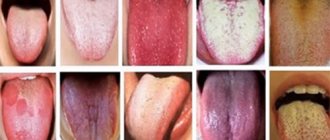
When red bumps appear on the tongue, at the tip or closer to the throat, you need to find out what this phenomenon is. Such rashes often bother not only adults, but also children. And since they arise for a wide variety of reasons
, you need to figure out whether pimples pose a danger and choose the optimal treatment method.
Classification of pimples
There are many types of pimples on the tongue. They are classified according to four characteristics: color, location, size and pain.
Color
- Natural, red-pink.
Growths that do not differ in color from the tongue and are painless are warts or condylomas. - When red or bloody pimples
, such as in the photo, their cause may be a burn, herpes, or allergic reactions. - Red bumps that turn black
are associated with mechanical damage or injury. The black color appears due to microhemorrhage.
Location
- On the tip of the tongue.
Often this place is subject to injury and various damage, which can cause inflammation. First, a small bump appears on the end of the tongue, then a painful red or black pimple. - On the side.
In most cases, pimples are localized in this place, as a result of stomatitis, as well as benign neoplasms. - At the larynx.
Red pimples on the tongue closer to the throat often turn out to be benign formations: condylomas, warts. - Under the tongue.
Lumps and bumps in this place (near the frenulum) in both adults and children indicate inflammatory processes: tonsillitis, sore throat, pharyngitis.
The size of the formations can be large, medium or small.
Presence of pain
- Painful sensations.
Pimples resulting from injuries, burns, inflammatory and infectious lesions of the oral cavity and larynx. Pain manifests itself when touching the tubercles; it hurts a person to speak or swallow. - There is no pain.
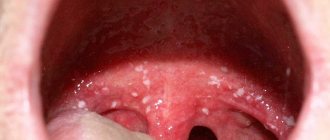
In most cases, painlessness is characteristic of warts and condylomas. Benign neoplasms often affect the root of the tongue; you can see how it looks with pimples in the photo.
Causes of pimples on the tongue
The main causes of rashes:
- Traumatic injuries, burns. It is not uncommon for the tip or side surface of the tongue to be damaged by cutlery, excessively hot food, or one’s own teeth.
- Weakened immunity. When pimples appear on the tongue closer to the throat, at its base or near the frenulum, this may indicate reduced immunity. A variety of pimples and bumps are localized here: condylomas and warts, candidal bumps.
- Development of benign and malignant tumors.
- Poor nutrition, bad habits. If you violate the rules of nutrition, excessive consumption of spicy, hot, rough foods, an irritating and traumatic effect on the mucous membrane occurs, which provokes the appearance of pimples. Excessive smoking and alcoholic libations also cause diseases of the mucous membranes in adults.
- The causes of lumps at the end and root of the tongue may be allergic. Allergic disease manifests itself not only on the skin, but also on mucous membranes.
Large bumps located close to the pharynx make it difficult to swallow food and can lead to breathing blockage.
- If pimples appear on the tongue closer to the larynx, they could be caused by various diseases of a chronic, viral and infectious nature.
- Neglect of hygiene rules. Eating unwashed foods and irregular oral hygiene not only in children, but also in adults, causes irritation of the mucous membrane and, as a result, the appearance of inflamed pimples.
Red bumps on the tongue closer to the throat - what are they?
In most cases, bumps at the base of the tongue, pimples on the side, growths on the tip of the tongue are manifestations of the following diseases:
- Diseases of the mucous membrane of an inflammatory nature (glossitis) are accompanied by the formation of painful red rashes on the mucous membrane, in severe form - abscesses, phlegmons.
- Metabolic disorders, vitamin deficiency. Such conditions are characterized by redness and enlargement of the taste buds, which often become inflamed and acquire a red-white color.
- Herpes, characterized by the appearance of painful red pimples and blisters.
If red bumps or nodules appear on the base of the tongue, this may be a symptom of pyogenic granuloma. The formations consist of blood vessels and are localized in the wounded area. Pathology occurs due to injuries and damage to the mucous membrane. When touching the formations, a person feels a sharp pain.
- Digestive disorders (malabsorption). Pimples on the root, all over the surface of the tongue, are one of the symptoms of this pathology.
- Candidiasis (thrush). A disease that often affects newborns. The child's tongue becomes covered with red bumps and a cheesy coating forms. The baby behaves restlessly, cries, and has difficulty swallowing; these symptoms are caused by itchy red-white pimples and dry mouth.
- HPV – human papillomavirus. Formations are localized in any area of the tongue: at the tip, root, side. The bumps on the tongue closer to the larynx cause particular discomfort, as they interfere with swallowing and create the sensation of a foreign object in the mouth.
- Allergic diseases. The rashes do not hurt, but they interfere with swallowing and speaking.
- Diseases common to children: chickenpox, measles.
Main symptoms of glossitis
Glossitis, the symptoms of which are very diverse and largely depend on the cause of the disease and the stage of development of the process, but the following signs are almost always present:
- coating on tongue uneven with spots
- ulcers in the oral cavity of varying depth and extent
- color changes (general or in the form of local spots)
- swelling of the tongue, the presence of “imprints” of teeth on its lateral surfaces and other sores
- limited tongue mobility
- bad breath problem
- salivation disorder
Often these changes are accompanied by a decrease in taste sensitivity, a burning sensation and pain at the slightest movements of the tongue while eating and when talking. Sometimes, as the inflammatory process progresses, there is a deterioration in general health: an increase in temperature, enlargement of the submandibular and cervical lymph nodes.
Treatment of pimples on the tongue
Carrying out an examination of the mucous membrane of the tip, side, and root of the tongue, the doctor examines the red pimples and growths. Based on laboratory tests, examination and medical history, the specialist makes a diagnosis, finds out why the disease appeared, and determines the therapeutic direction. The classic method of treatment is medication:
- Antibiotics are used to destroy bacteriological pathogens
. Effective drugs for local action: Bioparox, Fuzafyungin. As well as medications for systemic treatment: Amoxicillin, Cefadroxil. - To prevent the rashes from becoming inflamed, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed: Stomatidin, Ingalipt, Lugol.
- Antiseptic agents accelerate wound healing: Chlorhexidine (it is necessary to apply lotions and rinses).
- Dysbacteriosis, which can cause rashes on the mucous membranes, is treated with probiotics: Bifidumbacterin, Acipol, Linex, Bifiform.
- If pimples appear on a baby's tongue, they are often caused by fungal infections; thrush is treated with antifungal drugs
. It is worth doing daily rubbing of the tongue, cheeks and lips with a broad-spectrum solution of Candide. After just 1–2 days, less plaque forms, and after a week, the signs of the disease completely disappear. - Allergic reactions are eliminated with the help of antihistamines: Fenistil, Cetrin, Erius.
Pimples appeared on the tongue: treatment at home
Having determined the nature of the rash, the doctor can prescribe a comprehensive treatment of the disease (drug and herbal treatment) or non-drug treatment at home. Pimples on the root, tip, and near the frenulum of the tongue can be removed using folk remedies.
Herbal medicine
Herbal decoctions and infusions effectively remove pimples both on the tip and at the base of the tongue. The most effective rinses are chamomile, St. John's wort, and calendula. Herbal decoctions are especially effective when the rashes are inflamed.
Method for preparing the decoction: pour a teaspoon of herbs into a glass of boiling water, leave for about 15 minutes, and cool. You need to rinse your mouth 2-4 times a day.
Infusions and decoctions can be taken orally, this will help alleviate the symptoms of the disease, relieve inflammation, and help stabilize metabolic processes.
Compresses and lotions
If the formations are inflamed, pain and inflammation can be relieved by applying a cotton swab moistened with a herbal decoction of chamomile and calendula to the affected surface.
You can numb the surface of the tongue using therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste, which is applied for 2 minutes. The paste relieves pain, has a calming, anti-edematous and anti-inflammatory effect.
Rinsing with antiseptic solutions
They help treat inflammation of the mucous membrane, eliminate tubercles on the tongue both at the very beginning and closer to the throat. In the fight against the disease, the use of Chlorophyllipt and Chlorhexidine is common. The preparations can be used as rinses and are effective for irrigating the oral cavity. Procedures are carried out several times a day.
Diagnostics
Otolaryngologists are most often involved in identifying the causes of symptom development. According to indications, patients are referred to dentists, gastroenterologists, neurologists, and other specialists. During the conversation, the doctor finds out how long ago the foreign body sensation appeared, what manifestations were accompanied, and how the symptom changed over time. Conducts a general inspection. Based on the preliminary examination, the following diagnostic procedures can be prescribed:
- Oropharyngoscopy.
Basic research in otolaryngology. This is done using a spatula. Allows you to diagnose high-lying foreign bodies, inflammatory diseases of the tonsils and pharynx, peritonsillar abscess, and some neoplasms. - Endoscopic ENT examinations
. They are carried out using special mirrors, a rigid or flexible laryngoscope. Taking into account the localization of the pathological process, the patient may require pharyngoscopy, laryngoscopy, or endoscopy of the larynx. - Dental examination
. Aimed at detecting diseases of the tongue, neoplasms of the oral cavity, accompanied by a feeling of a foreign body. - Ultrasound of the thyroid gland.
Indicated for suspected endocrine pathology, to exclude organ hypertrophy in patients with pharyngeal neurosis. Reveals diffuse and focal pathological processes. If necessary, supplemented with TSH, T3, T4 studies. - Esophageal studies
. Fluoroscopy data are used in the diagnosis of dyskinesia and GERD. To confirm motility disorders with dyskinesia, esophageal manometry is performed. An esophagoscopy is performed to identify signs of gastroesophageal disease. - Magnetic resonance imaging
. MRI of the soft tissues of the neck is prescribed to exclude tumor processes that cause a foreign body sensation. MRI of the brain is informative in identifying pathologies of the central nervous system that provoke pharyngeal neurosis. - Lab tests
. Depending on the characteristics of the pathological process, microbiological, histological, and cytological studies of material from the larynx and pharynx (smears, biopsies) are performed.
Preventive measures
Simple preventative measures will prevent the onset of the disease. Basic rules of behavior and hygiene:
- Fruits and vegetables should always be washed before consumption.
- Food should not be excessively hot, cold, spicy or rough.
- The chewing process should be slow, which will prevent tongue biting.
- Personal hygiene should be observed: dental and oral care.
- It is necessary to have individual cutlery and a toothbrush.
- The brush should be renewed monthly. Change immediately after an illness.
- Regular visits to the dentist are recommended. It is necessary to treat diseases of the teeth and oral cavity in a timely manner, remove tartar and plaque, because these are the main sources of infection in the mouth.
- It is necessary to maintain adequate physical activity, which will increase immunity and the condition of the entire body.
Any pimple, growth or tubercle on the mucous membrane, both in an adult and in a child, requires close attention. You should not treat the bumps yourself; only a doctor can do this.
You should not pierce or try to squeeze out pimples on the mucous membrane; such actions can lead to negative consequences: the growth of foci of inflammation, the appearance of open wounds as a result of injuries.
The best thing a person can do if they have bumps on their tongue is to see a dentist or therapist. Such a decision will speed up recovery and prevent possible complications.
Herpetic stomatitis in children
There are several types:
- sharp;
- chronic.
This type of damage to the oral mucosa occurs when the herpes virus first enters the human body. Acute stomatitis is typical only for young children. Herpetic stomatitis that occurs repeatedly is called chronic. Herpes stomatitis in an infant appears due to infection of the child by the mother or other people who kiss the baby out of excess of feelings or taste food with the spoon with which he is then fed.
Acute herpes-type stomatitis
The herpes virus enters the baby's body after he reaches the age of six months. At this time, the antibodies the child received from the mother gradually cease to act. In the vast majority of cases (about 90%), the symptoms of stomatitis at such an early age are mild, and only in 10% of children the disease is acute.
Stomatitis in children under one year of age, the treatment of which takes about 2 weeks, is accompanied by weakness in the body, general malaise and muscle pain, which is explained by poisoning of the body. In some cases, the temperature during the first two days of the disease may rise to 40 degrees or higher. The lymph nodes become inflamed, and touching them causes pain to the baby.
A distinctive sign of the disease are small bubbles that appear in groups on the lips, palate, and tongue. The oral mucosa takes on a bright red hue. The bubbles are filled with a clear liquid that gradually becomes cloudy. After about 3 days, the blisters burst, leaving behind erosions covered with a yellow or white fibrinous coating.
Sometimes the gums near the teeth may turn red, so the disease is often confused with gingivitis.
Chronic stomatitis
Once the herpes virus enters the human body, it remains there forever. Symptoms may occur when:
- cold;
- lack of vitamins;
- stressful situations;
- exacerbation of sinusitis, tonsillitis and other chronic diseases;
- injury to the mucous membrane;
- gingivitis or caries;
- habit of breathing through the mouth (lips become dry, causing the skin in the corners of the mouth to crack).
Chronic stomatitis develops in exactly the same way as acute stomatitis, with the exception that the disease does not affect the general condition of the body, because intoxication is minimal.
Herpetic stomatitis in children: how to treat
Types of treatment:
- Use of antiviral agents. Ointments and gels, which are often used to treat herpes on the lip, should not be applied to the oral mucosa. Treatment is possible with suppositories or tablets. The most effective drugs include two drugs. The first of them is “Viferon”, which contains interferons that have an immunostimulating effect. Available in the form of suppositories and gel. There are no age restrictions on the use of the product. The gel should be applied directly to the affected mucous membrane, after drying it with a swab. The treatment period does not exceed one week, provided that the product is regularly applied three times a day. The second is the antiviral drug Acyclovir, which acts on the herpes virus itself, and does not simply increase immunity. The dosage regimen is the same for children over 2 years of age and twice.
- Rinse. It is necessary to use solutions whose action is aimed specifically at suppressing the herpes virus (such popular and cheap remedies as chlorhexidine and various herbal infusions are not suitable). The most effective drug is Miramistin, which should be rinsed three times a day. For greater results, you can apply Viferon a short period of time after rinsing.
- Use of symptomatic remedies. Antipyretic drugs are used when body temperature exceeds 38 degrees. At lower temperatures, such tablets will do more harm, since they will interfere with the formation of natural immunity and the production of interferons.
- Use of immunomodulators. If stomatitis in children, which was treated according to all the rules, makes itself felt again, you can resort to the use of immunomodulators, the most effective of which are:
- “Immunal” is a basic drug that increases immunity.
- “Imudon” stimulates the immunity of the oral mucosa. One course lasts 20 days (you need to take 6 tablets every day). 2 courses per year are recommended.
- Toothpastes with lactoferrin and lysozyme (these substances are contained in special Splat children's toothpastes).