Why is this complication dangerous?
The maxillary sinuses located above our upper jaw (their area extends from the inner corner of the eye to the outer) perform important functions. They can warm the air and thereby protect the respiratory tract from hypothermia and foreign particles. The sinuses are located under the bone tissue and if its thickness is too small, when cleaning the dental canals, filling masses can fall into these cavities. Once the filling is completed, it is no longer possible to remove the foreign material on your own, since this procedure can only be carried out by a specialized specialist who has the necessary tools. The doctor can perform this procedure without difficulty and it will not take much time. It is numbed with local anesthesia and after removing the foreign body from the maxillary sinus, the patient will need to stay in the clinic for several hours. In some cases, discharge occurs the day after this minimally invasive procedure.
Why does this complication occur?
Some patients find it difficult to imagine why dental material gets into the maxillary sinuses, and they often blame the doctor for this. However, the reasons for the appearance of this complication during treatment are usually completely different. Foreign material entering the maxillary sinuses occurs during the following dental procedures:
- Canal filling;
- Some methods of dental prosthetics.
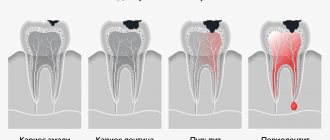
To better understand the essence of the treatment process and see possible ways of penetration of dental material into the maxillary cavities, it is necessary to study the tooth filling scheme. Such a clear example will help you understand that if the layer of bone tissue between the gum and sinus is too thin, damage to the wall of the jawbone can occur. Dental material passes through this small hole. A similar complication usually occurs during dental treatment by a dentist. Another way for filling material to penetrate into the sinuses can be a hole formed when drilling the root canal of a tooth and jaw bone. A similar complication during root canal treatment occurs if the roots and paranasal sinuses are very close to each other. The third option for dental materials to enter the maxillary sinuses is bone tissue augmentation, which is carried out during dental prosthetics. Such additional intervention is necessary for high-quality tooth restoration, and when introducing materials for bone building, damage to the bone tissue may occur, through which pieces of dental preparations will fall.
How does damage to bone tissue in the maxillary sinuses occur?
Looking at the diagram of the anatomical location of the maxillary sinuses and upper teeth, you will notice that there is only a small area of tissue between them. The bones of the upper jaw are especially easily injured during the treatment of second premolars and first and second molars. The likelihood that such damage will occur increases in various pathological conditions and diseases:
- formation and suppuration of cysts in the upper jaw;
- osteomyelitis;
- dental injuries;
- periodontal acute inflammation of the maxillary sinus;
- process of installing prostheses;
- removal of a tooth in the upper jaw, complicated by a suppurative process of the tissues of the upper jaw;
- augmentation of bone tissue of the upper jaw;
- caries complicated by pulpitis.
The severity of the complication associated with the entry of dental material into the maxillary sinuses is increased by the fact that bacteria from the oral cavity can also penetrate through the damaged opening. As a result, some microorganisms can provoke the development of severe purulent inflammation, which will lead to an even greater deterioration in the patient’s well-being and an increased risk of developing even more dangerous complications.
Root canal filling using lateral condensation of gutta-percha
- Selection of the main pin
The selection of the appropriate pin depends on the diameter of the canal after machining and expansion. - Filling the canal
Before installing the pin, the canal is filled with a special paste - sealer. It provides the necessary seal. - Compaction of the main pin
To compact the filling and free up space for new pins, a special tool is inserted into the canal cavity - a spreader. The reciprocating movements of the spreader push the pin toward the canal wall. - Insertion of additional pins
Depending on the diameter of the canal, at this stage 8 to 12 additional pins of small diameter are inserted and sealed. - X-ray examination
The filling density of the canals is checked using x-rays. If the canal is not sealed to the very top or, on the contrary, the filling material extends beyond the root, the pins are removed and the process is repeated again. - Removing excess sealer and gutta-percha
After the desired result has been achieved, remove excess parts of the filling materials protruding from the mouths of the root canals. For this, a special hot tool is used. - Installation of a temporary filling
The final stage of the procedure is the installation of a temporary filling. During the next visit, the doctor re-checks the quality of the filling and restores the crown of the tooth using a permanent filling. Simultaneous filling of canals and crowns is unacceptable.
What symptoms may indicate a foreign body in the maxillary sinuses?
After dental treatment, a person may suspect the development of this complication if the following signs appear:
- the appearance of pain when performing light taps on the facial bone under the eyes near the nose;
- severe, aching headache;
- prolonged and persistent runny nose;
- aching pain in the upper jaw, aggravated by chewing.
One of these symptoms or a combination of several may indicate that dental medications have entered the maxillary sinus cavity. This condition is a reason for mandatory consultation with a doctor and the visit should not be postponed. If the patient does not see a doctor on time or has a weakened immune system, the disease becomes more complicated. Because of this, a person develops thick, purulent and profuse nasal discharge with a specific odor. In addition, the progression of the inflammatory process causes an increase in temperature and a deterioration in general health. In some cases, immediately after dental mixtures enter the sinuses, inflammation does not develop. However, this condition is also unsafe for his health in the future, since various negative factors (for example, hypothermia, stress, injury or hypovitaminosis) can provoke the development of inflammation and a deterioration in general well-being.
What to do if the filling material goes beyond the canal
Due to the inexperience or inattentive work of the doctor, it happens that the filling material goes beyond the canal. The doctor must decide what to do in such a situation based on the complications that have developed. Most likely, this will be an opening of the channel.
If during treatment all the rules for medicinal and instrumental treatment of root formations were followed, then the risk of infection is quite low, and the patient will not be bothered by pain after filling.
If there is excessive removal of material and penetration of microbial organisms, the patient will have to undergo repeated treatment.
To do this, the canal is opened, washed with an antiseptic solution, and then the medicine is placed in it. If severe consequences of the initial treatment are observed, then surgical help cannot be avoided.
How can a complication be identified?
External signs of dental materials getting into the maxillary cavities and patient interview data may not be enough to make a correct diagnosis, and additional studies are carried out to confirm complications of the dental procedure:
- x-ray of the maxillary sinus;
- MRI;
- CT;
- puncture.
The diagnostic plan may include several procedures. Their number is determined by each doctor individually.
What dangerous consequences does a foreign body lead to?
A foreign object in the maxillary sinuses can lead to the following complications:
- bacterial or fungal sinusitis;
- encapsulation in the form of a cyst or other benign disease;
- granuloma formation.
In more complex cases, suppurative processes in the maxillary sinuses cause the development of the following complications:
- frequent colds and inflammation of the nasal cavity and sinuses;
- meningitis;
- hypertrophy of the mucous membrane;
- damage by coccal flora to other organs and systems (for example, heart muscle).
A particularly dangerous complication is inflammation of the meninges. When meningitis develops, the patient develops the following symptoms:
- significant increase in temperature;
- headache in the forehead;
- frequent vomiting that does not bring relief;
- rash on palms and soles.
If these symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor!
And the possible consequences of getting filling materials can only be prevented by timely consultation with a doctor and regular preventive examinations in the mode prescribed by the doctor.
How is a foreign body removed from the maxillary sinus?
To prevent the development of complications in the presence of foreign objects in the maxillary sinus, minimally invasive surgical intervention is performed. Its main purpose is to remove filling material. The operation can be performed using optical instruments such as an endoscope or laparoscope. When carrying out such interventions, significant trauma to bone tissue and incisions is not required. These minimally invasive operations are pain-relieved with local anesthesia and take no more than half an hour. Traditionally, endoscopic techniques are used to remove foreign bodies from the maxillary sinuses. To perform the operation, a small incision is made above the upper lip through which an endoscope is inserted. This optical device helps the surgeon detect a foreign body. The dental material is then removed. When performing laparoscopic surgery, tissue puncture is performed in the place where the bone tissue is thinnest. A special instrument is inserted into the laparoscope, which captures and removes the foreign particle. This technique is used in cases where endoscopic intervention cannot be performed for some reason. Sometimes operations are supplemented by such manipulation as curettage. This method is necessary in cases where, due to the filling material, a granuloma has formed on the tissues of the cavity. After surgical removal of a foreign particle, the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs to prevent inflammatory and purulent processes. To achieve the desired result, antibiotics, immunostimulants and other drugs may be prescribed. In addition, the affected sinus is washed with antibacterial, antiseptic and anti-inflammatory solutions. To increase the protective functions of the body, the patient is prescribed vitamin and mineral complexes. The best prevention of such complications is regular visits to the dentist. In addition, it is necessary to exclude facial injuries, try to avoid stress, eat right and lead an active lifestyle.
Features of the selection of filling material
To obtain the desired result when filling, the following factors should be taken into account:
- you need to use the best biocompatible material;
- it is necessary to follow the rules for treating the canal to avoid the spread of infection;
- Not only the main canal, but also its branches must be obturated;
- The filling material should not dissolve in the canal.
Not every material is suitable for such requirements. Until recently, root canals were filled with zinc-eugenol pastes, but this technique had its significant drawbacks. The paste did not allow filling all the branches of the canal, leaving voids. Thus, an infectious process developed inside her, which spread to the periodontal system. In addition, the paste had significant shrinkage, which meant that the root formation would have to be re-treated over time.
To find a suitable material for high-quality obturation, doctors put forward several requirements.
The filling material must:
- be completely biocompatible;
- do not have excessive shrinkage;
- have a bacteriostatic effect;
- be resistant to various types of liquids;
- give good adhesion to tooth tissues;
- create conditions for hermetic sealing;
- be X-ray contrastable;
- easy to remove from the canal cavity (if necessary).
Today, several types of materials are used for filling root formations: root-hardening cements, plastic materials (gutta-percha) and metal pins.
Pain after filling may be due to improperly treated canals
Due to the fact that an ideal material does not exist today, the combined use of pins and pastes is accepted.