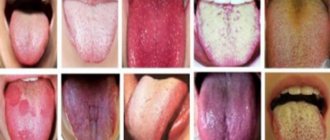
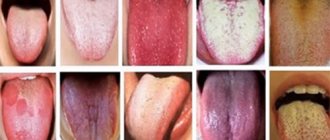
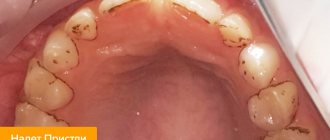
Natural color of the tongue in a healthy child
There are many cases when light-colored accumulations on the uvula do not require treatment. For example, during the examination in the morning, the mother may notice light deposits in a small amount. They are easy to clean off and are considered normal. At 1 year of age, such plaque is also diagnosed. These are often milk traces from mother's milk or its substitutes. Therefore, a thin light film is quite acceptable. But the natural shade of the surface of the tongue should be visible through it.
In healthy children, the color of the muscle organ is pale pink. At the same time, it must be mobile, all movements must be made unhindered and without difficulty. The condition of a child's tongue is significantly affected by humidity levels, as well as the temperature in the room where the baby is. For self-diagnosis, the mother needs to conduct visual examinations of her child’s oral cavity. Cleaning the baby's mouth is also necessary. First, this is done using special pharmaceutical wipes, and when the child grows up, a children's brush with a surface for treating the tongue is used.
Treatment of candidiasis
The main method of treating the disease is the use of local antifungal and antibacterial agents, as well as antibiotics. Antimycotic (antifungal) drugs can not only eliminate the symptoms of the disease, but also destroy the fungus in the oral cavity, as well as in other organs and tissues. For this purpose, antibiotics of the polyene series (levorin, nystatin, etc.), as well as clotrimazole, econazole and other imidazoles, are used. Fluconazole, Diflucan, and Nizoral also have a pronounced antifungal effect.
A significant part of antibiotics has a number of side effects and has a negative impact on the immune system. Therefore, when treating children, antibiotics are used only in the most severe cases, as well as in cases where there is a risk of complications and generalization of the process. At the initial stages of the disease and with a mild course of the disease, preference is given to local remedies. We recommend using ASEPTA series rinses, which contain chlorhexidine and other active ingredients that have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects. To remove plaque, you can use special ASEPTA Baby wipes. The individually packaged finger wipe is made of hypoallergenic materials and allows you to carefully clean the mucous membranes without the risk of damaging them or causing additional infection. It is also recommended to regularly treat the oral cavity with Lugol or silver solution. This procedure must be repeated every three hours.
For the prevention and treatment of candidiasis in children, diet and oral hygiene are also of great importance. It is recommended to exclude or strictly limit the amount of food containing simple carbohydrates - these are, first of all, confectionery and flour products. Make sure your child brushes his teeth regularly - it is best to use a special toothpaste for this, for example - ASEPTA Baby, Kids, Teens. The components contained in these pastes help prevent caries and, as a result, reduce the infectious load on the child’s immunity.
Causes of plaque
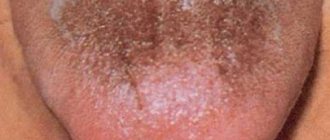
Factors that provoke the appearance of light masses can also be diseases. The reasons for the appearance of a white coating on a child’s tongue often arise due to disturbances in the functioning of the body. It is very difficult, almost impossible, to remove such dense layers.
- The surface of the muscular organ suffers when hygienic manipulations of the oral cavity are violated;
- A light film covers the mucous membranes when taking certain types of medications;
- Excessive development and active reproduction of pathogenic microflora has a detrimental effect on the health of the oral cavity, so there may be a white coating on the tongue of a newborn;
And this is only a small part of those aspects that have a bad effect on the health of the mucous membranes. If symptoms of plaque appear, a small child should be shown to a local pediatrician. This is the only way to accurately determine the factors that provoked the appearance of deposits. By the way, a child may not only have a dry and burning mouth, but also a high body temperature. Often a plaque with red spots is diagnosed, which in medicine is called geographic tongue. In any case, self-medication is prohibited. Contact your pediatrician, he will competently develop a therapeutic program.
Inflammatory processes
Often a baby will develop a white coating on the tongue due to stomatitis. The symptoms of the disease are very unpleasant. The disease is characterized by deposits that have a heterogeneous structure. Whitish grains are clearly visible on the muscle organ. If you try to eliminate them, blood is released. The baby is irritable and suffers from burning and pain in the mouth, as there are ulcers on the surface of the tongue.
At 3 years of age and earlier, as a rule, stomatitis of candidal origin. Light layers are present on the cheeks, gums, and even on the lips. The pain intensifies when eating sour-tasting foods. A visit to a medical facility is mandatory. Therapy consists of anti-inflammatory and painkillers that are used to treat the affected areas.
Fungal diseases
If the treatment of baby teeth is not carried out in a timely manner, this leads to the active proliferation of pathogenic microflora, including fungi. A white film on the lips and tongue often indicates that the baby has thrush (another name for candidiasis). In babies:
- the oral mucosa turns red;
- dryness appears;
- discomfort;
The younger the children, the worse they tolerate the disease. A one-year-old child becomes very capricious, he refuses to eat. Removing the film causes bleeding. The mucous membranes become covered with plaques and papules. To alleviate the condition, remove severe burning and itching, make an appointment with a pediatrician.
Caries
With caries, a dense white mass can form on the muscular organ and in the oral cavity. It doesn’t matter whether the child is 10 years old or a baby with baby teeth. This is due to the fact that the disease in its advanced form is a source of infection. Pathogenic bacteria thrive in the whitish mass on the tongue. They actively reproduce and aggravate the situation.
At 2 years old, when the baby has unstable teeth, parents should also monitor the oral cavity and prevent carious lesions on the units. Preventing the disease is possible. It is necessary to observe the rules of oral hygiene, and regularly. This is the only way that unwanted microorganisms will not settle on the mucous tissues of the tongue and a film will not form from the products of their vital activity.
Pathologies of the respiratory systems
If the tongue is covered with a white coating, this may indicate problems in the airways. Can be diagnosed:
- Viral form of the disease;
- Diseases of a bacterial nature;
With the flu or acute respiratory infections, the temperature rises, the throat turns red, a cough appears, and the tongue becomes covered with a whitish film. A sign of pharyngitis and tonsillitis is the covering of not only the tongue, but also the tonsils with white masses. Clumps on the tip of the tongue indicate bronchitis. Deposits with a foamy consistency indicate chronic bronchitis.
Infectious diseases
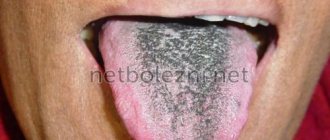
When an infection enters the body, the body defends itself by raising body temperature. In this case, whitish masses of dense and thick consistency often form on the muscular organ. With scarlet fever, reddish islands are visible on the white tongue. The tonsils and the root of the tongue are covered with a particularly thick coating. Severe intoxication is detected in the child’s body.
Diphtheria affects different areas of the oral cavity. It is not uncommon for a child to develop gum inflammation. There are dots with a white tint on the tonsils, and light grayish deposits on the tongue. Remember that the formation of pus requires an immediate trip to the doctor.
Gastrointestinal diseases
When bottle-fed, formula often leaves a slight residue, which is not dangerous for the baby. But it happens that quite serious diseases develop from such food:
- The film in the central zone of the muscular organ and the formation of cracks and grooves indicate gastritis.
- A one-month-old baby is more susceptible to dysbiosis than others, since his digestive system has not yet been adjusted. In such a situation, the tongue is completely covered with whitish masses.
- At the age of 7, when hormonal changes begin and baby teeth are replaced by permanent ones, children are susceptible to enterocolitis. Inflammation in the intestines leads to deposits on the back of the tongue.
Prevention
In order to prevent the appearance of plaque on a child’s tongue, there are a number of preventive measures that many experts emphasize (for example, Ukrainian pediatrician Komarovsky):
- The room in which the child lives should always be clean, well ventilated and humidified.
- You should not prescribe antibiotics to your child yourself. The use of such medications must be strictly justified.
- It is necessary to closely monitor the baby's health. If the slightest symptoms appear that indicate a possible disease from the internal organs, you should urgently seek medical help.
- Limit your child's consumption of sweets containing synthetic coloring pigments: sweet carbonated drinks, candies, chewing gum. This will not only prevent the appearance of active staining of the tongue, but will also preserve the health of delicate children's teeth.
If plaque does appear on the tongue, there is no need to try to remove or treat it yourself. Consult your doctor about the possible causes of this phenomenon and the necessary treatment for it.
Treatment of white plaque on a child’s tongue
Before starting treatment, you need to show the child to the pediatrician. Depending on the clinical picture, especially if there is bad breath, he may refer you to a gastroenterologist, dentist, internist, dermatologist, infectious disease specialist or toxicologist. In order to treat correctly, a diagnosis is made, and then a therapeutic program is developed.
- Most often, at 2 months and up to a year, children suffer from thrush. To combat this disease, antifungal drugs are prescribed, which are used to treat pathological areas.
- In one-year-old children and 2-year-olds, infections and viruses are a common problem. In such a situation, antibiotics and immunoglobulins are usually prescribed. For herpes stomatitis, the dentist prescribes solutions with an analgesic and wound-healing effect.
- Preschoolers and school-age children are most often diagnosed with aphthous and allergic stomatitis. The range of medications for older children is wider than for infants. Antiseptic therapy is carried out.
Parents must remember that only timely treatment and strict adherence to the doctor’s instructions will eliminate the problem and prevent the development of serious complications.
How and why does infection occur?
Infection occurs by airborne droplets, from a sick person, by using shared utensils and eating contaminated food, as well as by a number of other factors:
- weakened immunity;
- hypothermia or consumption of cold foods and drinks;
- mouth breathing (for chronic adenoiditis, deviated nasal septum);
- irritation of the nasopharyngeal mucosa with a runny nose;
- recent viral diseases;
- inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs (sinusitis, sinusitis, otitis);
- caries and other oral infections.
Secondary tonsillitis in children can occur against the background of scarlet fever, diphtheria, mononucleosis, as well as blood diseases.
In any case, a sore throat develops rapidly, in a matter of hours, and is especially acute in children, accompanied by the main symptoms—a sore throat when swallowing and an increase in body temperature.
Diagnostics
If a baby has a white spot in the mouth, to make an accurate diagnosis, a number of tests are prescribed, as well as certain procedures. Usually the doctor immediately notices the problem when examining the surface of the mucous membrane. In addition, the following may be additionally prescribed:
- Scrapings or smears from the cheesy film;
- Collecting anamnesis during a conversation with parents;
- Clinical blood test;
Purpose of the study: detection and confirmation of Candida fungi. If necessary, the mother must additionally show the child to specialized doctors. This will help identify the inflammatory processes that occur in the internal organs, which will help prevent serious complications. An oral smear plays an important role in making a correct diagnosis. After drying the applied scraping onto medical glass, staining and examination under a microscope are carried out. Identification of fungal colonies allows the doctor to select the desired therapeutic regimen, taking into account the characteristics of the body and the age of the patient.
Acute pancreatitis
The pain does not allow the patient to straighten up. Movement, coughing or even deep breathing sharply intensifies it. Only complete immobility in a bent state and shallow, rapid breathing, especially during an attack, can alleviate the patient’s suffering. With a progressive course, the child’s general condition quickly deteriorates:
- the temperature begins to rise;
- pulse quickens;
- shortness of breath appears;
- blood pressure decreases;
- sticky sweat appears;
- the tongue becomes dry with a heavy coating;
- the skin turns pale and acquires an earthy-gray color;
- facial features become sharper;
- on examination the abdomen is distended;
- frequent vomiting without relief
- dry mouth;
- nausea;
- bloating;
- gases
- sometimes hiccups and belching.
Treatment of acute pancreatitis is carried out only in the surgical department of the hospital (or in the intensive care unit)!
During an attack of acute pancreatitis, it is strictly forbidden to drink or eat. No water, no food! Complete rest for the pancreas!
It is better to breathe frequently and shallowly, so as not to compress the pancreas with the diaphragm and cause new attacks. Frequent shallow breathing, especially during an attack, alleviates the patient's suffering.
An attack of pancreatitis may be short-lived and imaginary relief occurs; in any case, immediately call an ambulance and do not refuse hospitalization.
Chronic pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis is a long-term (more than 6 months), slowly progressive disorder of the pancreas, accompanied by a lack of pancreatic juice secretion necessary for digesting food.
Chronic pancreatitis develops either after an attack of acute pancreatitis (in 50-70% of cases), or is primary and develops gradually and slowly (in 30-40% of cases). Periods of exacerbations are followed by remissions.
The most common reasons are:
- diseases of the gallbladder and biliary tract;
- taking medications;
- hereditary factors;
- as well as all of the above causes of acute pancreatitis.
Over time, chronic pancreatitis leads to gross deformation of the organ due to the replacement of gland tissue with scars. Diabetes mellitus may develop in 1/3 of patients.
Let's sum it up
Modern doctors, just like their ancient predecessors, rightly consider the condition of the tongue to be one of the criteria for human health. When examining the tongue, its mobility, density, color, moisture, presence or absence of plaque and other factors are assessed. A white coating found on a child’s tongue can be a “signal” of the onset of a disease, even in cases where other symptoms have not yet manifested themselves. In this case, the coating can cover both the entire surface of the tongue and its individual sections, be dense or loose, and be easily or difficultly removed from the surface of the tongue.
Diet for pancreatitis in children
With pancreatitis, the child must follow a diet.
The following foods and drinks are excluded2:
- fresh bread and pastries;
- sparkling water;
- fatty dairy products;
- smoked meats, seasonings and spices;
- store-bought juices;
- fat meat;
- cabbage;
- lemons;
- credit;
- legumes;
- coffee.
Slimy porridges prepared with vegetable decoctions are useful. You can use meat broths made from poultry (skinless chicken), veal, rabbit, which are previously steamed or boiled. During an exacerbation, food should be pureed and free of lumps and rough pieces that can injure the mucous membrane of the digestive tract.
Which doctor should I contact?
The first specialist you need to contact after identifying a tongue coated with a white coating is a pediatrician. After carefully examining the child’s oral cavity, the doctor will assess the condition of the teeth and gums and check the lymph nodes. After this, he will make a diagnosis and prescribe effective medications to eliminate the underlying disease.
If it was not possible to determine the cause of the formation of layers during the examination, the pediatrician will give a referral to an infectious disease specialist, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist or other specialized specialists. In some cases, doctors prescribe a bacterial culture from the surface of the tongue and a general blood and urine test. Based on the results of laboratory tests and examination, the small patient will be prescribed suitable treatment.
What should parents do?
In cases where a white coating appears on a child’s tongue only in the morning or after eating dairy food, is easily removed and does not return during the day, this should not cause concern to parents. For infants and children under one year of age, plaque from the tongue can be removed with a finger wrapped in a piece of clean gauze or bandage. Finger movements must be careful. For older children, plaque is removed from the tongue using a soft toothbrush. It is safe for children of any age to treat the oral cavity with a soda solution.
For a child over 3 years old, the solution is used as a rinse; for younger children, the tongue is wiped with a gauze swab dipped in a soda solution. If the white coating is difficult to clean off from the surface of the tongue, does not disappear within several days, or is accompanied by a burning sensation and painful sensations, parents should show the child to the doctors. These may be specialists such as a dentist, pediatrician, gastroenterologist. Only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment for a child.
Useful video
From this video you will learn how to treat oral thrush in children:
To understand whether plaque on the surface of the tongue of a preschooler or a child of primary school age is normal, you need to take into account not only the color of the deposits, but also their location, density, and structure.
It is important for parents to remember that pronounced symptomatic manifestations that persist for several days require contacting a medical institution for qualified help.
You cannot ignore the symptoms, because this can lead to extremely negative consequences.
Associated symptoms
In addition to a white coating on the surface of the tongue, when pathology develops, a child may develop other symptoms that can cause him a lot of inconvenience.
Reference! The following symptoms indicate the need to visit a pediatrician as soon as possible:
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- bad breath;
- fatigue, drowsiness;
- general weakness;
- heartburn or belching;
- nausea;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- excessive sweating;
- pale skin;
- muscle pain;
- redness of the tongue;
- increased body temperature;
- skin rashes;
- a sore throat;
- dry skin and mucous membranes;
- formation of ulcers or wounds in the mouth;
- constant thirst;
- irregular urination;
- change in urine color;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- headache;
- lack of appetite;
- redness of the oral mucosa;
- dark circles in the eye area;
- short sleep;
- passive state.