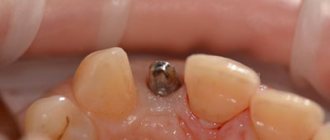
Implantation involves the restoration of lost teeth. The purpose of the procedure is to restore not only chewing, but also aesthetic functions. Before the operation, the condition of the bone, mucous membranes, and neighboring teeth is taken into account. The function of bone tissue is to hold the implant and distribute the chewing load on the support. The function of mucous tissue is to protect the bone, provide access to nutrients, and protect against infection. Therefore, for implantation to be successful, it is necessary to have a sufficient amount of bone tissue and healthy mucosa. If it is not enough, an increase is made.
The importance of sufficient gum volume during implantation
- Aesthetics . During implantation, not only the success of installing the implant itself is taken into account, but also the appearance of the structure relative to the dentition. Installation of an artificial root should not interfere with the fixation of the crown, prosthesis, or interfere with neighboring teeth. In this case, the aesthetic gingival contour must be recreated.
- Functionality . Soft tissues provide nutrition to the bone structure of the jaw and support implant structures. Therefore, even before installing implants, the doctor analyzes the volume and condition of the gums and decides whether augmentation is required.
- Prevention of rejection . A healthy mucous membrane that forms around the implant protects the structure from plaque and bacterial penetration, and reduces the risk of peri-implantitis.
When to remove gum sutures
Even if the wound was sutured with a self-absorbing thread, it is worth checking with your doctor whether it needs to be removed and when. The surgeon must ensure that the operation performed does not cause late complications. Therefore, you need a second visit to him after 7-10 days to determine how many days later to remove the sutures from the gums.
If there is no swelling, redness, or pain, the doctor will remove the stitches. If tissue healing is incomplete, you may need another visit in 2-3 days, during which the material used to close the wound will be removed.
Does it hurt to take it off?
When the suture thread is removed, the patient feels discomfort. Pain when pulling out suture material is rare, due to individual sensitivity or in the presence of a complication in the form of inflammation. If the patient's pain threshold is reduced, superficial anesthesia with Novocaine or Lidocaine spray is used.
How to remove sutures on the gums
Before removing stitches:
- The surgeon will treat the oral cavity with an antiseptic.
- Examine the mucous membrane of the oral cavity: it is necessary that there is no pain, fever, redness, swelling, and no fluid or pus is released from the wound area.
- The thread is cut with a special dental instrument. When the seam is continuous, the cut will be in several places; if it is intermittent, then all the stitches will be cut in half.
- Using fingers or tweezers, the surgeon will pull out pieces of thread and check how well the scar is formed on the wound.
After removing the stitches, the patient will rinse their mouth with an antiseptic.
For 1–3 days, unpleasant sensations in the jaw and gums are possible when moving.
The wound after tooth extraction heals completely within 2–3 weeks. In young people this process is faster. The sockets of single-rooted teeth can heal completely on the 14th day, multi-rooted ones - by the 20th day after surgery.
In case of purulent complications, healing will be delayed for a week for a single-rooted tooth, and 2 for a multi-rooted one.
The more traumatic the operation was, the larger the volume of tissue that was subjected to intervention, the longer the healing.
The surgeon still removes the absorbable sutures so that they, being on the gums for a long time, do not provoke inflammation.
Removing the suture material too early may prevent a clot from fully forming in the wound. In this case, inflammation is also possible.
Sometimes patients get in the way of the threads, and the question arises of how to remove the sutures from the gums on their own, at home, if there is no pain or swelling. What to do if the surgeon is far away, and it’s impossible to tolerate when the threads become hard and rub against the tongue or gums, causing irritation of the mucous membrane?
In principle, the stitches can be removed by the patient himself. But this is fraught with infection in the wound.
At home, you must follow all the rules of asepsis and antisepsis; you cannot keep your instruments sterile. Safe removal of the threads used to suture the gum wound is only possible by a dentist.
Indications for soft tissue augmentation
Gum augmentation is carried out when:
- initial lack of mucous tissue;
- loss as a result of improper installation of implants;
- exposure of the implant during operation.
Initial volume deficit
Insufficient soft tissue volume is manifested due to:
- prolonged absence of a tooth - both the bone and gums atrophy;
- wearing adhesive bridges - mechanical pressure has a bad effect on soft tissues;
- a thin biotype of the mucosa is a physiological feature of the body, in this case the extension is necessary to prevent a lack of soft tissue after implantation.
Errors when installing implants on the upper or lower jaw
Gum loss during implantation is possible if:
- mechanical damage at one of the stages of the operation;
- stretching soft tissue after suturing - healing occurs with defects;
- improper placement and pressure of the temporary prosthesis on the mucous membranes leads to slow growth and healing of the gums.
Exposing the artificial root
There are two types of gum around the tooth root:
- attached - motionless, fused with the periosteum;
- movable - moves when the lips and cheeks move.
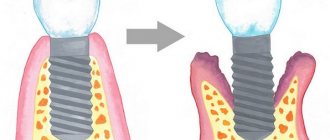
Exposure of the implant neck occurs due to a lack of attached gum, which breaks off, sinks, and pockets form. This provokes inflammatory processes:
- mucositis - inflammation of the soft tissue around the artificial root without involving bone structures;
- Peri-implantitis is a more severe condition where bone tissue detaches from the implant.
In such cases, along with gum augmentation, a number of procedures are performed to eliminate inflammation.
Related articles:
- Center guarantees
- Our advantages
- Press about us
The need for suturing in dentistry
Surgical intervention and, as a consequence, suturing are indicated for the following manipulations:
- Removal of wisdom teeth - third molars differ from the rest in the large size of the tooth crown and its root. Late eruption, the position of the “extreme” in the dentition very often leads to a violation of the physiological location of the tooth or even its impaction (partial or complete failure to erupt). In this regard, the procedure for removing a wisdom tooth is often accompanied by complications - extensive damage to the soft tissues of the oral cavity and alveolar process, ligaments, and blood vessels. To avoid this kind of consequences, dentists apply stitches to reduce the wound.
- Implantation - its implementation is always accompanied by the need for surgical intervention. A deep incision in the gum requires suturing.
- Maxillofacial operations - elimination of the consequences of traumatic injuries, congenital defects of the dentofacial apparatus.
- Removal of tumors of various etiologies - the integrity of the soft tissues of the oral cavity is damaged, often requiring layer-by-layer sutures.
At what stage of implantation is gingivoplasty performed?
If in case of bone grafting to replenish the volume of hard tissues, surgery is recommended as a previous stage of implantation, then augmentation of gingival tissues is allowed at different stages. Depending on the causes of gum deficiency, the procedure is performed during one of the stages:
- Before implantation . In case of initial deficiency of attached gum. But if the implant surgeon is skilled in perioplasty, the procedure is also possible during implantation.
- During implant installation . One-stage plastic surgery is indicated for thin gum biotypes, if there is not enough mucous membrane to cover the surgical area.
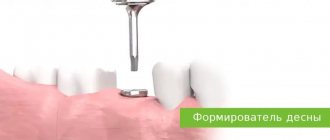
- During the opening of the implant after osseointegration. This period is often chosen for any indication. At the same stage, correction of errors after implantation is carried out. At the same time, the gum former is installed.
- After operation. It is carried out if the parameters of the mucous membranes were not taken into account in the early stages, and over time the implant neck became exposed. It is recommended to carry out the procedure as soon as possible to reduce the risk of bone recession and prevent rejection of the artificial root.
Types of sutures and materials used in dentistry
To facilitate and accelerate the healing process of postoperative wounds in the oral cavity, the following types of sutures are used:
- nodal - used when it is important to ensure equal tension on both edges of the wound (for example, between teeth);
- continuous - when a violation of the integrity of soft tissue occurs along several dental units;
- single - each stitch is knitted separately from each other.
Threads used for suturing in dentistry can be made of absorbable and non-absorbable material.
Absorbable threads:
- from catgut - which contains a foreign protein, which is perceived by the body as a foreign body, and therefore often causes inflammation of the damaged soft tissue of the patient’s oral cavity;
- “Vicryl” is a synthetic material made from polyclatin and polyglycomic acid, which does not cause the risk of developing inflammatory processes even during complex operations.
Threads made of absorbable material do not require the removal of sutures; they disappear within 2-5 weeks.
Material for non-absorbable threads:
- silk is an easy-to-use material, highly durable, but has a significant drawback - it causes inflammatory processes in soft tissues if not removed 7 to 10 days after surgery;
- monofilament is a thread made of polytetrafluoroethylene, which is durable and does not cause inflammation, but has a rigid structure that can damage the mucous membrane. To exclude this possibility, a bandage is applied to the wound surface;
- polyester is a woven thread often coated with silicone for elasticity and smoothness. A very durable material that does not lead to inflammatory processes, but requires careful fixation in the form of knots.
Methods
The surgical method is chosen by the doctor based on the gum parameters, width and thickness. Plastic surgery is performed using:
- using your own tissues from the intervention area;
- transplantation of a donor flap from the hard palate;
- application of collagen matrices or membranes.
Membranes are a progressive method of restoration. It differs from others in its high predictability, minimally invasiveness and short rehabilitation period.
Possible complications
Pain and swelling of the gums at rest, difficulty chewing, evening fever in the first two days after surgery and suturing are considered normal - this is a response to surgical trauma. If the symptoms increase, it means that a purulent complication is developing. A visit to the doctor is needed, opening the wound with removal of the suture threads, washing it, re-suturing or draining it, and taking antibiotics.
Complications arise when wound hygiene is not observed, infection occurs, or particles of a tooth or root are left in the wound.
Continued bleeding from the surgical area is possible if the stitches come apart.
Stages
The operation is performed within 30-60 minutes. If collagen membranes are used, the time is reduced to 10-15 minutes .
Preparation
The oral cavity is disinfected. If necessary, the doctor limits the surgical site from the rest of the mucosa.
Anesthesia
Infiltration or conduction anesthesia with nerve block is used. Painkillers and anesthetics approved by an allergist are used.
Plastic
Incisions are made in the gums (if the operation is performed simultaneously with implantation, no incisions are made). Depending on the clinical picture, local tissue is used to form the gum, a flap of the required size is applied, or a matrix is used.
Seams
Application of surgical sutures.
When are sutures placed after tooth extraction?
It is usually necessary to suturing a wound after tooth extraction in the following cases:
- The most common sutures are applied after the removal of a wisdom tooth - “eights” are usually considered the most difficult in terms of surgical interventions and often require a special approach.
- To prevent bleeding - if the dentist does not have the time and opportunity to find out reliably whether the patient has a tendency to bleed (the operation must be performed urgently, because there is no time to do blood tests).
- During the extirpation of impacted and dystopic teeth, as well as severely destroyed ones (when the crown, in fact, no longer remains above the gum surface) or with significantly curved roots. In all these cases, an incision is made into the gums and underlying tissues, and therefore, after completion of the operation, suturing of the wound edges will be required.
The dental surgeon tightens the edges of the wound (puts the gum flap in place in the area of the incision) and sutures them with catgut or polyamide thread. In the first case, the suture material dissolves on its own; in the second, the threads will need to be removed by the dentist.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
Recovery period - healing time, recommendations
After surgery, follow your doctor's recommendations:
- use a protective mouth guard to prevent damage to the surgical site;
- do not eat food during the first 5-10 hours , you can drink water after a couple of hours;
- don't smoke for 3 days;
- stick to a diet - take warm lean foods;
- carry out thorough hygiene - cleaning 2-3 times a day , it is not recommended to touch the surgical site with a brush, antiseptic drugs are used;
- take prescribed antibacterial drugs;
- limit physical activity.
The rehabilitation period depends on the volume of intervention and the chosen surgical method. On average, gums heal in 10-14 days.
We sewed up the gum after tooth extraction: recommendations
If a patient's gums are sewn up after tooth extraction, he should be extremely careful and make sure not to damage the seam or pull out the threads prematurely. There are general recommendations that the patient should follow:
- The seams should not be touched with hands or with any tools, improvised objects, etc.
- For the first hours after surgery, you should not eat, smoke, or rinse your mouth.
- Oral hygiene must be observed in full to prevent infection of the wound and the development of inflammation. However, cleaning and rinsing must be done with extreme caution.
- In the first days after surgery, you should not eat foods with contrasting temperatures or too hard foods.
- You can rinse your mouth only as prescribed by a doctor and only with the means that he recommends. It is better not to use ready-made rinses from a pharmacy or store, as they can irritate the wound.
- In the case where the sutures were applied with non-absorbable suture material, you must contact your dentist 7-8 days after the operation to remove them. Trying to remove the threads yourself is a no-no!
If all recommendations are followed, healing will proceed safely, but if the patient does not follow medical advice, the wound may become infected with suppuration of the sutures and the development of an inflammatory process - and this will require additional treatment.
Briefly about the introduction of dental implants
To install a metal structure into the bone tissue, it is necessary to make an incision in the mucous membrane. At the end of the surgical intervention, suturing is required. If the outcome of the operation is favorable and there are no consequences, the surgical threads are removed after about 10 days.
The operation process itself is completely painless for the patient, this is thanks to high-quality anesthetic drugs. A little pain is possible only during the rehabilitation period. If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, all troubles can be avoided, however, not always everything depends only on the patient’s behavior.