smear for microflora, which will show the presence of inflammation and help identify the causative pathogen.
Thrush on internal organs is even more difficult to detect: external symptoms may be absent. Blood, urine, and stool tests may be required to detect mycosis.
"ENT Clinic of Doctor Zaitsev"
Treatment of tonsillitis in children in Moscow is offered by many medical institutions: from district clinics and multidisciplinary centers to private clinics. The main thing is to make the right choice!
Our clinic accepts patients from the age of three. The ENT clinic has everything necessary for the successful treatment of sore throat and chronic tonsillitis: the most modern equipment and instruments, its own treatment methods, and most importantly, highly qualified ENT specialists with extensive practical experience. A visit to a doctor for a small patient is always stressful, and our task is to make the appointment as calm and easy as possible for the child. The examination takes place in a playful way: the baby no longer perceives the treatment as something scary and unpleasant, and the mother’s saved nerves are worth a lot. Our clinic is equipped with a children's corner where a child can play, read, or just drink tea and cookies while the mother and the doctor discuss the treatment regimen. Prices for our services have not changed for more than three years and remain one of the best in Moscow.
If you have discovered the first signs of a sore throat in your child, or he has been suffering from relapses of chronic tonsillitis for several years, please do not delay and make an appointment. We will help you cope with this illness.