Causes of dark plaque on the tongue
Thick deposits that cannot be cleaned off can indicate serious problems in the functioning of the body. The causes of deposits can be both internal and external. The latter include:
- Taking medications such as Faringosept, Malavit, steroids, drugs that contain bismuth.
- Deficiency of nicotinic acid or vitamins PP, group B.
- Black spots appear due to lead poisoning.
- Tobacco smoking, excessive indulgence in fatty foods, sweets, and alcohol.
- Dehydration or acidosis.
The reasons for the appearance of dark plaque lie in many diseases.
- Advanced oral candidiasis and stomatitis.
- Severe disturbance of the microflora of the oral cavity.
- Progressive diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in chronic form - gastritis, enterocolitis, dysbacteriosis, liver pathologies, cholecystitis, pancreatic diseases.
- Advanced infectious diseases - pneumonia, arthritis, blood diseases, tonsillitis, nephritis, cholera.
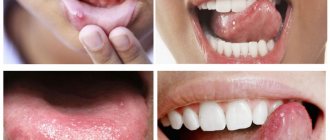
Black tongue
Fungus
Gastritis
Colitis
22467 September 28
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Black tongue: causes of appearance, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
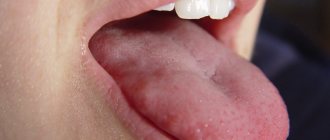
Black tongue is a condition in which a person's tongue is completely or partially dark or black in color. This symptom is more common among older people, although it occurs in all age groups, and is more common in men than women.
Varieties of black tongue
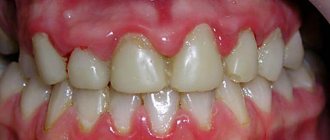
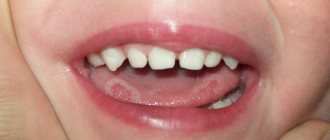
Normally, the tongue has a pale pink color, it is moist, with a smooth surface and clearly visible papillae.
Plaque on the tongue is formed by food debris and exfoliated dead cells of the mucous membrane of the tongue, which can become saturated with food dyes. The appearance of a thin, white, easily cleaned plaque that does not have an unpleasant odor is considered acceptable, and the formation of a dense plaque with a non-physiological color is regarded as a pathology.
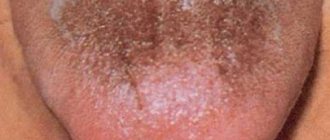
On the surface of the tongue there may be individual black dots, one large spot, the tongue may be colored on the sides or completely.
Most often, a black tongue is caused by staining from plaque, such as food or medications, but it can also result from excess melanin deposits or lead poisoning.
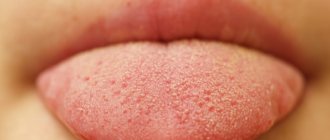
In addition, there is such a thing as “black hairy tongue” - a benign and temporary phenomenon in which the filiform papillae of the tongue lengthen, and the keratinized cells of the epithelium of the tongue do not exfoliate and become black or brown due to the activity of certain bacteria and fungi. The length of the papillae can reach 1-3 cm, and the diameter is 2-3 mm. Hyperplastic filiform papillae are located mainly on the posterior and middle third of the dorsum of the tongue. The tongue takes on a “hairy” or “furry” appearance. The disease occurs in both children and adults, but is much more common in older people. Patients may complain of a foreign body sensation on the tongue, itching of the palate, burning of the tongue, dry mouth, impaired taste sensitivity, and bad breath. If enlarged taste buds touch the palate, a gag reflex occurs, especially during conversation.
Possible reasons for the appearance of a black tongue
A black tongue is often associated with poor oral hygiene. In addition, people who abuse tea and coffee, smoke, suffer from alcoholism, and use intravenous drugs are at risk. Dry mouth contributes to the tongue turning black when, due to insufficient salivation, more bacteria accumulate on the tongue, the activity of which leads to the plaque becoming pathologically colored. Severe dehydration of the body is accompanied by the formation of a dark, sometimes almost black coating, which is difficult to remove from the tongue.
Some medications give the tongue a black color, for example, activated carbon, iron, bismuth, or antibiotics that disrupt the balance of microflora in the mouth.
A black tongue can also be observed in harmless situations, for example, after eating blueberries, red wine, and foods that contain dyes (sweets, chewing gum, lollipops).
Diseases that can cause the tongue to turn black
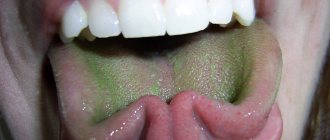
A black tongue is often observed with severe advanced candidiasis of the oral cavity, with sore throat, with pathology of the gastrointestinal tract (diseases of the liver, gallbladder, pancreas), adrenal insufficiency, acid-base imbalance and with the development of increased acidity (acidosis). If a chromogenic fungus has settled in the mouth, then the gums, teeth and tongue become covered with a black coating with a greenish tint. In adrenal insufficiency (Addison's disease), one of the signs of the disease is hyperpigmentation of the skin and mucous membranes due to increased levels of melanin. Pigmentation of the oral mucosa occurs, spots and stripes of brown or grayish-black color appear on the red border of the lips, in the corners of the mouth, on the gums and on the lateral surfaces of the tongue.
Predisposing factors to hypertrophy (enlargement) of the papillae with a black hairy tongue can be diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (anacidic gastritis, hypoacid gastritis, colitis, infectious diseases). In some cases, the formation of a black hairy tongue occurs against the background of a deficiency in the body of riboflavin (vitamin B2). In addition, black hairy tongue occurs with pulmonary tuberculosis, papillary pigmentary dystrophy, and after the use of certain medications (for example, antibiotics).
Which doctors should I contact if a black tongue appears?
If you have an oral disease that has caused the formation of a black coating on the tongue, you should consult a dentist.
If plaque is associated with an infectious disease, for example, sore throat or candidiasis, then treatment is carried out.
For diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, you should contact.
If the cause of the black tongue is Addison's disease (adrenal insufficiency), then consultation is required.
Diagnostics and examinations for the appearance of a black tongue
Some tests may be needed to determine the cause of tongue discoloration:
- general blood analysis;
Shades of dark color
The color of the tongue can really tell the doctor a lot about the condition of the patient's body. Dark masses on a muscular organ with various ailments have a certain shade.
- A signal about diseases of the digestive system, immunodeficiency, and hormonal imbalances is given by the dark green color of the tongue.
- Dark brown deposits occur with fungal infections, food poisoning, pulmonary diseases, as well as with hemolysis and adrenal insufficiency.
- Dark red deposits appear with scarlet fever, kidney infection, and advanced glossitis.
- With serious damage to the stomach and intestines, the plaque becomes dark gray.
- A black tint suggests cholera.
In addition, Crohn's disease is indicated by black spots on the receptor organ. Black deposits with an acetone odor indicate severe dehydration. Dark substrate and inclusions on the crowns indicate a chromogenic fungal disease. Any therapeutic program, as a rule, includes hygienic cleaning of the oral cavity. In our center it is performed by highly qualified hygienists.
Homeopathic remedies for black spots on the tongue
Many doctors, along with traditional remedies for the treatment of tumors on the tongue, also prescribe homeopathic medicines . Below we provide a list of medications that treat black spots by eliminating the main cause of the disease.
| Symptoms | Drugs |
| Fungal plaque, which has various shades from light to black. |
|
| Brown plaque, accompanied by dehydration and stomach diseases. |
|
| Brown plaque, necrosis of the pharynx and palate. |
|
| Brown and black spots in acute respiratory infections with elevated temperature and nasal congestion, the formation of cracks in the corners of the mouth, profuse snot and nasal congestion. |
|
| Brown and black spots, tongue is dry and itchy. |
|
| Dark brown plaque localized in the center of the muscle. |
|
| Black spots. |
|
| Black and black-purple spots on the root of the muscle. |
|
Diagnostics
To determine what disease led to the appearance of unpleasant symptoms, an examination is necessary. Diagnosis may include:
- General and biochemical blood test;
- Stool and urine analysis;
- Fluorography and ultrasound;
- Gastroscopy;
- Bacterial culture from the tongue;
- Coprogram;
If a dark coating appears on the tongue, adults should first consult a therapist, and young patients should be shown to a pediatrician. After examination, history taking, palpation of the abdomen and other manipulations, the patient is referred to a specific specialist. Most often, a consultation with a gastroenterologist and an infectious disease specialist is needed. Also, the patient can be referred to an endocrinologist, otolaryngologist, pulmonologist, or toxicologist. The dentist is very helpful.
Hypovitaminosis
In the course of careful research, it was discovered that with a lack of vitamins PP and B vitamins in the child’s body, the mucous membrane of the tongue changes its color. Black plaques or spots appear.
Special cases
Difficult to explain cases include the so-called “black hairy tongue.” The nature of this phenomenon is still being studied, and today doctors cannot give a comprehensive explanation. The picture looks like this: at the tip and root of the tongue, the normal pink color remains, while multiple dark papillae grow on the back.
Dark coating on a child's tongue
It happens that the blackness on the baby’s tongue could remain from his favorite berries - blueberries or currants. Maybe he saw through the ink refill? All this will be washed off after the first hygiene procedure! If these reasons are discarded, then a dark coating on the child’s tongue could appear against the background of pathologies of the child’s body.
- Diseases of the digestive system - enteritis, dysbacteriosis, gastritis, colitis, hepatitis, cholecystitis in advanced stages.
- Untreated infectious diseases - stomatitis, thrush, ARVI.
- Iron deficiency anemia, when children are prescribed iron supplements in liquid form. This product may stain the tongue. But, the unpleasant symptom will go away after the end of the course of therapy.
- Dehydration and acidosis.
- Lead poisoning.
- Black fleecy tongue.
At the slightest suspicion of these diseases, you need to consult a specialist after visiting a pediatrician. By identifying the internal factor that provokes dark color deposits, you can successfully eliminate it.
Dangerous symptoms and which doctor to contact
When black spots on a person’s tongue do not go away within two to three days, increase in size, new spots appear, and the temperature rises, you should go to the doctor.
The first thing you need to do is visit the dentist. If this nature of the problem is excluded, then the doctor will refer the sick person to the therapist’s office. You may need help from a specialist in gastroenterology or oncology.
The main method of diagnosing the disease is bacteriological culture of plaque to determine the type of pathogenic microflora in the mouth, donating blood for analysis. If there is a suspicion of problems with the gastrointestinal tract, a coprogram and ultrasound examination of the organs will be used.
Treatment of dark plaque
Patients with dark deposits on the muscle organ are advised to systematically treat their teeth. This will help avoid unpleasant symptoms. Oral hygiene procedures are mandatory. You should clean not only your incisors and molars, but also your tongue twice a day. You can use a special scraper and gels. It is important not to injure mucous tissues. Treatment of acidosis begins with drinking plenty of fluids.
Of course, it is impossible to get rid of dark layers if the underlying disease is not treated. Therapy is prescribed individually based on the established diagnosis.
- For stomatitis, you should rinse your mouth with a liquid containing antiseptics such as Hepilor or Chlorophyllipt.
- Antifungal agents eliminate candidiasis. These are Clotrimazole, Pimafucin, Fluconazole.
- The microflora in the intestines is restored by probiotics with bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. Most often, Linox and Acipol are prescribed.
- Prebiotics stimulate the body's production of its own beneficial bacteria. The nutrient medium for them is created by Duphalac and Lactusan.
- The body's defenses are increased by Cycloferon, Kagocel, Ribomunil.
- The secretion of gastric juice is stimulated by Limontar and Etimizol, which is important for low acidity.
- Aggressive gastritis is treated with antibacterial drugs, in particular Cephalexin.
- Toxic substances are well removed by a sorbent such as Enterosgel.
If the patient complains of heartburn, he is prescribed Rennie, Maalox and other medications. The gastric mucosa is well protected by De-Nol and Venter. Deficiency of vitamins PP and group B is eliminated by taking vitamin complexes. Dietary nutrition is often prescribed. The program is developed for each patient individually.
Measures to be taken
Photo 2: If the color of the tumors does not lighten within several days, then it is necessary to urgently visit a doctor to rule out pathologies such as tongue cancer, glossitis and other diseases.
Source: flickr (Olalla Esquimal). To get rid of stains, it is necessary to determine the root cause of their appearance and eliminate it . A number of diseases accompanied by this symptom can be easily cured with the help of medications and vitamin complexes. Along with medications taken orally, treatment of the organ surface . This procedure is carried out using the following means:
- decoctions of sage and chamomile;
- Imudon or Lysobact tablets;
- solutions of miramistin or chlorhexidine;
- treatment in a hospital with liquid nitrogen.
If fungal infection occurs , bifidobacteria and lactobacilli and probiotics are prescribed to normalize the microflora, as well as antifungal drugs such as nystatin, livarol, fluconazole or diflucan.
Laser treatment
The easiest way to remove a hemangioma is with a laser. This treatment method has several advantages:
- no risk of infection;
- This is a non-contact method of therapy;
- tumor cells are completely removed;
- the procedure is painless;
- It is possible to cure even cavernous tumors;
- the wound heals quickly.
Laser treatment does not take much time. The procedure uses a laser with a short beam length. Removal does not cause serious discomfort to the patient. The laser is absolutely safe, the procedure does not lead to side effects. After treatment of hemangioma of the tongue, no bleeding is observed.
Complete laser removal leads to rapid restoration of healthy tissue. The tongue heals and the patient returns to normal life. A special laser is used in clinics where they offer the procedure for removing hemangioma in this way.
Removal of tumors at Lazmed Clinic
Treatment
Your doctor will tell you how to treat various pathological conditions. The most difficult thing is to get an appointment with the right specialist and determine the problem, because treatment will be aimed not so much at eliminating the external defect, but at relieving the internal disease.
Therapy for some diseases may take only a few days, while for others it may take months or even years. The duration of treatment depends not only on the type of disease, but also on the degree of its neglect. That is why doctors recommend closely monitoring your health and not delaying a visit to a medical facility, even if the pathology seems insignificant. Don't ignore even a little redness.
Cost of hemangiomas removal
| Laser tumor removal | Prices, rub. |
| Laser removal of papillomas, single warts - Cat. I. difficulties | 1200 |
| Laser removal of papillomas, multiple warts - Cat. I. difficulties | 350 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - Cat. II. difficulties | 700 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - Cat. III. difficulties | 1500 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - IV category. difficulties | 3000 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - Cat. V. difficulties | 4500 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - Cat. VI. difficulties | 6100 |
| CO2 Laser callus removal (per unit) | 6100 |
| Removal of atheroma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - Cat. I. difficulties | 6 900 |
| Removal of atheroma, basal cell carcinoma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - Category II. difficulties | 9 400 |
| Removal of atheroma, basal cell carcinoma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - Cat. III. difficulties | 16 900 |
| Removal of atheroma, basal cell carcinoma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - IV category. difficulties | 22 400 |
| Removal of atheroma, basal cell carcinoma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - Cat. V. difficulties | 33 400 |
Sign up for laser removal of tongue hemangioma
- Full name
- Telephone
Treatment of black plaque
To determine the cause of unpleasant symptoms and properly treat the disease, you must first make an appointment with a therapist. After diagnosis, the patient may need:
- A dentist who provides dental and oral treatment.
- Infectious disease specialist to eliminate the source of infection.
- Gastroenterologist to eliminate inflammatory processes in the intestines and stabilize the microflora.
- A pulmonologist who deals with respiratory diseases.
- Toxicologist, endocrinologist and other specialists.
All this will eliminate pathological layers on the mucous membrane and return the tongue to its natural color. The body could use multivitamin support to stabilize its defenses. It is useful to rinse the mouth with pharmaceutical products and infusions of sage, St. John's wort, and chamomile. Use special products and decoctions as prescribed by your doctor. Only he can develop the correct therapy program.
As practice has shown, the best way to prevent plaque is systematic oral hygiene. In this case, soft brushes and scraping spoons recommended by a specialist are used. Rinse your mouth even after a snack. If possible, reduce the number of cigarettes you smoke per day. Don't get carried away with sugary energy drinks; it's better to switch to healthy and nutritious smoothies.
Our specialists
- Kiani Ali
Candidate of Medical Sciences, laser medicine specialist, dermatocosmetologist.
Sign up
- Stepanova Inna Igorevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, maxillofacial surgeon, specialist in laser medicine.
Sign up
- Fedotova Marina Andreevna
Surgeon, dermatocosmetologist, laser medicine specialist
Sign up
- Popovkin Pavel Sergeevich
Surgeon, oncologist, laser medicine specialist.
Sign up
Tongue injuries
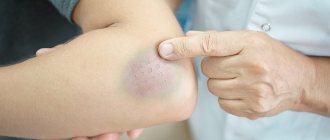
As a result of injury to the tongue, dark red or dark brown blisters may appear on it. They have this color because there is blood inside.
Dark spots can occur due to trauma to the tongue, especially if it results in sores. For example, due to piercings, dental surgery, tongue biting.
What else can cause a brown spot on the tongue?
Removal methods
When treating a tumor, the patient is prescribed removal. The method of removal depends on the complexity of the disease. If there is no risk of damaging surrounding tissues, then a surgical method is used. This treatment is used if the tumor has not penetrated inside. In this case, the surgeon will be able to remove all the affected cells.
Surgical treatment is not suitable if the tumor has penetrated deep into the tissue. There is a risk of damaging the tongue and not removing damaged cells completely. In difficult cases, the radio wave method is prescribed. It is used to treat cavernous hemangiomas. Affected cells are removed at ultra-high temperatures.
Treatment with ultra-low temperatures - cryotherapy - is also possible. During treatment, applications are applied to the tongue, which freeze the affected cells. The tumor tissues die and separate.
Symptoms
Pathology is immediately detected during a visual examination by a dentist. In the initial stages of the disease, the presence of a foreign object in the mouth is felt, other unpleasant signs gradually appear, then the upper part of the tongue noticeably turns black. In advanced cases, the affected area occupies two-thirds of the tongue. The disease is accompanied by unpleasant odor from the mouth, changes in taste sensations, a metallic taste appears in the mouth, a feeling of tickling and soreness on the surface of the tongue, as well as causeless nausea. In rare cases, there is a burning sensation and severe itching.
How to treat dark spots on the tongue
If a black dot appears on the tongue, which is not a sign of pathological processes, then it does not need to be treated. When a stain has formed due to medication or poor oral hygiene, it can be easily removed with a toothbrush.
In another situation, the doctor will prescribe treatment for small blackheads. This is done in two ways:
- Medication. If the spots are caused by an infection, an oral antibiotic will be prescribed. If it is a fungal infection, then appropriate medications will be prescribed.
- Surgical. When the black spots in the mouth are fibroids, the patient will have them excised.
If darkening occurs on the mucous membrane of the tongue, do not panic. You need to go to the hospital. The doctor will conduct an examination and prescribe appropriate treatment. The main thing is to remember to maintain oral hygiene. This will eliminate many health and appearance problems.
Symptoms and causes of formation
Hemangioma of the tongue can be:
- cavernous;
- capillary.
A simple capillary hemangioma grows in breadth without affecting the tissue. It consists of capillary tissue and is often affected during conversation or eating. Externally, the tumor looks like a spot or bruise. The formation must be removed - damage to the hemangioma can lead to infection.
Cavernous hemangioma of the tongue penetrates deep into the tissues; it protrudes noticeably above the surface of the tongue. This formation consists of many vessels and causes serious discomfort. The tongue may lose its mobility and increase in size due to the tumor.
The causes of hemangiomas have not been fully established. In children they occur mainly due to the growth of vascular tissue.