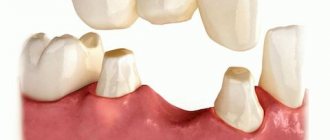
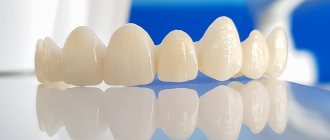
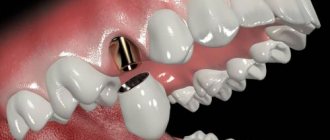
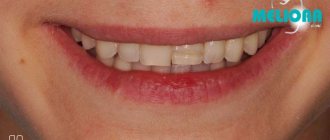
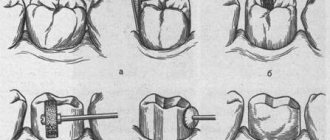
Clinical and laboratory stages of manufacturing a plastic crown.
Answer:
| Clinical stages (performed by a doctor) | Laboratory steps (performed by a dental technician) |
| K1. Odontopreparation. 2. Obtaining an impression. 3. Determination of crown color. | |
| L1. Making a plaster model. 2. Modeling a crown from colorless wax on a manufactured plaster model | |
| K2.1. Fitting a plastic crown into the oral cavity 2. Making adjustments to the shape of the crown, size, relationship with antagonists for various types of closure of the lower jaw. | |
| L2. Final grinding and polishing of the plastic crown | |
| K3. 1.Fixing the crown on the tooth with cement (preliminary disinfection and drying). 2. If there is excess cement, remove it using a probe. |
Metal stamped crowns, indications for their use. Rules for preparing hard tooth tissues for a stamped metal crown.
Metal stamped crowns, indications for use:
1) Significant destruction of the lateral (chewing) teeth as a result of caries, wedge-shaped defects, if the defects cannot be eliminated from fillings, inlays
2) In order to correct the abnormal position and shape of the chewing teeth.
3) For fixation of fixed dentures.
4) Splinting
5) Temporary fixation of orthopedic and orthodontic devices.
6) Convergence, divergence, advancement of teeth if significant grinding is necessary.
Rules for preparing hard tooth tissues for a stamped metal crown:
Odontopreparation of 5 tooth surfaces. A layer of tissue equal to the thickness of the crown (0.25-0.3 mm) is removed from the cutting edge or chewing surface. Sharp angles between the buccal and contact surfaces are smoothed out.
As a result of preparation, the tooth takes on a cylindrical shape with a crown diameter that does not exceed the diameter of the tooth neck. This makes it easy to apply a crown, the edges of which, entering the gingival pocket, will tightly cover the tooth neck.
Clinical and laboratory stages of manufacturing a stamped metal crown.
Answer:
| Clinical stages (performed by a doctor) | Laboratory steps (performed by a dental technician) |
| 1. Examination of the oral cavity and selection of prosthesis design. | |
| 2. Treatment of the tooth for a metal crown and separation. | |
| 3. Taking impressions of the upper jaw and lower jaw. | |
| 4. Casting models of the upper and lower jaws. | |
| 5. Plastering the models into the occluder in central occlusion. | |
| 6. Engraving and drawing of the clinical neck of the tooth. | |
| 7. Tooth modeling for a metal crown. | |
| 8. Cutting out a plaster die and drawing a laboratory neck of the tooth. | |
| 9. Casting a gypsum block. | |
| 10. Casting metal dies (2 dies for making one crown). | |
| 11. Selection and heat treatment of sleeves. | |
| 12. Crown beating (pre-punching). | |
| 13. Stamping of the crown (final). | |
| 14. Crown whitening. | |
| 15. Processing and polishing of the crown. | |
| 16. Trying on a crown. | |
| 17. Fixing the crown in the oral cavity with cement, that is, handing over the crown to the patient. |
Clinical and laboratory stages of manufacturing a combined stamped crown (according to Belkin).
Answer:
| Clinical stages (performed by a doctor) | Laboratory steps (performed by a dental technician) |
| K.1. 1. Odontopreparation 2. taking an impression 3. determining the color of the future structure | |
| L.1. 1. Making a plaster working model and a metal crown. | |
| K.2. 1. fitting the model into the oral cavity, then removing it. 2.Drilling a 2mm hole on the vestibular surface. 3. Pouring wax into the crown, fitting, excess wax is squeezed out through the hole | |
| L.2. 1. making a model. 2. Heating the crown on an alcohol lamp or boiling. 3. whitening and polishing the crown, cutting out the vestibular surface, modeling it with wax 4. replacing wax with plastic 5. processing, grinding, polishing. | |
| K.3. fitting and fixation of the finished crown. |
Cast crowns, metal-acrylic and metal-ceramic crowns. Clinical and laboratory stages of their production.
Cast crowns
| Clinical | Laboratory |
| 1. Odontopreparation 0.5-0.6 mm Stump shape 3-5g. Obtaining a 2-layer print. | |
| 1. Making a collapsible model. Wax modeling of a crown. Replacing wax with metal. Processing and polishing, grinding. Sent to the clinic. | |
| 2. Fitting and fixing the finished crown using cement |
Metal acrylic
| Clinical | Laboratory |
| 1. Odontopreparation is 0.5-0.6 mm, but in the vestibular side the preparation is deeper. Obtaining a 2-layer print. Definition of color. | |
| 1. Making a collapsible model, modeling the frame, creating contact points for attaching plastic to the vestibular surface. Replacing wax with metal. Frame processing | |
| 2. fitting the crown | |
| 2. Grinding, polishing, modeling the vestibular surface using wax on plastic. Grinding, polishing. | |
| 3. Fitting and fixing the crown into the oral cavity |
Metal-ceramic
| Clinical | Laboratory |
| 1. Odontopreparation up to 2 mm Creation of a ledge. Obtaining a 2-layer print. Definition of color | |
| 1.Making time. Plastic crowns for prepared teeth. Making a collapsible model, modeling the frame, replacing wax with metal. | |
| 2. fitting the crown. | |
| 2. Manufacturing of ceramic coating | |
| 3. Fitting the crown | |
| 3. Glazing (final production) | |
| 4. Fitting and fixing the finished crown using cement. |
Pin structures and their elements. Indications for use. Requirements for the condition of the root and surrounding tissues.
Pin structures and their elements. Indications for use. Requirements for the condition of the root and surrounding tissues.
A pin tooth is a permanent prosthesis that completely replaces the crown of a natural tooth and is strengthened in its root canal using a pin.
Pin tooth elements:
1. a pin entering the root canal;
2. artificial crown.
Indications for use:
• complete absence of crowns of the upper front teeth and first premolars.
Requirements for the tooth root:
1. The root should protrude above the gum or be at its level;
2. Stopped chronic processes in the area of the tooth apex;
3. The protruding part of the root must have solid walls not affected by caries;
4. The ratio of root length to crown length is 2:1;
5. Root stability.
The root canal must be sealed up to or beyond the root apex and be of sufficient length and width.
Stump pin teeth are solid-cast structures consisting of a pin, an inlay and a stump of the tooth crown. The stump of the crown (tooth) is covered with an artificial crown.
CHAPTER 16. MANUFACTURE OF METAL-PLASTIC AND METAL-COMPOSITE DENTURES
, solid dentures are now widely used
especially with aesthetic cladding.
Such prostheses, in addition to metal-ceramic,
include
metal-plastic
(metal-acrylic) and
metal-composite.
These structures have good mechanical properties, are very aesthetic and closely imitate natural teeth. Plastic has been used as a facing material for metal dentures, especially for front teeth, for quite a long time. However, its inherent disadvantages, such as the possibility of developing toxic-allergic reactions, high abrasion, low color stability, prompted the development of a new class of materials - composites. Currently, in orthopedic dentistry, a wide arsenal of veneering materials is used in the manufacture of metal-composite dentures.
16.1. SEQUENCE OF CLINICAL AND LABORATORY STAGES IN THE MANUFACTURE OF METAL-PLASTIC AND METAL-COMPOSITE DENTURES
Metal-plastic and metal-composite dentures are currently quite widely used in orthopedic dentistry clinics. These dentures are classified as non-removable; they consist of a metal frame and a facing layer made of plastic or composite materials. The manufacturing technology of such dentures includes the manufacture of a cast metal frame, covering it with a plastic or composite lining and contains the following steps.
— Stage 1 - clinical:
◊ examination of the patient, diagnosis, choice of treatment plan and design of the medical device - metal-plastic or metal-composite dental prosthesis;
◊ preparation of abutment teeth under anesthesia;
◊ at the same stage it is possible to obtain impressions and register central occlusion or central ratio; the prepared abutment teeth must be covered with temporary plastic crowns, especially for vital teeth.
— Stage 2 - laboratory:
◊ making dismountable plaster models of jaws and plastering them into an articulator or occluder;
◊ wax modeling of the prosthesis frame and preparing it for casting.
— Stage 3 - laboratory:
◊ obtaining a metal frame of a denture by casting (usually carried out in a foundry laboratory by a dental foundry technician).
— Stage 4 - laboratory:
◊ fitting a metal frame of a denture to a collapsible plaster model of the jaw.
— Stage 5 - clinical:
◊ fitting the metal frame of the denture to the supporting teeth in the oral cavity;
◊ determination of the color of plastic or composite cladding.
— Stage 6 - laboratory:
◊ production of lining (plastic or composite) on the metal frame of the denture;
◊ polishing a manufactured metal-plastic or metal-composite denture.
— Stage 7 - clinical:
◊ application and fixation of a metal-plastic or metal-composite denture in the oral cavity.
Pros and cons of using plastic crowns
Dentists, in the process of prosthetics, highlight the advantages of plastic crowns:
- the ability to restore the previous shape of a tooth in just an hour;
- the material does not differ in color compared to healthy teeth;
- plastic prostheses are cheap;
- support the structure of the dentition, preventing teeth from moving.
Temporary prosthetics also note the disadvantages of plastic crowns, which include the fragile structure of the materials, the possibility of inflammatory processes in the gums and the risk of allergic reactions.
Indications and contraindications
Plastic crowns can be installed on both front and chewing teeth. At the same time, there are indications and contraindications for plastic crowns that must be taken into account. The client must understand that prosthetics are a temporary phenomenon that cannot always be avoided.
During dental treatment, a dentist may identify the following indications for a plastic crown:
- Restoring the aesthetic appearance of teeth.
- Protecting the diseased tooth from further destruction.
- To maintain gum level during the production of a permanent denture.
There are practically no contraindications to prosthetics in dentistry, but the dentist must pay attention to whether the client has any allergic reactions to the material used.
What types of plastic crowns are there?
There are different types of plastic crowns, which differ from each other in the manufacturing method and material, and also have their own characteristics. In addition, dentures have different durations of wear. They can be temporary or permanent.
The manufacturing process uses plastic crown materials, which are obtained by mixing liquid and powder components. Thanks to this, the prosthetist receives an elastic mass with which he makes a crown for the tooth. Most often, dentists use ready-made pastes packaged in small packages.
Plastic materials for making crowns are divided into:
- acrylic monomer;
- acrylic non-monomer;
- plastic composite non-monomer;
- thermoplastic.
The type of plastic teeth is also influenced by the method of reinforcement. This is reinforced with special metal caps or fiberglass mesh. This way the plastic crown will be durable and resistant to wear.
Metal-plastic denture designs are based on a cap made of metal, and the polymer is used only to cover the visible part of the teeth.
What functions do dental crowns perform?
During dental treatment, the dentist may recommend installing a crown on the tooth. He does this in order to:
- strengthen the dentition;
- improve dental functions;
- restore correct shape.
Most often, fillings are installed on teeth damaged by caries, which protect the affected area from further development of the disease. But using a crown in this case is more effective. The production of plastic crowns takes place in a special dental laboratory using computer modeling. The process takes into account the bite, jaw movement, and tooth shape. Thanks to this, the crown precisely restores the damaged tooth surface.
In addition, plastic crowns will help a person get rid of the discomfort that he feels when smiling or communicating with other people. The aesthetic appearance of the dentition obtained by installing crowns will help him to be self-confident and behave more relaxed.