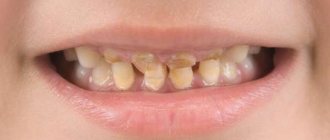
From the age of six months, children begin to bother their parents with frequent tears. And the cause of these tears is toothache. After all, it is at this age that babies begin to erupt their baby teeth. And only at the age of six these baby teeth are replaced by permanent ones. Many parents who worry about their babies begin to wonder about various questions regarding the structure of teeth. After all, this is the key to unraveling why and under what circumstances pain occurs. In this article we will tell you Are there nerves in a child's baby teeth?.
Is there a connection between the nerves of the molar and baby teeth?
According to statistics, every second parent wonders whether there are nerves in baby teeth? And at the same time, most are sure that baby teeth simply do not have nerves. However, such a statement is misleading. In reality, every tooth contains a nerve. It doesn’t matter at all whether we are talking about molars or baby teeth. It is worth noting that the nerve is the most important component of the tooth.
And although nerves are present in both teeth, there is no connection between them. That is why, if a disease such as pulpitis is detected in a baby tooth, there is no need to fear that it will necessarily be diagnosed in a permanent tooth. However, this does not mean at all that you can avoid treatment at all and not visit a dentist. Indeed, in cases where the children’s parents neglected treatment, the inflammatory process was guaranteed to penetrate the bone tissue. This has a negative impact on the process of permanent tooth formation.
When treating baby teeth, doctors must take into account the age of young patients. This need is due to the fact that closer to the age of 6, the roots of non-permanent teeth begin to dissolve. Consequently, at this age, during treatment, the risk that a molar tooth will be injured increases many times over. That is why, in cases where it is necessary to remove a nerve, the canals are processed exclusively at the mouth. In this case, the tooth that has been treated is covered with a solution. This solution helps it survive until the time when the molars are replaced.
What symptoms should you contact your dentist for?
Ideally, you should visit the dental clinic with your child every six months, and if signs of caries appear, treatment should begin immediately. But more often, parents turn to specialists when their child begins to suffer from severe toothache.
You should make an appointment with a dentist if your child exhibits the following symptoms:
- feeling of bursting and dull toothache;
- reduction of pain after eating hot food or during sleep;
- tooth sensitivity when eating;
- purulent odor from the mouth even after brushing your teeth;
- extensive carious cavity;
- other damage to the dental crown.
Pulpitis is characterized by rapid progression of the inflammatory process. If the nerve is removed at the initial stage, there will be no complications. In advanced cases, the pathological process can develop into a cystic or granulomatous form, or the infection begins to spread to the jaw bones or sinus tissue.
How are permanent teeth different from molars?
The most obvious difference is the number of teeth. A person has 28-30 molars, but only 20 primary teeth. There is a difference in the size of the crowns and even the roots of the teeth. According to dentists, baby teeth are smaller than molars. This is explained by the fact that children have a much smaller jaw than any adult. Consequently, it is not able to accommodate teeth the size of molars.
The thickness of dentin and enamel also differs significantly. In baby teeth they are much thinner. But if the dentin and enamel of primary teeth are inferior in thickness to molars, then in the case of pulp volume, it is the non-permanent teeth that take precedence. An interesting fact is that it is not necessary to visit a dentist to remove a baby tooth. But if we are talking about removing a molar incisor, you cannot do without the help of a qualified dentist. After all, this process takes much longer and is characterized by pronounced pain, increased body temperature, and slight bleeding from the gums.
Anatomy of a primary tooth in a child
We are talking about a full-fledged bone formation, the nutrition of which is carried out through numerous microtubules - due to this relationship, hard tissues are strengthened. The structure looks like this:
- crown - the visible part covered with enamel,
- dentine,
- pulp chamber - pulp or neurovascular bundle,
- root system.
The photo shows the structure of the tooth
. The enamel covering temporary incisors and molars is much more fragile and thinner than in adults. Next comes the dentinal layer with a network of microtubules leading to the pulp - it is this that provides nutrition to all surrounding tissues. It is permeated with blood vessels and nerve endings, and its inflammation leads to severe piercing pain. It should also be recalled that children grow only 20 temporary elements: 8 incisors, 4 canines, 8 molars.
Why do baby teeth sometimes have to be removed?
As was written above, most often such teeth can be removed without resorting to professional help. However, sometimes there is still a need to visit the dental office. Before we look at the reasons why you have to seek help from dentists, let's talk about the location of the dental nerve. It is located quite deep in the tissues. The enamel provides it with reliable protection from external influences.
Why does the body need to protect the dental nerves? This can be explained quite simply:
- nerve endings that are located in the pulp must always be sterile. After all, they have a connection with the general blood flow;
- Temperature changes, acids, alkalis negatively affect dental nerves. If they are exposed, the person begins to feel unbearable pain. Therefore, to relieve a person from pain, it is necessary to protect the nerves well;
- a tooth can perform its assigned functions only if the pulp is not affected by external factors.
From the above we can conclude that any violation of the integrity of dentin can lead to the removal of nerves. But is it possible to remove the nerve in a baby tooth? Will this have negative consequences? Removing the nerve is a safe and sometimes necessary procedure. The most common reasons for removing nerves from teeth are:
- pulpitis – is an inflammatory process that occurs in the pulp tissues;
- caries (deep) – thin enamel is not able to fully protect the tooth from the negative effects of harmful microorganisms. This is why the carious process quickly affects the tooth and spreads almost instantly;
- periodontitis - quite often children, afraid of a visit to the hospital, hide from their parents that the tooth hurts. Gradually, such neglect turns into a disease. Periodontitis develops, which occurs at the junction of the tooth and gum;
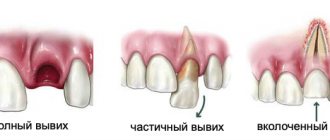
- Tooth trauma – trauma can cause damage to the enamel. In the future, this becomes the reason for removing the nerve.
Types of childhood pulpitis
Symptoms of acute pulpitis in a baby appear clearly. He is capricious, complains of pain, refuses to eat, and cries. Chronic pulpitis is often asymptomatic and can only be diagnosed in the dentist's chair.
At the Novostom Dental Center they treat different types of chronic pulpitis:
- gangrenous. The child does not feel pain, but due to the decay of the pulp, the tooth darkens and a putrid smell appears. Possible formation of a cyst or fistula, development of periodontitis;
- fibrous. A sharp exacerbation of chronic pulpitis is unpredictable. The cause is usually inflammation of the pulp - acute serous or purulent;
- rarely occurring hypertrophic. When a tooth decays, the pulp grows and bleeds.
Possible complications after nerve removal
Parents often associate complications that arise after removal with the low level of professionalism of the dentist who performed the procedure. They begin to ask another question: is the nerve always removed correctly? Perhaps this procedure is associated with certain risks? Indeed, this kind of thing happens. The need to seek re-treatment may arise in several cases:
- Re-infection, which became possible due to insufficient treatment with an antiseptic.
- Destruction of the installed filling, which was caused by a poorly performed filling procedure.
- Compression of the tooth root by an installed filling.
- A root fracture that can occur if the dentist works too hard with various instruments on the surface of the pulp.
Of course, this doesn't happen very often.
However, if the child complains that the pain does not go away, but rather gets worse, you should visit the clinic again. Never ignore your child’s words that something hurts! Moreover, never resort to painkillers. After all, pain is a consequence. To get rid of it, you need to look for the cause. And only a qualified dentist with enough experience can do this. Moscow metro station Zvezdnaya, Danube Avenue, 23
How is the depulpation procedure performed?
As part of the treatment of pulpitis in dentistry, the nerve is most often killed and removed, although in some situations only partial depulpation is possible - here everything is strictly according to indications. The doctor will need an x-ray to assess the extent of the inflammation and determine a further course of action.
If it is decided to remove the pulp, then after all preparatory measures the depulpation procedure will be carried out. Under local anesthesia or additional sedation, the doctor will open the tooth, remove all affected tissue and remove the neurovascular bundle. If necessary, he will clean the canals and carry out additional antiseptic treatment. Next comes the filling stage. A control X-ray may be required so that the specialist can make sure that there are no foci of inflammation or possible mistakes made.
This treatment is carried out under anesthesia
In some cases, a temporary filling with a medicinal composition is fixed. After the set time has passed, the doctor will replace it with a permanent one. For filling, special mummifying compounds are used, which have an additional disinfecting effect and protect against infections. Only the material itself is not durable, but it should last until the bite changes.
The front or chewing tooth after depulpation is considered dead - it will not respond to temperature changes and acid-base influences. However, it will become even more fragile and may soon begin to break down.
Prevention
Preventing the occurrence of diseases of primary teeth is much easier than treating them. Brushing your teeth regularly will help. Eliminate dental plaque, stones, and prevent harmful bacteria from multiplying.
There is no need to wait 5, 6 years - the age of natural change, if children's complaints of toothache and other symptoms are present now. Temporary teeth are susceptible to disease, just like permanent teeth. And because of their special vulnerability to external factors, their condition needs to be given especially close attention.
The article was prepared by an expert:
Peschanskaya Kristina Ivanovna
Pediatric dentist
Make an appointment
"Microscopic" treatment
Due to the fact that tooth enamel in adolescents and children is very thin, dental treatment can be difficult - there is a high risk of tooth destruction and damage to the enamel. To avoid risks, specialists at the Dentville clinic use a special dental microscope, which helps to enlarge teeth many times over and, with pinpoint precision, clean and sterilize dental canals and install miniature fillings that will last much longer than massive ones. Thanks to a microscope, the likelihood of keeping the tooth nerve alive and not damaging it is significantly increased.