Adentia is the acquired or temporary absence of teeth. Pathology may affect all teeth or some of them. The article will describe the symptoms, causes of the problem, features of the course and treatment options.
At the moment, it has not been possible to establish the causes of the disease; it is assumed that it develops during the resorption of the follicle. It can develop under the influence of general diseases or as a result of inflammatory processes. Follicle resorption is also possible under the influence of various toxic diseases.
Primary full
This type of missing dentition is recognized as a severe anomaly, but is rare. Occurs in the occlusion of permanent or baby teeth; with the disease, there are no rudiments of all teeth. The disease is extremely severe and inevitably leads to a violation of the proportions and symmetry of the facial skeleton. Also, in such individuals, the alveolar processes of the jaws develop with deviations, and the membrane in the oral cavity is pale and dry.
In the case of edentia, the rudiments of baby teeth are not detected, which can be diagnosed by palpating the jaw. The X-ray results show that the jaws are underdeveloped and there are no rudiments of teeth. This affects a significant reduction in the proportions of the lower jaw.
The problem with the permanent dentition is detected at the stage of changing teeth; as a result of x-rays, the absence of rudiments and the impossibility of forming a permanent bite are established. This is how the lower jaw rises closer to the upper, leading to asymmetry of the skull.
Causes (etiology)
The fundamental cause of adentia is the absence or unformation of tooth buds. In the primary condition, the pathogenesis may be inherited or due to detrimental effects during the construction of the fetal dental plate.
Complete adentia from birth in children is a fairly rare manifestation that occurs due to ectodermal dysplasia. The general state of health is complicated by: incomplete development of hair structures, layers of the epidermis, nail plates, excretory glands, eye lenses, and the central nervous system.
Other known reasons include:
- lack of minerals and vitamins in the intrauterine development of the fetus, resulting from illnesses of the mother during pregnancy;
- childhood diseases;
- genetics;
- pathology of the thyroid gland;
- disruption of the formation of the outer layer of the embryo;
- taking medications for the treatment of concomitant diseases (antibiotics, chemotherapy);
- inflammatory purulent processes in the jaws.
The origin of secondary loss of units can be complicated by caries, trauma, phlegmon and abscesses, poor-quality treatment and prosthetics.
Primary partial
This type of problem is much more widespread; in such a situation, the absence of several or one tooth (permanent or baby) is discovered. Tremas (gaps between teeth) are found in a person; they replace teeth that were not blocked. If there are too many of these three, the jaw will be underdeveloped.
Partial absence of rudiments manifests itself both with and without symmetry; incisors may be missing on both sides or different teeth on one and the other side of the jaw.
Secondary full
The problem relates to acquired diseases. With this form, teeth are completely absent in the lower and upper jaws. Deviation from the norm can occur both with baby teeth and with the loss of permanent teeth. It is formed as a result of tooth loss as a result of their falling out or surgical removal.
The absence of entire teeth leads to distortions of the jaw, its lower part is too close to the nose area, and it also leads to severe retraction of the soft tissues near the mouth. The body of the jaw itself and the alveolar processes atrophy, patients cannot clearly pronounce all types of sounds, chew and bite food.
Disease prevention
The best prevention of pathology will be high-quality care for teeth and gums: complete teeth cleaning, prof. examinations by a specialist once every 6 months, smoking cessation, proper nutrition.
If you or your family members are faced with this pathology, contact the specialists at West Dental. Experienced doctors at the branches in Yanino-1 and Vsevolozhsk will help you choose high-quality therapy.
Call and make an appointment by phone: +7 (812) 450-00-07. Our clinics are open every day from 9 am to 9 pm.
Symptoms
A specialist can determine the presence of the disease. The main symptom is the absence of the entire dentition or individual teeth. In addition, there are a number of indirect symptoms:
- alveolar processes are atrophied;
- one or all jaws have undergone reduction;
- a large number of wrinkles are visible around the mouth;
- the tissues around the face sink;
- the angle of the jaw is blunted;
- the muscles around the mouth are atrophied.
In the case of partial manifestation, the bite becomes distorted and deep, and over time the teeth shift towards the gap area. In parts where there are no teeth, the dentoalveolar processes of normal teeth become more extended.
Diagnostics
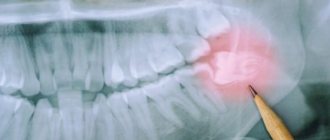
For an examination, you need to visit a dentist, he will examine the sweat cavity, taking into account the complete or partial absence of dentition. A mandatory measure is radiography for the lower and upper jaw. This is a particularly important point in the primary type of the disease, since the rudiments or their absence can only be established in this way.
In the process of diagnostic measures in young patients, preference is given to x-rays in the form of a panoramic image. It is as informative as possible not only about the rudiments of the dentition, but also tells about bone tissue and the structure of the roots of the alveolar processes.
During the diagnostic process, the doctor will be able to study all the factors, including studying contraindications for installing prostheses.
Among other things, a number of the following points are important:
- presence of exostoses;
- the presence of roots that have not been removed and are already covered with a membrane of mucous tissue;
- whether the patient suffers from diseases associated with the mucous membrane in the oral cavity;
- studying the anamnesis for processes with an inflammatory course or diseases associated with the development of tumors.
The factors listed above indicate the impossibility of treatment using prostheses. In many cases, prosthetics is possible with the preliminary elimination of factors that interfere with it.
What can lead to tooth loss
Tooth loss begins with periodontal disease.
The first cause of adentia is periodontitis.
The second reason for tooth loss is caries.
The next cause of tooth loss is pulpitis
Other causes of tooth loss include periodontitis and hypoplasia.
Another reason for the development of edentia is diabetes mellitus.
If tooth extraction was previously carried out in a patient with diabetes, then it is necessary to understand that diabetes in general accelerates the atrophy of tissues, bones, and all degenerative processes in the body: from vascular sclerosis to trophism of the limbs. And in this case, it also affects edentia.
Look at the example of one of the patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, how he developed atrophy. Of course, this does not happen instantly, over several years, but edentia is an inevitable fact, unfortunately:
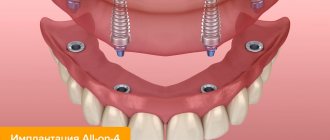
The professional experience of the specialists of the German Implantology Center allows us to successfully solve even such, sometimes very complex problems associated with atrophy and edentia by performing bone grafting and sinus lifting with subsequent implantation:
This clinical case and its successful treatment are reviewed in more detail - HERE
That is, there are two main reasons for tooth loss:
The first is periodontal disease (periodontitis), the second is caries and its complications (pulpitis and periodontitis), hypoplasia.
There are other reasons, but they are, let’s say, quite exotic and “don’t make a difference.” At the moment, there is no consensus on why caries and periodontitis occur and how to prevent them.
There are many theories, but there is no single answer to the question of how to prevent the development of these diseases. In my opinion, this suggests that these are multifactorial processes that involve genetics, nutrition, hygiene, the nature of the area in which a person lives, and so on and so forth... Why am I saying this? And to the fact that the reasons for development are a separate topic for discussion and we will return to it later, but now let’s look at the consequences of tooth loss.
Treatment
The problem can be treated exclusively by a dentist; the treatment of adentia is carried out by the orthopedic branch of dentistry. Treatment methods are determined by the doctor, taking into account the level of atrophy of the alveolar processes and tubercles.
In the primary form, the patient’s age group is taken into account; a pre-orthodontic trainer can be placed with further registration.
Partial absence of teeth in childhood requires careful attention to the approach to stimulating teething and taking measures to prevent the manifestation of deformities. Only after the seventh teeth (permanent) have erupted can the doctor think about prosthetics for those teeth that are missing.
The dentist may choose from the following options:
- installation of an adhesive bridge;
- performing prosthetics using metal-ceramic inlays or crowns;
- implantation to replace a missing tooth.
In the process of eliminating complete adentia, the doctor aims to restore the normal functioning of the entire system. Pathologies and complications are also prevented, for this reason prosthetics are performed taking into account all the nuances. Help from the psychological side is of great importance; patients suffer in the absence of normal dentition.
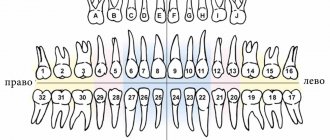
Classification of edentulism by the number of missing teeth
| Number of missing teeth | Classes | general description |
| Partial edentia (ICD K00.00) | Partial primary adentia. Partial secondary adentia. | With partial edentia, from one to 5 teeth or their rudiments are missing on one jaw. Most often, three teeth are missing. |
| Multiple edentia | Multiple primary adentia. Multiple secondary adentia. | Many experts combine the concepts of partial and multiple edentulism. Criteria:
And so on up to 15 units on one jaw. |
| Complete edentia (ICD K00.01) | Complete primary adentia. Complete secondary edentia. | Complete absence of teeth or missing teeth |
Consequences
Edentia is a complex disease in dentistry and significantly spoils life without proper treatment. And with complete edentia, a person cannot not only eat well, eating exclusively ground foods, but also reproduce intelligible speech. Malnutrition can lead to gastrointestinal diseases and lead to general problems, since the body will not receive many vitamins and microelements.
Without teeth, the patient will suffer from improper functioning of the joints in the temporomandibular region. They can also become inflamed. It is worth considering the decrease in self-esteem and social status; such patients are constantly under stress, which turns into nervous disorders. It is important to consult a dentist in time and choose the most effective treatment.
Complications
Adentia entails disturbances of an anatomical and aesthetic nature:
- in the place of missing units, the toothless bone structure of the jaw becomes thinner over time;
- the symmetry of the face and the connection of the lips are disturbed, facial folds on the chin and in the nasolabial area deepen, the corners of the mouth droop;
- non-anatomical development of the jaws. It is more pronounced when there are a large number of missing units;
- with a numerous shortage of units at the LF, it begins to protrude forward and form a deep bite, moving into the HF.
Anatomical underdevelopment of the jaw bones does not always occur, and in children and adults it manifests itself differently. However, with all types of anomalies, negative clinical manifestations occur.
Important characteristics of complete or numerous adentia are the formation of a pathological bite and disruption of the digestive system. The bolus of food is difficult to chew, and the person has to limit his or her food intake. This pathology reduces self-esteem and makes you feel uncomfortable.