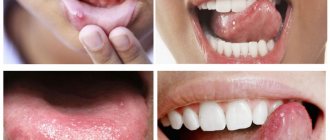
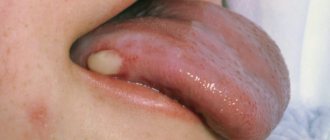
Polyps on the tongue are benign neoplasms that form from different structures of the mucous membranes of the pharynx and tongue. Few small growths are practically not felt when talking or eating. Large neoplasms with multiple spread worsen the patient’s quality of life and require mandatory treatment. The mucous membrane of the tongue receives a colossal load every day, so initially benign neoplasms can grow, become damaged, and become malignant. 80% of patients with tongue cancer had a history of various benign tumors.
Polyp on the tongue - what is it?
A tongue polyp is a dense, tuberous neoplasm on a wide stroma. The polypous lesion rarely has a long stalk. Such growths can occur under the tongue. Given the high risks of injury under the influence of temperature, food and mechanical factors, the polyp is unstable and prone to infection and bleeding.
The main tumors are adipose tissue, lymphatic and blood vessels, muscle fibers, and epithelial cells. Thus, polyps constitute a whole group of benign tumors of the tongue, including tongue papillomas, retention cysts, fibromas, and botryomycomas.
Pathological neoplasms are rarely encountered in dental practice. Against the background of polypous lesions of the tongue, combined pathologies are often diagnosed in the form of anomalies of the osseous-facial bones, cartilaginous apparatus and tongue.
Classification
The main feature of tongue polyps is their slow growth outside the oral cavity. The stroma of growths can be formed from mucous and submucosal structures of the organ, epithelial and non-epithelial tissue.
According to morphological structure
Classic polyps are smooth, round growths with clear outlines.
There are several main types:
- Angiomatous . Growths form not only on the tongue, but also inside the oral cavity (for example, you can find a polyp in the mouth on the cheek, on the inner surface of the lips, gums, and the surface of the palate). The structure of the neoplasm is filled with abundant vascular components, which stimulate its accelerated growth. It is angiomatous polyps that tend to spread throughout the entire oral cavity.
- Fibrous . Neoplasms have a dense base consisting of epithelial and muscle tissue. Polyps grow deeply inside the tongue and reach impressive sizes without adequate treatment. Large fibrous polyps worsen the quality of life, disrupt jaw occlusion and the chewing process.
- Giant cell . The growths are characterized by rapid growth inside the mucous membranes and over the entire surface of the oral cavity. Many small growths often form entire conglomerates, reminiscent in appearance of a cauliflower inflorescence.
Regardless of their morphological structure, neoplasms are prone to trauma, bleeding and infection. Oncological risks directly depend on the volume and nature of polypous structures, as well as on the patient’s hormonal background.
Note ! Angiomatous growths in children form mainly on the gums. They are often mistaken for teething. An adequate immune response ensures spontaneous disappearance of the pathology.
By type of growth
Polypous units, depending on the stroma, are also classified by height:
- Exophytic – growing inside the oral cavity;
- Endophytic - growing inside the tissues of the pharynx and tongue;
- Mixed - when the root grows deep inside the tissues, and the body rises above the surface of the mucous membranes.
Classification helps to narrow the clinical picture, determine the type of tumor and prescribe the correct treatment.
Difference between papilloma and polyp
Papilloma and polyp have a similar nature, but are fundamentally different pathologies:
- A polyp is a benign tumor that does not cause critical harm to health. With timely treatment, there is little chance of developing into a malignant neoplasm and oncology. The reason for the growth of polyps is not known exactly to modern medicine.
- Papilloma is necessarily the result of infection by a virus upon contact of any kind (except airborne) with a cross-striped person.
The big difference in determining the type of neoplasm is its location. The polyp grows on the mucous membranes and is difficult to detect on its own. Papilloma forms on the external tissue, it is not difficult to recognize it.
Causes
There is no specific reason that would directly influence the occurrence of tongue polyps.
The following factors can provoke the occurrence of neoplasms::
- papillomavirus infection (papillomas in the human mouth);
- reduced immunity;
- previous surgical diseases;
- hormonal imbalance;
- bad habits, especially alcoholism, smoking;
- inadequate oral hygiene;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
The formation of polyps is affected by:
- heredity,
- some congenital anomalies of the development of the maxillofacial bones, bite, shape and size of the tongue.
Polyps
Hysteroscopy is an endoscopic examination of the uterine cavity, during which it is possible to perform diagnostic curettage, take a biopsy, and remove polyps.
Cystoscopy (endoscopic method) and cystography (x-ray method with contrast) can detect a formation in the bladder.
Which doctors should I contact?
ENT doctors examine and treat patients with polyps of the nose and paranasal sinuses. To select therapy, you may additionally need to consult a pulmonologist and/or an allergist-immunologist.
For polyps of the gastrointestinal tract, patients are observed by coloproctologists and surgeons.
manage patients with polyps of the female genital organs.
– with pathology of the bladder.
Treatment of polyps
Treatment of polyps is mainly surgical. Often, endoscopic techniques are used for this purpose, especially for small polyps. Removed polyps are sent for histological examination.
In the initial stages of polypous rhinosinusitis, therapy usually begins with local anti-inflammatory drugs - intranasal glucocorticosteroid sprays, which are used for several months. In some cases, glucocorticosteroid hormones can be prescribed in a short course orally (in tablets). If drug therapy is ineffective, if there are abnormalities in the structure of the nose, or if the process is unilateral, surgery may be recommended.
Neither diet nor drug therapy can cure stomach or intestinal polyps.
Such polyps must be removed using endoscopic intervention.
In relatively rare cases, when the polyp is large, blocking the intestinal lumen, in the presence of bleeding from the polyp or a histologically confirmed malignant formation, resection (removal) of a section of the intestine is performed. But even then, whenever possible, minimally invasive (laparoscopic and transanal) treatment methods are used. After removal of polyps, repeated endoscopic examination is carried out after 6-12 months.
Since a common cause of the formation of uterine polyps is hormonal imbalance, its correction is considered as one of the treatment options.
Adequate hormonal therapy can stop the growth of the polyp and reduce the likelihood of its reoccurrence after removal.
However, not all experts recommend drug therapy, considering its effect to be temporary. The gold standard is polypectomy (removal of a polyp). Removal can be done using radio wave or laser surgery.
If bladder polyps do not increase in size, do not obstruct the outflow of urine from the bladder, and are not accompanied by bleeding, then in some cases dynamic observation is possible. If necessary, removal is performed using endoscopic equipment.
Complications
Large polyps can narrow the lumen of the organ, disrupting its function. Bleeding is possible.
In some cases, polyps of the gastrointestinal tract, urinary tract, and uterus can degenerate into malignant neoplasms.
Endometrial polyps are sometimes considered as a possible cause of infertility.
Prevention of polyps
Prevention and adequate treatment of infectious diseases of the nose and paranasal sinuses, surgical treatment of abnormalities in the structure of the nose can help prevent the development of polypous rhinosinusitis.
Preventive measures to prevent polyps in the stomach: smoking cessation, limiting alcohol consumption, balanced diet, treatment of chronic gastritis, eradication (elimination) of Helicobacter pylori
.
It is believed that the content of so-called coarse fiber in food (vegetables, fruits) reduces the risk of developing formations in the intestines. On the contrary, alcohol abuse can contribute to their occurrence.
People over 50 years of age are recommended to undergo an annual quantitative immunochemical test for occult blood in feces 2401. If it is detected, a colonoscopy is prescribed. Examination of persons whose close relatives have had cases of malignant intestinal diseases is considered mandatory.
A timely diagnosis and treatment provide encouraging results.
The basis for the prevention of bladder polyps is the treatment of cystitis and smoking cessation.
Sources:
- .
- Boltrukevich P.G. The incidence of colon polyps depending on the topographic and anatomical structure of its various parts. Smolensk medical almanac. 2016. pp. 38-41.
- .
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor.
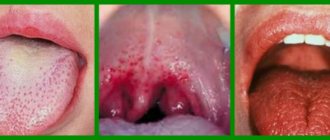
How do polyps appear on the tongue, closer to the throat or under the tongue?
Small, few tumors do not lead to unpleasant symptoms and do not cause discomfort when talking or chewing.
With large growths, complaints arise of a constant sensation of a foreign body, bad breath, and impaired occlusion.
Other unpleasant symptoms are:
- sore throat;
- bleeding, pain in the localized area;
- thickening of the inner surface of the cheeks;
- difficulty chewing;
- pigmentation of the mucous membranes of the pharynx;
- change in voice timbre.
Large multiple polyps complicate daily oral hygiene, lead to food deposition, secondary infection, bad breath, and the formation of dense plaque.
If the polyps are located closer to the throat, then patients experience the following sensations:
- foreign body;
- difficulty swallowing;
- dry cough due to irritation of the laryngeal mucosa;
- voice change.
The danger of such localization is the possibility of blocking the larynx and breathing problems. This usually occurs in the absence of medical intervention.
When the polyp is localized on the tip of the tongue, the perception of taste is disrupted, pain appears when exposed to irritants: temperature, friction against the teeth when talking, chewing.
Tumor growth is always stimulated by unfavorable factors. Inflammation and spread of polyps along the inner surface of the pharynx is aggravated by dental history.
Diagnosis of tongue polyp
Diagnostic measures are aimed at establishing the nature of the neoplasms.
Diagnosis consists of the following examinations:
- Dental examination (oral cavity, condition of teeth: integrity, carious cavities);
- Polymerase chain reaction;
- Biopsy - tissue sampling for histological examination.
The latter analysis makes it possible to evaluate the morphological structure of tumor-like growths and eliminate oncological risks.
The patient's hereditary and clinical history must be studied. Persons over 45 years of age whose close relatives have suffered from cancer of the tongue and oncology of other localization deserve special attention.
Differential diagnosis
The structure of the base of the polyp is of key importance in the final diagnosis and determination of treatment tactics.
Tumor-like growths are represented by the following types:
- Papillomas . The main cause is the human papillomavirus. Papilloma takes its base from the squamous epithelium, is located on the back or tip of the tongue, the shade matches the mucous membranes of the organ. Papillomatous rashes are a bit like herpes. If there is keratosis (keratinization) on the surface of the papilloma, malignancy is suspected.
- Adenoma . The basis of the tumor is the glandular structures of the tongue, localized mainly on the back and under the organ. At the root of the tongue, the adenoma disguises itself as a polyp from the heterotopic mucosa of the esophagus. On the tip of the tongue they talk about cystadenomas.
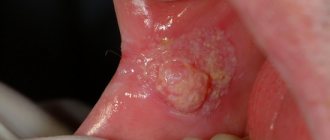
- Botriomycomoma . Flat or spherical growths, often having a lobular structure. The new growth is red or light pink, but as it grows the color becomes dark burgundy. It is characterized by slow growth, but if left unattended it grows up to 4.5 cm in diameter. The surface can be rough, smooth or coarse. The main reason is traumatization of the tongue, the formation of cracks and microcracks.
- Fibroma . A round neoplasm with connective tissue structures at the base. The consistency is soft, the color matches the mucous membranes of the organ. Resembles a glandular fibrous polyp.
- Lipoma . Lobulated neoplasm of soft consistency. The basis is the submucous membranes of the tongue. Localized on the inner and lateral surface of the organ.
- Retention cyst . The cystic component is formed from the nunnia glands, which are located in the muscle layer. Localized on the lower surface and tip of the organ. Usually 2-5 units occur at the same time.
- Struma of the tongue . A rare type of tumor consisting of thyroid tissue from the thyroid gland. These cells are atypical for linguistic structures and arise as a result of impaired embryogenesis.
Additionally, polyps are differentiated from fibroids, hemangioma (capillary, cavernous), neurofibroma, and lymphangioma. If any form of benign tumor is unstable, it is recommended to consult an oncologist and collect tumor markers.
Treatment
Treatment of polyps depends entirely on the morphological structure and oncological risks of the disease. A promising direction is radical removal - surgery.
Conservative
Drug therapy and physical therapy are prescribed if surgery is impossible, in early childhood. In children, polyps tend to disappear on their own after some time.
Recommended for local treatment:
- treatment with vitamin A (oil in capsules) several times a day;
- application of interferon solution (used for viral tumors: herpes, papillomas);
- treatment with Panavir (prevents the division of pathogenic cells and the growth of tumors).
Additionally, systemic stimulation of the immune system with vitamins and immunocorrectors is prescribed.
When a bacterial infection occurs, antibiotics and mouth rinses with antiseptics (Furadonin, Furacilin) are prescribed. Additionally, it is possible to prescribe physiotherapy: warming up, compresses, inhalations.
Traditional methods
Non-traditional treatment methods can complement drug therapy, but are not used if the tumor is unstable.
Popular means are:
- cauterization with celandine juice or Supercelandine preparation 2 times a day (necessarily pointwise, within healthy tissues);
- processing with potato juice (juice is squeezed out of fresh potatoes and the mouth is rinsed);
- tincture of potato sprouts (150 g of young sprouts are poured into a bottle of vodka and infused for 14 days, the remedy is effective against pain and polyp growth).
If surgery is not possible, conservative methods of therapy are possible. You shouldn't expect good results right away. Improvements may only appear after a month.
Surgical
Removal of polyps on the tongue is the only adequate measure in the treatment of neoplasms. Removal instantly solves the problem of growths and eliminates all symptoms. Recovery occurs quite quickly, thanks to the active regeneration of the mucous epithelium.
The main methods of surgery are:
- Polypectomy . The polyp is removed with a metal loop, and the wound surface is coagulated using a laser or electric current. The polypectomy loop is placed over the growth and tightened until complete excision is achieved. If there is no protrusion for gripping, an artificial leg is created. Suitable for single small polyps.
- Scalpel method . It involves excision of the tumor with a sharp scalpel within the healthy membranes. The wound surface is cauterized, and if the area is larger, it is sutured.
- Cryodestruction . Cauterization of the growth with a nitrogenous compound, which freezes the tumor and leads to subsequent self-amputation. The only drawback is possible damage to neighboring healthy tissues.
- Cavity method . A serious amount of surgical intervention, when prompt access to the site of the polyp is carried out through incisions on the outer surface of the neck and face. At the same time, the destruction of osteochondral structures and the condition of the mucous membranes around the tumor are assessed. The method is used when the polypous lesion needs to be removed along with the periosteum. Rehabilitation is long, the patient requires an inpatient stay.
Each method requires mandatory anesthesia. For small surgical procedures, local anesthesia is required (Lidocaine, Novocaine, Ultracaine); for the abdominal and scalpel methods, general anesthesia is indicated. To achieve high therapeutic results, several methods are combined with each other.
Recommendations after removal
After removal of polyps on the tongue, it is important to follow all medical recommendations.
In the early postoperative period it is recommended:
- semi-liquid and liquid food;
- plenty of warm drinks (can be done through a straw);
- antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity (chamomile decoction, Furacilin, Chlorhexidine).
Intensive rinsing of the mouth is not recommended due to injury to the wound surface. It is enough to take liquid into your mouth, hold it for a few seconds and spit.
Brush your teeth without toothpaste or simply clean them with cotton pads. You cannot kiss or visit hot saunas or baths.
In the long term, it is recommended to visit the dentist at least 2 times a year to monitor the condition of the wound. If atypical cells are detected based on histology results, it is important to be examined by oncologists.
A woman's breasts require special care and attention. A change in the appearance of the nipple or the color of the areola may indicate that a milk duct papilloma has formed. The disease requires adequate comprehensive treatment to avoid the development of complications. Find out how to remove papillomas on the face at home here. But do not forget that before using any means it is necessary to determine the type of papilloma.
Recommendations after treatment
Just getting rid of the growths will not be enough for a complete recovery - after intensive use of drugs and/or surgical intervention, preventive measures become necessary. To prevent further occurrence of tumors, you need:
- For the first days after surgery, eat semi-liquid or liquid food so as not to injure the wounded surface by chewing;
- Drink plenty of clean, warm water (using a straw will make the process painless);
- Treat the oral mucosa with antiseptic agents (sold in pharmacies);
- Avoid using toothpaste that irritates the mucous membrane for the first 2-3 days (it is recommended to clean the enamel with a cotton pad).
After treatment of polyps in the tongue, a visit to the dentist is required twice a year to monitor the condition of the oral cavity, prevent relapse or degeneration of the pathology into a malignant tumor.