Causes of tongue tingling
Physiological factors
Tingling, burning throughout the tongue occurs after eating spicy foods and some spices.
Unpleasant sensations occur directly during eating and last for several hours. To reduce discomfort, a person drinks cool water and rinses his mouth. The tingling sensation is accompanied by increased production of saliva, which must be constantly swallowed. Externally, the tongue is unchanged, sometimes due to irritation and increased blood flow, it looks bright pink. The second typical reason is drinking too hot drinks or food. A superficial burn of the tongue occurs, which manifests itself as painful tingling, burning and tingling. With mild damage, symptoms persist for 12-24 hours, after which increased sensitivity of receptors to hot or spicy foods persists for several days.
Dental diseases
Constant tingling occurs when the tongue is traumatized by the sharp edges of carious teeth, incorrectly selected crowns or dentures. Discomfort is felt in the same place where maximum friction or scratching of the tooth on the surface of the tongue occurs. An epithelial defect is formed in this area, so when spicy food enters, the tingling intensifies.
Xerostomia
Low saliva production causes the tongue to dry out, which results in a painful feeling of tightness and tingling. Symptoms are aggravated by talking for a long time or eating dry solid food. Gradually, xerostomia progresses, so burning, tingling, and discomfort persist constantly. To alleviate the condition, patients regularly rinse their mouths and drink water, but such manipulations only help for a short time.
Tingling tongue
Glossalgia
With this pathology, the patient complains of a variety of painful sensations: tingling, pinching, rawness. Symptoms are not associated with ingestion of food or hot drinks. The tingling sensation is most pronounced on the lateral surfaces and tip of the tongue. The localization of sensations changes periodically. Externally the language has not been changed. Secondary glossalgias are manifested by:
- Endocrine disorders
: diabetes mellitus, Cushing's disease, hypothyroidism. - Gastrointestinal pathologies
: gastritis and gastroduodenitis, pancreatitis, hepatitis and cholecystitis. - Damage to peripheral nerves
: neuropathy of the glossopharyngeal nerve, ganglionitis of the sublingual autonomic ganglion, sympathalgia. - Diseases of the central nervous system
: encephalitis, neurosyphilis, residual effects after a stroke. - Connective tissue diseases
: scleroderma, dermatomyositis.
Glossodynia
Paresthesias are observed, manifested by tingling, burning, and a sensation of “crawling goosebumps” that have no apparent cause. At first, the discomfort symptoms affect only the tip of the tongue, but gradually they spread over its entire surface like an “oil stain.” The root of the tongue is the last to be affected, but often no tingling occurs in this area at all.
Discomfortable sensations last for 3-5 minutes and appear several times a day. As glossodynia progresses, episodes of paresthesia lengthen and are accompanied by a feeling of enlargement and swelling of the tongue. The pathognomonic feature of the disease is the absence of tingling at the time of eating. Therefore, people constantly chew something, which ultimately leads to weight gain and dental caries.
Desquamative glossitis
Periodically during the day, patients experience an unpleasant tingling and burning sensation in the mouth. Tingling spreads over the entire surface of the tongue or to its individual areas that are affected by the inflammatory process. It is common to experience increased discomfort while eating, especially when eating hot or spicy foods. Symptoms bother the patient for several weeks or months.
With desquamative glossitis, unlike glossalgia and glossodynia, the appearance of the tongue changes. Bright red foci of inflammation appear on its mucosa with detachment of the epithelium, noticeable cracks or furrows form. In areas of desquamation, pain and tingling are most pronounced. The wounds heal quickly, then new erosions form elsewhere - an ever-changing “geographic pattern” on the tongue.
Hypovitaminosis B12
Tingling and pinching of the tongue is caused by atrophy of the papillae and the development of Gunter's glossitis. Discomfort is observed constantly, it is not associated with food or other external factors. With increasing deficiency of vitamin B 12 and the occurrence of macrocytic anemia, the symptoms worsen. Patients complain of a constant painful burning sensation and pain when eating. The tongue becomes bright red, “polished” and shiny.
Oral candidiasis
Tingling of the tongue is characteristic of chronic candidiasis, while in the acute form, severe burning and pain are more common. The feeling of discomfort extends not only to the back of the tongue, but also to the mucous membrane of the cheeks and the red border of the lips. Patients notice a thick grayish plaque, after peeling it off, bright red inflamed areas of the epithelium remain. With the development of chronic atrophic candidiasis, tingling is complemented by severe dry mouth.
Allergy
Paresthesia in the tongue is one of the signs of a food allergy or reaction to animal fur or plant pollen. In this case, the tingling is combined with painful itching, to relieve which patients try to “scratch” the back of the tongue with their teeth, which increases the discomfort. Symptoms appear against the background of other allergic manifestations: lacrimation, sneezing, digestive disorders.
Causes of pain in the tongue
13.09.2021
Pain in the tongue can occur for a variety of reasons, and describing them all is difficult. But still, let's try to sort out the most
the main sources of its occurrence, because depending on the cause of the pain, its nature and location, proper treatment is prescribed.
The most common causes of tongue pain include:
• mechanical damage; • inflammatory processes in the oral ; • blockage of the salivary glands; • neuralgia ; • allergies ; • oncological diseases.
The tip of the tongue hurts
It is not always necessary to resort to drug treatment for pain in the tongue, so let's take a closer look at the main
the reasons for its occurrence. For example, symptoms of mechanical injuries are: pain on the tip of the tongue, edge or sides.
In most cases, such damage occurs while eating. The most common sources of origin of these microtraumas include:
• burns from hot food or drinks; • biting with your own teeth ; • scratches or cuts that appear from certain foods; • injuries caused by sharp edges of poor quality fillings.
Therefore, for example, if pain occurs in the tip of the tongue, there is no need to worry too much right away. Most likely it arose as a result of a trivial mini-trauma,
for example, such as a burn or accidentally biting your tongue.
Despite the unpleasant sensations resulting from such injuries, they do not require special treatment and go away on their own, without any negative consequences.
consequences. But it also happens that seeking medical help is still necessary. For example, when painful inflammatory processes appear in
oral cavity , such as: glossary, glossitis and stomatitis.
Pain under the tongue
The localization of pain in inflammatory diseases of the tongue may be at its base. For this reason, pain also occurs under the tongue. There may be pain
concentrated in one place, or move throughout the entire oral cavity.
Such discomfort can also be caused by one of the following diseases:
• allergies ; • gastrointestinal disease; • vitamin deficiency.
If you experience severe pain, excessive salivation, bad breath , swelling of the tongue, which makes speech and breathing difficult, you should
pay attention to such dangerous diseases as abscess or phlegmon . With these diseases, the listed symptoms are accompanied by problems with closing the mouth .
The above diseases are a serious reason to consult a doctor , who, after making a correct diagnosis, will prescribe appropriate treatment,
depending on the causes and nature of the pain.
The base of the tongue hurts
If pain bothers you in the area of the lateral surfaces of the tongue, then in addition to mechanical damage, the following factors can also be its causes:
Smoking can often cause severe pain in the tongue; neuralgia - you should think about it if you do not smoke and have not noticed mechanical
damage, but the pain in the tongue still continues.
Above, we have listed the most common causes of tongue pain, now let’s move on to ways to eliminate this ailment.
Troubleshooting
As already mentioned, if your tongue hurts severely, the first thing to do is seek medical help. Doctors dealing with diseases
oral cavity specialists are an otolaryngologist and a dentist . During the examination, a specialist will exclude possible mechanical damage and determine the main cause.
the occurrence of pain, as well as the nature of its course. Then he will make a diagnosis and determine the required treatment.
Compliance with hygiene rules will help to minimize the risk of inflammatory processes in the mouth , such as: do not neglect hand washing;
do not eat unwashed fruits and vegetables; rinse your mouth after every meal. Also, it is necessary to give up bad habits and constantly
monitor the condition of your teeth . Let us remind you that following these simple rules will help you in the fight for oral health .
Published in Articles without category Premium Clinic
Diagnostics
With complaints of tingling of the tongue, first of all, contact a dentist, who carries out an examination and identifies the most common causes of this condition. If there are no obvious factors, a comprehensive examination is prescribed with the participation of a therapist, neurologist and other specialists. To detect the etiology of tongue tingling, the following are used:
- Instrumental diagnostics
. For dry mouth, ultrasound of the salivary glands and sialography are recommended. To identify gastrointestinal diseases that cause tingling, EGD and radiography with oral contrast are performed. Electromyography is informative to determine areas of paresthesia in glossodynia. - Laboratory research
. A general blood test determines the level of hemoglobin, the presence of macrocytes or megaloblasts, indicating B12-deficiency anemia. Additionally, the content of cyanocobalamin in the blood is examined. For differential diagnosis, a saliva test is performed to measure the pH value. - Microbiological analysis
. To confirm candidiasis, microscopy of plaque on the tongue is performed, during which pseudomycelium and budding cells are detected. Confirmation of the diagnosis requires inoculation of the biomaterial on nutrient media. To exclude syphilitic glossitis, microscopy of the scraping is done for Treponema pallidum.
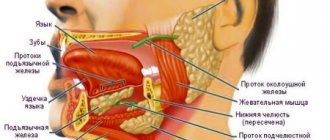
Examination of the tongue and oral cavity
Numbness of the tongue
Unfortunately, such an early complication as tingling and numbness in the tongue is a fairly common phenomenon after implantation. At the same time, impaired sensitivity does not always indicate the appearance of serious pathologies. As a rule, tissues become numb only in the first few hours after surgery and only due to the effect of local anesthesia.
Depending on the individual characteristics of each patient’s body, paresthesia can last from 4 to 13 hours. In addition to the effect of the drug, numbness can occur for a number of reasons. First of all, we are talking about accidental damage to the nerve with a needle during the injection of an anesthetic into the gum. Also, the nerve can be affected by the implant itself if its size was not selected exactly. In addition, the endings may be compressed due to tissue swelling.
Also, the reason may be a large amount of intervention on the part of the doctor, for example, in the case of reconstruction of individual sections of the jaw bone, plastic surgery, etc. In rare cases, sensitivity is lost for up to 1 year. If the cause is a nerve injury, then, thanks to the action of special medications and physical therapy, the condition returns to normal after a few weeks.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
To reduce tingling and burning, doctors recommend following a diet. All hot and spicy dishes are excluded from the menu; food should be warm, but not hot. Products are prepared by steaming, boiling or stewing so that they are soft and do not injure the surface of the tongue. It is necessary to regularly rinse your mouth with water or a weak solution of chlorhexidine: this helps get rid of tingling and also prevent inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity.
Conservative therapy
Treatment for a tingling tongue begins with dental care. The doctor sanitizes the oral cavity and, if necessary, changes fillings and incorrectly selected dentures. If after this the symptoms do not disappear, treatment is prescribed for the underlying disease causing glossalgia. Therapeutic regimens are selected by a specialized specialist: neurologist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist.
Pathogenetic treatment includes medications that affect the nervous system, which help reduce painful paresthesias. Herbal sedatives, bromine preparations, and “daytime” tranquilizers are effective. For refractory symptoms, injections of B vitamins and trimecaine blockades are used. Local remedies provide a quick effect: lubricating the tongue with anesthesin, pyromecaine, oil solutions (vitamin A, rose hips).
Those suffering from desquamative glossitis are often prescribed physiotherapy, which includes medicinal electrophoresis, ultrasound therapy, and SMT therapy. For prolonged glossalgia, reflexology and ozone therapy help relieve tingling. To reduce the intensity of symptoms, laser therapy is used, which has an additional anti-inflammatory effect. Paresthesia of a neurogenic nature requires psychotherapy sessions.
What it is
As an isolated disease, glossalgia is statistically extremely rare among visits to dentists.
Glossalgia of the tongue is expressed in periodic or constant pain without obvious reasons.
Initially, the patient may experience itching, tingling, anemia, burning sensation in the tongue, and dry mouth. Some do not even attach much importance to this disease, because it always appears against the background of serious diseases and dysfunctions of the body, be it the gastrointestinal tract, liver, nervous or endocrine system.
At the moment the symptoms of glossalgia appear, the patient has more important problems on which he concentrates his attention. And when the underlying disease, the main cause of the formation of painful sensations in the tongue, is eliminated, glossalgia itself most often disappears without a trace.
Most patients have no idea what glossalgia is and what causes it. Many people attribute tingling, swelling and burning of the tongue to injured teeth, defective fillings or poorly fitting dentures. However, glossalgia is a problem not at all associated with all of the above factors.
Most often, this disease is diagnosed in women of menopausal age. Men are much less susceptible to it. Symptoms appear against the background of serious problems with the gastrointestinal tract, blood vessels, hormones, blood circulation in the brain, as well as during stressful conditions, depression, and nervous system disorders. Also, tongue disease often occurs in suspicious people.
Scientific research associates the development of glossalgia, or as it is also called glossodynia, with disruption of the hypothalamus. And since this part of the brain is responsible for the functioning of the nervous, cardiovascular, digestive and excretory systems, regulation of metabolism, emotions and much more, malfunctions in its work affect, among other things, the vagus and glossopharyngeal nerves. In this regard, the patient begins to experience false painful sensations in the absence of any traumatic element.
The appearance of plaque on the tongue
The normal condition is considered to be a pink tongue with a small amount of white coating. This plaque can be easily removed with a regular toothbrush. Heavy deposits may appear after the implantation procedure, but most often the reason lies in something completely different. The origin of the plaque can be judged by its shade; for example, in smokers it becomes more yellow.
If the patient does not adhere to a diet and drinks large amounts of coffee, tea, wine, chocolate, then the tongue may change its color to brown. This can also happen due to taking certain medications. In this case, the side effect disappears immediately after completing the course of taking them. If a person has a peptic ulcer, gastritis, or fungal infection, the tongue may acquire a bright color.
Another cause for concern is the appearance of heavy plaque and heaviness in the hypochondrium. This may indicate liver or gallbladder disease.
Treatment will depend directly on the reason why the plaque forms. It is very important to first consult with specialists (dentist, gastroenterologist, etc.) Based on the results of the examination, antifungal drugs, a diet, adding vitamin B to the diet, and much more can be prescribed. Sometimes it is enough to change your toothpaste, choose suitable products for use at home and have your mouth professionally cleaned.