When visiting a dentist, you have probably heard them more than once say such phrases as, for example, “lower left five” or “16th tooth” or “2nd premolar.” Experienced patients know that this is the numbering of the teeth, which is necessary for the doctor to describe the condition of the oral cavity when filling out the card. There are several systems used in dental practice for this purpose.
Location of teeth by numbers
Despite all the individual characteristics of each person, the location of the teeth and their name are the same for everyone. This is explained by the fact that dental elements begin to form long before birth (approximately 2-3 months of embryogenesis), and at birth the child has all the dental buds located deep in the jaw.
In both adults and children, the dentition is symmetrical - the upper and lower jaws have the same number of teeth of the same name (the reference point is the midline of the face).
The table shows the order of the teeth and their correct name.
| Serial number | Dairy | Permanent |
| 1 | central incisor | central incisor |
| 2 | lateral incisor | lateral incisor |
| 3 | fang | fang |
| 4 | first molar | first (small) premolar |
| 5 | second molar | second (small) premolar) |
| 6 | — | first (large) molar |
| 7 | — | second (large) molar |
| 8 | — | third (large) molar |
As can be seen from the table, only the front teeth (incisors and canines) have the same names and locations in children and adults. The rear (or “root”) have significant differences.
Alternatives
An alternative method for restoring sixes is a bridge prosthesis. This is a structure consisting of crowns tightly connected to each other. To restore one tooth, the bridge consists of 3 crowns. The two outer ones are fixed on the teeth on both sides of the defect. The supporting teeth are ground down to form the internal cavity of the outer crowns of the prosthesis. The middle crown is hinged and imitates the lost six.
This option is cheaper than implantation, but has disadvantages - grinding the enamel of living teeth leads to a reduction in their service life. Another important point is that the bone under the hinged crown does not receive stress during chewing, so bone tissue atrophy is inevitable.
Why is tooth numbering necessary?
All human teeth have their own specific location according to numbers. But how can you understand whether it is located on the upper or lower jaw, or on the left or right? You can use full formulations (for example, the first permanent molar of the upper jaw on the right). But such cumbersome names create certain difficulties for dentists and can often cause mistakes, which are especially dangerous if the patient is undergoing extraction of a diseased tooth.
In order to optimize the work of doctors and simplify the designation of tooth numbers as much as possible, special numberings were invented.
Guarantees
In our Center, implants are installed with a lifetime warranty from the manufacturer - Nobel Biocare. We provide guarantees:
- lifetime for the installation of implants;
- 1 year for crowns.
The warranty program includes a complex for the implant, surgery, bone reconstruction and prosthetics.
The guarantee is valid provided that the patient follows the doctor’s recommendations, care rules and regularly visits the dentist.
Tooth numbering schemes in dentistry
Currently, tooth numbers in dentistry are systematized according to several schemes:
- Universal numbering system.
- Square-digital or Zsigmondy-Palmer system.
- Haderup system.
- American numbering or alphanumeric system.
- European numbering Viola or WHO system.
Let's take a closer look at the features of each of them.
Universal system
This numbering scheme is based on assigning each permanent tooth a specific number from 1 to 32. In primary occlusion, each tooth has its own letter. In this case, the count is carried out from the right half of the upper jaw clockwise from the wisdom tooth.
The dental formula of a permanent set according to the universal system looks like this:
Milk teeth are marked according to the same principle, but only using letters of the Latin alphabet:
Zsigmondy-Palmer system
This numbering is the most imperfect, since it still indicates the teeth under numbers without a more precise indication of their location. At the same time, Arabic numerals from 1 to 8 are used for the permanent set, and Roman numerals (IV) are used for numbering dairy products.
The digital system does not exclude errors when carrying out diagnostic or therapeutic measures, therefore, today it is used only by orthodontists (for example, when installing and marking braces) or maxillofacial surgeons. And entries on it in the patient’s medical record are made only on a special diagram.
Haderup system
Numbering according to the Haderup system also applies to digital numbers. To designate the teeth of an adult, Arabic numbers 1-8 are used with a plus or minus sign in front of them. The “+” sign is used to number the upper ones, and the “-” sign to indicate the lower ones.
The numbers of children's teeth are similarly written in Arabic numerals with the signs “+” or “-”, but at the same time the number “0” is placed in front of them.
The inconvenience of such a system is the need to indicate the location of the tooth on the left or right side of the jaw.
American alphanumeric system
This numbering is widespread in the USA. The alphanumeric system is based on assigning a letter value to each group of teeth (capitals for a permanent set, and capitals for a primary set), as well as a digital code that indicates the location of the tooth in a correct bite.
Letter meanings of teeth:
- I (i) - permanent (deciduous) incisors;
- C (s) - permanent (deciduous) fangs;
- P - premolars (absent in primary dentition);
- M (m) - permanent (deciduous) molars.
American numbering also does not take into account the left- or right-sided position of the tooth, which can cause certain difficulties.
European international numbering Viola
Today, this is the newest and most advanced teeth numbering system. Its essence lies in the fact that the jaws are divided into segments (2 on top and 2 below), each of which is assigned its own number. For adults, numeric values are used 1-4, and for children - 5-8. As a result, each tooth receives a two-digit number, the first digit of which indicates a specific segment, and the second - a serial number.
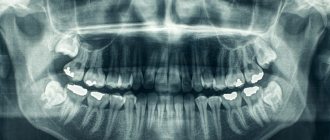
The convenience of the Viola system lies in the absence of cumbersome names while accurately indicating the location of the required tooth and the minimal risk of error. This numbering is indispensable when sending a patient for an x-ray, as well as when identifying teeth on a panoramic image.
How to determine the tooth number - practice with examples
Determining which teeth numbers are quite simple, you just need to practice a little with examples.
Tooth number 37 - which one is it?
To an unknowing person who is not familiar with the numbering systems in dentistry, it may seem that we are talking about an extra 5 teeth in the mouth. But that's not true. According to the Viola system, teeth with numbers starting with three are located on the lower jaw on the left. And serial number 7 corresponds to the second molar. This means the 37th tooth is the second lower molar on the left.
What number corresponds to the upper right wisdom tooth (eight)?
The third molar will be designated differently in different systems.
- In the universal number scheme - number 1.
- According to the Zsigmondy-Palmer scheme - “upper right eight”.
- According to the Haderup system - “+8 on the right”.
- In the American scheme - “upper M3 on the right”.
- According to the Viola system - number 18.
For a school-age child, the dental formula says that next to tooth 21 there is tooth 62. How can this be?
In children at 6-7 years old (less often at 8-9 years old), the replacement of milk teeth begins. Therefore, both teeth from a temporary set and already erupted permanent teeth can be located in the mouth at the same time. In this situation, they are numbered according to the Viola system, and their numbers indicate that the central upper incisor on the left (number 21) has already been replaced by a molar, but the lateral incisor is still from the primary bite (therefore it is marked under number 62).
Reasons for creating the formula
Why is numbering of row elements necessary and how does it work when performing dental work? Each tooth has its own structural features, as well as a range of tasks performed. Some elements are involved in the process of biting off large pieces, others grind and crush foods for further better absorption in the body. Only wisdom teeth, which are inherited from ancient ancestors, do not take part in the process of chewing food. Due to the heat treatment of foods and the consumption of softer foods, the size of the jaw of modern humans has decreased, and wisdom teeth have ceased to perform their functions.
However, doctors strongly advise caring for eights, treating them if necessary, like other elements. Wisdom teeth prevent the development of bite pathologies and can be used for prosthetics if, for example, sevens are missing.
The dental formula must be entered into the patient’s outpatient record in order to minimize the risk of errors during further treatment. In dentistry, it is customary to number the dentition from the central part of the jaws. Concise markings allow clinicians to quickly complete the information in the chart so that it is understandable to another dentist or dentist. Doctors cannot use individual calculation schemes, as this will complicate the work of another specialist and change the information in the patient’s hospital record.
And there is also a special formula with which parents can determine the required number of milk units in the baby’s mouth. It looks like this: N = n - 4, where N is the number of milk elements in a child, and n is the baby’s age in months. The result calculated using the formula does not always coincide with the actual number of elements erupted in the child. Mismatches in the formula are not a reason to panic. Each child’s body is individual and minor deviations from the norm are acceptable. This calculation formula only applies to children under 2 years of age.
Symptoms that require consultation with a doctor include:
- complete absence of teeth in the oral cavity in a child older than 12 months;
- the presence of less than 10 teeth in the mouth of a 3-year-old child;
- non-compliance with the pattern of eruption of milk elements (for example, if the canines or premolars erupt first, and not the incisors);
- defects on the enamel.
Numbering for an abnormal number of teeth
If a person has a normal number of teeth in his mouth, then their numbering does not cause difficulties and remains constant both at a young age and after 60 years.
If some teeth are lost (for example, due to various diseases or developmental anomalies), then in the dental formula next to the corresponding number its absence is simply indicated.
But there are diseases of the dental system, which are characterized by an increase in the number of teeth with an atypical arrangement. With such options, the use of any numbering schemes is difficult and most often dentists refuse to use them. In this case, complete information about the number of teeth, their description and location is entered into the patient’s medical documentation.
Price
Our Center has a case payment system, which means that the case includes all materials and necessary manipulations.
The cost of implant installation includes:
- implant and superstructures;
- work of an implantologist;
- anesthesia;
- basic bone building complex;
- primary and repeat CT.
The price of implants varies depending on the type of bone. Nobel Biocare PMC (cheaper) is intended for weak tissue, and Nobel Biocare Conical Parallel CC (more expensive) is intended for dense tissue.
The cost of the crown includes:
- production of a prosthesis by a technician;
- taking impressions;
- installation of a crown.
Tooth extraction (for simultaneous implantation), bone grafting or sinus lifting are paid separately. Prices for services can be found here.