Removing temporary teeth in a child has its own characteristics. They are related to the nature of their structure and available indications. This is an extreme measure, as their premature loss has a negative impact on the health of your smile. Baby teeth fall out on their own, and permanent teeth appear in their place - this is a natural process. However, sometimes situations arise when you need to extract them in advance, that is, delete them. For advice on the advisability of such a procedure, you can contact our pediatric dentistry in Maryina Roshcha.
Features of tooth extraction in children
Pediatric dentistry is focused on the treatment and prevention of oral diseases. In this case, psychological support for the baby is important. Specialists must act delicately, instilling trust and relieving the child of fears. This is especially important in case of forced tooth extraction. Therefore, there are several unspoken rules of the pediatric dentist.
- Do not use the word “pain” or the particle “not.” Children do not accept denial and react sharply to unpleasant phrases.
- Do not discuss the details of the procedure in the office. Medical terms and unfamiliar words frighten the baby.
- Try to hide dental instruments from the eyes of the small patient. Forceps, packages of syringes and drill attachments can drive even the most courageous tomboy into hysterics.
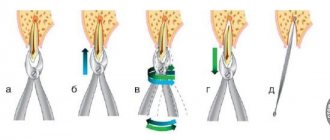
This procedure requires high professionalism and great care from the doctor. With one careless movement, he can damage the germ of a new tooth and the tissue of the socket, which will cause a delay in eruption and various dentofacial deviations.
How to remove a tooth without damaging the child’s psyche?
How to extract a baby tooth from a struggling and crying baby is a very pressing problem. Much depends on the professionalism of the doctor and the attitude of the parents. A good specialist will remove the tooth quickly and painlessly. The task of parents is not to be afraid themselves and not to groom their child with oohs and aahs. The child, seeing your fuss, will instantly decide that something terrible is about to happen. Try to give him examples of other, more flexible children, or play on the desire to be bolder than the rest of his peers. And, of course, your presence in the dental office with your child is simply necessary.
Baby teeth play an important role in the formation of permanent occlusion; the health of molars depends on them. Therefore, removing them prematurely can only be done as a last resort. Only parents are able to protect their child from such troubles by regularly attending preventive examinations and monitoring the child’s compliance with the rules of oral hygiene.
General indications for tooth extraction in children
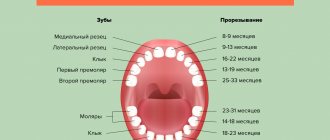
The child’s dentition is formed according to certain patterns: the incisors erupt first, followed by the molars. Then the baby teeth are gradually replaced by permanent teeth. If this process occurs correctly, without deviations from the norm, there is no need to specifically remove baby teeth. However, there are situations when this is necessary:
- advanced caries;
- the last stage of development of a cyst on the gum;
- severe tooth injury;
- a tooth that fails to develop and erupt.
Removing a child’s front tooth is a particularly unpleasant procedure, as the aesthetics of the smile suffers. Usually, surgery is resorted to in the following circumstances:
- exposure of the pulp due to a fracture of the coronal part;
- severe tooth decay with the impossibility of prosthetics;
- inflammatory diseases that cannot be treated.
Most often, children have to part with their teeth in the chewing area. Molars are more susceptible to destruction than premolars and incisors. Removing a child's molars, which are the last in the dentition, is complicated by their inaccessibility and strength: they fit quite tightly to the gums, have wide roots and massive walls.
Sometimes children develop an anomaly such as an extra tooth, which can move the “neighbors” and lead to curvature of the entire row. If it does not interfere with the normal formation of the remaining teeth, you can leave it and try to integrate it into the bite, but most often they resort to removing the supernumerary tooth in the child.
The factors described above are the general and most common indications. Let us consider separately the reasons for the removal of baby and permanent teeth.
Is it necessary to treat minor caries in baby teeth?
So, we found out that the consequence of premature tooth extraction can be a disruption in the physical and emotional development of the child. But it is important to understand that even if you notice small caries on your baby’s teeth, you should consult a dentist. An untreated baby tooth can cause problems such as:
- Defective rudiment of molars. A diseased milk tooth can infect with caries the germ of the permanent tooth being formed underneath it. If the rudiment is damaged, there is a high risk of developing a defective tooth or its absence.
- Gastrointestinal diseases. It is teeth affected by caries that cause many somatic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Gastritis, duodenitis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, pancreatitis, dyspepsia, pancreatitis and other unpleasant diseases often develop against the background of damaged teeth.
- Development of diseases of the ears, nose and throat. Few parents know that caries provokes chronic runny nose, tonsillitis, sinusitis, inflammation of the tonsils and other respiratory diseases.
- Bad breath. Many parents wonder why their child has bad breath. The cause of the smell, as a rule, is precisely caries, invisible to the inexperienced eye. The baby begins to develop complexes and problems with communication appear.
- Pulpitis. Untreated caries will eventually transform into pulpitis, which means the child will suffer from pain and insomnia and will have to undergo painful treatment from a doctor.
Removal of baby teeth in children
Milk teeth maintain the gum contour and ensure proper development of the jaw and chewing muscles. Therefore, it is important to wait until they fall out on their own. Unfortunately, this does not always happen, and the dentist is forced to prescribe surgery if there are the following indications for the removal of baby teeth in children:
- the tooth is loose, but has not fallen out for a long time;
- the temporary tooth caused inflammation of the oral tissues;
- The permanent tooth has begun to emerge;
- a fistula has formed on the gum;
- a cyst appeared on the root;
- The tooth has decayed due to caries.
Removal of a child's front milk tooth may be associated with fractures, chips and other injuries, as well as inflammatory processes.
How does baby teeth fall out?
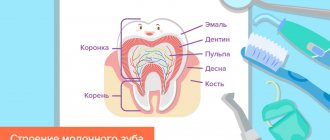
The replacement of baby teeth with permanent ones is a physiological process. By the age of 3, a child grows 20 milk teeth in his mouth, which differ in structure from permanent teeth. They have thinner enamel and walls, and more branched roots. Then, gradually, the roots of baby teeth begin to dissolve. At the age of 5-6 years, baby teeth begin to loosen and fall out in the order in which they appeared, and in their place permanent teeth grow from the rudiments. The period of formation of a permanent dentition lasts up to 13-14 years and the appearance of 7 teeth - the second molars - ends. Healthy baby teeth and natural, timely replacement of teeth guarantee the child healthy teeth in his permanent dentition. Therefore, it is best if baby teeth fall out on their own and do not require additional doctor intervention, but this does not always happen.
Removal of permanent teeth
Removal of a permanent tooth in a child is carried out only in the following situations:
- Caries.
If the doctor sees that a decayed tooth cannot be treated, most likely he will suggest removing it. - Fracture.
A tooth fragment can injure the mucous membrane; it can either be restored or removed. - Crowding.
When installing braces or plates, it is sometimes necessary to remove one tooth to allow others to develop freely. - Complications after treatment.
Sometimes, after poor-quality dental procedures, problems arise that can only be solved by getting rid of the tooth.
Anesthesia
When a child needs to have a tooth removed, the question of anesthesia always arises. In most cases, when a loose tooth whose root has almost completely resolved is to be extracted, no special anesthesia is required. A friendly attitude from the doctor and a positive attitude from the parents are enough.
If a more complex procedure of tooth extraction or nerve removal is required, then the best option for pain relief is local anesthesia in a dosage calculated for each child individually. The latest generation of drugs are used for this, which rarely cause allergic reactions and eliminate pain as much as possible. But, despite all the advantages of such drugs, a mandatory step before pain relief is to conduct a test for a possible allergic reaction. Only in the case of a negative test can the drug be considered safe.
In exceptional cases, when the child’s reaction to a visit to the dentist’s office is extremely negative or there is a need to treat a child under one and a half years of age who is not yet fully accessible to contact, then removal under anesthesia is possible. For this purpose, drugs administered intravenously are used. This procedure is available only in large dental centers that have a pediatric anesthesiologist on staff and have received a special license to perform it.
Wisdom tooth removal
Typically, wisdom teeth appear at the age of 20 or older, but in some cases it is recommended to remove their buds. There are the following reasons for the removal of wisdom teeth in children:
- displacement of the follicle of the third molar;
- prerequisites for malocclusion;
- lack of space for wisdom teeth.
A specialist can recommend removal of a child’s wisdom teeth only after a thorough examination and consultation with other specialized doctors. You must first determine what position the molar is in and what place it will later occupy in the jaw.
Anesthesia for tooth extraction
In modern clinics, various types of anesthesia are used to remove teeth for children without pain. The specialist selects the appropriate drug in accordance with the severity of the clinical picture. During the operation, one of the following methods of pain relief is used:
- Sedation is putting you into a sleepy state to reduce anxiety.
- Application anesthesia - treatment of the gums with an anesthetic solution to remove a loose tooth or before injection.
- Local anesthesia is the administration of an anesthetic through an injection.
- Anesthesia is used in difficult cases and when removing teeth for a child under 2 years old.
Removal without pain
In pediatric dentistry, it is very important to ensure the child’s comfort during the tooth extraction procedure. This applies to all stages of treatment. To prevent the baby from being afraid, double anesthesia is used:
- Anesthetic gel. It is necessary to reduce the sensitivity of the gums and prepare for further anesthesia.
- Injection anesthesia. After the gel begins to take effect, the nurse will inject an anesthetic into the gum. Thanks to the action of the gel, the child does not feel pain from the injection.
Many drugs for local anesthesia, which are used to anesthetize tooth extraction, are strong allergens. In order to exclude the possibility of an allergy, the child is given a skin test.
Care after tooth extraction
What frightens the parents more than the removal procedure is the condition of the baby after the operation, since they have already left the specialist’s office and are left with the problem alone. In this situation, all mothers and fathers have almost the same questions.
What to do after a child’s tooth extraction?
The doctor will give the little patient a cotton pad or gauze pad that needs to be placed in the empty hole to stop the bleeding. Removing a baby tooth does not cause excessive blood flow, so after half an hour you can safely remove the cotton wool, but removing a permanent tooth is accompanied by severe bleeding.
The appearance of a blood clot means that the healing process is going well, as it protects the bone from air and prevents inflammation.
What medications should I take?
If the dentist prescribes an antibiotic after a child’s tooth extraction, follow the recommendations and do not give the child other medications so as not to provoke complications.
How to rinse your child's mouth after tooth extraction?
For three days after surgery, rinsing your mouth is strictly prohibited, so as not to dislodge the blood clot and cause an infection. Three days after tooth extraction, the child can rinse the mouth using any means - strengthening tinctures of tree bark, soothing herbal decoctions or medicinal solutions.
How much can you eat after a child’s tooth extraction?
For the first few days, you should refrain from hot dishes and fermented milk products, eating only soft and liquid foods. It is best to chew on the side opposite the extracted tooth.
Contraindications
It is not recommended to remove a child’s baby teeth in the following cases:
- Severe chronic conditions (heart defects, epilepsy, etc.).
- Inflammation in the oral cavity (stomatitis, gingivitis).
- Problems with blood clotting.
- Infectious diseases in the acute phase (ARVI, influenza, scarlet fever, chickenpox, etc.).
If there are contraindications, tooth extraction can be dangerous. But not all contraindications are absolute. For example, if the baby has an inflammatory process or an infectious disease, the tooth can be removed after treatment. The final decision about the procedure will be made by the dentist.
Complications after surgery
Do not give in to panic and call the ambulance service at the slightest ailment of the baby. Some consequences of tooth extraction do not harm children's health in any way. The following symptoms are considered normal:
- The child’s gums ache after tooth extraction - apply ice, this will reduce the discomfort.
- After tooth extraction, the child has swelling - after the third day it will begin to subside; ice also helps eliminate the discomfort.
- A swollen cheek after tooth extraction in a child indicates a slight inflammatory process, which will go away on its own after some time.
- Light bleeding in a child after tooth extraction should also not cause concern; even the next day the saliva may be slightly reddish.
- A low temperature after tooth extraction in a child is the result of the child’s worries and nervous overstrain; when he calms down, the temperature will drop.
What role do baby teeth play?
It was not by chance that nature provided for the replacement of temporary teeth with molars. Baby teeth help the baby switch to a regular adult diet, stimulate the development of jaw bone tissue and create favorable conditions for the teething of a permanent set. If there had not been such a change, then the molars simply would not fit on a small child’s jaw and would not be able to fully perform their immediate functions.
Flux, fever and diarrhea after tooth extraction
More serious negative consequences when removing a baby tooth in children can only arise as a result of poor quality work by the doctor or due to infection. If the following signs are detected, parents must immediately contact a specialist.
- Flux after tooth extraction in a child, preventing swallowing, breathing and muscle movement.
- Prolonged bleeding.
- Severe and prolonged pain in the gums that does not go away even after taking painkillers.
- After tooth extraction, the child’s temperature rose above 38 degrees.
- Abdominal pain, vomiting and diarrhea after tooth extraction in a child.
What to do if a child has a baby tooth removed early?
If trouble happens and the child has one or more milk teeth removed ahead of schedule, it is necessary to take measures to restore the dentition and preserve the space after the extracted teeth.
For this purpose, special dentures are used - removable plates with artificial teeth or special orthodontic structures are installed. In any case, after early removal, you must take the child for a consultation with an orthodontist - he will suggest the right solution. For more information about the treatment of malocclusion problems in children, read: “Children’s orthodontics - correcting the bite in children.”
How much does tooth extraction cost?
Many people believe that the cost of the procedure for adults is much higher than for children, and the price for removing a baby tooth in children is lower than for extracting a permanent tooth. This is not entirely true. The amount of payment for the pediatric dentist depends on the complexity of the case, and the cost of removing temporary and permanent teeth is determined by the indications and concomitant diseases. In the table below, we have listed the main problems with which people turn to a pediatric dentist and the prices for tooth extraction for children.
| Service | Price |
Consultation | from 500 rubles |
Removing a baby tooth | from 1,100 rubles |
Removal of a permanent single-root tooth | from 1,200 rubles |
Removal of a permanent multi-rooted tooth | from 3,000 rubles |
Complex tooth extraction | from 4,000 rubles |
Wisdom tooth removal | from 3,000 rubles |
Removal of a supernumerary tooth | from 1,200 rubles |
Application anesthesia | from 250 rubles |
Local anesthesia | from 500 rubles |
Sedation | from 1,500 rubles |
General anesthesia for 30 minutes | from 4,000 rubles |
General anesthesia for 60 minutes | from 10,000 rubles |
General anesthesia for more than an hour | from 12,000 rubles |
Application of anesthesia
If the tooth is very loose, then most likely you will not need pain relief, but the doctor may suggest topical anesthesia (spray or gel), as well as infiltration anesthesia (an injection with an anesthetic drug).
General anesthesia can be used:
- for children 1-4 years old;
- children with mental illness;
- with organic brain damage;
- if you are intolerant or allergic to local painkillers.
Baby teeth are very important for the formation of the bite, as well as the health of permanent teeth, so only a pediatric dentist at a dental clinic should decide on their premature removal.
How to prepare a child for tooth extraction
If tooth extraction is unavoidable, try your best to minimize the child’s stress. For example, tell him a fairy tale about how one tooth began to behave badly and interfere with the others, so it needs to be “pulled out.” Before going to the clinic, you can also discuss some pleasant event with your child, be it going to the movies, the circus, or buying a toy, which you will do immediately after removing a capricious tooth. The main thing is not to panic, and then the confident and calm attitude of the parents will certainly give the child the strength to courageously endure this frightening but necessary procedure.
You can avoid tooth extraction surgery in children if you carefully monitor the condition of the oral cavity throughout the entire period of dentition formation, monitor the quality of hygienic procedures and regularly take children to preventive appointments with the dentist.
Treatment at the SHiFA clinic
The Shifa clinic employs experienced pediatric dentists, who in their activities are guided by the principle “noli nocere” - do no harm!
Sparing no time and effort, specialists fight for every tooth, trying to extend its service life. They convince parents and children of the need to preserve the integrity of the dentition. The skill and painstaking work of professionals brings excellent results - painless and high-quality treatment of primary occlusion becomes a guarantee of the harmonious development of the maxillofacial area.