Neurosis of the larynx and pharynx does not exist as a nosological unit. This is what is usually called persistent sensations: a lump in the throat, convulsions. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital conduct a comprehensive examination of patients who complain of tension in the throat muscles and establish the cause and type of neurosis.
Global or partial changes in sensitive receptors of the mucous membranes, which cause pharyngeal neurosis, occur as a result of impaired neurotransmitter communication and infectious diseases. The most common cause of laryngeal neurosis is osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. A lump in the throat with neurosis can be felt due to the influence of the following factors:
- Inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs;
- Atrophy of cells of the laryngeal mucosa;
- Disorders of the central nervous system;
- Overwork.
Patients who have symptoms of throat neurosis are treated at the Yusupov Hospital with modern medications and methods of psychotherapy. Doctors individually select a treatment regimen. Medical staff respects the psychological problems of patients.
Types of pharyngeal neurosis
There are 3 forms of pharyngeal neurosis:
- Anesthesia;
- Hyperesthesia;
- Paresthesia.
Anesthesia of the pharynx is manifested by a decrease or absence of throat sensitivity and impaired swallowing. The disease develops in patients suffering from brain tumors, syphilis, and hysterical neurosis. The patient may aspirate food or saliva into the airway and develop aspiration pneumonia.
Pharyngeal hyperesthesia is accompanied by an increase in the pharyngeal and gag reflex. The patient has a cough and tries to cough up non-existent phlegm. This type of throat neurosis can develop after severe stress or a chronic disease of the pharynx or larynx. Patients experience a spasm, a sore throat, and a sore throat. He may feel a “scratching” sensation on the surface of the larynx.
Pharyngeal paresthesia occurs under stress. Patients feel soreness, itching and a “lump” in the throat. Women who are in menopause, impressionable and irritable people are susceptible to the disease.
Is this bronchospasm?
With asthma, a special paroxysmal dry cough with shortness of breath and wheezing also occurs. A child suffering from such a cough should definitely be shown to a pulmonologist, although it may not be asthma, but, for example, bronchospasm. Some children (usually preschool age) are prone to its development. This is a feature of their physiology. But you still can’t ignore such a symptom; you need to deal with it carefully, without putting it off for later. After all, 80% of children with bronchial asthma develop the disease in the first 5 years of life.
It is important to listen to the exhalation. If, as you exhale, the patient emits a high, thin whistle that can be heard even from a distance, you can already suspect that this is not a case of an ordinary ARVI. Although viral infections can become a trigger for asthma.
To alleviate the child’s condition, doctors can use glucocorticoid drugs (can be administered in the form of tablets orally, intravenously or through a nebulizer, as well as rectally in suppositories). Usually on the second day the child feels better, and after a week the baby recovers.
Symptoms of throat neurosis in adults and children
Throat neurosis is characterized by stable symptoms that differ depending on the type of disease. The main manifestations of the disease are tissue numbness and weakening of the swallowing reflex. The disease is accompanied by severe pain throughout the body. Patients may experience increased sensitivity of the hard tissues of teeth.
Throat neurosis is manifested by the following main symptoms:
- Feeling of lack of oxygen even after taking a deep breath;
- Feeling of a lump in the throat that does not go away after drinking liquid;
- Dryness in the larynx;
- Intense thirst;
- Bronchial spasm, which is accompanied by a gag reflex and is not relieved by bronchodilators;
- Sore throat, itching, sore throat, worsening at the moment of greatest irritation;
- Pain in the neck;
- Shooting pain in the ear.
Symptoms of throat neurosis are aggravated when a person is in a dusty or smoky place. An increase in reflex reactions leads to a gag spasm during a hacking dry cough.
Symptoms of throat neurosis intensify with excitement, irritability, psycho-emotional lability, and a migraine attack. Patients' mental and physical activity decreases.
A lump in the throat with neurosis provokes the occurrence of additional symptoms:
- Mood swings;
- Disturbances in sleep and wakefulness;
- Decreased appetite;
- Hypochondria;
- Manifestations of depression;
- Fear of suffocation.
It is especially difficult to diagnose throat neurosis in children, since they are susceptible to colds, the symptoms of which are similar in symptoms to those of pharynx and larynx neurosis.
Under the influence of provoking factors, the function of the child’s immature nervous system is disrupted, which leads to the loss of neural connections between active cells of the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract. Children are psycho-emotionally immature. They react sharply to all irritating factors of a psychogenic nature.
For this reason, throat neurosis in children is often accompanied by somatic pathology. The child's sleep may be disturbed and emotionality may increase. Children can swallow whole pieces of food, which leads to disruption of the digestive system. Sometimes children suffering from throat neurosis develop hoarseness or aphonia (complete absence of voice while maintaining whispered speech).
2. Reasons
Laryngospasm is a neuromuscular reflex that can be caused by many factors.
The main groups of such reasons include:
- inflammation in the respiratory system (pneumonia, bronchitis, tracheitis, laryngitis, etc.);
- neurodegenerative diseases (especially those affecting the spinal cord);
- infections and tumors of the central nervous system;
- severe generalized infections (eg, tetanus);
- irritation of the larynx with chemicals, allergens, medications, very cold or hot air;
- deficiency of vitamins and/or microelements;
- vascular pathology (severe hypertension, aortic aneurysm, etc.);
- neuropsychic factors (psychotrauma, hysterical attack, nervous overstrain, severe crying in children, fear or laughter);
- foreign bodies or tumors in the upper respiratory tract.
Visit our Otolaryngology (ENT) page
Diagnosis of throat neurosis at the Yusupov Hospital
In order to establish the cause of throat neurosis, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital conduct a comprehensive examination of the patient. Using radiography of the cervical spine, osteochondrosis is detected or excluded. More accurate information is obtained after a computed tomography scan of the spine. Patients undergo laboratory tests (general and biochemical blood tests, thyroid hormone levels).
In order to exclude the organic nature of the disease, doctors perform magnetic resonance and computed tomography of the throat. A comprehensive examination includes Doppler ultrasound of the vessels of the brain and neck, and electromyographic study. Patients are consulted by an otolaryngologist, neurologist, vertebrologist, and psychotherapist.
Endocrine pathologies
The feeling of squeezing of the throat and lack of air is sometimes caused by pathology of the thyroid gland. This is due to the pathological growth of organ tissue - goiter. The throat is subject to compression in moderate to severe cases of the disease. Then the pain may join.
Severe muscle spasms in the throat are also caused by damage to the parathyroid gland. A decrease in the level of parathyroid hormone leads to a pronounced lack of calcium and an excess of phosphates in the blood. Such an imbalance in the body is the cause of painful cramps.
The pain affects almost all muscle groups, including the esophagus.
Treatment of throat neurosis
Symptoms of neurosis of the pharynx and larynx disrupt the quality of life of patients. At the initial stage of the disease, it is performed on an outpatient basis. The patient is recommended to change his lifestyle, maintain the correct daily routine, alternate between wakefulness and sleep, go to bed on time, and get a good night's sleep. If the cause of neurosis is sleep, the symptoms of the disease disappear after several days of rest.
In the presence of an inflammatory process, anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out. A patient with throat neurosis is prescribed herbal sedatives. The selection of medications and dosage is carried out by a doctor. After several days of taking medications, the symptoms of neurosis of the pharynx and larynx disappear. If the patient feels a lump in the throat during neurosis, pureed liquid food is prepared for him, which does not irritate the mucous membrane of the pharynx. You should stop smoking, drinking alcohol, and eating spicy foods.
If the therapy is ineffective, doctors prescribe small doses of antidepressants in the presence of depression and asthenic syndrome. To treat throat neurosis, which manifests itself as hypochondria (constant worry about the possibility of contracting a serious illness), antipsychotics are used. If the cause of throat neurosis is a disease of the cervical spine, neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital treat it using medications, physiotherapeutic procedures and modern rehabilitation methods. In some cases, manual therapy is performed.
Psychotherapeutic techniques include hypnotherapy and cognitive behavioral therapy. Psychological correction techniques are aimed at teaching the patient effective ways to relax. Treatment has the following goals:
- Leading the patient to understand the true causes of the pathology;
- Identification of psychotraumatic factors;
- Eliminating them or learning to adapt to them.
Children suffering from neurosis of the throat and larynx are observed by several specialists: an otolaryngologist, a psychologist, a speech therapist (depending on age). Correct parental behavior increases the effectiveness of treatment. Most of the psychogenic factors that cause neuroses in children come from home.
Children with throat neurosis undergo restorative therapy, which includes vitamin complexes and mild sedatives. During the treatment of throat neurosis in a child, it is important to suppress obvious physical symptoms. When there is a sore throat, children are prescribed rinses, inhalations, absorbable tablets, and medications that increase the level of immunity. For infectious diseases, dekasan or trachysan are prescribed.
Psychotherapy for children involves classes on general development, training in relaxation techniques, which include breathing exercises. Babies receive a full body massage aimed at finding blocks and relaxing them. Psychotherapists recommend that parents change the psychogenic situation at home, reconsider their behavioral reactions and correct them. It is important that the child follows a daily routine. He needs to introduce healthy foods into his diet, enriched with vitamins and minerals.
A child with neurosis of the pharynx and larynx should be treated carefully. There is no need to scold him, but hysterics must be stopped immediately. With neurosis, a spasm of the throat is often observed. During an attack, it is necessary to help the child cope with the situation, calm him down, and explain how to breathe correctly.
Laryngospasm. Spasm of the larynx. Help with laryngospasm.
Laryngospasm is a sudden involuntary contraction of the muscles of the larynx. Causes partial or complete closure of the glottis and occurs with inspiratory dyspnea (difficulty breathing).
Sometimes it is combined with tracheospasm, when the smooth muscles of the posterior membranous part of the trachea simultaneously contract.
This condition can occur in adults, but most often it affects children aged 3 months to 2 years, especially if there are risk factors. This is due to the fact that precisely at the age of up to 2 years, the physiological lumen of the glottis is very small, and the nervous system is too labile and unstable, which can easily provoke a sudden attack of laryngospasm. Attacks of laryngospasm can last from a few seconds to 1-2 minutes, and occur several times a day.
Etiology of laryngospasm
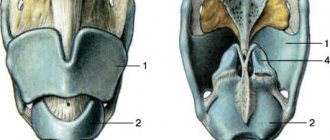
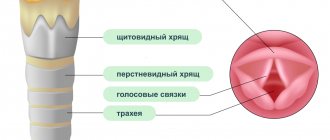
The reason for this pathological condition is the increased reflex excitability of the neuromuscular apparatus of the larynx. During an attack, the aryepiglottic ligaments (two sheets of mucous membrane, separated by connective tissue, are located at the entrance to the larynx) are brought to the midline, the vocal cords are tightly closed, the arytenoid cartilages (paired cartilages to which the vocal cords are attached) are brought together and everted. Therefore, after a noisy inhalation, breathing first becomes shallow, and then may stop altogether, since air cannot pass through. The mucous membrane of the larynx does not change in any way.
Causes of laryngospasm in children:
• lack of calcium in the body;
• deterioration of the body's reactivity;
• birth injury;
• metabolic disorders;
• presence of diseases: chorea, spasmophilia, bronchopneumonia, rickets, etc.;
• pathological changes in the organs of the respiratory system – trachea, lungs, pharynx;
• instillation of various active substances (for example, adrenaline) into the nasal passages.
Laryngospasm in children occurs during:
• severe cough;
• hysterical crying;
• laughter;
• fright.
Etiology of laryngospasm in adults:
• the effect of various medications used to treat the laryngeal mucosa;
• infringement of a benign tumor;
• inhalation of air that contains a certain amount of allergens (dust, pollen, various aromatic substances, etc.);
• swelling of the surface of the larynx;
• inflammation of the surface of the larynx;
• irritation of the recurrent laryngeal and vagus nerves (for example, due to an aneurysm, stressful situations that are accompanied by severe anxiety).
!!! A characteristic feature of laryngospasm is its unexpected appearance.
Symptoms of laryngospasm:
• noisy, whistling and difficult breathing develops;
• unable to clear throat;
• the skin turns pale, a bluish tint appears, and the nasolabial triangle is clearly visible;
• the muscles of the face, neck, and abdomen are tense, the mouth is open, the head is thrown back;
• profuse sweat appears;
• the pulse is hard to palpate, and the breathing process may temporarily stop;
• the reaction of the pupils to light is absent or weakened.
Symptoms of severe laryngospasm:
• loss of consciousness;
• depression of cardiac activity;
• limb spasms;
• foam at the mouth;
• involuntary urination, defecation.
!!! In case of a prolonged attack, if help is not provided immediately, death from asphyxia will occur.
In adults, hysterical laryngospasm is combined with convulsions of the pharynx, esophagus and limbs. As a rule, the attack quickly stops on its own. This attack resembles an epileptic seizure. In mild cases, there is a short-term narrowing of the glottis, a prolonged wheezing breath, pale or blue discoloration of the face, short shortness of breath, and sobbing.
Diagnosis of laryngospasm
The diagnosis of laryngospasm is made based on the clinical picture of the attack and the patient’s complaints.
First aid for laryngospasm
With laryngospasm, it is not the attack itself that needs to be treated, but the cause of its occurrence. To avoid complications, you should call a doctor or an ambulance at the first sign of laryngospasm. Until the doctor arrives, adults should do the following:
1. During an attack, the patient should be reassured, a calm environment should be created, and fresh air should be provided (unbutton the collar, bring it to the window).
2. Reflex methods for relieving spasms: splash cold water on the face and body, or irritate the nasal mucosa with a cotton swab, or blow into the nose, apply ammonia or press on the root of the tongue with a spatula.
3. In the event of a severe attack, the child should be laid on a flat, hard surface, since cardiac arrest is possible, requiring resuscitation measures.
4. It is imperative to administer calcium gluconate intravenously at a dosage of 1 ml per year of life, since the cause of spasmophilia is hypocalcemia. In especially severe cases, the world's only depolarizing muscle relaxant, succinylcholine, is used.
5. If there is no effect, perform intubation or tracheotomy to ensure airway patency.
6. In case of cardiac arrest, resuscitation measures are carried out: indirect cardiac massage.
7. Considering that hypoxia develops as a result of laryngospasm, oxygen therapy must be administered after breathing is restored.
Prevention of laryngospasm
Hardening procedures and restorative treatment are prescribed. Often prescribed are vitamin D, medications containing calcium, ultraviolet irradiation, consumption of dairy and plant foods, long walks in different places (forest, park, embankment).
Relaxation activities for children are recommended. This could be some special games, massage, drawing. The main rule: the child cannot be forced to do this, as this will no longer be relaxing. When choosing a distraction activity, it is very important to observe what the child likes and what calms him down. A balanced diet and vitamin intake can also contribute to a speedy recovery.
Only by following simple recommendations and regularly being examined by an ENT doctor can you get rid of laryngeal muscle spasms forever.
Prognosis for laryngospasm
With timely and adequate treatment, the prognosis is favorable. It is also worth noting the fact that often, as the child grows up, laryngospasm completely disappears and treatment is no longer required.
So, as you understand, laryngospasm is a life-threatening condition, therefore it is very important to recognize it as early as possible and also quickly provide first aid and call a doctor.
Relieving throat muscle tension during neurosis
Tension of the throat muscles during neurosis causes breathing problems. In the complex treatment of neurosis of the pharynx and larynx, breathing exercises can give good results. It helps relieve spasm and tension in the respiratory muscles, restore breathing rhythm, reduce the dosage of medications, and speed up the healing process. You need to take an active short breath and a natural passive exhalation. The air should be inhaled through the nose, making a short, strong movement, and exhaled through the mouth.
The breathing movement and inhalation must coincide in time. The rhythm of breathing movements should correspond to the rhythm of the march. Breathing exercises for throat neurosis can be done standing, sitting or lying down. Their effectiveness improves in fresh air. To determine the cause and type of throat neurosis, exclude the organic nature of the disease and undergo a course of effective therapy, call the contact center of the Yusupov Hospital.
Night guest
False croup, or stenosing laryngotracheitis, is one of the manifestations of ARVI. It occurs in the larynx, where swelling forms, which interferes with the breathing process. A viral disease does not necessarily have to be severe for an attack to develop. Sometimes the child had only a slight runny nose and a slight cough the day before.
As a rule, false croup occurs closer to the night, but a few hours before this, the child already begins to experience warning signs. Due to the narrowing of the airways, the baby's voice becomes hoarse and a whistling sound appears when breathing. Hearing this, sometimes parents begin to suspect that their child has begun to develop bronchial asthma. But in fact, any doctor who hears such a sound will understand that this is not so. Indeed, with obstruction of the lower respiratory tract (bronchial asthma), the patient inhales normally (problems arise only with exhalation), but with false croup, on the contrary, it is not exhalation that is difficult, but inhalation. The child inhales noisily, making the so-called inspiratory breath. In addition, with false croup, a special cough occurs - barking. For some, it resembles the caw of a crow or even the sound of iron on glass. As the airway narrows, symptoms increase, requiring emergency medical attention. If necessary, emergency doctors will give the child an injection of glucocorticosteroids. Of course, not every child’s false croup can reach the suffocation phase, but if there is a predisposition to such a complication, it is better to have such drugs in your home medicine cabinet.