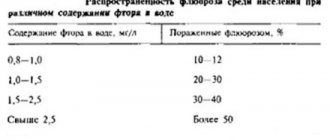
Traumatologist-orthopedist
Shelepov
Alexander Sergeevich
13 years of experience
Doctor
Make an appointment
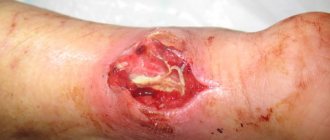
An accumulation of clots or liquid blood in the soft tissues of the body, formed due to rupture of blood vessels, is called a hematoma. The most common type of pathology is an ordinary bruise. However, this concept includes much more severe and complex cases that cannot be left without qualified medical care. Blood flowing from the vessel irritates the tissues surrounding it, resulting in pain, tissue swelling and other signs of developing inflammation. In addition, the hematoma compresses the tissues or organs located next to it, which can lead to the development of complications.
General information
The main cause of hematomas are bruises - closed injuries to soft tissues resulting from a blow or fall. A strong blow leads to rupture of the walls of small blood vessels, due to which blood begins to flow through the breakout sites into the subcutaneous tissue, soft tissues or body cavities. Hematomas form in different parts of the body - on the limbs, torso and even on the head. In addition to bruises, hematomas are caused by intense compression and stretching of tissues due to dislocations or fractures.
Small lesions, as a rule, do not require any treatment and resolve on their own within a few days. When large hematomas form, there is a risk of infection and the development of suppuration. Most often, hematomas form in representatives of younger age groups - children, adolescents and young people, who are characterized by high physical activity. Another “risk group” are people with increased fragility of the vascular wall, as well as with blood clotting disorders.
What you should absolutely not do
If blood appears on the tongue, it means there is an open wound on its surface. In order not to aggravate the situation and not provoke the development of inflammatory processes, it is important to adhere to some restrictions. So, if you inadvertently injured the main speech organ, refrain from the following actions:
- cauterizing the wound with alcohol - this will only further injure the mucous membrane,
- drinking hot tea will increase bleeding,
- treating the wound with brilliant green or iodine,
- pressing the wound with a bare finger or teeth, trying to stop the bleeding by pressing the tongue to the roof of the mouth.
Until the bleeding has completely stopped, do not eat or put anything foreign in your mouth until the wound has completely healed. It is also strictly forbidden to self-medicate with antibacterial drugs - they can only be prescribed by the attending physician.
Why does a hematoma change color?
Doctors identify three distinct stages of a hematoma through which it must go before completely disappearing. Each of them is characterized by a certain skin color, through which the hemorrhage is visible.
- Appearance of a bruise. Immediately after a soft tissue bruise, a sharp pain is felt, the area of skin in the damaged area becomes purplish-red and swells due to tissue swelling, then the red color gradually changes to blue. The red color comes from red blood cells containing large amounts of hemoglobin. After a few hours, hemoglobin begins to break down, and the bruise site turns blue. Due to swelling and inflammation of the tissue in the damaged area, the temperature rises.
- Greening. After two or three days, swelling and temperature decrease, the condition of the tissues more or less returns to normal, but minor pain when pressed remains. The blue tint of the skin gradually turns into a greenish color.
- Yellowing. By about the fifth day, the swelling completely disappears, the remaining hemoglobin disintegrates and is removed from the tissues. The site of the bruise becomes yellowish, then acquires its normal color.
Visual symptoms of hematomas are most clearly visible in cases where the effusion of blood occurs in the subcutaneous layer. If a clot forms in the deeper layers of soft tissue, then only a small but painful swelling is noticeable on the outside. Such formations are much more dangerous, since the process occurs unnoticed and can be accompanied by complications.
Are you experiencing symptoms of a hematoma?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Diseases accompanied by a blood bubble on the tongue
Stomatitis
With various types of this pathological condition of the oral cavity, blood sacs can also form on the inside of the cheeks, on the gums, palate, and tongue. Stomatitis is caused by pathogenic microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi), a weakened immune system and injury.
Often this disease is of herpetic nature. Associated symptoms are swelling of the tongue, the presence of a yellow-white coating on it, wounds that cause severe pain and discomfort while eating and speaking.
If the disease is caused by the herpes virus, then it is accompanied by the presence of a large number of blisters on the surface of the tongue, which after some time combine into one blister.
When it bursts, erosion forms in its place. In addition to these manifestations, body temperature may rise, weakness, malaise, and loss of appetite may appear.
Syphilis
In this pathological condition, a characteristic feature is the presence of syphilitic chancre on the surface of the tongue; they are an ulcer or erosion that has a round shape.
The edges of the chancre are uniform, smooth, and the bottom is hard, from which liquid flows out when pressed.
Their sizes can vary from 1 mm to 2 cm.
There are ulcers on the tip, back of the tongue or on its lateral surfaces. The person does not feel pain or discomfort.
2-3 weeks after the occurrence of such ulcers, an increase in regional lymph nodes occurs.
Cancer
This disease, which has an ulcerative form, occurs with the formation of wounds on the tongue with a black bottom, which have unclear edges and blood oozes from them. The location is the edges of the tongue and its tip.
Obvious signs of this disease are pain, discomfort in the oral cavity, a putrid odor, swelling of the face and neck, difficulty swallowing, talking, and chewing.
Tuberculosis
After Mycobacterium tuberculosis enters the human body through the mucous membrane, ulcers appear at the site of the lesion. They can form on the tongue, lips, gums, cheeks, and palate. Externally, the ulcer looks like a pink crack, covered with a white-yellow coating, its edges are soft and scalloped.
If you try to remove the plaque, its granular bottom begins to bleed. In most cases, yellow-red bumps form around the affected area.
With tuberculous ulcers, pain, discomfort in the oral cavity, and difficulty eating and speaking are noted.
The healing process of wounds occurs quite slowly. When palpated, regional lymph nodes cause severe pain and are enlarged.
Necrotizing periadenitis
With this disease, there is increased salivation, bleeding, and foul odor from the mouth.
In a recurrent condition, the ulcers are localized on the side; they affect not only the tongue, but the lips and cheeks.
Before they form, the mucous membrane thickens, the edges at the site of the lesion rise.
Inside the ulcers there is an inflammatory infiltrate, which contains blood, lymph, and cellular accumulations.
With this disease, there is increased salivation, bleeding, and bad odor from the mouth.
In advanced forms, the ulcers deepen and fill with purulent contents, which provokes increased body temperature, a feeling of weakness and poor health.
They are very painful and very difficult to cure. This period can last several months. Treatment here must have a comprehensive approach.
Afty Bednary
This pathological condition most often affects small patients under 1 year of age who are bottle-fed or breast-fed. Aphthae can form due to excessive pressure on the nipple or when using an uncomfortable bottle.
After some time, they turn into ulcers covered with a gray-yellow coating, which is quite problematic to remove. The inflammatory process occurs with a change in color, the aphtha has a red color and swelling appears around it.
Given the severe pain that is characteristic of such ulcers, the child refuses food and begins to be capricious, which is easy to notice. Aphthae can also appear on the tongue, cheeks, and gums in older children as a result of constant sucking of hands, fingers, and toys.
Endocrine pathologies
If there is an acute shortage of nicotinic acid, then there is an increase in the size of the tongue, a dense coating on it, and the presence of furrows.
In diabetes mellitus, due to trophic changes in the tongue, decubital wounds appear, filled with a dense infiltrate in the center.
They heal very slowly and cause a person a lot of unpleasant sensations. The tongue becomes red and swells.
Gastrointestinal diseases
Blood blisters on the tongue, under it, are formed due to disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Thus, ulcerative glossitis can develop with enterocolitis and hypoacid gastritis.
Worm infestation
Ulcers with a white-yellow coating, hyperemia of the tongue, its swelling, severe pain, increased salivation, bad breath may indicate the presence of parasites in the human body.
Hypovitaminosis/vitaminosis
With a lack of vitamin A, a person complains of a feeling of dryness in the mouth, which leads to the formation of cracks and ulcers on the surface of the tongue.
If there is an acute shortage of nicotinic acid, then an increase in the size of the tongue, a dense coating on it, and the presence of furrows are observed.
When removing plaque, irritation of the mucous membrane occurs, which causes discomfort and pain in the affected area. In case of vitamin C deficiency, blood vessels become fragile and blisters form when they rupture.
The papillae may atrophy, the tongue acquires a folded structure, and ulcers appear on its surface. Such manifestations on the tongue are characteristic of a lack of vitamin B6.
Types of damage
The faster a hematoma forms, the more difficult the recovery. Injuries of this type are divided into:
- lungs that develop within a day, accompanied by mild pain and not requiring special treatment;
- moderate severity, the appearance of which requires no more than 5-6 hours, accompanied by noticeable swelling and pain, worsening the motor function of the limb;
- severe, forming within 2 hours after a bruise, accompanied by dysfunction of the limb, acute pain and noticeable swelling.
Treatment of moderate and severe hematomas should be carried out under the supervision of a physician to eliminate possible negative consequences of injury.
In addition to the severity of the damage, there are other criteria for classifying hematomas:
- by depth of location - under the skin, under the mucous membrane, deep in the muscle tissue, under the fascia, etc.;
- according to the state of spilled blood - uncoagulated (fresh), coagulated and lysed (filled with old blood that is not capable of clotting);
- by the nature of blood distribution - diffuse (blood permeates the tissue and spreads quickly), cavitary (blood accumulates in the cavity between the tissues) and encysted (over time, the cavity filled with blood is surrounded by a “bag” of connective tissue);
- according to the condition of the vessel - pulsating (blood flows freely from the vessel and flows back) and non-pulsating (the rupture of the vessel is quickly sealed by a thrombus).
Almost always, hemorrhage poses a health hazard, so to eliminate its consequences, you need to seek medical help immediately after the injury.
What you need to know about the oral mucosa
The tongue and the mucous membrane around it have 5 main functions. Namely:
- protection;
- suction;
- selection;
- thermoregulation;
- taste perception.
It is the protective function that “monitors” that the negative influence of the environment does not cause harm. But we are talking not only about various viruses and microorganisms, but also about mechanical damage. The mucous membrane withstands irritants of all types: from mechanical to temperature and chemical.
Interesting! The mucous membrane of the mouth is endowed with the fastest regeneration.
Often, it is by the mucous membrane that the doctor can determine whether there are serious disturbances in the body’s functioning or not. Most diseases leave their mark on its condition, for example, in a patient with diabetes mellitus, the tongue will be red, with cracks and erosion. Therefore, any changes in the tongue, and especially a bruise, should cause an urgent visit to the clinic.
Examination methods
To diagnose hematomas, you need to contact a traumatologist. When the hemorrhage is localized deep in muscle tissue, joints or internal organs, a visual examination provides too little information for the doctor to objectively assess the severity of the lesion and the degree of danger of injury. In such situations, the patient is prescribed:
- Ultrasound of a damaged body part, organ or joint;
- X-ray of the damaged part of the body;
- CT or MRI;
- puncture (puncture with a special needle) of a joint or organ in which blood is believed to have accumulated.
Based on the examination results, the doctor prescribes appropriate procedures.
Useful tips
Found a hematoma in your mouth? It would be helpful to do the following:
- give up irritating foods: salty, smoked, spicy, etc.;
- rinse your mouth with antiseptic drugs;
- make an appointment with a doctor and be sure to visit him if hematomas appear;
- adhere to medical recommendations.
In addition, when identifying a hematoma on the tongue (blood or regular), you cannot:
- pierce it so that it heals faster (you must remember that it is easy to get an infection into the wound);
- injure in any other way;
- refuse to go to the doctor in the hope that everything will go away on its own;
- panic and invent dangerous diseases and their symptoms.
How to remove hematomas?
After establishing the nature and characteristics of the hematoma, treatment is prescribed in accordance with the information received:
- prescribe UHF procedures;
- a surgical opening is performed to remove accumulated clots and rinse the cavity;
- the patient is hospitalized in the surgical department for opening and drainage, followed by antibiotic therapy.
Recovery time depends on the extent of the lesion, the presence or absence of infection and other factors.
Frequently asked questions
How to get rid of a hematoma using traditional methods?
Folk remedies only help with minor and non-dangerous superficial damage. To speed up resorption, you can apply a compress of mashed cabbage leaves, bodyagu mixed with Vaseline, or tampons soaked in a mummy solution to the bruise. For deep or extensive injuries, you should consult a doctor.
Why is a hematoma dangerous?
The greatest danger to health, and sometimes to life, are hematomas that form deep in the tissues, inside organs or joints. Large hemorrhage is dangerous due to the possible development of infection, inflammation and suppuration. If the joint is damaged, bursitis, synovitis or hemarthrosis may develop, resulting in disability. Blood in the peritoneal cavity leads to peritonitis. Brain hematomas lead to dysfunction of this organ with serious consequences in the form of deterioration of cognitive functions, paralysis of body parts, etc.
How to treat a hematoma in the first hours after injury?
Immediately after a bruise, it is necessary to provide first aid to the victim: apply ice to the injured area, then tightly bandage the injured limb to block the flow of blood into the tissue. The dressing should not remain on for more than two hours. During this time, it is necessary to get to the emergency room, where the patient will receive the necessary professional help.
Correct treatment
Eliminating the cause means curing the disease faster. This statement is truer than ever. But only if the cause is not a serious illness. It is clear that large hematomas take longer to disappear than small ones. Despite this, even a tiny bruise can be a reason to go to the clinic. The fact is that in order to avoid serious consequences, surgical intervention is sometimes necessary, during which the hematoma is removed. When contacting a doctor, it is better to choose an oral and maxillofacial surgeon.
In order for the hematoma to go away faster, you need to maintain oral hygiene, namely:
- brush your teeth after and before bed, and preferably after every meal;
- if you cannot brush your teeth after eating, chewing gum can perform hygienic cleaning, removing food particles;
- Rinse your mouth with antiseptic solutions several times a day.
It must be said that only the attending physician prescribes treatment methods for a bruise. True, most often it is the most common and is based on rinsing. Only if the hematoma grows or conservative treatment fails, something more serious is used.