The presence of milk teeth in adults cannot be attributed to the realm of fantasy or humor. This phenomenon can sometimes be encountered in dental practice. What contributes to the fact that a baby tooth can be preserved in adults and what to do with such a childhood “relic”?
Echo of childhood
Most people believe that baby teeth are closely associated with a touching and carefree childhood. It’s not for nothing that James Barry, a Scottish writer, in his fairy tale about Peter Pan - a boy who wants to always be young and not grow up - specifically describes that there were many milk pearl teeth in his mouth, and none of them had fallen out yet. Replacing baby teeth with permanent ones can be considered the same step into adulthood as the first room at school and the first two.
Teeth begin to change at about 5-6 years of age, and this process ends at about 12-14 years. Currently, according to the observations of many doctors, the replacement of baby teeth with permanent ones occurs in younger children than happened in past decades. But it also happens that baby teeth can be preserved in adults. Such cases can be encountered at 20, 30, and sometimes at 50 years of age. Why does this happen and what to do in such a situation?
Milk teeth and their features
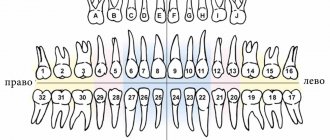
Temporary and permanent teeth have certain differences in structure. The shape of baby teeth is the same as in molars (permanent), but their size is much smaller, the roots are shorter, and the number is different - there are only 20 of them versus 32 permanent teeth (including wisdom teeth). “Children’s” teeth are characterized by a short service life: their roots dissolve over time (as dentists say, “resorb”) approximately 2-3 years after they are fully formed. This process begins with the area touched by the crowns of the permanent teeth growing underneath them.
But it happens that for one reason or another the formation of the rudiments of permanent teeth does not occur. In this case, the roots of baby teeth are more often resorbed as a result of the influence of the rudiments of permanent adjacent teeth. But it happens that this does not happen and “children’s” teeth can then remain in adults - dentists call them persistent (translated from Latin persistere - to remain, to remain).
Reasons for the development of edentia
Primary dental edentia is a genetic disorder, the origins of which have not been fully studied. The frequency of pathology in different years is recorded in 1-2% of the population.
Complete and partial secondary adentia are diseases that dentists constantly encounter. Doctors name several reasons for the loss
dental units:
- Advanced caries, pulpitis. An indirect cause that triggers the destruction of tooth tissue. After removal of the neurovascular bundle, the tooth becomes fragile and requires careful attention. If the patient comes late, the doctor resorts to removing the unit.
- Diseases of periodontal tissues. The ligament cannot hold the tooth in the socket, and the crown begins to loosen. In the absence of proper treatment, the process spreads to the gums and destroys the structure of the jaw bone.
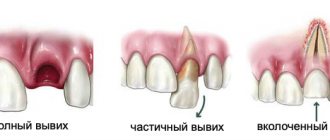
- Injuries. Dislocations, fractures, bruises, cracks of teeth and roots resulting from mechanical stress often lead to partial or complete loss of a row.
Less commonly, adentia becomes a consequence of previous somatic ailments - endocrine, oncological or others, accompanied by changes in tissue structure and weakening of the immune system.
Why may there be no rudiments of permanent teeth?
There are a variety of reasons that contribute to the absence of permanent tooth buds. These include hereditary characteristics, osteomyelitis of the jaws and their traumatic lesions, metabolic disorders, pathology of the endocrine glands. In addition, acute and chronic inflammation of baby teeth, in particular, untreated periodontitis in a timely manner, can also damage the rudiments of permanent teeth and contribute to their death.
Sometimes it happens that the rudiments of permanent teeth are formed, but can lie quite deep without touching the roots of milk teeth. This may occur due to the incorrect position of the permanent tooth or lack of space. In such cases, baby teeth can also be found in adults.
Problems that accompany the loss of chewing teeth
The absence of teeth primarily affects the inability to eat properly. If teeth are removed only on one side, then an increased load falls on the other, which means that the jaw joint is overloaded in a certain area, a crunch appears when the jaw moves, headaches develop, and over time, facial asymmetry may occur. If teeth are missing on only one jaw, then those located on the opposite jaw begin to shift, i.e. fall out of the sockets because they do not receive full support from the antagonist teeth. Naturally, bone tissue atrophy occurs in the area of missing teeth, which remains without the natural chewing load.
The absence of chewing teeth also entails aesthetic disturbances. Even if the defect is not noticeable when smiling, the cheeks become sunken and a large number of wrinkles form. Problems of the digestive tract also arise, especially if chewing teeth are missing on both sides at once - this is the result of inadequate and poor-quality chewing of food and a transition to softer foods.
Do adults need to have their baby teeth removed?
Undoubtedly, baby teeth can often cause problems in adults. Firstly, their service life is short, which is why their resistance to caries is much lower compared to permanent ones. Secondly, teeth that do not fall out on time can interfere with the growth of permanent teeth and also cause them to be incorrectly positioned. But this does not mean that if a baby tooth is found in an adult, it must be removed. Everything is individual and depends on the specific situation. Very often, it is recommended to leave baby teeth in adults that are well preserved so that they last as long as they can. After all, sometimes it happens that permanent teeth may never appear in their place.
In any case, what to do with a baby tooth in adults needs to be decided after an X-ray examination is carried out, which will help determine the presence or absence of the rudiments of an unerupted permanent tooth, as well as whether the process of resorption of the baby tooth root is ongoing. If the rudiments are not found and the roots of a baby tooth have not been reabsorbed, and it looks aesthetically pleasing and immobile, then such a baby tooth should not be removed. The same applies to cases where it is X-ray proven that the position of the permanent tooth is such that even after removing the milk tooth, it will not be able to erupt. However, in this case it is better to consult an orthodontist.
Classification of edentia
In dentistry, several types of adentia are differentiated. Based on the time of onset and etiology of the disease, the following are distinguished:
- primary (congenital);
- secondary (acquired);
- edentia of permanent and temporary teeth.
If the patient does not have the rudiments of teeth, he is diagnosed with “congenital adentia.” In some cases, adjacent crowns grow together. And in this case, “false adentia” is diagnosed. Partial edentia means the absence of no more than 10 teeth. Otherwise, a multiple form is observed.
There is also a Kennedy classification of the disease. According to it, the following defects are distinguished:
- double end;
- one-sided end;
- included defect in the lateral areas of the dentition;
- included defect in the anterior part of the dentition.
What to do if a baby tooth can cause problems?
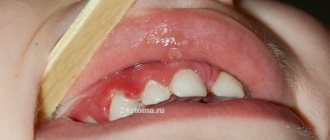
If you are not satisfied with the aesthetics of a baby tooth or it is mobile, you still need to start with an x-ray examination. Having discovered on an x-ray that there are no rudiments of a permanent tooth, and the roots of a baby tooth have been reabsorbed, and mobility of the 3rd - 4th degree is observed (the tooth is very mobile), then it needs to be removed and then a decision must be made about what type of prosthetics to use in this case. case.
If you are not satisfied with the appearance of the tooth, you also need to use an x-ray to determine the condition of the roots of the baby tooth and the rudiments of the permanent tooth. Further, the decision must be made individually in a specific case. It depends on the age of the patient, as well as on the place of the baby tooth in the dentition. If there are no rudiments and the roots of a baby tooth are present, a veneer can be installed on it or the tooth can be restored, making it invisible in the dentition. Those who want to completely transform their smile will benefit from Lumineers.
If there are rudiments of a permanent tooth, you need to estimate how long it will take before erupting and decide to remove the baby tooth and pull out the permanent one.
Although the presence of baby teeth in adults can be considered an anomaly, this is not a reason to part with them - after all, very often they can serve you for many years. But sometimes it happens that such “greetings from childhood” can become an obstacle to the eruption of a permanent tooth. Therefore, if you discover that you have a baby tooth, be sure to take an x-ray and consult a specialist.
Symptoms of adentia in children and adults
Diagnosis of this disease takes a long time. But there are a number of symptoms indicating its presence. It is especially important to take them into account when determining dental edentia in children. These factors include:
- reduction of jaws (both or just one);
- signs of retraction of the cheeks and lips;
- deformation of the alveolar processes;
- the appearance of wrinkles and folds approximately in the places where the twos are located;
- manifestations of muscular atrophy of the oral cavity;
- change in jaw angles.
All these symptoms can lead to the formation of a malocclusion. Malocclusions, in turn, cause certain shifts of the teeth and the formation of gaps in the jaw. In some cases, growths may form that affect the appearance and make chewing difficult.
Complete secondary adentia can be caused by caries, periodontitis, or surgical intervention. The doctor may also notice scars from injuries that led to tooth loss. Another symptom that explains the loss of masticatory organs is the presence of cancer.
It is worth noting that there is a steady downward trend in the age of edentulous dental patients. Poor ecology leads to the fact that young people are increasingly faced with this problem.
Diagnosis and detection of the disease
Edentia is a serious problem, and to solve it it is very important to promptly and accurately identify the presence of pathology and its type.
The first stage of diagnosis is to conduct a visual examination. Based on the results obtained, the doctor determines whether adentia is primary or secondary.
Then it is necessary to take an X-ray of the jaw, especially if the initial examination showed that the disease is congenital. This can only be confirmed with an x-ray, in which a specialist will check for the presence of dental follicles or identify signs of abnormal development.
When identifying the causes of adentia in children, at the initial stage of diagnosis it is necessary to find out the structure of the root system and find out how things are under the gums. Therefore, in the treatment of childhood adentia, the method of panoramic radiography is used. It allows the doctor to obtain a detailed picture, including information about the structure of the bone tissue of the alveolar processes.
Why is timely diagnosis so important?
Timely detection of adentia is of such high importance for one serious reason. The fact is that before starting any therapeutic actions, it is necessary to diagnose and eliminate all existing pathologies.
First of all, these include inflammatory infections of the oral cavity. During treatment, it is recommended to preserve the roots of the teeth as much as possible, since the absence of roots can lead to the loss of the entire masticatory organ. In addition, it is necessary to carry out complete disinfection of the oral cavity.
If the doctor suspects the development of acquired adentia, it is necessary to find out the cause of the disease as soon as possible. This is due to the fact that some pathologies can lead to complications during prosthetics. To eliminate these risks, the dentist checks for the following symptoms during the examination:
- exostoses (benign growths on bones consisting of bone or cartilage tissue);
- unremoved roots covered with mucous membrane;
- tumors and inflammatory processes;
- infections of the oral mucosa.
Types of adentia and their diagnosis
General symptoms indicating the presence of the disease were discussed above. But there are also a number of signs characteristic of different types of adentia. Their knowledge can also help to identify pathology in a timely manner.
Primary complete edentia
The rarest type of disease and at the same time the most serious. With primary complete adentia, the patient does not even have the rudiments of teeth and their roots. This pathology leads to serious consequences, namely:
- facial symmetry is disrupted;
- the correct formation of the alveolar processes of the upper and lower jaws is difficult;
- the secretion of mucus and saliva in the mouth slows down, which can cause additional inconvenience to the patient.
One of the symptoms of primary complete adentia may be paleness of the mucous membranes. The absence of baby teeth in children can also be easily determined by palpation. If such signs are present, it is necessary to urgently take appropriate measures.
Primary partial edentia
It is expressed in the congenital absence of some teeth in the patient. If partial adentia is detected in a child, the x-ray will show gaps in the root system. It should be noted that the absence of wisdom teeth is not considered edentulous.
As the disease develops, diastemas and tremata are formed - spaces between the chewing organs. In simple terms, the teeth begin to “creep”: if you look at a photo of edentia in children, you will notice large gaps between the teeth.
Primary partial adentia can be symmetrical or asymmetrical. In the first case, there are no paired teeth - doubles or fangs. Asymmetrical adentia means the absence of teeth in different places of the jaw.
Secondary complete edentia
This type of disease is diagnosed when it is acquired. Its symptoms can be observed on all jaws or only on one. Both primary and permanent teeth may be missing. Secondary complete adentia is diagnosed when all the chewing organs have fallen out or needed to be removed due to another disease.
One of the main unpleasant consequences of this pathology is jaw deformation. It becomes closer to the nose, soft tissues begin to retract. Also, this type of disease is characterized by muscle atrophy, leading to disruption of the shape of the entire jaw or one or both alveolar processes.
In addition, the loss of all teeth immediately leads to everyday problems - the patient will not be able to chew independently, and will also begin to swallow some sounds.
Secondary partial edentia
This is the most common type of disease, in which several masticatory organs are missing from the dentition. The loss of canines, twos or other teeth often leads to increased sensitivity of bone tissue. This is due to the gradual wear of the side walls of adjacent teeth.
With this complication, the patient faces discomfort, due to which he gradually stops eating solid food, which is difficult to chew. Both children and adults face this problem.
Possible consequences of edentia
Tooth loss is a serious disease that can lead to various unpleasant consequences, including the development of other serious diseases. Among them are the following:
- impaired jaw development, which leads to difficulty pronouncing various sounds;
- the patient is forced to exclude solid foods from his diet, which causes problems with intestinal motility and disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- development of persistent psychological discomfort. The patient’s self-assessment is distorted and depression may develop;
- in the complete absence of teeth, the jaw develops abnormally and can put pressure on any area of the head, thereby provoking the appearance of temporal tumors.
Prevention of edentia
By following simple preventative measures, you can avoid serious health complications that can be associated with edentulism. Thus, the risk of developing primary adentia in the fetus can be minimized by strictly following the rules even at the stage of pregnancy planning and immediately at the time of bearing the child. It is necessary to monitor calcium levels and eat enough foods rich in this element for the normal development of the baby. If your child has not been teething for a long time, it is necessary to make an appointment with a pediatric dentist.
To prevent acquired adentia, doctors recommend regularly visiting the dental office for examinations, as well as thoroughly cleaning the oral cavity twice a day and professional sanitation at least once every six months. If for some reason several teeth have already been lost, then you should not hesitate with prosthetics or implantation. It is necessary to find out the cause of tooth loss and eliminate it, restoring the integrity of the dentition.
Diagnosis of edentia
Making a diagnosis does not require serious research or additional tests. A careful visual examination by a specialist and an x-ray of the jaw are sufficient.
Additional examinations may be needed to identify factors that interfere with prosthetics:
- inflammatory process;
- tumor;
- damage to the oral mucosa;
- exostosis.
During the examination, the doctor pays special attention to clarifying the nature of the origin of adentia - primary or secondary. For this purpose, radiography is usually prescribed.