- Signs of tonsillitis
- Diseases associated with chronic tonsillitis
- Treatment methods for chronic tonsillitis
- Surgical methods for treating chronic tonsillitis
- Conservative methods of treating chronic tonsillitis
- Physiotherapeutic methods of treating chronic tonsillitis
Chronic tonsillitis is a chronic inflammation of the tonsils.
The palatine tonsils are an organ that takes an active part in the formation of the body’s immunobiological defense mechanisms. There are two forms of chronic tonsillitis:
- compensated
- decompensated.
What are tonsils, structural features
The immune system consists of many components. They participate in the formation of the body’s immune response to pathogenic agents when attempting to introduce them. The tonsils are considered an important part of it. They are accumulations of lymphoid tissue. The tonsils are located in the mucous membrane lining the pharynx. Formations become the first filter on the path of infection into the body.
Together with other accumulations of lymphoid tissue, they form the pharyngeal ring. Tonsils have a complex structure. They are pierced by winding deep channels called crypts. Branching reaches the third or even fourth order. Their number is usually from 16 to 18 pieces. The epithelium covering the walls of the crypts is associated with lymphoid tissue over a large area.
These formations are most developed in the area of the upper pole of the tonsil. In their lumen, desquamated epithelial cells, food debris, leukocytes, and lymphocytes accumulate. Bacteria actively multiply in this environment. This structure promotes the development of chronic inflammatory processes inside the crypts.
What are the indications for adenoid removal (adenotomy)?
Adenotomy
- Cost: 50,000 - 80,000 rubles.
More details
- Poor nasal breathing during the period when the child is healthy. This is dangerous because the child’s body experiences hypoxia (oxygen starvation). Insufficient oxygen supply to the body can lead to a delay in the psychomotor development of the child; the child may be adynamic, or, conversely, hyperactive. Due to the fact that the child constantly breathes through his mouth, the facial skeleton (adenoid face) is formed incorrectly. The quality of life of such children certainly suffers.
- Hearing loss or frequent inflammation in the ears are also direct indications for adenotomy. The mechanism of occurrence of this pathology occurs as follows. Where the adenoids are located, there is the mouth of the auditory tube (Eustachian tube) - an organ that connects the middle ear (what is located behind the membrane) and the nasopharynx itself. If, with your mouth closed, you pinch the tip of your nose and exhale into your nose, then air will enter your ears due to this very organ. Due to the close anatomical location of the adenoids and the auditory tubes, the inflammatory process from the adenoids can move to the mouth of the auditory tubes, causing in turn inflammation and, as a consequence, dysfunction of the auditory tube. In addition to the chronic inflammatory process in the auditory tubes, when adenoids grow, they can cover the mouths of the auditory tubes, leading to the development of adhesive otitis media or the formation of exudative otitis media (fluid in the middle ear). Frequent purulent-inflammatory phenomena in the cavity of the middle ear (sound transmitting apparatus) lead to the formation of adhesions and scars between the auditory ossicles, which subsequently leads to hearing loss in adulthood. In these cases, between the organ of hearing and the natural filter in the form of adenoids, we choose the organ of hearing.
- It is also necessary to part with adenoids if the child often suffers from adenoiditis, which, with local treatment, does not produce significant positive dynamics, but only leads to recovery for a short period of time. This is a consequence of the fact that the adenoids do not carry out their immune function, they have worn out themselves as a natural filter, are a source of chronic infection and need to be sanitized (removed). Adenoiditis can also often be associated with herpes viral infection (Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, type 6 virus), which live in the lymphoid tissue, leading to a decrease in immunity, including local immunity. If your child suffers from ARVI more than 6 times a year, there is cervical lymphadenitis (enlarged lymph nodes), conservative treatment of adenoiditis helps for a short time, in this case you need to contact a pediatrician for further examination for a herpes viral infection. When this group of viruses is detected, adequate treatment is prescribed, and if positive dynamics are observed in the adenoids during therapy, the child should be observed and there is no need to rush into surgery.
But if, together with treatment from a pediatrician, no effect is observed, then, according to the law of surgery, the tissue that prevents a person from living is removed.
Methods for treating inflammation of the tonsils
Chronic tonsillitis is usually treated using conservative and surgical methods, which are used only as a last resort.
The following types of therapy are used:
- antibiotic therapy prescribed by otolaryngologists taking into account the sensitivity of bacteria; treating the throat with antiseptic solutions (“Octenisept”, “Miramistin” and others); antihistamines to relieve swelling of the mucous membrane; immunomodulators to stimulate the immune system; painkillers.
The patient must strictly follow a diet. Exclude solid foods, cold or hot dishes and drinks, alcohol, soda.
When should you wash your tonsils?
The fact is that pathogenic microorganisms and dead leukocytes not only accumulate inside the tonsils, but they also cannot leave their location, since inside the tonsils there are many voids and tortuous “passages”. If you influence them with the same drug, then sooner or later addiction occurs - microorganisms (streptococci and staphylococci) become resistant, adapt to the antibiotic, and it is no longer powerless to cope with them. This is where a special procedure comes to the rescue - washing the tonsils.
Washing the tonsils is prescribed to a person who has long suffered from chronic tonsillitis with constant exacerbations, who feels constant weakness, soreness in the throat, in the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes.
What methods of hardware washing of tonsils are there?
Washing the tonsils is a procedure that is performed only by an ENT doctor. This can be done in several ways:
- Using a special syringe. During the procedure, the doctor uses a syringe with a curved metal tube attached to it. It is introduced into the lacuna. This breaks the traffic jams. The syringe contains a solution of an antiseptic - furacillin, potassium permanganate and others. Liquid is pumped into the lacuna. It pours out, squeezing out pus. Vacuum washing method. Removal of purulent plugs occurs under the influence of ultrasound. Radiation promotes the penetration of drugs into deep lacunar passages. This type of washing can produce almost complete cleansing of lacunae. Cavitation method combined with ultrasound. When ultraacoustic vibrations pass through a liquid, cavities with air are formed in it. When they collapse, a shock wave is formed. It damages the cell membranes of bacteria.
Using these techniques, together with drug therapy, it is possible to achieve a significant reduction in exacerbations of chronic tonsillitis.
Types of pathologies
Tonsils are the first barrier that traps pathogenic microorganisms. Therefore, inflammatory and infectious lesions of the tonsils are quite common, especially among children from 5 to 10 years old.
Angina
The term tonsillitis (acute tonsillitis) refers to acute inflammation of the palatine or pharyngeal tonsils. The main signs of the disease are dry, sore and sore throat, hyperemia and enlargement of the tonsils, increased temperature, and symptoms of intoxication.
There are several forms of angina, most often diagnosed:
- Catarrhal. The symptoms are mild and, with appropriate treatment, disappear within 3-5 days.
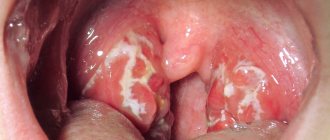
- Follicular. Follicles are affected. A characteristic symptom is pain when swallowing, radiating to the ear. The temperature can rise to 38 degrees or higher; upon examination, enlarged tonsils with whitish-yellow dots are visible.
- Lacunarnaya. The manifestations are similar to follicular, however, the symptoms of intoxication can be more pronounced. A yellowish-white coating covers most of the inflamed tonsils.
Treatment of sore throat involves the use of antibiotics, frequent gargling, and lowering the temperature if necessary. In the first days of acute inflammation, bed rest is necessary; compliance with it reduces the risk of complications.
Chronic tonsillitis
Most often it is a consequence of an untreated form of acute tonsillitis. It occurs with periods of relapses and remissions. A chronic focus of infection often becomes the cause of the development of dangerous diseases such as rheumatism, lupus erythematosus, and nephritis.
The treatment is complex. Antibiotics and drugs that enhance immunity are selected for the patient. If there is no effect from conservative therapy, partial or complete removal of the tonsils is recommended.
Hypertrophy
Tissue proliferation in most cases is characteristic of the nasopharyngeal tonsil. The disease is otherwise called adenoiditis and young children who often suffer from ARVI are susceptible to it. Primary signs are a frequently recurring runny nose, noisy breathing and snoring during sleep, a cough that gets worse at night, and mucous discharge from the nose.
Advanced forms of adenoiditis lead to chronic hypoxia, which causes lethargy and inattention. Lack of timely treatment can cause improper formation of the bones of the facial skull. Depending on the severity of hypertrophy, treatment can be medicinal or surgical.
Abscesses
They are characterized by the formation of cavities filled with pus near the tonsils. Most often, abscesses occur against the background of a sore throat. Symptoms are severe pain on the affected side, fever, high temperature, intoxication of the body. Abscesses are opened surgically.
Neoplasms
Cysts can form on the tonsils. A malignant lesion cannot be excluded, which at an early stage is manifested by tissue enlargement and periodic pain.
There are many reasons for the development of tonsil diseases. The main ones are infection with staphylococci, streptococci, and E. coli. Inflammation can be caused by hypothermia, mechanical injury, or chemical burn. The likelihood of pathologies increases with hypovitaminosis and low immunity. Pathogenic microorganisms can enter the tissues of the lymphatic ring not only directly, but also through the blood during chronic and acute diseases of other organs.
Indications and contraindications for washing the tonsils
Most often, the procedure is performed to treat chronic forms of tonsillitis in adults. The doctor decides whether this procedure is necessary for the patient. The main indication is the presence of purulent plugs in the lacunae of the tonsils.
Contraindications for treatment are as follows:
- state of exacerbation of inflammatory processes; oncological processes; pathologies of the retina; severe heart defects; decompensation of hypertension.
This manipulation is not recommended for pregnant women and children under three years of age.
What to do if your throat constantly hurts? Is this an infection?
No, persistent sore throat is most often caused by non-infectious causes. The most common cause is acid from the stomach entering the back of the throat through the esophagus. This condition is medically called gastroesophageal, or extraesophageal, reflux. This is a very common illness that can occur without abdominal pain or heartburn. If heartburn occurs constantly and your throat often hurts, then the connection between these events is obvious and you need to deal with this particular problem, and not try to cure your throat.
How is the tonsil rinsing procedure performed?
No special preparation is required before performing this procedure. Washing on this device occurs in several stages:
- first, the tonsils are treated with lidocaine; a vacuum attachment is fixed to the surface of the formation; the device creates negative pressure; the nozzle pulls out purulent plugs and removes them into a special container; the lacunae are washed with an antiseptic solution. Ultrasound injects a drug into the tonsil.
The procedure relieves inflammation, activates tissue regeneration, and removes swelling.
Are there any contraindications?
Despite the simplicity and apparent safety of washing, the procedure is not allowed for everyone. Contraindications to its implementation are:
- children under 3 years of age;
- pregnancy in the 1st and 3rd trimesters;
- oncological diseases;
- any acute infectious processes in the oropharynx;
- retinal detachment;
- heart defects;
- pathologies of blood vessels and heart in the stage of decompensation;
- intolerance to used antiseptics.
A relative contraindication is hypertension. The patient's condition is assessed individually. If the likelihood of a crisis developing is low, then washing is allowed.
An absolute prohibition is not only acute inflammation of the tonsils. Any inflammatory processes, even caries, when washed, can cause infection of nearby tissues and provoke complications.
In case of chronic tonsillitis, washing the tonsils can be an alternative to removal. Washing the lacunar folds is an unpleasant procedure. But sometimes this is the only alternative to tonsil removal. Regular sanitation cleans cavities, prevents exacerbation of the chronic process and helps restore lost organ functions.