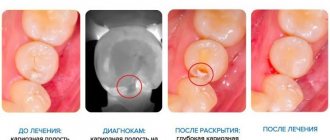
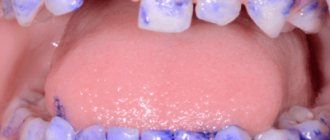
If a carious stain goes unnoticed, the tooth continues to decay and superficial caries develops. Like the previous stage, the lesion is localized within the enamel.
Various reasons contribute to the development of the disease:
- predominance of sugars and acids in the diet;
- deficiency of vitamins and microelements;
- hereditary factor;
- disturbances in the composition of saliva;
- poor oral hygiene.
Contact numbers of our clinics:
Belorusskaya (+7
or Leave a request and we will call you back
Leave feedback
Treatment of caries of children's primary teeth
Caries of primary chewing and front teeth has long been treated without the slightest pain.
New modern techniques have reduced the use of drills and drilling to a minimum, and timely scheduled examinations make it possible to detect the disease at a very early stage. The doctors at Aza&Buka Pediatric Dentistry who work with young patients are distinguished by an amazing sense of tact and constant positivity. Knowledge of the child’s psychology allows doctors to build communication and dialogue in such a way that children sit in the dental chair without the slightest fear. If the child already has some dental phobia, then adaptation techniques can solve the problem.
Caries on baby teeth in children is treated using the following technologies:
Diagnostic methods
Clinical diagnosis, carried out as part of an examination of the oral cavity, involves the use of various techniques to determine the degree of development of pathology. Over time, superficial caries can develop into a more severe form that affects dentin and the pulp chamber, so it is important to promptly select the optimal treatment method.
Current examination methods used in clinics include:
- Visual inspection and percussion - assessment of the condition of the dentition by tapping the elements, allowing to identify the patient’s reaction;
- Probing is a technique that allows you to determine the presence of superficial caries by detecting a rough texture on the surface of the enamel;
- Staining – the use of special dyes that form markers in affected areas characterized by insufficient mineralization;
- Antiseptic drying - applying a special composition to the dentition, which, under the influence of a directed light flux, indicates defective areas;
- Differential diagnosis is a procedure that involves comparing the basic symptoms observed in the patient.
The final cost of dental services consists of many factors - as a rule, the price for caries treatment in St. Petersburg clinics is agreed upon based on the results of a preliminary diagnosis, which determines the structure of the treatment plan.
Classic filling
requires a special approach when treating young patients, since the doctor has to use dental equipment, which often causes fear in children.
Aza&Buka dentistry uses both traditional and modern methods of treating caries of primary teeth, selecting a method taking into account the age of the child and the degree of neglect of the process.
Plaksina Margarita
“Modern parents are great! They themselves are not afraid of dentists, and children are taught the same thing: to come on time for preventive appointments and examinations. In such cases, doctors can intercept the very beginning of a cavity infection and prevent tooth decay without drilling.”
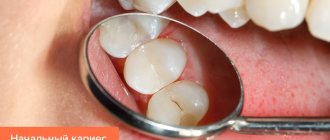
Characteristics and symptoms of pathology
From a dental point of view, superficial caries is considered as one of the initial forms, which is due to the absence of deep damage to the dentinal structure. The pathology occurs without obvious symptoms and can remain undetected for a long period of time. Signs that allow you to diagnose the disease at home include:
- Formation of small spots with a yellowish tint on the enamel;
- Increased tooth sensitivity to hot and cold, as well as sweet and sour foods;
- The occurrence of discomfort during mechanical action, including brushing teeth;
- The appearance of a palpable rough structure, noticeable upon tactile contact.
The presence of one or more symptoms is the basis for undergoing a dental examination, based on the results of which treatment for gum or dental caries can be prescribed.
Milk caries: initial, superficial, medium, deep
Doctors distinguish 4 stages of the formation of carious areas:
- Initial caries - tooth enamel becomes covered with small spots of white or yellowish tint.
- Superficial caries - the enamel begins to deteriorate, small and light cavities are observed.
- Medium – the layer of tooth enamel is destroyed, the affected area extends deeper.
- Deep - the layers of dentin have already been affected, and the pulp is under threat.
It is necessary to treat milk caries at the very first stage, although it does not cause any discomfort in the child. The fact is that the enamel and crowns of temporary teeth are subject to rapid destruction, and the development of caries occurs very quickly. Deep caries often provokes irreversible changes, which leads to premature removal of the baby tooth.
Rodikova Tatyana
“Medium and deep caries most often occurs in schoolchildren, almost teenagers. Children brush their teeth poorly, and they talk about problems only when caries has already affected the pulp. In this case, the treatment turns out to be more unpleasant, since removal of the pulp cannot be avoided. That’s why I always ask parents to carefully monitor their teenagers’ hygiene and bring them to appointments on time.”
Pathogenesis
The development of the disease is influenced by many factors. In particular, the frequency and quantity of consumption of sweet and starchy foods, as well as poor oral care, are important. The more often a person eats sweets and the longer they act on tooth enamel, the more actively plaque forms and the faster demineralization of the enamel occurs.
Bacteria actively multiply in dental plaque and produce organic acids during their life. They cause changes in the acid-base balance towards an acidic pH, which also helps to weaken and corrode the enamel and create favorable conditions for the removal of the minerals most important for the strength of teeth - calcium, fluorine and phosphorus.
In the oral cavity, the processes of mineralization and demineralization, as well as neutralization of organic acids, occur simultaneously. At the moment when the rate of removal of minerals from hard tissues begins to prevail over the rate of their entry into the dental structures, and also when the process of acid formation dominates over its neutralization, a defect is formed. Initially, it does not go beyond the boundaries of the enamel-dentin junction (the area where the enamel borders the dentin).
If the process is left without treatment, then caries destroys the deep layers of dentin, gradually reaches the location of the neurovascular bundle (pulp chamber) and pulpitis begins, and later periodontitis. Without medical intervention at this stage, tooth loss may occur.
Reasons for the development of caries in temporary teeth
When visiting a dentist, parents are invariably interested in the reasons for the appearance of such an unpleasant disease. This is important because it helps prevent damage to new teeth. Sometimes it is enough to change eating habits and hygiene patterns so that the child forgets about fillings for a long time, and only comes to the dentist for examinations.
Causes of caries:
- Poor or insufficient oral hygiene. Food remains in the interdental space and on the enamel are an excellent environment for the development of carious bacteria.
- An unbalanced diet with a preponderance of sweets and carbohydrates - during the fermentation of simple carbohydrates, acids are formed that provoke the destruction of enamel.
- The lack of solid foods in the menu leads to a decrease in the frequency of chewing, reduces salivation and becomes a common cause of caries of primary teeth in young children.
- Long-term use of nipples, including on bottles and sippy cups, increases the risk of developing single or multiple bottle caries of the anterior milk teeth in children.
- Rickets is a pathology that provokes the destruction of dental tissues.
- Genetic predisposition of the child.
- Problems with bite – various anomalies in the formation of the dentition.
- Decreased natural immunity due to frequent acute respiratory viral infections, chronic diseases, and taking various medications.
- Damage to tooth germs in the prenatal period - due to maternal illness or neglect of health in the first trimester.
Symptoms of caries on the contact surface
Symptoms of superficial damage to the contact (approximal) surface are quite scarce. They can be divided into objective (i.e. those that both the doctor and the patient see) and subjective (that only the patient feels).
Objective
The dentist will see a surface defect on which the probe will cling. The color of the enamel in the affected area can vary from cream to light or dark brown and even black. The x-ray will show a surface defect that does not extend beyond the enamel layer. In this case, a defect can also form on the adjacent tooth (“kissing” surfaces). Transillumination of the tooth with a narrow beam of light (transillumination) and targeted X-ray diagnostics help identify this form of the disease.
Subjective complaints
In addition to the aesthetic defect - a small dark spot, there may be complaints of mild, quickly passing soreness (soreness) upon contact with cold or hot (much less often), sour, sweet, and sometimes salty. The patient may indicate that food is stuck between the teeth. In some cases there are no complaints.
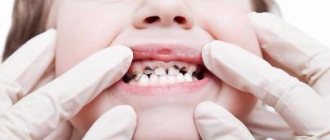
Diagnosis of caries in children
How to recognize caries in a child? A parent cannot always do this, since caries in children becomes noticeable only when there is already a hole in the tooth. Often a child is brought to the dentist “just to check his teeth,” and the doctor finds several caries after examining him with instruments.
The usual methods for diagnosing caries are inspection and probing. As a rule, this is enough to determine the presence of caries. The depth of the lesion can be assessed based on the child’s complaints and by x-ray examination.
Deep caries in a child is visible to the naked eye. At the same time, deep carious lesions on a tooth will almost always require x-rays so that the doctor can understand how far the carious process has gone, whether it is possible to save the tooth or whether removal is necessary.
What complications can there be after treatment?
- Inflammation or even necrosis of the pulp - the tissue that fills the tooth cavity. Occurs after a long time due to inaccurate preparation of rotted tissue and excessive pressure on the pulp;
- secondary caries occurs due to the fact that during preparation some parts of the tissue affected by bacteria were not removed;
- inflammation of the gums due to injury;
- periodontitis, which occurs due to increased pressure on the tooth that occurs after the formation of an anatomically incorrect filling;
- loss of a filling due to insufficient strengthening or improper formation of a carious cavity.
How is the treatment carried out?
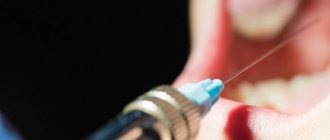
During treatment, a drill is used and the dental nerve is affected, so it is impossible to do without anesthesia if you want to achieve high-quality treatment. If the nerve was once removed from the tooth, then you do not need to use an anesthetic.
Modern anesthetics are used as anesthesia - Ultracain, Septanest and other drugs with a similar effect.
Removal of infected tissue
Since patients turn to the dentist when caries has already penetrated not only into the enamel, but also into the dentin, it is necessary to remove tissue damaged by putrefactive processes in order to prevent the further spread of bacteria, as well as to form a cavity suitable for filling.
Modern technologies suggest replacing the drill with a laser, but this method is not characterized by reduced pain, and its cost is often unreasonably high, since laser tissue removal is not common in all clinics and is used extremely rarely.
After cleansing the caries-pigmented tissues, it is necessary to rinse the cavity and treat it with an antiseptic.
Treating the cavity with an antiseptic
Chlorhexidine or drugs with a similar effect are used as an antiseptic, which disinfect tooth tissue and reduce the activity of enzymes, which are a breeding ground for bacteria.
Dental nerve extraction
Removal of the dental nerve is indicated only in the case of a complicated form of acute caries, when destructive processes have already reached the nerve, exposing it. In this case, the patient experiences acute pain.
Now the removal of a nerve, both partial and complete, is most often completed in one visit to the dentist; the procedure is assisted by an X-ray machine, which allows you to evaluate the accuracy of the manipulation during the treatment process. Thanks to modern painkillers, there is no pain when the nerve is removed.
Restoration of the anatomical shape of the tooth
The last stage of restoring a tooth that has undergone caries is restoring its original shape. The materials used for this are composites, which are placed into the hole, and then ground and polished so that the finished filling does not cause any inconvenience to the patient, does not rub the cheek, does not injure the gums and tongue, and does not interfere with neighboring teeth.
For chewing teeth, which are subject to increased load, composites and ceramic inlays and onlays are used as cement. There are times when a doctor uses several types of material to restore the function and shape of a tooth.
Special offer
Participate in the promotion
Promotion “1+1”: child and parent
You have entrusted NovaDent with the treatment of your child’s teeth, as a token of gratitude we are giving you a free consultation with any specialist (surgeon, implantologist, therapist, orthodontist, hygienist), as well as an orthopantomogram (panoramic photograph of the teeth) sent by email.
Take time for your health and take advantage of this great offer! Participate in the promotion
Expert of the article you are reading: Lapshina Maria Aleksandrovna Dentist, pediatrician
21 years
Clinical experience
Krasnogorsk
Moscow region, Krasnogorsk, Podmoskovny Boulevard, 5
+7
Free consultation with this specialist