Types of pediatric anesthesia How does it work?
Signs of proper sedation Drugs Indications Contraindications Possible complications Alternatives Most people associate going to the dentist with fear and stress. And if we are talking about a child, then the whole family is afraid of the visit. Therefore, the promises of dental clinics about dental treatment under anesthesia for children, without pain, in their sleep, sound like a balm. What is meant by “pain-free treatment” and is it as safe as we are told?
Sedation
– this is inhibition (depression) of the nervous system in order to relax and reduce anxiety. It does not exclude the use of local anesthesia, but simply helps overcome the fear of treatment. This is the main difference between dental treatment under sedation in children and the use of anesthesia.
But the word “sedation” did not catch on among the people, and gradually even dentists began to use expressions like “treatment of children’s teeth under anesthesia” in order to be understood by a wider audience. In this case, what is often meant is not general anesthesia, but rather sedation, a condition in which consciousness is suppressed while all protective reflexes are preserved and the possibility of contact with the patient is preserved.
Types of anesthesia for children during dental treatment
Depression of consciousness can be deep, medium and superficial.
Medicines can be administered in different ways:
- Orally
. This is how we take regular pills. - Intravenously
. Oddly enough, some children are more comfortable with an injection than with a mask on their face. - Inhalation
. This is the most common way of administering drugs. Nitrous oxide is most often used.
Which is safer: Sevoran or Propofol for children?
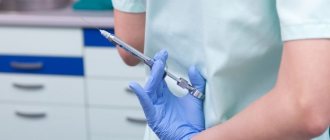
The doctor should take part in deciding which drug to use for treatment, whether to give the child propofol or sevoran. In terms of effectiveness and safety, these drugs are almost identical - Sevoran is slightly (several percent) ahead of Propofol, but it is more convenient to administer Propofol, since during dental procedures intravenous administration through an infusion pump is better, which makes it easier to control the dosage than administration of gaseous Sevoran through a special mask.
But the most important thing is that Propofol and Sevoran have different active ingredients, so their safety, effectiveness and possibility of use may differ in any particular case due to the individual characteristics of the child’s body (for example, the presence of an allergy to a certain substance) and this can be determined only a doctor.
How it all happens
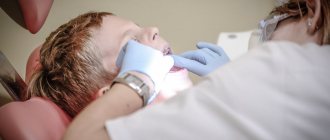
Treatment of children's teeth under anesthesia begins with an acquaintance and conversation with the doctor. Sometimes they play cartoons in the office, and some clinics offer toys. Then he is allowed to examine the mask, is asked to try it on, and they begin to supply pure oxygen, to which nitrogen is gradually added, increasing its concentration. After a couple of minutes the child falls asleep. After this, sensors for monitoring his condition are connected to him and treatment begins.
The duration of dental treatment in a dream varies depending on the defect, complexity of the process and other factors. At the end, they are given oxygen again. After the procedure is stopped, the child wakes up gradually. He is under the supervision of doctors for at least an hour in a specially designated room. That day it is better for him to stay at home and not visit the children's group.
When using tablets or intravenous drugs, the algorithm of action is the same, only without a mask and oxygen.
Reviews
The first visit to the dentist can be a daunting experience for children and their parents. In each of the clinics of the Natadent network, we have created a truly warm and comfortable environment. We welcome every feedback - you help us become better.
LEAVE FEEDBACK
What drugs are used
Nitrous oxide or other drugs are used for inhalation anesthesia. The instructions for use of such drugs list as side effects: respiratory problems, cardiac depression (depending on the dose), nausea, vomiting. But worst of all, with a genetic predisposition, a dangerous disease can develop
[1] – hyperthermia. The chances of this happening are slim, but no one does genetic testing before dental treatment, so the possibility cannot be ruled out.
Other drugs are used intravenously and orally (in tablets), which also have side effects, although not as pronounced.
Indications and contraindications
There are certain indications for the use of anesthesia. This:
- a large volume of therapeutic and surgical manipulations necessary for complete rehabilitation;
- duration and pain of the planned intervention;
- the presence of purulent processes (abscesses, phlegmon), in which local anesthesia is ineffective;
- the possibility of carrying out a complete rehabilitation in one session;
- mental characteristics of the child;
- neurological diseases;
- allergies to medications used for local anesthesia;
- pronounced gag reflex;
- bronchial asthma;
- Dental phobia - an insurmountable fear of visiting the dentist, based on previous negative experiences;
- the desire of the parents, but there must be no contraindications.
In dental practice, there are also contraindications for general anesthesia, which the doctor must take into account. These include:
- acute respiratory diseases;
- decompensated cardiovascular pathology;
- liver and kidney diseases;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- severe form of rickets;
- recent vaccination;
- recent food intake;
- body temperature is higher than normal.
When is it worth treating children's teeth under general anesthesia in dentistry?
Due to the fact that the terms “sedation” and “anesthesia” are often used interchangeably, it is not always clear which procedure is being referred to.
If you were offered dental treatment for children in a dream, clarify this means sedation or anesthesia.
The main rule is that if you can avoid anesthesia, it is worth doing. Sedation is preferable, although it is also not a panacea. Studies on the long-term effects of general anesthesia show that the use of anesthesia can lead to problems in the development of cognitive functions
[2], especially if it is used repeatedly, which happens when treating children’s teeth in clinics where they take general anesthesia lightly.
There is a risk when using anesthesia
[3]:
- Airway obstructions
. This may be due to anatomical features (adenoids, enlarged tonsils), incorrect position of the jaw or tongue, or accumulation of sputum. Equipment failure can also lead to collapse. - Hemodynamic problems
. Complications include: slow (bradycardia) or, conversely, rapid (tachycardia) pulse, drop in blood pressure, puncture of a vein with a needle.
After such anesthesia, children may experience nausea, vomiting, impaired thermoregulation, muscle tremors, allergic reactions, and inappropriate behavior.
Anesthesia is recommended only in cases of absolute intolerance to local analgesics; in other situations, local anesthesia or, in extreme cases, sedation should be preferred.
Sedation does not have such a radical effect on the body, but the risks remain the same - problems with breathing and circulation.
In the vast majority of cases, complications during the use of anesthesia are caused by a doctor’s error. You need to be absolutely sure of:
- doctor's qualifications and experience;
- equipping the clinic with the necessary equipment to monitor the condition during anesthesia and to provide assistance if something goes wrong.
Although dentists have special training in the administration of sedatives, anesthesia should only be administered by an anesthesiologist.
Preparing your child for a trip to the dental clinic
Of course, under no circumstances should you put off your first trip to the dentist until a critical situation occurs. It is necessary, at a time when there is no worry, to take the child to the doctor, to show him that the dental chair is not at all scary, and the prevention of dental diseases helps to avoid serious problems. In addition, you can encourage your child’s calm behavior with something pleasant for him (but not sweets). Thus, the child’s fear and anxiety towards the doctor are minimized. It is also worth noting that children under three years of age have a reduced pain threshold and thus you can fearlessly take a very young child to the doctor, without fear for him and reinforcing the correct perception of the doctor as an assistant in maintaining health.
Among other things, be sure to provide psychological preparation to your child, talk to him and explain the benefits of regular visits to the doctor. Ask your child what worries him about the upcoming trip to the dental clinic, and do not let him instill fear in himself. Be calm and confident, and your good mood will definitely be passed on to your child.
In addition, you can prepare your child for a trip to the doctor by taking him with you to an adult clinic and demonstrating by personal example that there is nothing wrong with this. However, it is worth warning the doctor about the presence of the child, explaining the rules of behavior and choosing a time for visiting with the least number of patients, so as not to disturb the baby.
However, even if all of the above tips have been taken into account, they do not always guarantee that the child will not worry at all before going to the doctor. It may also happen that it will not be possible to implement all the recommendations on time. In any case, under certain circumstances, parents begin to become interested in the possibility of performing dental procedures with minimal discomfort for the child. As a rule, the first thing that comes to mind is general anesthesia. And if earlier the idea of dentistry under general anesthesia, especially for a small child, seemed completely impossible, now many clinics provide such a service. However, before going for it, it is necessary to arm yourself with the most complete knowledge about the procedure.
Premedication for children before visiting the dentist
In order to facilitate anesthesia and reduce risk factors for side effects and complications, one or more medications are used that are taken before dental procedures, which is called premedication. As you know, pain has 4 main components: The sensory component of the pain reaction is removed by a local anesthetic (lidocaine, benzocaine and articaine), removing sensitivity at the site of intervention, but the psycho-emotional, autonomic and motor components of pain must be reduced or removed before local anesthesia is administered. The psycho-emotional component can be reduced through persuasion and suggestion. However, you should still use medications that have a sedative effect. They are directly shown if it occurs:
- epilepsy;
- bronchial asthma;
- diabetes;
- thyroid dysfunction;
- insurmountable fear of treatment;
- tendency to hysteria;
- emotional stress;
- increased skeletal muscle tone, etc.
15-20 minutes before treatment, an anxiolytic drug is prescribed - chlordiazepoxide, better known to everyone as diazepam, Elenium, Valium, Relanium, Sibazon, Seduxen, Napoton, Radepur 10 or chlozepid. It can be taken by children from 4 years of age in a dosage of 5 to 10 mg, from 7 years of age - 10-20 mg, from 15 to 18 years of age - 20-30 mg per day in 2-3 doses. It is advisable to start taking diazepam a day before a visit to the dentist, and take the last dose required 15 minutes before the visit. Also, at home, you can prepare a decoction of valerian and motherwort roots and drink it a day or three before going to the dentist in accordance with instructions from the doctor and instructions on the packaging of the collection. In addition to sedative premedication, you should definitely take an antihistamine, preferably of the 4th generation, this can be: cetirizine (allowed from the age of 6 months), cyproheptadine (from 6 months), loratadine (from 2 years ) to prevent possible allergic reactions.
Sedation
Due to the fact that premedication is not always effective, and sometimes is impossible due to lack of time, in modern pediatric dentistry they resort to such a method of preparing for surgery as sedation. Sedation can be deep - with entry into a state of sleep and respiratory depression, and superficial – when the child is able to maintain contact with the dentist and follow his instructions, while breathing remains smooth. In pediatric dentistry, superficial sedation is used. Sedation is carried out by inhalation, immediately before the start of dental procedures, using a mixture of nitrous oxide (N2O) and oxygen (O2) - ZAX. At the beginning of sedation, the child receives pure oxygen through a mask, to which nitrous oxide is gradually mixed over about 15 minutes. Although the permissible concentration of nitrous oxide in the mixture can reach 70%, for children it is usually stopped at 30%, the remaining 70% is medical oxygen. Sedation with the ZAX mixture causes a feeling of relaxation, good mood, calm, and slight drowsiness in a small patient. The child sees and hears his parents and the dentist, but does not experience fear or anxiety. The supply of a sedative mixture and the evacuation of exhaled gases from the mask are carried out using special electronic-automatic devices. By the time the necessary dental procedures are completed, the proportion of nitrous oxide in the mixture decreases inversely and the proportion of oxygen increases to 100%, after which the inhalation mask is removed. The effect of nitrous oxide disappears without a trace within 5–10 minutes, evaporating from the child’s lungs unchanged. Nitrous oxide has a certain analgesic effect, but it is not enough for dental operations, so local anesthesia is additionally performed. Sedation with a ZAX mixture is carried out starting from the age of four the age of the child when you can establish contact with him. The main task of the dentist is to persuade the little patient to independently apply the mask to the breathing apparatus; for this purpose, special aromatic, delicious-smelling masks are used, which make the child want to inhale “laughing gas” without forced action on the part of parents and the doctor. Modern private clinics go further on the path to stress-free treatment of children - they show cartoons during sedation, tell fairy tales, etc. How harmless is ZAXL sedation? Judge for yourself: in pediatric dentistry in all developed countries, sedation is used in up to 80% of cases, so we can safely say that this is a proven method.
Developmental features or concomitant diagnoses of the patient
Sleep treatment under anesthesia is suitable for children with autism, cerebral palsy, Down syndrome, and epilepsy.
Whims, tears and reluctance to be treated are corrected by adaptation. Aza&Buka doctors have extensive experience in communicating with different patients and find an approach to everyone. Treating teeth today is not painful, fun, interesting. And if a doctor recommends treatment in a dream, then there really are indications for this.