A child’s first tooth erupts is a joyful event for parents. But what if there are no teeth at 6 or 8 months or even later? Is this really a problem or can it wait?
Milk teeth: by the age of 2–2.5 years, exactly 20 of them should grow
Sometimes the replacement of teeth with permanent ones is delayed, so sometimes an examination may be required to determine whether everything is in order.
Why may teeth not grow on time?
Individual characteristics
The average time for the appearance of the first baby tooth is 6 months, but teeth can begin to erupt at three months or a year, and both options are normal. If the child’s teeth do not appear, but there are no other complaints and the pediatrician does not notice any problems, then there is no need to worry until the child is a year or more old.
The same applies to the late beginning of the change of milk teeth to permanent ones. For some children, permanent incisors begin to appear already in the senior group of kindergarten, while others experience this moment at school. The normal period for the formation of a permanent bite is from 7 to 13 years.
Later than the average period, teeth may erupt in weakened, often ill children.
What to do?
Monitor other complaints, contact doctors if necessary, and if there are no complaints, then nothing. You cannot influence the rate at which teeth appear.
Examination and treatment
If a child has no teeth at 10–12 months, the pediatrician may prescribe an examination to determine the reasons for the delay. A panoramic x-ray shows whether there are baby tooth buds in the child's jaw. In case of partial edentia, specific treatment is prescribed to allow the embryos of permanent teeth to develop correctly. To ensure that the jaw is formed correctly and food is chewed efficiently, special removable dentures are made to compensate for missing baby teeth for a 3-year-old child.
The doctor may prescribe an ultrasound scan of the abdominal organs, blood tests, stool tests, urine tests of the child and others, if necessary. Vitamins and minerals are prescribed to strengthen the immune system, primarily vitamin D and calcium. The child should spend as much time as possible outdoors. He is given ring toys as a stimulant. A light massage of the gums with a clean finger is helpful.
Parents should be alerted if the incisors erupt too early, before 3 months. In some cases, this may indicate disorders in the endocrine system, but more often than not, early teething in children is an individual feature.
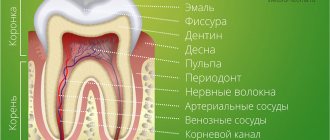
Before appearing from the outside, the incisor passes through the bone tissue surrounding it, and then through the mucous membrane of the gums. Do I need help with teething? Trying to speed up the process of its appearance with a piece of sugar, a spoon or other objects, you can damage the gums and introduce an infection into it.
According to a good ancient tradition, the one who discovers the child’s first tooth gives him a silver spoon. It is believed that she will bring him health and wealth. She can lightly tap the tooth and make sure that it has erupted and all anxious expectations are left behind.
When should you see a doctor?
Teething causes a lot of discomfort for the baby. This does not require medical attention. But there are situations when you cannot do without the help of a doctor. You should contact him in the following cases:
- Painful cough.
- The temperature does not subside for a long time.
- There is mucus and blood in the stool.
- Diarrhea
- and purulent nasal discharge.
- Constipation.
- Mouth ulcers.
- Unnatural color of the shoots.
Symptoms from teething hide the manifestation of diseases, for example, ARVI or infectious diseases. It is important to consult a doctor if negative symptoms occur. Exercise caution in such cases rather than regret later what you didn’t do.
How a dentist can help
If you are not ready to wait a year, seek help from a good pediatric dentist. The specialist will take an X-ray of the jaw to ensure the presence of tooth buds. If everything is fine, all you have to do is calmly wait for the process to begin - gum enlargement and increased salivation. Now it's time to help the baby:
- a ring stimulator will moderate itching, reduce discomfort and speed up teething;
- You can gently massage your child’s gums with a clean finger or a small spoon;
- stimulates tooth growth and fortified complementary foods - healthy juices and purees. While there are no teeth, solid complementary foods cannot be introduced.
This is interesting: Treatment methods for periodontitis in primary teeth with unformed roots
If your health is fine
The timing of eruption depends on heredity, including grandparents, and on external factors. It is believed that in hot climates, teeth appear earlier, as early as 4 months. When a child is healthy and his development corresponds to his age, but there are still no teeth, although they should already appear in accordance with average standards, this causes concern among parents. Modern doctors indicate only approximate dates for the sequence of growth of the first teeth. The standard teething pattern looks like this: from 5–6 months - on each jaw there are 2 central incisors (first from below, then from above), from 8 months - lateral incisors, by the year the child has only 8 teeth. They are known to appear in pairs and alternately on both sides.
What to do if a child has only grown one tooth and there are no signs of a second one? You need to know that the sequence of teething may be different and this is not considered an anomaly. There are many options for their appearance. At seven months they can erupt 2 - from below, then 1 - from above, then the third and fourth - in the bottom row, and only after them the missing top one.
Many mothers tend to associate the whims of a 3-4 month old child, poor sleep or appetite with the imminent appearance of the first incisors. There is no doubt left if the baby also puts everything into his mouth and drools profusely. Sometimes it seems to mothers that the gums are already red; they look into the child’s mouth in the hope of seeing that swollen white ball from which the long-awaited tooth is about to emerge. But days and weeks pass, the child is already 7 months old, and there are no teeth? No need to panic.
If the baby’s health is fine, you just need to wait, especially since all the dates are individual and there may be deviations in one direction or another for six months. Some children have their first incisors at 4 months, while other babies can already walk by the time they begin to emerge.
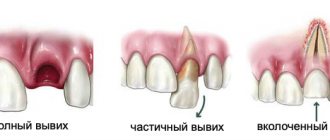
Partial edentia
Adentia is the congenital absence of tooth buds. Most often, the top two “twos” are missing. Moreover, there may be a lack of both milk and permanent teeth, or both.
Adentia is a congenital condition; it occurs due to a malfunction in the embryonic period during the formation of the main organs and systems.
It is very difficult to notice partial edentia of baby teeth: the teeth are small, they are all of a similar shape, and others take the place of the missing ones. Such adentia does not harm the chewing process in any way.
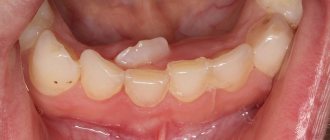
If permanent teeth are missing, this is already noticeable visually. In this case, malocclusion may develop, since the “threes” are pulled up to replace the missing “twos”, and the following teeth are also displaced.
Partial edentia - absence of upper incisors
Partial edentia - there are no upper incisors, but “threes” have taken their place
The exception is wisdom teeth, also known as “eights.” Their functions are not so important; in most people they remain impacted, and if they are lost, they are not replaced with prosthetics. Their absence does not affect the health and aesthetics of the smile.
What to do?
If there is a partial lack of permanent teeth, it is most often necessary to correct the bite and prepare a place for prosthetics. If you do not make dentures, but cover the empty space with neighboring teeth, then this will not be a complete solution to the problem - the dentition will be narrower than it should have been.
Parents' actions
Why did a newborn baby vomit blood during feeding - reasons
Parents should be wary only if their baby is completely missing teeth by the age of one. If there are simply few of them, then these are the individual characteristics of the child.
After a consultation with a pediatrician, tests can be performed and, if necessary, an x-ray of the baby’s jaw to determine the reasons for the delay in teething. If there are no abnormal processes or congenital pathologies, then you just need to wait.
In some cases, your doctor may recommend taking vitamin D. However, parents should not decide on their own how to take it.
Teething in most cases is accompanied by general and local symptoms, which can be more or less irritating for the baby. Overall, these are minor and temporary disruptions. The most common are:
- swollen and inflamed gums;
- excessive salivation;
- excitability;
- disturbed sleep;
- in some cases, lack of appetite, fever, diarrhea.
At 7 months of age, it is still too early to worry and you should not take any action to speed up teething. However, you can help your baby ease this process if his teeth are about to come out:
For your information. All activities must be done in compliance with the necessary hygiene.
- When a child puts everything that comes into his hands into his mouth, it is necessary to prepare a special children's toy or rubber rings. They massage the gums and stimulate teeth to come out. In addition to toys, you can give your baby pieces of fruit or vegetables, but they should be large enough to prevent part of the fruit from getting into the throat;
Baby with teething ring
- Cold eases the itching and pain of teething, so before giving it to your baby, you can put the toy or rings in the refrigerator (but not in the freezer!);
- You can massage your gums with your hands, placing sterile gauze soaked in cold water on them;
- Anti-inflammatory and analgesic teas (sage, chamomile) are very effective in combating gum pain. They are sold at the pharmacy. You need to give your child tea from a spoon; you can apply it to the gums with a cotton swab;
- If your baby is drooling a lot, it is best to wear a bib during the day. The skin around the mouth must be kept dry, otherwise redness and irritation will appear.
Parents must be patient and remember that each child is different. For him, there are only his own timing and order of teething, which may differ even from the timing of his siblings. Not all children cut their teeth according to average patterns, just as not all of them suffer when the first tooth comes out.
Completely edentulous
This is a rare phenomenon - the complete absence of tooth buds (deciduous or permanent). In this case, teeth cannot erupt because they are simply not in the jaw bone.
Complete edentia in the picture
In medicine, cases have been described when a patient had milk teeth, but permanent teeth were completely absent. The loss of baby teeth was timely, but permanent teeth did not appear in return. At this moment, the child’s parents paid attention to the problem, and the dentist made a diagnosis.
In addition to congenital, adentia can be acquired if the child has undergone severe treatment (chemotherapy) at an early age. Due to the toxic effects of drugs, tooth buds may be damaged.
What to do?
Edentia is clearly visible on a CT image. If such a diagnosis is made, the only option is complete prosthetics. Since the case is rare, the question of when to get dentures and in what way should be decided individually.
If you do not replace missing teeth with prosthetics, the chewing process cannot be complete. Even the lack of 2-3 teeth affects digestion. Bone tissue, if the jaws do not receive enough load when chewing, undergoes resorption (resorption), and this leads to weakening and loosening of the remaining teeth, increasing the risk of periodontal disease.
Therefore, if you have any complaints about your child’s teething being too slow, you should consult a doctor. In most cases, it turns out that there is no pathology, all teeth are fine and will grow a little later. But in rare cases, prosthetics may be required, which is better to know in advance. Then you can schedule treatment on time.
Other articles:
If a child does not want to be treated by an orthodontist...
When should your child see an orthodontist?
How to help your child not be afraid of dentists
Reasons why there may be more teeth than normal at 8 months
There is another problem - parents think there are too many teeth. That is, a child at 8 months has grown more than 8 teeth. Is this really a pathology, and should parents worry?
There is no need to panic. When the first teeth appear after 3 months, this is an indicator of the norm. This happens if the expectant mother constantly takes prenatal vitamins or drinks them while breastfeeding. This is also possible in bottle-fed children. This means that the child’s body has enough microelements and essential substances.
This is interesting: The best electric toothbrushes for children: rating and which one to choose for children
It’s another matter when the first incisors appeared before 3 months of age. In this case, there is reason to suspect diseases of the endocrine system. You need to show your baby to a doctor and undergo an examination.
Reasons for retention
Most often, the reason for the development of retention is associated with the incorrect location of neighboring teeth, which become an obstacle to the eruption of retention teeth. In other cases, the problem may be due to too dense bone or gum tissue.
Other factors influencing the development of pathology include the following phenomena:
- supernumerary (abnormally large number of teeth),
- diseases of internal organs, which leads to disruption of the full development of the entire skeletal system,
- loss of baby teeth at too early an age,
- genetic predisposition.
Description and symptoms of the problem
The germ of a retention tooth is located in the bone, but its further growth does not occur for a number of specific reasons. This phenomenon is considered anomalous if the element has not erupted within two years from the due date.
In the partial form of the pathology, part of the crown is located above the gum or its outline is visible through the gum tissue. With complete retention, both the crown and root remain completely hidden. Typically, this problem affects the incisors, canines and the outermost “eights”. To clarify the position and shape, an x-ray examination is often required.
Typically, patients note an increase in body temperature and general malaise during teething, swelling and a change in the shade of the mucous membrane. In addition, if the element is fully formed in the bone tissue, but does not appear on the surface, pronounced pain may occur (most often it is monotonous). This indicates that the tooth is pressing on the roots of its neighbors. In some situations, facial numbness is also noted, which is caused by pressure on the nerve endings. It is also worth noting that in some cases the pathology does not provoke the appearance of any obvious symptoms.