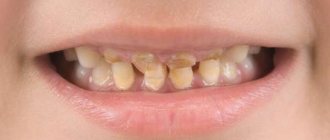
No teeth at one year of age
Why does a child’s teeth not grow after a year of life?
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Unsuitable climate.
- Poor quality of food and water.
- Diseases and infections.
- Vitamin and calcium deficiency.
To dispel or confirm suspicions, you need to take your baby for examination to a therapist and dentist. To determine the causes of delayed jaw development, blood tests, urine tests, ultrasound examinations of organs, and testing of thyroid function may be necessary. To exclude edentia (lack of teeth) from the diagnostic field, fluoroscopy is performed.
Why a one-year-old child has no teeth: reasons
Vitamin D and calcium have virtually no effect on the timing of the appearance of the first teeth. These factors have a greater impact on the quality of teeth and enamel. The reasons why a baby has no teeth at one year can be:
- genetic factors, if the parents had late teeth, then their baby is also likely to have the same problem
- oddly enough, even climatic conditions can influence this process; in a warm climate zone, children’s teeth grow better
- a lot depends on the quality of water, nutrition
- Severe infectious diseases negatively affect the rate of tooth growth
- lack of vitamins and calcium can slow down this effect
If at the age of one and a half years the baby does not have a single tooth, then he needs to undergo a comprehensive examination. Sometimes teeth do not grow due to pathology - adentia .
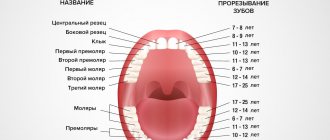
How many teeth should a child have before 1 year of age?
Initial signs of teething, as a rule, appear at six months of age: active salivation, inflammation of the gums, refusal to eat. During this period, the lower incisors begin to break through, which is accompanied by swelling, diathesis, tearfulness, drowsiness, runny nose, cough, fever and even vomiting, diarrhea or constipation. Symptoms disappear 3-7 days after the exacerbation.
Eight- and nine-month-old babies grow up to six teeth. As a rule, the lower incisors are already fully formed, and the upper ones are just beginning to develop. The child learns to chew and bite food independently.
At 10-11 months, as a rule, the incisors of both rows are already formed in the mouth, and adjacent teeth are also breaking through. At this time, after eating food, it is recommended to give the baby water. To avoid caries, you should not accustom him to sweets. Maintain hygiene and cleanliness of the pacifier and spoon from which you feed your baby. If a child’s lower front tooth does not grow at this age, there is no need to panic - experts define this situation as standard and not requiring intervention. To get rid of false suspicions, you can go for a medical examination. Our VTV clinic is always happy to help with any dental problem.
Work examples
(images are clickable)
What does it look like?
The implant surgeon together with the orthopedist, at a free consultation, decides whether this type of prosthetics is possible, namely: is the bone mass, its thickness, and the condition of the bone tissue sufficient. It is necessary to take into account how and why the patient lost all his teeth - the result of injury, age or a systemic disease of the body.
A surgical template is made individually for the patient, after which implantation can begin. After the specialists have examined the patient and studied his orthopantomogram, if the verdict is positive, the patient is sent to a computed tomography scan, which will allow all bone structures to be seen in great detail and anatomical measurements to be measured down to the micron. structures and make “markings” for planning the operation.
First stage
The first stage is the installation of eight implants on one jaw. This amount often raises questions from patients and disputes among doctors. But you can’t fool physics, and orthopedics is an area where the main processes are physical, and therefore eight implants are needed to withstand the necessary load of a full arc.
Second phase
The second stage begins after 3 months: a control image is taken - an orthopantomogram, assessing how the implants have healed. If successful, the surgeon places eight healing abutments. The patient walks with them for 2 weeks.
Third stage
Then the orthopedic dentist begins work.
At the first appointment, impressions are taken and the laboratory begins to manufacture a “new jaw”. The technicians’ task is not easy: using eight implant supports, attach an arch, usually consisting of fourteen teeth, to them.
The doctor’s task is to fix the structure so that the patient cannot (and does not want) to remove the bridge and put it in a cup.
The patient will have no less difficult work: getting used to the feeling of suddenly having a “mouthful of teeth” is not easy, but the result is worth it!
The entire journey will take 4 months.
How much does this kind of work cost?
- implantation - 24,000 x 8 = 192,000 rubles;
- production of a surgical template = 4000 rubles;
- control shot - 900 x 2 = 1800 rubles;
- installation of shapers 3000 x 8 = 24,000 rubles;
- crowns for implants - 13,000 x 8 = 104,000 rubles;
- metal-ceramic crowns 7500 x 6 = 45,000 rubles;
- total - 370,800 rubles (payment is made in stages over 4 months).
Scares
option for
370,800 rubles
? Perhaps you don't need it.
Two complete removable dentures
will also solve the problem of complete absence of teeth.
Price: 30,000 rubles. The duration of prosthetics is 2-3 weeks .
Savings compared to implantation - more than 90%!
4 times
faster In conclusion, I would like to remind you that keeping your teeth intact and beautiful is much easier and cheaper. Visit your dentist regularly for examinations, come for professional hygiene once every six months, and immediately go to the doctor if the first signs of the disease appear.
Be healthy!
Here are answers to frequently asked questions from our clients about dental prosthetics. If you have a question, send it to us using any method specified in Contacts.
- What is the price for prosthetics? For crowns? For removable dentures?
Prices for prosthetics vary depending on the complexity of the work and the material. Metal-ceramic crown - 9,000, the cheapest crown is metal - 6,000 rubles, the most expensive is zirconium (about 22,000 rubles). Removable dentures - from 17,000 rubles per denture.
- What are crowns made of? Who is the manufacturer?
The most popular crowns are metal-ceramic. They have an alloy base (CoCr, NiCr) and a ceramic coating. More expensive crowns: all-ceramic (without a metal base) and zirconium (zirconium dioxide base and ceramic lining). All crowns are made individually according to your impressions in a laboratory in Moscow. The material (ceramics) used for production is produced in the USA by Densplay.
- What is included in the price of a crown?
The cost of a crown includes taking impressions, making models, determining the bite, making a crown in the laboratory, fixation, and correction.
- What is the guarantee for crowns?
Warranty for fixed prostheses (crowns and bridges) 1 year. On average, a crown lasts about 10 years.
- How long will the crowns cost?
Metal-ceramic crowns usually last about 10 years, but we often see patients who have them for 15 or 20 years. In any case, it is important to understand that caring for both your teeth and crowns will significantly extend their service life.
- How long does prosthetics take?
The duration of prosthetics depends on the volume and complexity of the work. Everything is individual: from 7 days to a month.
- Which prosthesis is the best?
The best prosthesis is the one that suits you. Crowns, bridges, removable dentures, implant prosthetics... There are many types of prosthetics, as well as clinical cases when it is necessary. We recommend going to several clinics for a consultation to hear the opinions of different doctors.
The prices given in the text are indicative and may differ from actual prices. Current prices can be found in the “prices” section.
Photos of the dental offices of the clinic Our Dentist in Krasnogorsk
(images are clickable)
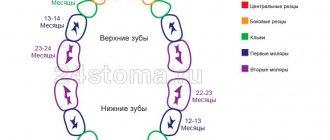
Over 1 year old
At one year of age, children, as a rule, already have eight full milk teeth in their mouths. This age limit is the optimal time to visit the dentist. The doctor will evaluate the condition of the oral cavity and help prevent problems.
At the age of 1.5-2 years, a child can have from 4 to 14 teeth. We must begin to accustom him to oral hygiene, showing him how cleaning is done by example. By the age of 2.5 years, children, as a rule, acquire two dozen milk teeth, which serve them until the age of 5-6 years. A visit to the dentist or orthodontist may be necessary if:
- premature development of the jaws, which is facilitated by endocrine dysfunction;
- growth retardation, often caused by rickets, digestive problems, infections and genetic inheritance;
- incorrect position of the incisors, indicating deeper bone disorders.
Until the age of six, the number of teeth remains the same - about 20. At this time, you need to continue to develop in the child a love of oral hygiene, wean him from finger sucking and nail biting.
The first replacement of baby teeth with molars begins at 6-8 years of age. By the age of 14-15, the jaws are completely renewed.
Absence of milk teeth – edentia. Second row of teeth. Do adults have baby teeth?
Very, very rarely, but such an anomaly of the dental system occurs as adentia, that is, the absence of milk teeth and even their rudiments. Adentia is determined no earlier than 12-15 months, using an X-ray examination using an X-ray machine, and only after examination by a qualified dentist.
Our clinic has a more modern device that allows us to adequately and efficiently examine the condition of the dental system from any angle, completely safe for children - a radiovisiograph.
Adentia can be primary - when the rudiments of baby teeth are completely absent, and there is a lack of teeth in the oral cavity due to their retention in the jaw - retention. All teeth may be missing (completely edentulous) or only some (partially edentulous). Absence of teeth is more often observed with permanent teeth - in adults, and much less often - with milk teeth.
The causes of edentia in children are most often health problems in the mother during pregnancy (genetic diseases, viral infections, poisoning, stress, etc.), smoking, treatment with strong drugs, which prevents the formation of tooth buds or their death at later stages. With edentia, the jaws also develop poorly, the face becomes asymmetrical, and the bite is distorted. During the period of primary occlusion, partial adentia is more common - the absence of individual teeth and the formation of large gaps between three existing teeth. Treatment at an early age is aimed at medicinal stimulation of teething and jaw development. At an older age, it is possible to make removable dentures that fill the dentition. Fixed dentures for children are unacceptable, and for those under 21 years old they are not recommended.
The child is growing a second row of teeth
The situation is completely opposite - the child is growing a second row of teeth. This pathology is rare in primary dentition and is quite common during the growth of permanent teeth. If a child has supernumerary teeth, they interfere with the development and growth of permanent teeth, move them to the side, or turn them around an axis, and therefore must be removed.
We are often asked whether all children’s teeth change, and whether adults still have baby teeth. In the natural course of events, all milk teeth should fall out, and in their place permanent teeth should grow, plus 12 molars for a complete adult set - 32 teeth. But sometimes there is a malfunction - and a baby tooth, and sometimes even a few, don’t fall out. The fact is that under the milk tooth the germ of a permanent tooth does not form or dies, which means that the root of the milk tooth does not dissolve and it does not fall out at the appointed time. The second reason may be that the germ is very deep or underdeveloped, and therefore it cannot push out the baby tooth. Milk teeth that have not been replaced by permanent ones are called residual or persistent. What to do about it? You should contact your dentist about this problem. If the loss of baby teeth in children was not complete, and by the age of 16-17 the child still has baby teeth, contact a specialist at the Utkinzub clinic. Only after a thorough examination will the doctor decide whether to leave the tooth if there is no permanent tooth germ underneath it, or remove it if there is a germ germ, with parallel stimulation of the growth of the permanent tooth.
It is more important to know the causes of this pathology. This may be heredity, injury or inflammatory diseases of the jaw bones, disruption of the hormonal system, in particular the thyroid gland. And one of the most common causes is inflammation in baby teeth that is not cured in time - pulpitis and periodontitis. The disease spreads to the germ of the permanent tooth and destroys it in the jaw. It is for this reason that we constantly draw the attention of parents to the need for careful care of baby teeth (“Care for baby teeth”) and timely treatment of caries and other diseases.
What to do to ensure that your child’s teeth develop normally
Before and during pregnancy:
- Maintain dental health.
- Eat well and varied.
- Eat more foods high in calcium.
- Do not smoke or drink alcohol.
- Walk in the fresh air more often to maintain a healthy level of hemoglobin in the blood.
- Treat in strict accordance with medical recommendations.
After childbirth:
- provide the child with a rich and balanced diet;
- monitor the baby’s hygiene;
- walk in the fresh air to harden the child’s body;
- prevent infection and diseases of internal organs;
- Consult a doctor in a timely manner in case of painful syndromes.
How to eliminate teething problems?
To ensure that your baby does not have any disorders, it is important to think about the future newborn even when planning a pregnancy. Therefore, prepare for this systematically.
- Treat your teeth in advance, eat right, take vitamins, and do not limit yourself in consuming foods rich in calcium.
- Get outside more often, make sure you have normal hemoglobin.
- Do not drink strong drinks or smoke under any circumstances.
- Do not self-medicate, do not take medications that your doctor has not prescribed to you.
After childbirth:
- Make sure your baby gets adequate nutrition
- strengthen your baby, take daily walks
- Contact your pediatrician promptly if you notice any changes in your child’s health.
- take care of your child's hygiene
IMPORTANT: Monitor your baby’s immune system as a whole. Diseases may cause teething problems.
If a new tooth does not grow in place of a baby tooth
The loss of baby teeth, as well as their appearance, does not occur simultaneously, but in accordance with the development of the jaws and the growth of permanent replacement. The concept of a protracted renewal is quite relative, because for some the radical will show itself in a week, and for others in a month or two. And in the second case, we are not always talking about deviation.
Often baby teeth are “pushed out” by molars, which almost immediately make their way out, but if a child’s tooth falls out and a new one does not grow and is not visible, you need to wait a few weeks.
Reasons to see a doctor:
- lack of replacement 2-3 months after the loss of a baby tooth;
- swelling and redness of the gums, pain without signs of germination of a molar;
- sequential loss of other teeth without the appearance of new ones.
Reasons why a child’s tooth does not grow for a long time:
- Infectious diseases, including past ones.
- Lack of calcium in the body.
- Oral diseases.
- Mechanical injuries.
A child’s tooth has fallen out and is not growing, but the situation does not correspond to the reasons indicated? Perhaps the delay is provoked by poor ecology, incorrect or poor-quality diet, stressful situations, or even genetic preconditions.
When does a child cut his first tooth?
According to pediatricians, the timing of teething is individual for each baby. In some children they appear at 2-3 months, while in others at 9 months or a year. Oddly enough, this phenomenon is considered the norm. The main thing is that by the time your daughter or son reaches the age of three, she already has 20 baby teeth in her mouth.
Every mother should prepare both mentally and physically for such a responsible task.
- You will have to be patient with your child's whims. Surround your child with affection, care, love.
- Do daily cleaning, keep toys clean, and also maintain your and your child’s hygiene. After all, babies during such a period often put everything in their mouths; your task is to prevent the child from catching an intestinal infection.
- To make teething easier, you can buy special teethers (gum massagers). They have an anti-pain effect.
- Special gels are good for gum pain relief. Just don’t think that they help teething. They only relieve inflammation, relieve some pain and soothe irritated gums.
- If a child's temperature rises above 38, then visit a pediatrician. The cause of elevated temperature can be not only teething, but also various diseases.
IMPORTANT: Before using gels to soothe gums during tooth growth, consult with your pediatrician which drug is best to use.
Pathological causes of delay
If a child’s teeth have fallen out and new molars do not grow for a long time, the reasons for the delay should be sought in pathologies:
- Retention is a complete or partial delay in eruption. Partial retention is observed when the crown of a molar tooth appears in the socket of a milk tooth, but growth stops there. Often the cause is early loss of a baby tooth, accidental or surgical. That is, a replacement for him has not yet been formed.
- Adentia – absence of teeth. This rare problem is common in older people, but can also occur in children. As a rule, it is triggered by taking strong medications during pregnancy.
What to do if a child does not have a single tooth in one year?
Previously, it was considered a deviation from the norm if a baby does not have a single tooth per year. Doctors first of all suspected that the baby had anemia or rickets. This version has now been refuted. Studies have shown that many children start teething at 1-1.2 years of age. However, parents should not be careless and just wait for the process to manifest itself. When your child turns 1 year old, be sure to tell your pediatrician about the problem that has arisen.
He, in turn, should establish the reason for the delay in tooth growth. If it is heredity, he will tell you when to come back for an appointment. He will prescribe the use of vitamins necessary for teeth growth and advise on how to feed the baby correctly. If not, he will send you for tests or to a dentist. You may be asked to do:
- biochemical tests of urine, blood
- ultrasound examination of organs
- check your thyroid gland
IMPORTANT: To exclude a disease such as adentia, the dentist will order an x-ray of the lower jaw. If the diagnosis is confirmed (there are no teeth rudiments), then after a while dentures are installed. However, do not get upset right away - this pathology is extremely rare.
Recommendations for avoiding delay
- After tooth loss, you should not eat or drink hot drinks for several hours.
- The plug that forms in the hole cannot be removed to avoid infection. It will disappear on its own.
- It is not advisable to eat solid food for the first time after the loss.
- If you experience pain, redness, swelling or other signs of exacerbation, you should immediately contact your dentist. Remember, our specialists are always ready to help and answer your questions by phone.
Adentia - symptoms and treatment
Complications of adentia are psychosocial, neurological, dental, and sometimes systemic in nature.
In the complete absence of teeth, atrophy of the alveolar processes occurs first. This leads to a violation of the aesthetics of the smile, as a result of which people with this disease develop psychological problems.
Why does bone tissue decrease in the absence of teeth?
When teeth are lost, the chewing load is transferred to the mucous tissue and bone support of the gums. Due to the load, the blood supply to this part of the masticatory apparatus is disrupted, venous stagnation occurs and vascular tone decreases. Redistribution of pressure also leads to the activation of osteoclasts (cells that destroy bone tissue) and damage to cancellous bone.
When there is edentulism in one jaw, the antagonizing (opposite) teeth in the dentition are crowded or piled on top of each other. In this case, individual teeth are located outside the dentition or are impacted.[2]
Changes are observed in the composition of oral fluid.[19] These disorders create favorable conditions for the occurrence of diseases of the dental system, which, at times, the body’s adaptive mechanisms are no longer able to cope with:
- the rate of saliva secretion decreases;
- the reaction of the environment changes;
- the amount of protein in the oral fluid decreases;
- indicators of antibacterial and antiradical protection change.
In 100% of cases of secondary adentia, macroglossia occurs over time, i.e., enlargement of the tongue: its microvascular bed undergoes changes.[20]
The periodontium of the remaining teeth experiences functional overload, in particular, the endurance of the periodontium of the teeth limiting the defect decreases.[23] This leads to the formation of pathological bone pockets, atrophy of the dental alveoli and localized gingivitis.
Violation of the closure of the dentition causes pathological changes in the structure of the temporomandibular joint: the movements of the articular heads are limited, the histological structure of the tissues changes.
The mutual influence of the structures of the masticatory apparatus creates the prerequisites for the formation of neurological phenomena. One of the most diverse manifestations is Costen's syndrome. It may be accompanied by:
- pain, mainly in the parotid region;
- congestion in the ear and hearing loss;
- dizziness;
- violation of taste sensitivity.
Due to the lack of chewing teeth and insufficient mechanical processing of food, disorders associated with digestion are formed - gastritis, colitis, stomach ulcers.[22]
With all this, experience shows that increasing the medical literacy of the population reduces the number of cases of possible complications, which obviously leads to an increase in the level of dental health of the population.[27]