Sputum with wet cough
Before treating a wet cough in an adult, it is necessary to conduct a laboratory test of sputum to determine the nature of the disease. Tracheobronchial secretion may have a liquid, thick or viscous consistency. The presence of a large amount of mucus in it signals the presence of an allergic or cold-infectious process in the bronchi and lungs. The yellowish-green color of sputum, caused by impurities of pus, may indicate the development of bronchitis or pneumonia. The appearance of white, cheesy discharge during expectoration warns of the likelihood of a fungal respiratory infection, and clear, watery sputum usually accompanies viral infections or chronic diseases of the respiratory system.
It is important to know!
When treating a wet cough accompanied by sputum discharge, the use of antitussive drugs is contraindicated. By blocking the central or peripheral parts of the corresponding reflex, they lead to the accumulation and stagnation of a large amount of mucus, which is a favorable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic microflora. Drugs for the treatment of wet cough are mucolytic agents. The group of modern effective mucolytics made on the basis of plant components includes Doctor MOM® syrup and Doctor MOM® herbal lozenges.
Causes of viscous sputum
Chronical bronchitis
Viscous sputum is typical for exacerbations of bronchitis, when the patient is bothered by a wet cough and a slight deterioration of the condition.
Up to 100 ml of cloudy, thick mucus is secreted per day. Coughing up bronchial secretions is preceded by pain in the chest and shortness of breath. A coughing attack is caused by inhalation of smoke and strong odors, but often there are no provoking factors. Catarrhal bronchitis usually occurs with this clinical picture. When an obstructive component is attached, shortness of breath and painful coughing attacks occur, ending with the release of a small amount of thick mucus. If purulent bronchitis develops, streaks of pus appear in the viscous sputum coughed up, and in severe exacerbations it becomes profusely purulent.
Bronchial asthma
The discharge of thick glassy sputum is a pathognomonic sign of an asthmatic attack. Initially, an attack of suffocation and dry cough occurs. Breathing is gradually restored (on its own or after inhalation through a nebulizer), a wet cough appears, during which scant clear mucus is released. Often, the patient has difficulty coughing up viscous sputum and is bothered by the feeling that it is stuck in the respiratory tract.
The separated mucus indicates the end of the attack of bronchial asthma, and soon the patient’s condition improves. If shortness of breath increases and sputum is not coughed up, they speak of status asthmaticus, which requires emergency medical attention. Paroxysms of suffocation are provoked by physical exertion, psycho-emotional stress, contact with allergens - pollen, animal hair.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Cough attacks with thick sputum occur in mild to moderate cases of the disease. At this stage, patients are occasionally bothered by a cough, which is accompanied by expectoration of scanty, thick, cloudy mucus. During the day, sputum is released in a volume not exceeding 60 ml. During an exacerbation of COPD, mucus leaves in greater quantities and thins out, acquiring a yellow-green color and an unpleasant odor.
There may be shocking photos of medical operations hidden here that show blood and guts.
Are you over 18 years old?
Yes
No
Viscous sputum
Congestive pneumonia
With this disease, a cough develops with the release of viscous mucous or mucopurulent sputum. Congestive pneumonia is mainly detected in patients who are on bed rest for health reasons, as a result of which mucus is more difficult to expectorate. Usually phlegm accumulates in the throat and mouth, and a person cannot get rid of it. Weakness and shortness of breath increase.
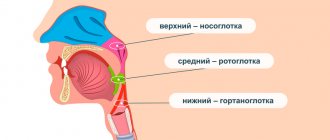
Laryngitis and tracheitis
The appearance of thick sputum is characteristic of the chronic course of laryngotracheitis. At first, after coughing, liquid mucus is expectorated, but after 2-3 weeks, if treatment is ineffective, it becomes viscous, and the amount of discharge decreases. Sputum accumulated in the area of the vocal folds leads to voice disturbances, the person feels difficulty breathing. When you try to cough, a scanty amount of cloudy mucus comes out.
Inflammation of the upper respiratory tract
In chronic rhinitis and sinusitis, postnasal drip syndrome is observed. The discharge spreads along the back wall of the pharynx and causes a coughing attack with viscous sputum of a mucous or purulent nature. Cough paroxysms often begin in the morning immediately after waking up or after being in a lying position for a long time. Symptoms are more common in children.
Tuberculosis
When infected with Koch's bacillus, coughing with the release of thick, scanty sputum predominates. Symptoms last for several months. There is a gradual increase in cough and an increase in the amount of viscous mucus discharged. In addition to respiratory symptoms, causeless weakness and fatigue, and night sweats are troubling. An exacerbation of tuberculosis is indicated by a severe cough, accompanied by chest pain and expectoration of viscous mucous sputum.
Cystic fibrosis
Clinical manifestations manifest in early childhood. In the pulmonary form of cystic fibrosis, paroxysms of painful cough with thick mucopurulent sputum attract attention. Due to congenital disorders of the biochemical composition, the mucus is very viscous, therefore it accumulates in the bronchi, causing prolonged bronchitis and bilateral pneumonia.
Blockage of the bronchial tree with thick sputum leads to difficulty breathing and mixed shortness of breath. After a coughing attack and expectoration of secretions, the condition improves. With long-term cystic fibrosis, in addition to coughing attacks with thick mucus, symptoms of respiratory and heart failure are observed. Children often get sick and lag behind in physical development.
Bronchiectasis
Patients with bronchiectasis experience the discharge of copious, thick sputum, which is purulent in nature and has a foul odor. The symptom is especially pronounced in the morning: after a coughing attack, phlegm is released “a mouthful” in an amount of 50-100 ml or more. During the day, a cough constantly occurs, combined with expectoration of thick pus. When blood vessels rupture due to strong cough paroxysms, blood inclusions are visible in the viscous sputum.
Inhalations for wet cough
A productive wet cough without fever can be treated with inhalations. These procedures, based on the inhalation of medicinal and biologically active substances, help reduce thickness and viscosity, more actively liquefy and remove sputum. To treat coughs, steam inhalers and nebulizers are used, to which special medications are added. Inhalations that help moisturize the mucous membrane help to quickly reduce pain, reduce the viscosity of sputum, eliminate spasms and relax the muscles of the bronchi. You can use Doctor MOM® Phyto ointment, which is locally irritating , distracting, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect.
Principles of treatment of cough with sputum
If a person is suffering from a cough with sputum, it is recommended to provide plenty of fluids; it is possible to use drugs or herbal remedies that have an expectorant, anti-inflammatory, enveloping and bronchodilator effect. There are several groups of medications that are prescribed to relieve the symptoms of wet cough:
- expectorants . They are prescribed for viscous sputum to facilitate the process of its removal from the respiratory tract. A similar effect is achieved through reflex stimulation of the glands located in the bronchial mucosa. When using these drugs, the amount of mucus may increase due to the dilution of sputum;
- mucoregulating agents. They help reduce the secretion of sputum and, like expectorants, allow it to be removed from the body. In case of exacerbation of bronchial asthma, the use of these drugs is contraindicated, therefore, before taking, you should consult with your doctor;
- mucolytic agents. They improve the removal of sputum by stabilizing the release of bronchial secretions. These drugs are usually prescribed for tracheitis, bronchitis, pneumonia and other diseases;
- antihistamines. They are prescribed if the cough is a consequence of allergies. They help alleviate the consequences of the body's reaction to certain irritants. If you are bothered by a sore throat, sputum of unusual color and consistency, cough, fever and other unpleasant symptoms, you should consult a doctor. Such manifestations are a consequence of a number of diseases, so consultation with a specialist is necessary to make a diagnosis and select therapy. This will help avoid complications and start treatment in a timely manner.
Drink plenty of warm fluids for wet coughs
When answering the question of how to cure a wet cough in an adult, it is worth mentioning another necessary and effective method of treatment: drinking plenty of vitamins. During a cold, you should drink more liquid than usual to moisturize the mucous membrane and quickly thin the mucus. This can be warm mineral water, herbal decoctions, teas, fruit drinks, milk in combination with honey, etc.
Mucolytic drugs against wet cough
One of the remedies indicated for use for coughs with the discharge of viscous sputum is Doctor MOM® syrup. The components included in this medicine have a complex of therapeutic properties, due to which the syrup has the following effects:
- Anti-inflammatory;
- Mucolytic;
- Bronchodilator;
- Expectorant.
For inflammatory diseases of the respiratory tract, accompanied by an unproductive cough, the use of Doctor MOM® drugs helps reduce negative symptoms and restore the normal state of the bronchi and lungs. To avoid disruption of the discharge of liquefied sputum, expectorant herbal syrup is not recommended to be taken in combination with antitussive drugs, which are aimed at blocking the cough reflex, and not at treating cough.
How to remove phlegm from the lungs?
Stimulating the removal of excess pathological bronchial secretions not only facilitates general well-being, but also improves respiratory function and reduces the frequency of coughing.
You can use medications to ease the passage of sputum when coughing. For this we use:
- decoctions of herbs that stimulate the removal of phlegm (sage, calendula);
- drugs that make thick sputum less viscous, making it easier to expectorate when coughing (mucolytics);
- pharmacological agents that stimulate the expectoration process (secretomotor agents);
- bronchodilators that facilitate breathing and improve the discharge of bronchial secretions;
- inhalation with drugs of mucolytic and secretomotor action.
Also, the removal of sputum can be stimulated by breathing exercises and postural drainage, i.e. patting and tapping the chest in front and behind.