Speech is a complex motor skill implemented by a large number of anatomical structures. The structure of the human vocal apparatus includes the organs of the respiratory system, larynx, tongue, teeth, etc. If the integrity of any of them is violated, the sound production process is disrupted. Knowledge of the anatomical structure and operating principle of the articulatory organs is important not only for singers or other professions related to music, but also for ordinary people. Speech disorders can occur in both children and adults, leading to disruption of the processes of social adaptation and learning.
Causes of pharyngeal cancer
The following are the main causes of throat cancer:
| Causes | Description |
| Smoking | Tobacco products containing harmful substances contribute to the development of the disease |
| Alcohol | Alcohol-containing products weaken the body and damage the immune system if abused. |
| Lack of oral hygiene | Lack of care and hygiene increases the risk of developing throat cancer |
| Heredity | If there are people in your family with throat cancer, the likelihood of it occurring in the future generation increases |
| papillomavirus | Infection increases the likelihood of developing cancer. |
How much do you have to smoke to get throat cancer? Studies conducted by scientists have found a connection between the number of cigarettes smoked per day, smoking experience and the likelihood of throat cancer. The higher the first 2 indicators, the higher the risk of cancer. Other forms of tobacco use also increase risk. There is a potential risk of laryngeal cancer in both smokers and those who chew tobacco. In individuals who have both of these habits, the risk of developing throat cancer increases by 3-4 times. Excessive consumption of strong alcoholic beverages is the first reason that increases the risk of developing the disease.
Laryngeal cancer associated with human papillomavirus has characteristic biological features. In its treatment, less aggressive organ-preserving chemotherapy regimens are used. How long does it take for throat cancer to develop? The process of transformation of normal cells into atypical ones is individual for each person. Throat cancer does not develop immediately. It is preceded by long-term precancerous diseases:
- Dyskeratoses of the larynx (leukoplakia, leukokeratosis);
- Pachydermia;
- Fibroma;
- Papillomas;
- Cysts;
- Chronic inflammatory processes in the larynx, which are accompanied by frequent alcohol consumption and smoking;
- Scars of the larynx as a result of illnesses or injuries.
The cause of the development of laryngeal cancer may be exposure to harmful factors at work, a weakened immune system, ionizing radiation, or gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Provoking factors are paints, wood dust, asbestos, sulfuric acid, nickel. How quickly does throat cancer develop? It may take months or years from the appearance of the first changes in the cells of the mucous membrane of the pharynx or larynx to the clinical stage of the disease.
Recently, in Russia there has been an increase in the number of newly diagnosed throat cancers. This is due to the influence of external and internal factors. Around the world, the statistics are no less comforting. Every year 15,000 new cases of pathology are diagnosed. The ratio of sick men to women is 1000:8.
Possible diseases
Diseases of the nasal cavity are divided into four categories.
Allergic. Symptoms of such diseases manifest themselves through redness and sore throat, lacrimation, itching, and nasal discharge.
Inflammatory. With such diseases of the nasopharynx, general intoxication of the body is most often observed:
- chills,
- apathy,
- febrility,
- appetite and sleep disturbances.
And with tonsillitis - an increase in the size of the nasopharyngeal tonsils.
Traumatic. This category includes diseases characterized by bleeding, bone crepitus, sharp pain, redness and swelling of the affected area.
Oncological. Symptoms characteristic of this group of diseases include the presence of a malignant neoplasm, difficulty swallowing or breathing, a decrease in body weight by 7–10 kg over a month, general weakness of the body, an increase in the size of lymphatic formations, persistent low-grade fever for more than half a month.
Most of the causes of nasopharyngeal diseases can be corrected with medication or by leading a healthy lifestyle. However, a predisposing factor in the occurrence of oncological and allergic pathologies of this organ is burdened heredity, which in no way can be neutralized.
More dangerous pathologies
Any diseases of the nasopharynx are under the supervision of an otolaryngologist. The most common and dangerous pathologies are:
- Sore throat and complications caused by it (inflammation of the tonsils).
- Abscess is a purulent inflammation of the tonsils (a complication of tonsillitis).
- Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx.
- Adenoid vegetation - an increase in the size of the nasopharyngeal tonsils. With this pathology, breathing through the nose is completely impaired.
- Laryngitis is an acute inflammation of the mucous membrane of the larynx.
You can protect yourself from diseases of this organ by taking the following preventive measures:
- Rational and proper nutrition.
- Consumption of mineral and vitamin complexes.
- A healthy lifestyle is partly sports and physical exercise.
- Daily ventilation of living spaces.
What are the first signs of throat cancer?
The first signs of throat and larynx cancer are very varied. They depend on the shape and location of tumor growth and the degree of its spread. The initial stage of throat cancer is hidden. The first symptoms of throat cancer are mild. If they are present, you must immediately make an appointment with an otolaryngologist.
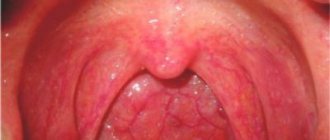
What does throat cancer look like in its early stages? Initially, the tumor can be in the form of a nodular or papillomatous formation, a polyp, or diffuse infiltration. The surface of the tumor is usually uneven and may be gray, red or dark. Cancer of the laryngeal ventricle first appears as a small, gradually increasing upward bulge of the ventricular ligament. Cancer of the epiglottis appears in the form of a limited infiltration or a lumpy, mushroom-shaped mass on its laryngeal surface, spreading into the preepiglottic space.
The first signs of laryngeal cancer depend on the location of the tumor. In the early stages of cancer of the middle part of the larynx, where the vocal cords are located, the first symptoms of throat cancer are hoarseness and other voice changes. The sensation of a lump or foreign body in the throat intensifies while eating or swallowing water.
Swallowing dysfunction occurs when the tumor is localized in the epiglottis. First, a sore throat appears, radiating into the ear on the affected side when chewing, and then there is a constant feeling of a foreign body in the throat. Because of the pain, the patient begins to eat less, which leads to weight loss and exhaustion of the patient.
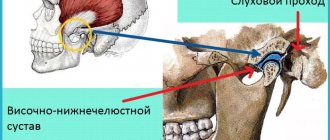
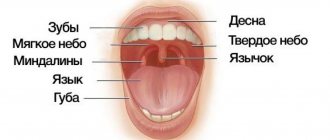
Functions of the human pharynx and larynx: photo with description
Pharynx and larynx
The throat consists of 2 sections: the pharynx and larynx. These departments are interconnected. The anatomy of the pharynx and larynx is directly related to their functions.
Functional features of the laryngeal region:
- Protection - the mucous membrane is equipped with a special movable layer with many glandular tissues. When pieces of food pass by, the nerve roots carry out reflexive movements, causing a cough. With its help, pieces of food fall from the laryngeal region back into the mouth.
- Breathing has a direct relationship with protective functions. The hole, which is equipped with vocal binding muscles and glands, sometimes decreases and sometimes increases, directing air flows.
- Education of the voice, speech - the timbre of the voice directly depends on the anatomical structure of the larynx and the condition of the connecting muscles and tissues.
Functions of the larynx
The functional features of the pharynx are similar to the functions of the larynx. The differences are in the following nuances:
- Respiratory feature - all individual parts of the pharynx are involved: nose, mouth, throat. Oxygen enters it from the nose, and then further into the body.
- Voice, speech - sounds appear (consonants and vowels) and are formed in the soft tissues of the palate and with the help of the tongue. These parts are a “curtain” for the nasopharynx, due to which the timbre sounds and pitch of the voice are formed.
- Protection and pathologies in the pharynx are associated with nasal breathing . The lymphoid circle of the pharynx, together with nearby soft tissues and lymphs, forms one entire immune system of the body. If a person has defects (congenital or acquired), tissue growth occurs, their sensitivity decreases and bacteria begin to multiply. The pharynx protects other parts of the throat by collecting all pathogens. If there is inflammation in the throat, then the nose and ears suffer.
- Eating - This functional feature involves swallowing and sucking. On top of this section there are ciliated receptors. When they work, soft tissues begin to function, a contraction process occurs, fluid is released in the form of mucus and a pharyngeal, gag or cough reflex occurs. All harmful substances that have accumulated on the eyelashes are eliminated by coughing or we swallow them.
The trachea originates in the subvocal section of the larynx, which also plays a huge role in the digestive and respiratory systems of our body.
Symptoms
How does throat cancer start? At the beginning of the disease, there are no symptoms of the disease. Throat cancer manifests itself with common symptoms characteristic of oncology:
- A slight increase in temperature (up to 37.5°C);
- Drowsiness and constant fatigue;
- Weakness and general malaise;
- Fatigue quickly.
When the tumor of the throat and pharynx increases in size, symptoms characteristic of a malignant neoplasm appear. Signs of laryngeal cancer depend on the location of the pathological process.
What are the symptoms of throat cancer located in the vestibular part of the larynx? Initially, the patient does not show any complaints. As the laryngeal tumor progresses, the symptoms become specific. There is pain and discomfort when swallowing. This occurs due to deformation of the epiglottis and damage to the nerve endings. The epiglottis is deformed and does not completely close the entrance to the larynx. For this reason, the patient constantly chokes.
Malignant neoplasms of the vestibular region are aggressive. The tumor quickly spreads to surrounding organs and metastasizes to the lymph nodes of the neck. The reason for this is the well-developed lymphatic system of the vestibular region and its numerous connections with the lymphatic vessels of the pharynx.
What are the signs of throat cancer localized in the supraglottic part of the larynx? At the initial stage of development of cancer of the supraglottic larynx, there are no symptoms or manifestations of the disease. As the size of the tumor increases, the patient's voice changes and discomfort is felt when swallowing. When the tumor grows into the surrounding tissues, acute pain appears during swallowing, which radiates to the ear and hoarseness of the voice.
What are the symptoms of throat cancer when the pathological process is localized on the vocal cords? With this location of the malignant tumor, pain appears even with a small size of the tumor. The patient experiences the following symptoms of throat and larynx cancer:
- The voice is impaired;
- Hoarseness and hoarseness appear;
- Sonority and melody are lost.
The patient begins to get tired even after a short conversation. If the tumor grows into the lumen of the glottis, the patient's breathing becomes impaired.
Cancer of the middle part of the larynx has the most favorable course. The lack of lymphatic vessels in this area explains the rare metastasis of malignant tumors. Hoarseness, which occurs even with small tumor sizes, forces a person to consult a doctor soon after the onset of this symptom.
How does throat cancer manifest if the tumor is located in the subglottic region of the larynx? Malignant tumors in this area also have a number of features:
- Endophytic growth form;
- Resistance to ionizing radiation;
- Metastasis mainly to the preglottic and pretracheal lymph nodes.
There are no early symptoms of the disease. The first sign of laryngeal cancer is a dry, paroxysmal cough. After the tumor grows into the vocal cords, the patient's voice is impaired. As the pathological process progresses and the malignant tumor grows into the lumen of the larynx, the patient develops symptoms of throat and larynx cancer, such as breathing problems with attacks of suffocation. If the disease enters the final stage and begins to destroy surrounding tissues, putrid breath and a cough with blood clots appear.
How do you know if you have throat cancer? Malignant neoplasms of the pharynx and larynx do not have specific symptoms. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital establish an accurate diagnosis after examining and instrumental examination of the patient. If there is throat cancer, symptoms of the disease, doctors take photos during the examination. It can be sent to a partner clinic and advice from other specialists can be obtained.
Stages of tumor formation in the throat
There are 4 stages of laryngeal cancer:
- The first stage - the neoplasm is localized in the mucous membrane. The tumor is limited and does not occupy the entire larynx. The neoplasm does not affect nearby tissues and organs and does not metastasize;
- The second stage - a tumor or ulcer occupies one entire section of the larynx, but does not extend beyond it. The mobility of the larynx is preserved. Metastases are not detected in regional lymph nodes;
- The third stage is divided into 3A and 3B. At stage 3a, the tumor spreads to adjacent parts of the larynx, causes immobility of the corresponding half of the organ, or, although it is limited to one floor of the larynx, it is accompanied by immobility of the ligament or arytenoid cartilage, or ligament. Stage 3B throat cancer is characterized by tumor spread to organs adjacent to the larynx and regional lymph nodes;
- Stage four – an extensive tumor occupies most of the larynx, infiltrates neighboring tissues, there are fixed metastases in the lymph nodes of the neck, or a neoplasm of any size with distant metastases.
With stage 1 throat cancer, patients develop a constant cough and the timbre of their voice changes. After properly selected treatment, tumor recurrence does not occur within five years in 80% of patients. Stage 2 of throat cancer is manifested by disruption of the vocal folds and breathing problems. The patient's voice becomes hoarse and there is pain when swallowing. The five-year survival rate is 70%.
Stage 3 throat cancer is manifested by a complete absence of voice due to damage to the vocal cords. With stage 3 laryngeal cancer, the life expectancy of 60% of patients is 5 years.
The diagnosis of stage 4 laryngeal cancer is manifested by symptoms of damage to the larynx and internal organs in which the metastases are localized (esophagus, lungs and bronchi, digestive organs). Metastases to the liver and brain are less commonly detected. Is it possible to cure stage 4 laryngeal cancer? With stage 4 throat cancer, life expectancy is short. Five-year survival rate is less than 25%.
Anatomy of the human pharynx and larynx: photo with description
Anatomical structure of the pharynx
The pharynx and larynx are located nearby, they have similar functions and they participate in the process of absorption of food and the respiratory process together. Let's look at these departments separately:
Pharynx:
The pharynx or pharynx begins at the end of the mouth and continues to the bottom of the neck. In its shape, this section is similar to a conical pipe, which is widened towards the top, and the narrow part is located at the base of the larynx. On the outside of the pharynx there is a lot of glandular tissue, which produces a mucous fluid necessary to lubricate the throat during stress: speaking and eating. The pharynx consists of 3 parts:
Nasopharyngeal section:
- Beginning of the department. Soft palatal tissue protects the nasal passages from food particles getting into them
- At the top are the adenoids - tissues that accumulate on the back.
- The nasopharynx, throat and middle ear are connected by the Eustachian tube.
- The nasopharynx is almost motionless.
Oropharynx:
- Middle of the department. It is located in the mouth - behind, deeper than the nasopharyngeal region.
- Promotes air to the pulmonary and bronchial tubes.
- The mouth contains the tongue, which pushes food into the esophagus.
- The tonsils are the most important organ of this department. They protect against infections, but they themselves are most often exposed to diseases.
Swallowing department:
- The lower part of the pharyngeal region. Equipped with nerve roots that help in the work of both breathing and the esophagus.
- Thanks to this department, everything happens correctly: pieces of food enter the esophagus, and air enters the lungs, and all this at one moment.
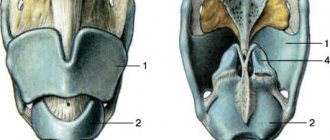
Anatomical structure of the larynx
Larynx:
It has a skeleton with cartilage, which is held together by articular and muscle ligaments. The larynx consists of the hyoid bone, adjacent to the thyroid gland. It functions by contracting the hyoid muscles. The larynx is a complex department that is responsible for the important process of functioning of the body in this area. Each part of this department is responsible for the functionality of one or another part of the throat.
The laryngeal muscles are responsible for the following work:
- Narrowing and increasing the diameter of the glottis with the help of the thyroarytenoid, cricoarytenoid, oblique arytenoid and transverse muscles.
- The ligaments work with the help of the vocal and cricothyroid soft tissue.
Inlet section of the larynx:
- Behind the inlet section are the arytenoid cartilages, consisting of small tubercles.
- Anteriorly, the epiglottis is located.
- On the sides there is aryepiglottic folded tissue consisting of blade-shaped tubercles.
Cavity region of the larynx:
- Origin - extends from the vestibular fold tissue to the epiglottis. This tissue consists of a moistened shell.
- The interventricular section is the narrowest part of the larynx. It starts from the vocal cords and ends at the top, near the vestibular cords.
- Subvocal section - located below, near the slit, which is responsible for the voice. At the end it has an extension from which the trachea begins to extend.
Laryngeal membranes:
- Mucous membrane - consists of a covering with many nuclei and a prism.
- Fibrous-cartilaginous - delicate, soft, hyaline cartilage. They are surrounded by fibers. Together all this forms the laryngeal frame.
- Connective tissue - connects the laryngeal region and other parts of the neck from the inside.
The anatomy of these two sections is related to their functional characteristics.
Diagnosis of laryngopharyngeal cancer
How to diagnose throat cancer in the early stages? If there are symptoms of throat cancer, diagnosis should be comprehensive. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital diagnose cancer of the throat and larynx using the following methods:
- Direct and indirect laryngoscopy,
- Hypopharyngoscopy;
- Computed tomography;
- Histological examination;
- Trial laryngofissure;
- Cytological examination of prints from the larynx and lymph nodes;
- Determination of tumor marker levels.
How to recognize throat cancer? Otolaryngologists first perform indirect laryngoscopy. When examining the true vocal cords, attention is paid to their mobility during phonation and the asymmetry of the lesion inherent in the tumor process, and the size of the tumor lesion and its location are specified. To examine the posterior parts of the larynx, they are examined with a laryngeal mirror from bottom to top, when the doctor sits in front of a standing patient.
How to diagnose throat cancer in an elderly person if the picture is not clear enough or if the tumor is masked by secondary inflammatory phenomena with decay, infiltration and edema? In this case, otolaryngologists resort to local anesthesia, elevating the epiglottis, palpating with a probe, using a magnifying mirror, and also tilting the patient’s head accordingly. If a lesion of the subglottic region or lower parts of the pharynx is suspected, direct laryngoscopy and hypopharyngoscopy are used.
How to check your throat for cancer using computed tomography. This research method expands diagnostic capabilities for tumors that are localized in the area of the ventricular and true vocal cords and laryngeal ventricles, as well as when the tumor has spread to the subglottic region. At the Yusupov Hospital, patients are examined using the latest generation computer tomographs with high resolution capabilities.
How to check the throat and larynx for cancer using laboratory methods? Histological examination determines the nature of the tumor, its structure, the degree of differentiation of cellular elements and the degree of malignancy of the tumor - all these details influence the course of the disease and are taken into account when choosing a treatment method
To avoid stimulation of increased growth and spread of the tumor process due to damage to the lymphatic and blood vessels during biopsy, oncologists perform several sessions of radiation therapy before surgery.
How to diagnose laryngeal cancer using other methods? In cases where the biopsy data are not convincing enough or it is impossible, a trial laryngofisure is used. Since during the procedure, contamination of surrounding tissues with atypical cells may occur, in such cases, a histological examination is urgently performed at the operating table, having previously obtained the patient’s consent for radical intervention. Cytological examination of prints from the larynx and lymph nodes is carried out in cases where the patient categorically refuses surgery and a biopsy is not indicated.
How to detect throat cancer at an early stage? For early diagnosis of throat and larynx cancer, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital examine the level of tumor markers SCC and CYFRA 21-1. Highly qualified doctors, equipping operating rooms with modern diagnostic equipment and instruments allows oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital to improve five-year survival rates for throat cancer.
How to treat laryngeal cancer? Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital have extensive experience in treating laryngeal cancer. The treatment method is selected depending on the stage of the disease, type and spread of the tumor. The following methods are used:
- Surgical interventions (chordectomy, laryngectomy);
- Organ-preserving laser surgery for laryngeal tumors;
- Operations to remove tumors using a shaver;
- Radiation treatment (external gamma therapy);
- Neoadjuvant, adjuvant and curative chemotherapy;
- Palliative treatment.
Expert opinion
Author: Alexey Andreevich Moiseev
Head of the Oncology Department, oncologist, chemotherapist, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Throat cancer accounts for 3% of all cancers. At the same time, the tumor is the most common among neoplasms of the upper respiratory tract. It is diagnosed in 50–70% of cases. As throat cancer progresses, permanent disability occurs. As a result, the tumor remains a problem for clinical medicine.
Recently, in Russia there has been an increase in the number of newly diagnosed throat cancers. This is due to the influence of external and internal factors. Around the world, the statistics are no less comforting. Every year 15,000 new cases of pathology are diagnosed. The ratio of sick men to women is 1000:8.
The Yusupov Hospital provides a full course of diagnostics necessary to identify pathology even at the formation stages. The earlier the examination is performed, the more favorable the prognosis. The quality of treatment meets international standards. An individual therapy and rehabilitation program is developed for each patient, aimed at improving the quality of life and preventing relapse.
The main treatment method for laryngeal cancer is surgery. Radical surgical intervention for a malignant tumor is removal of the larynx. The consequences may vary. After surgery, some patients lose their voice and tumor growth resumes.
A laryngofissure is applied when the exophytic tumor is localized on the free edge of the anterior two-thirds of the true vocal cord, without the tumor spreading to the anterior commissure and the arytenoid region.
If a significant area of the larynx is affected by the cancer process, and mobility in the affected area is very limited or even completely absent, the process is macroscopically one-sided, surgeons perform throat surgery for oncology - resection of half of the larynx. Hemilaryngectomy is indicated not only for internal cancer that does not grow through the cartilage of the larynx, but also when the tumor process has spread to the anterior commissure and the area of the arytenoid cartilage.
If the tumor is localized in the anterior two-thirds of one true vocal cord with transition to the anterior commissure or even to the anterior part of the other true vocal cord, a half resection of the larynx according to Otan is performed. During this operation, the anterior parts of the larynx are removed, leaving its posterior wall. After the intervention, swallowing and voice function are preserved. Partial surgical interventions for laryngeal cancer include frontal resection of the larynx. It is used for damage to the anterior commissure.
Currently, the most common organ-preserving operations for localized laryngeal cancer remain chordectomy and diagonal resection of the larynx. After surgery, patients' voice function is impaired; they note hoarseness, fatigue during conversation, and a significant deterioration in sound when overloaded. An undesirable consequence of sagittal resection of the larynx is a disorder in swallowing after surgery.
How to cure throat cancer at an early stage? Laryngeal surgery (tumor removal) is performed using a shaver. During the operation, healthy tissue is not injured. The operation is performed endoscopically. A tracheostomy for laryngeal cancer is performed after total removal of the organ. The Yusupov Hospital provides nutrition after removal of the larynx for throat cancer.
Throat cancer is treated with anticancer drugs. Oncologists practice two treatment options: monotherapy and polychemotherapy. In monotherapy, one drug is used, to which cancer cells are especially sensitive. The drug is prescribed in large doses. For polychemotherapy, several cytostatic drugs are used sequentially or simultaneously.
Chemotherapists at the Yusupov Hospital use combinations of cytostatics recommended by the International Association of Oncologists to achieve the greatest effectiveness of treatment. They use drugs that are highly effective and have minimal side effects. Patients at the Oncology Clinic have the opportunity to receive the latest anticancer drugs thanks to a research program in which the Yusupov Hospital participates. The effectiveness of radiation therapy for throat cancer is assessed by professors and doctors of the highest category.
A combined approach to the treatment of laryngeal cancer can improve treatment results. Radiation therapy for throat cancer is used both as primary treatment and as part of combination therapy. Is there a cure for throat cancer? Most patients with early stages of laryngeal cancer are cured with radiotherapy. How suitable radiation therapy for laryngeal cancer is for a particular patient depends on the volume and location of the tumor, and is determined by the depth of its growth in the throat tissue.
In the early stages of the disease, treatment in most cases is carried out with radiation sessions 5 times a week for 3-7 weeks. The radiotherapist calculates the total radiation dose to laryngeal cancer for the entire course, and then divides it into fractions. This separation allows you to reduce the undesirable consequences of treatment. Can throat cancer be cured? If complex treatment is started on time, the prognosis for recovery improves many times over.
Diagnosis of laryngeal tumors
Methods for diagnosing throat cancer
:
- throat examination,
- palpation,
- fibrolaryngoscopy – a piece of tissue is taken with a special instrument, hard-to-reach areas of the throat are examined,
- a separate point should be the cytological and histological examination of samples taken from the throat,
- computed tomography is used to look at cartilage,
- MRI is necessary to study the folds, subglottic region and other parts,
- Ultrasound of the lymph nodes of the neck and liver is necessary if there is a danger of metastases spreading there.
Survival prognosis
How long do people live with laryngeal cancer? When a patient is diagnosed with throat cancer, the prognosis directly depends on the location of the tumor and the extent of the cancer process.
Table No. 1. Survival prognosis depending on the location of the laryngeal tumor
| Location of the tumor | Five-year survival forecast |
| Postcricoid region | 20% |
| Posterior wall of the larynx | 21% |
| Pyriform sinus | 50% |
Is throat cancer deadly? If the disease is recognized in a timely manner, there is a high probability that the disease can be defeated. The five-year survival rate for patients with stage 1 throat cancer is 85%. When stage 4 gora cancer is detected, the prognosis is less optimistic. If stage 4 throat cancer is detected, how long do they live? The five-year survival prognosis for patients with stage four laryngeal cancer is 20%. Much depends on whether the patient agrees to surgery to remove the larynx and vocal cords, which could render the person mute.
Long-term survival of patients with throat cancer has remained virtually unchanged over the past 20 years, but the quality of life of cured patients has improved significantly. If radiation therapy does not lead to the expected result, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital use preservation surgery methods that allow the patient to partially preserve speech.
Speech apparatus and defects
The degree of development of the speech apparatus determines the quality of pronunciation of sounds. Diseases of any of the departments are manifested by a deterioration in sound pronunciation and change the characteristics of a person’s voice. The task of speech therapists and doctors when identifying phoniatric symptoms is to identify the causes of their occurrence and select methods to eliminate the defects.
Due to the complexity of the structure of the speech apparatus, there are many possible causes of impaired sound pronunciation. Diagnostic measures should always be comprehensive and selected individually for each person. There are several reasons for the development of speech defects, which occur most often:
- organic disturbances in the structure of individual structures;
- their functional immaturity, which causes incorrect movements during the conversation;
- neurological disorders in those parts of the central and peripheral nervous system that are involved in the formation and formation of sounds.
With these defects, a person often notices problems with breathing, swallowing food and liquids. Such symptoms gradually lead to a decrease in the level of quality of life and can cause impaired adaptation in society, depression and other negative consequences. If you have delayed speech development or other defects, you should always seek professional help from doctors or a speech therapist. Specialists will conduct the necessary examinations and select corrective measures to eliminate the organic or functional defect.
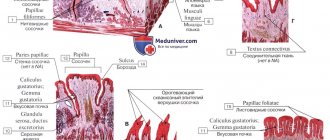
The human vocal apparatus has a complex structure and consists of three main parts: respiratory, vocal and articulatory, or sound-pronouncing. All structural departments act in concert, determining not only a person’s voice, but also the formation and pronunciation of all sounds and words. The regulation of the speech process is carried out by the central nervous system, namely the cerebral cortex, subcortical extrapyramidal systems and the nuclei of the cranial nerves. Knowledge of anatomy allows you to promptly identify changes in the speech organs, primarily located in the oral cavity.
Prevention
Throat cancer is a disease whose development is largely associated with the consumption of alcohol, nicotine and other toxic substances. Oncologists recommend that patients addressing this issue give up bad habits to reduce the likelihood of pathology.
Another provoking factor is carcinogenic substances, the inhalation of which causes irreversible changes in the mucous membranes. Patients at risk are advised to limit manipulations with substances of increased carcinogenicity: benzene, asbestos, oil industry products, phenolic resins, coal dust. If, while performing work duties, contact with these substances cannot be avoided, respirators should be used to protect the respiratory tract.
Timely treatment of respiratory diseases is an important preventive measure to prevent the pathological process. Oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital advise patients at risk and inform them about factors that negatively affect the respiratory tract, manifestations of throat cancer at the initial stage and methods of prevention.
Causes of mechanical neck pain
Let’s summarize and focus on the most common causes of neck pain, since they can affect everyone. That is, we will focus only on mechanical, non-pathological pain. And this is what causes them:
- Overstrain of the neck muscles and blocking of the facet joints (these are the joints that allow movement between the vertebrae and prevent the discs from stretching). Such changes occur due to the head being in one position for a long time. This is the scourge of office workers who spend hours frozen with their heads bowed over their desks. Every unconscious movement of the head forward to peer at the computer is a strain on the muscles. An uncomfortable posture during sleep can also be detrimental.
- Sprain and slight deformation of the neck ligaments.
- Sudden head movement.
- Forced flexion of the neck followed by extension or, conversely, extension-flexion, causing the so-called whiplash injury (microtears of muscles).
- Hypothermia of the neck. Leads to muscle inflammation.
Risk groups for neck pain:
- People with problems with the spine and feet (flat feet)
- People with poor posture
- Professionals engaged in activities that require repetitive actions/severe bending of the cervical spine or prolonged holding of the head in one position.
- Smokers.
- People over 40 years old.
- People experiencing stress, mental trauma, overwork.
All this leads to muscle spasms and severe neurotic pain in the neck.
Treatment in Moscow
Treatment of throat cancer in Moscow using modern methods is carried out by doctors at the Yusupov Hospital. The Oncology Clinic specializes in the treatment of laryngeal cancer. The consultation is conducted by leading oncologists in Moscow, who have scientific titles and the highest medical category. Candidates and doctors of medical sciences and authors of scientific works take part in the treatment process.
Patients are in comfortable rooms. Medical personnel provide hygienic care for the tracheostomy. Cooks provide patients with special meals. The cost of treatment is lower than in other throat cancer clinics. The price of services provided to the patient corresponds to their quality. You can find out how much treatment for throat cancer costs by calling the Yusupov Hospital.