According to statistics, 98% of people are afraid of visits to the dentist. As a result, solutions to dental problems are postponed until the last minute, until one day we discover that the tooth has rotted. Then a visit to the doctor is inevitable, but a lot of work remains.
Contrary to popular belief, rotten teeth are not only a result of poor hygiene.
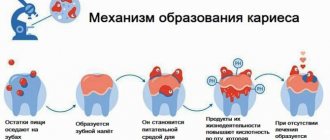
Causes of tooth decay
Yes, we all know that you need to brush your teeth 2 times a day, be sure to use dental floss and visit the dentist 2 times a year. Many patients follow these recommendations, but their teeth still deteriorate and rot. Poor hygiene is not the only reason why teeth deteriorate. There are other factors:
- Gum diseases
provoke the proliferation of bacteria, which literally gnaw through the enamel and destroy tooth tissue; - genetics
plays a role in the ability of teeth to resist pathogenic factors; - an unfavorable ecological environment
leads to the fact that in industrial areas there are more dental problems than in places where there are no factories; - Water quality
directly affects teeth. Low content of useful minerals (fluorine, calcium), high content of heavy metal salts can destroy teeth, despite hygiene; - bad habits
. Smokers have worse teeth than non-smokers and treatment is more difficult; - general diseases
, for example, problems with the gastrointestinal tract, negatively affect the condition of the teeth; - carbohydrates
in the diet , as well as hard food products that injure the gums and enamel lead to tooth decay.
To understand why teeth rot, you need to undergo an examination. Don’t be surprised if the doctor asks you to take tests or do an ultrasound. Dental treatment requires a comprehensive approach and diagnosis is more important than ever. Having found out why teeth are rotting, the doctor will prescribe adequate treatment.
Complications
Bad teeth are a direct path to a heart attack
. When the tooth's protection is destroyed, bacteria enter directly into the bloodstream. There they can provoke the development of blood clots, inflammation of blood vessels, and this leads to the development of coronary artery disease, which is not far from a heart attack.
Gastrointestinal problems
Rotten teeth make it difficult to chew food well. Not only do poorly chewed pieces irritate the mucous membrane, pathogenic flora from damaged teeth enters the stomach and intestines, where they can multiply uncontrollably, causing diseases such as gastritis, pancreatitis, stomach ulcers and duodenal ulcers. Competent gastroenterologists always advise visiting a dentist.
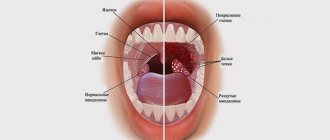
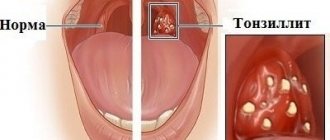
Diseases of the throat and nose
A constant source of infection in the mouth means that any malfunction in the body will cause a relapse of diseases such as sore throat and sinusitis. Purulent infections are dangerous because they can lead to blood poisoning. And such diseases are difficult, often causing complications. Inflammation of the tonsils often causes rheumatism and heart problems. Those who struggle with chronic sinusitis need to especially carefully monitor the condition of the oral cavity. Chronic manifestations will not go away if there are rotten teeth in the mouth.
And the head too
An advanced inflammatory process can spread to the trigeminal nerve. It is closely connected with the brain, and this is a serious matter. Chronic migraines, memory problems, even Alzheimer's disease are associated with oral health. Although there is no direct evidence that Alzheimer's is caused by the same bacteria that cause inflammation in the mouth, it is better to be on the safe side.
Abscesses and cellulitis are also the result of bacterial inflammation.
Stages
Caries, like a secret agent, begins to act on the sly and may not make itself felt for years. Its initial stage is called the “white spot stage.” Well, how can you see white on white? That is why it is important to visit the dentist regularly - the specialist will highlight the white spot against the background of the enamel and cure caries in time. And if you start it, the disease goes to the next level:
- Surface.
The enamel is still intact, but in the area of the stain it becomes rough. The stain deepens. The tooth begins to react to cold and hot. - Average.
Caries penetrates to the dentin, but it does not provide access to the pulp. A damaged tooth reacts to temperature, mechanical, and chemical stimuli. But the pain is not constant, it goes away quickly. - Deep.
The pain is sharp when touched, but gradually subsides. A carious cavity is visible to the naked eye.
What is the danger of this disease?
Caries is dangerous because there are no symptoms for a number of years. It is detected more often in an advanced stage, when tooth extraction becomes the solution.
Visual diagnosis is difficult because all destructive processes occur inside the tooth. Pronounced plaque or tartar hides any stains on the enamel.
The root is hidden under the gum and external irritants do not affect it until a certain time. On the other hand, the root walls are thin, so they are destroyed quickly and with complications.
Why do children's teeth rot?
In children, the composition of saliva is not the same as in adults. Its antibacterial properties are low; in a warm, humid environment, microbes multiply quickly. The disease is not only common, it progresses rapidly. Caries spreads in width and depth. Single events are rare; usually several teeth are affected at once. For children, timely identification and treatment of problem teeth is of particular importance. Rotten teeth can cause:
- pulpitis and periodontitis;
- malocclusion;
- loss of milk and permanent teeth;
- inflammation of the maxillofacial apparatus.
Bad teeth affect the social adaptation of children and lead to psychological problems.
Prevention includes hygiene procedures, limiting sweets, a balanced diet and regular dental examinations.
Symptoms of the disease
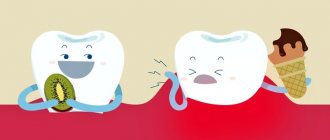
The process usually occurs without symptoms, but pain may occur when brushing a toothbrush, eating sour, salty, sweet, cold or hot foods.
After eliminating the irritant, everything goes away. The patient can see a doctor if a stain is found on the front surface of the incisors, but often it is hidden under plaque or tartar.
The ongoing carious process gradually reaches the dentin junction, penetrating first into its surface layers and then further. The cavity deepens with bacteria and food debris. There is a smell from the mouth. Irritants cause pain more and more frequently.
With cement caries, teeth become mobile and lose their support, and bleeding gums occur. These are already symptoms of periodontitis. Now, even when chewing food or brushing teeth, severe discomfort occurs.
Digestion begins to suffer. Teeth become hypersensitive to hot or cold.
Next, the process follows the Leus classification:
- Active lesion - the edges of the cavity are undermined. The cavity is filled with softened tissues and tends to grow.
- Suspended caries - no increase in the affected area is observed. The cavity is clean, the bottom is shiny and smooth, the edges are even and dense.
- Secondary caries - occurs under a filling.
Teeth and pregnancy
We found out why children's teeth rot. There is another group of people particularly at risk of tooth decay. These are pregnant women. Some scientists classify pregnancy as an immunodeficiency state - the body's resistance to pathogens decreases to such an extent. It’s no wonder that during pregnancy, general diseases worsen and dental problems begin. The increased content of hormones in the body reduces the barrier ability of the epithelium, microorganisms more easily penetrate the gums and begin to multiply.
Help protect your teeth:
- rational and balanced diet;
- multivitamin complexes;
- professional oral hygiene;
- herbal baths;
- applications with calcium and phosphates.
Lifestyle
If you have learned about the risk group for root caries (older age), this does not mean that you can relax. Caries has many causes and can occur at any age if basic precautions are not followed.
Those at risk include smokers, diabetics, pregnant women and even children. The provoking factors in this case are:
- smoking and lack of oral hygiene;
- infrequent brushing of teeth and lack of fluoride;
- poor nutrition with preference for desserts;
- frequent stress;
- alternating hot and cold;
- structural features of the oral cavity;
- alcohol abuse - alcohol breaks down into sugars and acids;
- abuse of coffee and strong tea, which creates an acidic environment in the oral cavity;
- lack of water intake, and therefore lack of saliva;
- gum injuries.
What to do if a tooth is rotten
Until recently, the only solution to the problem was deletion. Today, dental science offers various methods and techniques for restoring teeth.
The method of influence depends on the specific case. What matters is the depth of the lesion, its area, the stage of the disease and the degree of destruction.
Treatment at the initial stage
At the stain stage, you can do without a drill, because it is this that frightens you the most and makes you put off visiting a doctor.
Apply:
- Ozone therapy
. Ozone treatment destroys bacteria, and special preparations restore enamel. - The laser
also destroys bacteria, without heating the tissue and serves as a good preventive measure for gum disease. - Infiltration treatment
.
The chemical composition destroys bacteria, and the infiltration material “seals” the enamel pores and prevents pathogens from penetrating inside.
Treatment for moderate and severe stages
If the disease is advanced, the dentist will still try to save the tooth. At the same time, you can no longer do without a drill. After the examination, the doctor decides how to treat the decayed tooth. But the general principles are the same: after the administration of anesthesia, all dead tissue is removed, the cavity is disinfected and a filling is placed.
If the crown of a tooth has rotted, but the root has been preserved, after treatment the tooth is prepared for prosthetics using:
- Inlays under the stump.
They replace damaged tooth tissue. Inlays are made from zirconium, ceramics, and precious metals. One part of the tab is inserted into the dental canal, and a crown is put on the other. - Pins.
A pin is a rod that is inserted into the dental canal, and a crown is installed on top. They are made of metal or fiberglass.
Modern prosthetics offer a huge variety of materials. Crowns are made from traditional materials: metals and metal-ceramics, composites, zirconium alloys, and modern metal-free compounds.
Treatment
Sick teeth need to be treated, the sooner the better. The dentist’s task is to save the tooth, but if measures are not taken in time, it will have to be removed to avoid serious consequences.
Methods:
- Remineralization Applications of calcium and fluoride preparations and electrophoresis help restore enamel at the initial stage.
- Filling the cavity The affected tissues are removed, their place is filled with filling material.
- Partial prosthetics A crown is placed on the tooth, which protects it from mechanical and biological influences. The crown is placed on a previously depulped, dead tooth.
- Removal If the pulp is affected and the inflammatory process threatens to develop into an abscess, the tooth is pulled out. You should not resist the removal of rotten teeth - they do nothing but harm.
It is easier to prevent any process than to take a long time to eliminate the consequences. By following simple preventive measures and regularly visiting the doctor, you can avoid tooth decay and maintain your smile and self-confidence for many years.
Implantation is a solution for advanced cases
Alas, if the root of a tooth has rotted, then the only solution is removal. But even here, dentists offer a method that will help restore a rotten tooth - implantation. The implant will stop bone loss, prevent loosening and tilting of neighboring teeth, and restore your smile. The immediate loading method involves placing an implant immediately after tooth extraction. There is no need to wait for the hole to heal and you can chew almost immediately.
Diagnosis of the disease
The diagnosis is made in stages. Listening to complaints and visual examination make it possible to diagnose caries only in 13% of cases. Classic probing with a sharp probe and inspection with a mirror are informative. This allows you to examine the dentition.
Thermal diagnostics, electroodontometry and x-rays are also performed. If the patient has massive dental plaque, changes in the enamel will not be visible. In this case, professional teeth cleaning is first carried out to remove plaque and stone. All this is possible in a dental clinic.
At the dental clinic
The following types of studies can be performed at the clinic:
- Probing with a thin probe with a curved end - it is inserted under the gum, while the doctor has the opportunity to examine the structure of the tooth, its integrity, the presence of irregularities and chips. With rapidly progressing caries, the edges of the cavity are uneven and sharp. In the remission stage, the surface of the pathological focus is shiny, smooth, hard with smooth edges.
- Electroodontometry - can determine nerve damage and the depth of inflammation. The pulp reacts differently to the current strength.
- Thermal diagnostics - treatment of different areas of the tooth with a stream of water and heated wax. Unpleasant sensations that disappear after removing the irritant indicate caries.
- X-ray - a targeted photograph of one tooth or computed tomography. The presence and localization of obvious or hidden inflammation is determined with millimeter precision.
- Visiography is a special device - a visiograph scans the received data and transfers it to a computer, where the picture is studied from different angles and in detail, revealing the hidden process of inflammation.
How to deal with this disease?
In any case, an integrated approach is used to treat rotting teeth. First of all, the original cause of the disease must be established . After this, appropriate medications and procedures must be prescribed .
This is necessary because if the cause is not eliminated, then treating the symptoms will only give short-term results.
Simultaneously with the elimination of the cause, the necessary dental treatment . Depending on the stage of the disease, these measures may vary. However, in any case, foci of infection are also identified and must be eliminated.
The complex of treatment measures will most likely include giving up bad habits, restructuring the nutrition system, and strengthening hygiene measures.
In any case, you should not try to cure rotting teeth yourself, as the problem can be significantly worsened and then more difficult to eliminate. Modern dentistry is painless and very effective, so you should not be afraid of going to the doctor.
And don’t forget about prevention and proper care, because any illness is easier to prevent! Let's watch a short video:
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
Toothpaste “Crest” – description of varieties
Next article
Splat toothpaste – types, features and reviews
How to prepare your child for an orthodontic appointment
The initial appointment with an orthodontist takes place without any preparation. The child just needs to brush his teeth and eat beforehand. The latter is desirable, as it will help reduce salivation and facilitate the examination procedure. The child should also be told about the doctor’s specialization. In simple words, explain who this pediatric orthodontist is and what he treats.
An orthodontic examination is a painless procedure. It does not cause fear or discomfort in the baby, but it helps to identify deviations in the development of the dentition as early as possible.
Soldatenkova Alina
Typically, the removal of decayed milk teeth involves the extraction of several units at once. At Azabuka, we recommend performing this procedure under anesthesia or sedation. It is completely safe for the child, and most importantly, it does not leave traumatic, unpleasant memories in the child’s memory.
Why treat baby teeth?
Rotten baby teeth do not always attract the attention of parents. Especially if the pathological processes are painless and do not bother the child. Adults think that when the bite changes, the bad teeth will disappear by themselves, and instead of rotten teeth, normal molars will grow. Dentists warn about the fallacy of such a misconception.
Rotten milk teeth are:
- damage or destruction of tooth germs - a high risk that the root units will grow sick or not appear at all;
- early loss of primary occlusion units - leads to displacement of existing teeth, the appearance of crowding, and the formation of a pathologically abnormal bite;
- an ugly smile, an unaesthetic appearance - the appearance of complexes due to appearance in young children, decreased contact with peers, uncertainty, isolation;
- deterioration of diction - rotten, breaking teeth interfere with the correct movements of the tongue during speech, leading to a lisp, burr;
- gradual spread of infection - damage not only to the surface of the teeth, but also to the pulp, development of pulpitis, the appearance of an abscess, as well as a tendency to ENT diseases and gastrointestinal diseases.