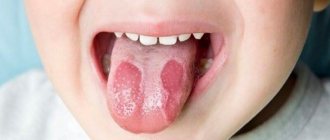
Tongue diseases do not develop as often as pathologies of teeth and gums. However, they cause a lot of trouble and pain. As a rule, people are faced with the problem of enlargement of the papillae, changes in their color and texture. Their hypertrophy causes pain and discomfort, signaling an inflammatory process and problems in the body.
The cause of an increase in receptors may be infections of the oral cavity, bacterial microflora, tongue injuries, or hidden ailments. Each specific case is individual, so if you have a similar problem, you should see a dentist. After diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe effective therapy.
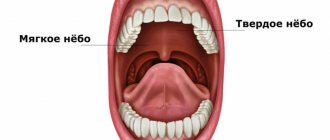
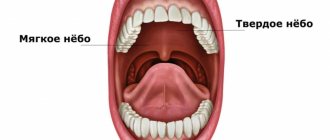
Anatomy of the tongue with photos
The tongue is formed by striated muscle tissue covered with a mucous membrane. It is involved in digestion, speech formation, allows you to express emotions, sense tastes, and regulates salivation. In a healthy person, the tongue has a pale pink color, with an even hollow running along it. Normally, it is covered with a whitish coating, which allows the grooved papillae of the tongue to be clearly visible.
Anatomically, the tongue consists of a root (1/3) and a body (2/3), separated by a terminal groove, as can be seen in the photo. The part facing the sky is called the back. On the lower surface there is a frenulum attached to the floor of the mouth. The tongue moves freely in the oral cavity and is rarely at rest. Thanks to the muscles, it can rise, shorten and thicken.
INTERESTING: photo of the root of a person’s tongue and the reasons for its color change
Material and methods
Biopsies of the dorsal surface of the tongue were studied in 7 (3 men and 4 women) patients with a non-erosive form of GERD and, as a comparison group, in 6 (3 men and 3 women) people without pathology of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Informed consent from the patients for the study was obtained. The average age of patients with GERD was 35 years (interquartile range 23; 42), disease duration was 4.8±2.7 years. The diagnosis of GERD was based on diagnostic criteria recommended by the Russian Gastroenterological Association: a set of clinical data, 24-hour pH-metry, esophagoduodenoscopy and a specialized GerdQ questionnaire [3]. At the time of biopsy, patients were not receiving therapy.
Biopsy specimens were studied using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and fluorescence confocal microscopy (FCM) in the laboratory of molecular biology and genetics (Dr.Med.Sci., Prof. S.A. Gusev, DSc.Med.Sci., Prof. G. I. Lukina) Federal State Budgetary Institution Federal Scientific and Clinical Center for Physico-Chemical Medicine of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia. To perform SEM, biopsies measuring 0.5×1.0 mm were fixed in a mixture of 2% formaldehyde solution and 1.4% glutaraldehyde solution (pH 7.4) on the 1st day at a temperature of 40 °C, washed in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) and distilled water for 2 hours at each stage. After dehydration in ethyl alcohol of increasing concentration, the samples were dried using the liquid substitution method by transitioning the critical point using a Hitachi HCP-2 apparatus (Hitachi, Japan) and coated with a 10 nm thick layer of gold by sputtering in a JEE-420 vacuum unit (Joel) , Japan). The study of filiform papillae in the obtained preparations was carried out using a scanning electron microscope S-570 (Hitachi, Japan).
For FCM, unfixed biopsy specimens were immediately stained with fluorescent dyes - synthetic fluorophores carboxyfluorescein (fluorescence emission in the green-yellow region of the absorption spectrum, λ 520 nm) and tetramethylcarboxyrhodamine (fluorescence emission in the red region of the absorption spectrum, λ 576 nm) (Synthol, Russia ). These dyes freely penetrate cell membranes and stain the nuclei of epithelial cells, as well as bacterial chromatin.
Types of papillae on the tongue, their functions
Papillae are growths of the mucous membrane on the body of the tongue, covered with non-keratinized epithelium. Their main function is to analyze touch and taste. Receptors are located along the edges and on the back of the tongue, the highest concentration is observed in the anterior sections. There are 5 types in total: filamentous, leaf-shaped, groove-shaped, mushroom-shaped and conical. Each has its own characteristics:
- Thread-like stretched along the edges of the tongue. Their number is greatest, their function is to touch and hold food in the mouth, they do not perceive taste.
- Conical ones are located together with filiform ones and are similar to them in structure and functions. They are designed for mechanical processing of food and contain temperature and pain receptors.
- The groove-shaped papillae are located closer to the root. They include the body, ridge and glands, and are responsible for the perception of bitter taste.
- Leaf-shaped are located near the palatine arches. They have an oval shape, like folded leaves. Deep down there are glands that detect bitter taste.
- Mushroom-shaped taste buds resemble white caps covered with epithelium. They are randomly located on the body of the tongue, excluding the center of the back. Responsible for the perception of sweets.
Causes
Factors that provoke the development of inflammatory processes include:
- Diarrhea and food poisoning - harmful substances released during bowel movements negatively affect the papillae;
- An inactive lifestyle - this contributes to the appearance of stagnant processes in the pelvis;
- Constipation, in which the papillae are injured during bowel movements;
- Abuse of enemas - with frequent procedures, the mucous membrane of the anal canal is damaged;
- Drinking alcoholic beverages;
- Allergy to personal hygiene products, underwear material;
- Proctological diseases: critpitis, proctitis.
Why do the papillae sometimes become inflamed and enlarged?
Hypertrophy of the taste buds of the tongue often occurs in children and unbalanced people. The first ones to put dirty toys and hands into their mouths cause infection. The latter may bite their nails or stationery, from the surface of which pathogenic bacteria enter the mouth.
Inflammation of the white fungiform papillae of the tongue is provoked by viruses, bacteria, fungal infections, and systemic diseases. In this case, quite unpleasant symptoms are felt: burning and loss of taste, sensation of a foreign body on the tongue, pain when eating, talking, brushing teeth. READ ALSO: for what reasons can inflammation on the side of the tongue occur and how to eliminate it?
The cause of red spots is often irritation of the circumvallate papillae. They can become inflamed due to chemical and thermal burns of the oral cavity, gastroesophageal reflux disease. People with dentures and lovers of hard sweets and lollipops also complain about this problem. Inflammation cannot be avoided in the presence of chipped teeth that injure the mucous membrane of the tongue.
READ ALSO: tongue diseases with descriptions and photos
Inflammation of the papillae in children
The most common cause of inflammation of the papillae on the tongue of children is desquamative, allergic, traumatic or fungal glossitis. In children, inflammation of the papillae on the root of the tongue occurs in a more acute form than in adults. Therefore, if the baby’s oral mucosa begins to become inflamed, it is necessary to immediately seek advice from a specialist. Treatment of inflammation and enlargement of the papillae on the child’s tongue should be carried out in strict accordance with the pediatrician’s recommendations.
Diagnosis of tongue diseases
The dentist diagnoses tongue diseases by its appearance, size, thickness, and state of the receptors. Almost always there is an abnormal shade of its surface, uncontrolled copious secretion of saliva, and immobility of the organ. It increases in size, making it difficult to swallow, and an unpleasant odor appears from the mouth. When examining the oral cavity, the specialist pays attention to the condition of the teeth and gums, the presence of pustules, pimples and rashes.
READ ALSO: what does it mean if pimples appear on the tongue, located closer to the larynx?
In addition to visual inspection, the following tests are carried out:
- smear to determine the causative agent of the inflammatory process,
- biochemical and general blood tests to assess the condition of the body,
- blood tests for viral, bacterial infections, AIDS,
- tissue histology (in the presence of an abscess),
- if necessary, a referral is given to an immunologist, infectious disease specialist, rheumatologist, gastroenterologist, otolaryngologist and other specialists.
Glossitis
Glossitis is caused by bacteria and viruses (most often herpes and Candida fungus). The spread of infection occurs through injuries and microcracks of the mucous membrane, consumption of hot foods, alcoholic beverages, and smoking. Sometimes it is a symptom of iron deficiency anemia, HIV, lichen planus, and oncology.
A characteristic sign of glossitis is red dots on the tip and in the area of the root of the tongue (vallate papillae enlarge), its inflammation and swelling (we recommend reading: bright red tongue: causes and methods of treatment). The surface of the organ becomes smooth, it hurts when swallowing and talking. Additionally, the patient complains of a constant burning sensation in the mouth and that the tongue has become very enlarged (more details in the article: why does the tongue sometimes swell a lot?). If you consult a dentist in time, treatment for glossitis will be quite simple and quick. In advanced cases, respiratory dysfunction and swelling of the tongue are possible (we recommend reading: tumor under the tongue: causes, photos and treatment).
General treatment recommendations and consequences
The formation of small blisters or ulcers, the appearance of white or pink papillae on the tongue, the proliferation of villi are the first symptoms of the inflammatory process, which can subsequently lead to hypertrophy of the grooved, mushroom-shaped and other types of papillae.
The dangerous consequences of glossitis are suppuration and the spread of infection to the respiratory and digestive organs. The pain that accompanies the enlargement of receptor structures interferes with talking and eating, and in children it causes severe anxiety and even weight loss. Therefore, any symptoms of glossitis require immediate treatment. The treatment tactics for inflammation of the tongue papillae depend on the cause of its development.
Treatment of tongue papillae inflamed due to injuries and burns
Burns and traumatic injuries to the mucous membrane of the tongue lead to the development of papillitis. In the absence of other alarming symptoms - fever, severe swelling and suppuration of tissues - papillitis can be dealt with at home. Carrying out at home:
- Rinsing the mouth with disinfectants. It is better to take decoctions of medicinal herbs, for example, calendula.
- Treating the tongue with agents that accelerate healing and restoration of soft tissues. Solcoseryl ointment, Lugol's solution, Chlorophyllipt, and sea buckthorn oil can be used.
- Use of analgesics: Lidocaine, Anestezin. It is better to consult your doctor about the dosage and regimen of taking painkillers.
During the treatment of inflammation of the taste buds of the tongue, you need to adhere to a special regime that allows you to create gentle conditions for soft tissues damaged by papillitis:
- It is undesirable to smoke and drink alcohol.
- You should not eat food with a strong salty or spicy taste.
- Temporary removal of removable dentures may be necessary.
If the cause of inflammation of the tongue papillae is a prosthesis, you should definitely consult a dentist to correct the shape or completely replace the uncomfortable design.
Treatment of infectious inflammation
In case of inflammation of the oral mucosa, glossitis and papillitis, you must adhere to the following rules:
- If the papillae on the root and edges of the tongue are enlarged, you should not drink alcohol-containing drinks, and it is not advisable to smoke.
- Food should be moderately salty, without hot spices, not hot and not very cold.
- If the cause of the appearance of red papillae on the tongue is an infection or disease of an internal organ, or the patient’s temperature rises, you should definitely go to the doctor to find out why the inflammation has developed. Such inflammatory processes pose the greatest danger to children, so you should contact a pediatrician immediately.
Papillitis and glossitis are serious diseases that not only cause discomfort, but also entail other dangerous consequences. If a person notices that his papillae on the tip or back of his tongue have enlarged, he should immediately consult a doctor in order to identify and treat the disease at an early stage. Mild forms of glossitis can lead to the development of more severe ones, accompanied by complete death of enlarged papillae and the risk of poisoning the body with microorganism toxins .
Prevention of papillitis
To avoid inflammation of the anal papillae, it is recommended:
- Observe hygiene procedures: rinse the anus after each act of bowel movement;
- If gastrointestinal diseases are detected, undergo timely treatment;
- Move more to eliminate congestion in the pelvic area;
- Get rid of bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol);
- Avoid “heavy” foods;
- In case of constipation, use laxatives.