Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract have a complex effect on the health of the entire digestive system, which includes the oral cavity. First of all, this effect is due to a lack of vitamins and minerals, which leads to inflammatory processes, and in addition, aggravates existing oral diseases.
Of course, in such cases, treatment of the problem should be comprehensive - you should also contact a dentist
, who will eliminate the manifestations of diseases in the mouth, and to an endocrinologist, who will directly eliminate the root of the disease.
Let's look at the main examples of gastrointestinal diseases that directly affect the condition of the oral cavity and teeth.
Types of gastritis
The largest division of gastritis is acute and chronic. The first occurs immediately after irritating factors come into contact with the gastric mucosa. In case of improper nutrition, it manifests itself in a catarrhal form, in case of poisoning or infection - in a fibrinous form.
Chronic is often caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. The disease is characterized by a sluggish course with periodic exacerbations. Based on the localization of the inflammatory process, the following forms are distinguished:
- antrum - in the lower part of the stomach;
- fundal - in the middle section (sometimes extends to the bottom of the organ);
- reflux gastritis - in the area of the pylorus of the stomach.
The chronic type of the disease is characterized by dysfunction of gastric secretion. Its excessive activity causes increased acidity (this form is called hyperacid). With secretory insufficiency, acidity is reduced (this form is called anacid).
Symptoms of gastritis
So, how can you recognize that you have begun to develop gastritis? It is worth listening to your body and analyzing why pain bothers you, at what time it occurs and how often it happens.
Symptoms of gastritis:
- abdominal pain: sharp paroxysmal or constant painful;
- nausea is constant or intermittent, often occurring immediately after eating;
- heartburn;
- belching with a sour smell;
- repeated vomiting (in the case of acute gastritis, vomiting with blood is possible, since internal bleeding may open in the stomach);
- increased salivation;
- sometimes dry mouth;
- bowel dysfunction: constipation or diarrhea;
- from the whole body: severe general weakness, dizziness, headache, sweating, increased temperature, decreased blood pressure, increased heart rate - tachycardia;
- decreased appetite;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach after eating;
- bloating, rumbling in the stomach, flatulence;
- anemia, brittle and dry hair, split nails.
Types of damage to the mucous membrane
Gastritis can also be classified according to the degree of change in the gastric mucosa. The mildest form is superficial, when the inflammatory process affects only the upper part of the mucosa. More dangerous forms include the following:
Although hyperplastic gastritis is characterized by the appearance of neoplasms, they are predominantly benign.
The atrophic form often leads to stomach cancer. Each of these types can be focal or diffuse: the first covers a small area of the mucous membrane (although there may be several of them), the second spreads over its entire surface.
Types of gastritis by etiology
The mucous membrane of the stomach can become inflamed for various reasons. Gastroenterologists, according to this criterion, divide diseases into several groups:
There are also mixed types. Thus, AC inflammation means that reflux is caused by autoimmune factors. It happens that autoimmune effects are combined with Helicobacter pylori infection. Then we are talking about AB gastritis.
How to clean your tongue
If you don't have any health problems that affect the plaque, just follow these guidelines and remember to brush until all the plaque is removed and your tongue is pink again. Typically, tongue hygiene takes only 20–30 seconds.
Recommendations for adults
- Proceed with the procedure only after brushing your teeth
and rinsing your mouth. - Use special tools
: scrapers, nozzles and others. - Clean your tongue using sweeping movements
and light pressure. - Start from the root of the tongue
and end with the tip. - Do not brush your tongue with cross movements and do not press
too hard - this can damage it. - Don't forget to clean the instrument
after the procedure. - Be sure to rinse your mouth
with water.
Should children have their tongues cleaned?
Children also need tongue care, but not earlier than 3–4 years.
For younger children, tongue cleaning is pointless. They don’t eat junk food, especially not in the same quantities as adults, and they don’t drink tea and coffee. Until 3–4 years of age, normal oral care is sufficient. From 3–4 to 8 years
This is how you should clean your tongue.
- Move from the root of the tongue to the tip
with smooth sweeping movements, with even weaker pressure than with adults. - Similarly, clean the sides
of the tongue and the inside of the cheeks. - Be sure to rinse your mouth
.
From the age of 8
you can already use scrapers.
Causes of acute gastritis
This disease appears suddenly. In rare cases, the cause may be the bacteria Helicobacter pylori entering the body. But usually it does not make itself felt instantly, but is the causative agent of sluggish chronic gastritis.
It is usually not difficult for an adult to determine the cause. It is enough to analyze what he ate and drank several hours before the attack. Inflammation can be caused by:
Infections can also cause an attack. Among the most likely, gastroenterologists identify cytomegaloverus, syphilis, and staphylococcus infection. People with weakened immune systems are more likely to become infected. Another reason for the development of an acute inflammatory process is exposure to bile. This only applies to type C gastritis.
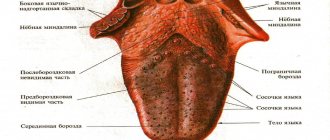
Is my tongue my doctor? What diseases can be identified by the organ of taste?
The tongue is one of the most important organs in the body. It contains receptors that allow you to recognize all shades of taste of products entering the oral cavity.
As scientists noted back in ancient times, human language has a connection with various organs of the body. When diagnosing, they divided it into conventional parts: basal, middle and tip. And they believed that in case of pathology of a particular organ, the lesion would be observed strictly in one of these areas. AiF.ru looked into what diseases leave their mark on the language together with Professor, Doctor of Medical Sciences, head of the laboratory for the development of an interdisciplinary approach to the prevention of chronic non-infectious diseases of the Federal State Budgetary Institution "State Research Center for Preventive Medicine of the Ministry of Health of Russia", expert of the National Health League Mehman Mamedov .
Color spectrum
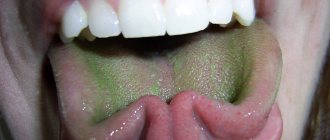
When examined by a doctor, you are often asked to show your tongue. And they do this not out of idle curiosity. After all, even by the color of the tongue it is quite possible to determine whether there is a particular disease. For example, the tongue of a healthy person should be pale pink: this is what is accepted as the norm. If there is a white coating on the tongue, we can talk about fungal infections of the body or disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. A gray tongue is usually the result of chronic pathologies. Bright red - will indicate infectious and inflammatory processes in the human body; if the red color has a shade of scarlet, doctors will suspect problems with the circulatory system. A burgundy tint is a clear sign of an acute infectious process. The tongue is part of the gastrointestinal tract, and is also connected with the respiratory system, because located in the oral cavity. With stomach and duodenal ulcers, problems with the gallbladder, liver and intestines, there may be changes in the color of the tongue. Each disease has its own manifestations - in some places it can be more contrasting, in others it can be lighter.
It also happens that the color of the tongue changes to blue and purple. In this case, they talk about problems with the lungs or severe kidney ailments. Yellowing of the tongue is not only a characteristic feature of a heavy smoker, but also a signal of problems with the gastrointestinal tract. If there is a lack of vitamins in the human body, the tongue may completely lose color.
It is worth considering that a shade that is too dark and saturated is a sign of problems that require immediate medical intervention, or even hospitalization.
Additional factors
However, not only color matters. If the tongue is too dry, the following diagnoses may be made: dehydration, intestinal obstruction, peritonitis. Often, dry tongue is observed with an increase in body temperature. If the situation approaches critical, the taste organ may even crack due to dryness. In this case, an additional threat is created: it is easily infected with bacteria, resulting in suppuration and severe inflammation.
The type of coating on the tongue is also of particular importance. So, if it is thin, it means that the disease is in the initial phase, and if it is frankly fatty and thick, then the problem most likely lies in pathologies of the gastrointestinal system: this usually happens if mucus has accumulated there and food stagnates. A spotted and purple coating indicates the development of blood stagnation. Malfunctions in the digestive system will cause the tongue to become slightly swollen and wet. In this case, it is recommended to be checked for gastritis, cholecystitis, ulcers and even appendicitis.
Doctors pay special attention to the place where plaque accumulates. So, if it is more adjacent to the root of the tongue, then problems are noted in the large intestine: most likely, many human waste products have accumulated there and cannot find a way out. Plaque in the middle indicates problems in the small or duodenal intestine or stomach. If the plaque is so thick and the tongue is so swollen that you can see teeth marks along the edge, you need to reconsider your diet: with a high degree of probability it can be said that the intestines cannot cope with the food that a person eats.
The presence of deep wrinkles and cracks located transversely should alert you and send you to a neurologist - as a rule, this problem manifests itself with a predisposition to vascular disorders of the brain.
The tongue can even indicate serious cardiac and vascular problems, which may occur without any symptoms for some time. For example, a tongue that is slightly shifted to the side or slightly bent will indicate a hemorrhagic stroke, cerebrovascular accidents, or problems with the functioning of the cerebellum.
An increase in the volume of the taste organ may be a consequence of problems with the thyroid gland, malfunction of the pituitary gland, or mental disorders.
Shaky and grainy
Sometimes a person may notice that his tongue... trembles. This condition indicates nervousness and problems with the central nervous system. In such a situation, doctors recommend changing the psychological environment, as well as working on your lifestyle. It is also worth checking with a doctor if your sense of taste begins to decrease. After all, it does not develop out of the blue: there must be a reason why a person no longer feels the tastes to which he is accustomed. Moreover, it is important to understand that there are certain zones and areas on the tongue that are responsible for the reaction to different tastes: spicy, salty, sweet, etc. If a malfunction is noted in any of the parts, this may indicate that the nervous system is suffering. or endocrine system. Loss of taste in the taste buds of the tongue manifests itself as a result of metabolic disorders in the human body, as well as malfunctions of the central system of various etiologies, the development of anemia and the presence of cancer.
Also, people often begin to notice that the tongue has become rougher: this is due to an increase in the size of the papillae on the surface of the organ. When swollen papillae are localized at the tip, it is worth being examined by a cardiologist. If the tongue becomes “spiky” around the edges, you need to check the liver. An affected middle part of the tongue indicates problems in the stomach and intestines. At the same time, you should not rejoice when the tongue becomes smooth and “mirror-like”. After all, this is also a pathology. This happens with anemia, exhaustion or severe pathologies of the stomach.
Causes of development of chronic gastritis
The second most important cause of chronic inflammation of the gastric mucosa (after the bacterium Helicobacter pylori) is poor nutrition. This includes not only harmful products. Violation of the eating schedule is also detrimental to the stomach. Inflammation can result from:
The influence of other diseases (endocrine, metabolic, infectious, hypoxic) cannot be excluded. External factors (harmful working conditions, stress) also become causes of gastritis.
Prevention of gastritis
To prevent gastritis, you should adhere to a healthy lifestyle: stop smoking, do not abuse alcohol, avoid stress and engage in any type of physical activity. It is especially important to monitor your diet. It must be complete and balanced. Try to include less junk food in your diet, do not skip meals, make sure that your body fully receives the necessary substances: proteins, fats, carbohydrates, minerals, micro- and macroelements, vitamins.
You can make an appointment with a gastroenterologist at the Naedine Clinic by phone in Kirov: (8332) 32-7777 or through the form on the website
General signs of gastritis
Regardless of the type (acute or chronic), it always manifests itself as pain in the epigastric region (only its nature differs). Pain appears after eating or, conversely, from hunger. Other symptoms from the digestive system are possible:
Symptoms in adults are more severe than in children. In children, attacks are often accompanied by weakness, fever, and bruises under the eyes. Parents may confuse the first signs of gastritis with poisoning.
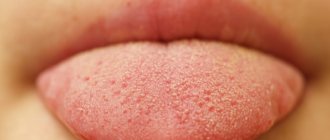
Another noticeable symptom of many types of this disease is a white (less often yellow) coating on the tongue. It is not cleaned during normal hygiene procedures. In most cases, plaque indicates a decrease in acidity.
Stomach ulcer
The symptoms of the disease and its nature are generally similar to the symptoms of gastritis, but its manifestations are more striking and persistent. Standard gastrointestinal pathologies can develop into a gastric ulcer due to increased stress, frequent and unnecessary medications, alcohol and tobacco abuse, or genetic predisposition.
Dental symptoms - swelling of the tongue, plaque on the oral mucosa, enlargement and increased sensitivity of the papillae of the tongue, increased temperature in the mouth, gingivitis and stomatitis
.
Treatment:
similar to the treatment of chronic gastritis or gastroduodenitis.
How to treat the disease
Since there are many types of gastritis, and each of them has its own causes, you cannot limit yourself to one treatment method. To combat each provoking factor, appropriate drugs are needed.
The doctor must determine by characteristic signs whether the patient’s acidity is increased or decreased. Depending on this, a suitable treatment regimen is selected.
Treatment of gastritis is usually complex, it is carried out in the following areas:
If the bacterium Helicobacter pylori is detected, it is important to eradicate it (complete destruction) with antibiotics. This is necessary to eliminate ulcerations, accelerate their healing and prevent the development of peptic ulcers and stomach cancer.
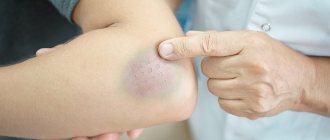
Causes
If we exclude everyday causes associated with mechanical damage to the mucous membrane of the tongue, swelling is almost always a symptom of other diseases. Therefore, you cannot delay visiting a doctor. The most common reasons are:
- Allergic reaction. Swelling can be caused by taking medications or foods that cause allergies. Typically, patients prone to allergies are aware of their problem. If you suspect allergic edema, you should consult a doctor. A severe allergic reaction can cause angioedema or angioedema. This condition develops rapidly, quickly spreading to the lips, cheeks, and larynx. The patient finds it difficult to breathe. In the most severe cases, angioedema can be fatal.
- Mononucleosis. A disease characterized by inflammation of the throat. Swelling of the tongue with mononucleosis is one of the accompanying symptoms.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Edema develops against the background of colitis, enterocolitis, peptic ulcer, gastritis and other diseases. This reason is one of the most common.
- Hormonal disorders. For many diseases associated with hormonal imbalances, a swollen tongue is one of the symptoms.
Swelling of the tongue is not always a symptom of other diseases. Swelling often appears for everyday reasons:
- Bite.
- Burn.
- Mechanical damage (dentures, braces, poor-quality fillings, piercings, etc.).
How is acidity level determined?
The main acid found in the stomach and determining its acidity level is hydrochloric acid. It is produced by parietal cells. The alkaline components of gastric juice neutralize hydrochloric acid. They are produced by accessory cells of the mucosa. The two substances interact and the acidity level changes throughout the day.
You can find out its level using intragastric pH-metry. To do this, a thin probe with a measuring electrode is placed into the patient's stomach. It gradually moves deeper and shows the pH in different areas of the organ.
In the part of the stomach where acid is produced, in an adult patient the pH should be from 1.6 to 2.0, and in the zone of alkali production and acid quenching - up to 5.2.
The doctor also pays attention to the symptoms. With high acidity, the patient suffers from heartburn, belching and a burning sensation in the throat; with low acidity, the patient suffers from bloating, flatulence and bad breath.
Is plaque on the tongue dangerous - how to treat it
An ultrasound of the stomach will help clarify the diagnosis.
Plaque itself does not pose any threat to health. As soon as the underlying disease is cured, the condition of the tongue will return to normal.
As for gastritis, long-term treatment with careful adherence to the recommendations of a gastroenterologist will help relieve its symptoms.
Perhaps the doctor will conduct research aimed at clarifying the diagnosis: FGDS, ultrasound of the stomach, laboratory tests of blood and gastric juice. The following drugs will be prescribed as treatment:
- Antibiotics of 2-4 types, taken in combination:
- Pro- and prebiotics;
- Vitamins;
- Antacids;
- Proton pump blockers.
Patients with gastritis must follow a strict diet aimed at sparing the gastric mucosa and not provoking the release of excessive amounts of hydrochloric acid. With this treatment, not only the gastric mucosa, but also the condition of the tongue will definitely return to normal.
Treatment of acidity disorders
If there are signs of low acidity, replacement therapy with enzyme preparations is prescribed. Its main task is to normalize the production of pepsin. Preparations containing acedin-pepsin help with this. Drug stimulation of gastric juice secretion is also necessary.
If the diagnostic results reveal increased acidity, the patient is prescribed antacids. They neutralize acid, weaken the activity of pepsin, and in some cases have an enveloping effect. To eliminate symptoms, medications are recommended that stimulate gastrointestinal motility and relieve spasms of smooth muscles. Additionally, you can use folk remedies - herbs, flax seeds, potato juice.
Why are gastroprotectors needed?
To prevent complications such as peptic ulcers and malignant tumors, it is important to keep the structure of the mucous membrane intact. Gastroprotectors are used for these purposes:
They should be taken when signs of gastritis appear. The doctor will determine which medications will fit into the selected treatment package. For prevention purposes, you do not need to drink them.
The stomach contains natural gastroprotectors - prostaglandins. They stimulate the formation of mucus, improve microcirculation and protect cells from destruction. If they are not produced enough, the gastroenterologist may prescribe their synthetic analogues. If the patient is being treated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, drugs with prostaglandins prevent ulcerative lesions of the mucous membrane.
Forms and stages of gastritis
Inflammatory processes in the mucous tissues of the stomach develop gradually. In the initial stages, gastritis can be practically asymptomatic. But sooner or later the disease makes itself felt and becomes acute.
Acute gastritis is characterized by a sharp deterioration in health, the appearance of acute pain and heaviness in the stomach. Often, an exacerbation can be triggered by some irritant, for example, after taking medications, spicy food, alcohol, etc.
If acute gastritis is not treated in time, the disease may progress to the next stage. Chronic gastritis develops in 85% of cases. Periods of remission are followed by exacerbations of the disease, which in the future can lead to such serious consequences as gastric ulcers or even oncology.
Preventive measures
Since gastritis is now diagnosed not only in adults, but also in children, prevention should begin as early as possible. First of all, you should normalize your diet:
When the first symptoms of inflammation of the gastric mucosa appear, it is important to minimize (or better yet eliminate) the consumption of chocolate, coffee, spicy and fried foods.
Gastroenterologists recommend regularly checking for parasitic infestations. When they are detected, it is important to carry out timely treatment, because they often attack the digestive system.
How to clean your tongue
Do not use regular toothbrushes for cleaning - they will not be able to remove plaque. It is better to pay attention to special tongue cleaning products.
Scrapers
The most common devices are scrapers. The tips of the scrapers are made in the shape of a spoon. They are usually made of plastic, sometimes with stiff bristles. The flat shape prevents the gag reflex that may occur when brushing the root of the tongue. This scraper needs to be changed every six months.
Irrigator attachments
Tongue attachments are also made in the form of a spoon. The irrigator, unlike a conventional scraper, delivers a stream of water, which additionally washes the surface of the tongue.
Attachments for electric brushes
Most brush manufacturers offer special attachments for their products to clean tongue deposits. As a rule, they have a flat, textured rubber surface.
Tongue gels
You should not clean your tongue with toothpaste - it is intended for teeth. Pastes contain abrasives and menthol, they can irritate the mucous membrane. Special gels that gently dissolve plaque and also disinfect the oral cavity are better suited for the tongue.