In the first year of life, a child develops rapidly. He learns to sit, crawl, walk. He also develops something that indicates general physiological development and maturation of the digestive system. He is preparing to transition from eating exclusively milk or formula to a new stage - to eating semi-solid and solid foods and the appearance of the first milk teeth .
The eruption of the first baby teeth is influenced by genetic characteristics, health, nutrition and other factors. It has even been established that teething in infants depends on the region of residence. Thus, in the northern regions of Russia, there is a frequent deviation from the average timing towards later eruption [1].
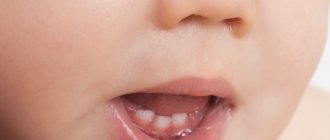
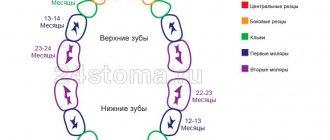
On average, the first baby tooth appears at 6-7 months. Within three years, all 20 baby teeth will take their place in the dentition. Some babies start teething at 4-5 months, others wait until 10-12 months. All this is within the normal range [2].
There are several theories explaining the process of teething [2]:
- Hunter's theory - pushing a tooth out of the bone alveolus occurs due to the pressure of growing roots;
- Yasvoin's theory - the appearance of a tooth above the gum is provoked by differentiation processes in the tissue of the dental papilla;
- Katz's theory - an increase in tissue pressure in the area of the bottom of the alveoli directs the tooth to the surface.
But none of them can fully explain this complex mechanism.
By the time the tooth erupts, the area of bone covering the crown of the tooth is reabsorbed.
The same processes are observed in the gums. During the growth of the tooth root, bone restructuring and gradual deepening of the dental alveoli also occur. At the same time, morphological changes occur in the tissues surrounding the tooth: increased blood flow, changes in vascular permeability, increased production of the main substance of the pulp and periodontium. “Can the physiological process of teething in infants be pathological?” Doctor of Medicine, Professor, Chief Pediatrician of the Central Federal District of the Russian Federation, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation Zakharova I. N. [2]
It is not surprising that the appearance of teeth causes discomfort in children at any age, but this process is especially difficult for infants.
Symptoms of teething in a child
The appearance of primary teeth is a natural physiological process, however, a number of children develop a symptom complex, which, according to the International Classification of Diseases, is classified as teething syndrome (ICD code - K00.7). Numerous examinations of young children indicate that the most common symptoms accompanying the appearance of teeth are:
- increased salivation - processes in the oral cavity are activated;
- irritability - the child experiences severe discomfort and cannot communicate this in any other way than by changing behavior;
- sleep disturbance - the pain is so severe that the baby cannot sleep or often wakes up during the night;
- itching of the gums - children try to compensate for this by trying to bite the breast or pacifier, by trying to hold their hands, toys, clothes in their mouth.
Such precursors of the appearance of a tooth occur in 35-60% of children. But some infants may experience nonspecific symptoms [2]:
- cough;
- runny nose;
- rash;
- diarrhea;
- heat;
- refusal to eat.
On average, symptoms appear 5-8 days before the tooth appears. When several teeth erupt at the same time, this usually increases discomfort.
Even if the picture of the child’s illness is very similar to the symptoms of teething, consultation with a specialist is necessary. Be sure to consult a doctor if you experience diarrhea or fever for a long time.
Causes
Swelling of the cheek can occur for various reasons, the main ones:
- mechanical injury or bruise;
- development of dental diseases;
- a bite of an insect;
- if the swelling is accompanied by pain in the ear, then we can talk about an inflammatory process in the ear canal;
- redness of the cheek may be a symptom of an allergic reaction;
- If it becomes difficult for a child to breathe, you need to immediately call an ambulance; it could be Quincke's edema.
Since we are talking about a baby, there is no need to guess and find out the cause; you need to see a doctor or call an ambulance as quickly as possible.
A swollen cheek can be a symptom of various dental diseases:
- Deep caries. Symptoms: pain, swelling of not only the cheeks, but also the gums.
- Pulpitis. Symptoms: severe aching pain, bad breath.
- Periodontitis. The main symptom, in addition to swelling of the cheek, is pain while eating.
- Periostitis (flux). Symptoms: pain, swelling of the gums, high body temperature.
Pain and swelling of the cheek can also develop as a result of the following reasons:
- Removal of a tooth. After the procedure, swelling may persist for the first couple of days.
- Orthodontic treatment. Installed braces may cause slight swelling of the cheek.
- Treatment of pulpitis. Improper canal filling can lead to pain after treatment and an enlarged cheek.
- Teething. The appearance of teeth may be accompanied by slight swelling not only of the gums, but also of the cheeks.
An enlarged cheek does not always indicate problems with teeth or gums; there are other factors and diseases that can cause a similar condition:
- Sinusitis is an inflammatory process of the nasal mucosa. In this case, nasal congestion and difficulty breathing are observed.
- Lymphadenitis is inflammation of the lymph nodes. Manifested by enlarged lymph nodes.
- A cyst is the formation of a small lump in the oral cavity.
- Impaired kidney function can be accompanied by swelling of various parts of the body, including the cheeks.
- Facial neuritis. Swelling occurs due to pressure on the nerve.
All of these diseases require immediate help and treatment.
If the cause is injury or bruise, swelling should be accompanied by a hematoma. In this case, the damage most likely occurred due to biting the mucous membrane or due to careless handling of the brush while brushing the teeth.
If a hematoma is not observed, the injury may be the result of an incorrect bite or poorly installed fillings that injure the oral mucosa.
A severe burn due to eating too hot food can also cause cheek enlargement.
Ways to relieve discomfort
To make teething easier for your baby, you need to:
- provide additional attention and care from parents;
- if the baby is breastfed, put him to the breast more often, as this has a slight sedative effect;
- purchase several silicone teethers that can be cooled and offered to the child throughout the day;
- massage the gums with a finger wrapped in a clean gauze swab or a special silicone nozzle;
- promptly blot away any saliva with a clean napkin to avoid irritation of the skin around the mouth;
- if necessary and in consultation with a doctor, use medications.
Today, there are pharmacological and non-pharmacological methods of therapy for the eruption of primary teeth.
Local preparations
As a symptomatic aid for severe discomfort associated with teething, the pediatrician prescribes gels and ointments.
Such gels and ointments for teething with proven effectiveness are divided into 3 groups [1]:
- Preparations with an anesthetic effect based on anesthetic (lidocaine, choline, benzocaine). Sometimes lidocaine-based drugs contain anti-inflammatory or antiseptic components, providing a combined effect of the gel.
- Medicines based on anti-inflammatory or antiseptic agents.
- Preparations based on medicinal plant extracts. They use extracts of Roman chamomile, boswellia, aloe, marshmallow, Indian ivy, rhubarb, calendula and other components of plant origin.
Homeopathic remedies for teething are also produced, but their effectiveness has not been scientifically proven [1].
Systemic drugs
In cases of severe pain and hyperthermia, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used, which reduce body temperature and have a systemic analgesic effect. The dosage and drug suitable for the child should be selected by a pediatrician.
Distractions
These include: the gum massage described above and baby teethers, which help the child temporarily reduce itching in the gums.
Baby's red cheeks: should I worry?
Children's skin is incredibly sensitive to both environmental influences and the child's general well-being. Therefore, in some cases, red cheeks are a reason to think about the baby’s health.
Response to environmental influences
Red spots on a child's cheeks may be a banal reaction to cold or heat. The process of heat exchange in infants does not proceed the same way as in adults, so red cheeks can signal overheating or, conversely, too close contact with frost. In the first case, the baby must be immediately cooled, and in the second, apply protective cream to exposed skin 20 minutes before going outside.
Manifestation of allergies
Have your baby’s cheeks turned red, started to peel and even itch? This may be a manifestation of an allergy - food, household chemicals, dust or animals. Often the redness of the cheeks in this case is also accompanied by the appearance of redness in the area of the shoulders, forearms and groin. Be sure to consult a doctor to find out why your child has red cheeks and to eliminate the allergen from the environment that causes such a reaction in the baby.
Atopic dermatitis
Babies suffering from atopic dermatitis often experience redness, which is accompanied by severe dryness, itching and even crusts. As a rule, there are pockets of dermatitis on other parts of the body, and dryness and redness do not go away with the use of conventional moisturizing creams. Atopic dermatitis is a serious reason to see a doctor.
Enzyme deficiency
Enzyme deficiency usually manifests itself in children in the first year of life. One of its symptoms is redness of the baby’s cheeks (in this case, the child may not gain weight). When a baby eats more than his body can absorb, the unprocessed protein causes an allergic reaction and, as a result, reddening of the cheeks. In this case, you should carefully monitor the amount of food offered to the child, especially when artificial feeding.
Teeth cutting
Redness of the cheeks and swelling of the gums are sure signs that a new tooth will soon appear. At this time, the baby’s behavior may also change: he rubs his ears and cheeks, becomes irritable, and sleeps restlessly. You can alleviate the baby’s condition with special teethers or a soothing gel (as prescribed by a doctor).
Viral or infectious diseases
Red spots on a child’s cheeks are far from the only symptom that parents should pay attention to. For example, with ARVI this can be a fever, cough and runny nose, and with infantile roseola - loose stools, fever and a rash (first on the cheeks, and later throughout the body from the face to the feet). Red cheeks combined with pale lips and the tip of the nose can also be a sign of pneumonia. In all these cases, it is necessary to contact your pediatrician as soon as possible.
Everything is fine!
The most common cause of red cheeks in a child is an allergic reaction. But it is quite possible that the child simply spent an active day, moved and laughed a lot, or took a long walk in the fresh air. Such a blush is a joy for the mother and a sign of the baby’s excellent health!
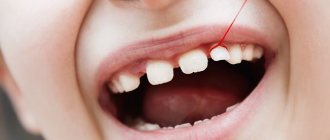
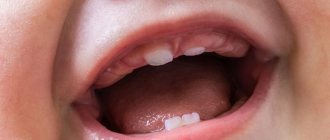
Examination of erupted teeth
Swelling and redness of the gums gradually disappear as the baby’s teeth erupt and grow, but require observation. Normally, teeth should be evenly positioned in the dentition, without whitish or colored spots, or unevenness in the enamel.
Violation of the timing, pairing and sequence of eruption of primary teeth can serve as a marker of various diseases and disorders. For example, rickets or hypothyroidism [2]. It is important to record the date of appearance of each tooth and its location in the mouth. This is convenient to do using photos saved in a separate folder on your smartphone.
Or maybe this rash is not on the teeth?
The rash can be caused by a variety of viruses and is usually associated with fever.
According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, teething may be accompanied by a slight increase in body temperature (below 38C), but this is not considered fever, which is characteristic of viruses.
Red, puffy patches may also be eczema, known as atopic dermatitis. True, most often, unlike a rash on the teeth, eczema appears on the folds (behind the knees and ears, in the inner bends of the elbows and on the hands).
Rules for caring for emerging teeth
To clean infants' teeth, use special silicone fingertips with soft bristles. Toothpaste must be labeled to indicate that it is suitable for young children and does not contain substances that are hazardous if swallowed: high concentrations of fluorides, parabens, sodium lauryl sulfate.
As soon as the first tooth appears above the gum surface, it requires special care . The enamel has not yet fully formed, it is very thin, so childhood caries develops rapidly. Only 10% of children succeed in avoiding caries, and it is almost impossible for adults to avoid caries [5]. Therefore, you should not postpone the preventive fight against it.
To maintain the health of baby teeth, some of which will remain with the child until 10-12 years old, it is important to regularly visit the dentist once every 3-4 months. After a year, it is necessary to visit an orthodontist to make sure that the bite is developing correctly.
List of sources
1. Zaplatnikov A. L., Kasyanova A. N., Maykova I. D. Teething syndrome in infants: a new look at an old problem 2018 // https://www.rmj.ru/articles/pediatriya/Sindrom_prorezyvaniya_zubov_u_mladencev_novyy_vzglyad_na_staruyu_problemu / (date of access: 05/28/2020).
2. Zakharova I. N., Kholodova I. N., Dmitrieva Yu. A., Morozova N. V., Mozzhukhina M. V., Kholodov D. I. Can the physiological process of teething in infants be pathological? 2016 // https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/mozhet-li-fiziologicheskiy-protsess-prorezyvaniya-zubov-u-mladentsev-byt-patologicheskim (date of access: 05/28/2020).
3. Kleshchenko E. I., Zhdanova I. A., Lukisha A. N., Krakovets I. V., Smychkova E. V., Kartavtseva A. V. Symptoms of teething in infants: condition or disease? 2022 // https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/simptomy-prorezyvaniya-zubov-u-mladentsev-sostoyanie-ili-bolezn (date of access: 05/28/2020).
4. Kiselnikova L.P., Drobotko L.N. Eruption of primary teeth in children // https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/prorezyvanie-vremennyh-zubov-u-detey 2017 (date of access: 28.05. 2020).
5. 90 percent of children and 100 percent of adults suffer from caries, Komsomolskaya Pravda, 09/04/2016 // URL: https://www.kp.ru/daily/26429.7/3300802/ (access date: 07/21/2020).
How can you prevent tooth rashes from appearing?
Here are some tips to help avoid dental rashes:
- Wipe drool gently and frequently with a soft cloth to remove the irritant.
- Stock up on soft bibs that will stop drooling.
- Change clothes wet from drool to dry ones.
- Use petroleum jelly or a healing baby ointment containing petroleum jelly (for example, Aquaphor), which will create a barrier to protect the skin from drooling.
Dr. Jones assures that getting a small amount of ointment on a child's lips is harmless.
You can also use lanolin ointment.