Author:
- Golonova Yulia Yurievna
otorhinolaryngologist, clinic director
3.00 (Votes: 4)
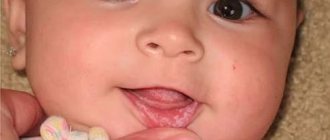
In the first year of a child’s life, when his first milk teeth are cutting, a fairly common picture is swelling of the gums at the site of teething, profuse salivation, the child’s capriciousness, the desire to put everything in his mouth and chew in order to relieve itching and discomfort from the gums. Due to excessive salivation, coughing and even (very rarely) vomiting are possible, when there is really a lot of saliva and the child chokes on it.
Why do babies get caries?
Yes, caries in children under 3 years of age still surprises parents. "How so? After all, the baby doesn’t even know cigarettes and soda yet?” - they shrug their shoulders. In fact, there are two main groups of reasons for the appearance of caries in babies: poor lifestyle during pregnancy and insufficient oral care for the child after birth. Let's look at each group separately.
Pregnancy
The expectant mother should be especially attentive to herself. The baby's teeth begin to develop around the 12th week of pregnancy. It is important for a woman to understand that the process of feeding a child is a process that begins with conception.
For the health of the baby’s teeth, hair, nails, skin and other organs, the expectant mother should choose natural products that contain the daily requirements of essential vitamins and minerals:
- Dairy
. First of all, the expectant mother should choose cottage cheese, natural yogurt and hard cheeses. These treats contain calcium, protein, vitamins B, D, and Omega-3 polyunsaturated fats that baby’s teeth need.
- Nuts
- This is a storehouse of vitamins and nutrients necessary for the formation of teeth in a baby. Nuts contain selenium, magnesium, vitamin E, phytic acids and Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids.
- Fish and seafood
. Everyone knows that fish contains the phosphorus needed by bones and teeth and beneficial vitamin D, which strengthens the nervous system of a pregnant woman and baby.
- Meat, liver
. Important cell building materials are meat and liver. These products contain the protein necessary for a growing body. The liver is rich in iron and B vitamins.
- Chicken and quail eggs
. These products contain more than 10 useful vitamins and microelements that affect the growth and abilities of the baby.
- Vegetables
. Vitamins, fiber, microelements and organic acids necessary for the development of healthy baby teeth are found in abundance in vegetables. Avocados, broccoli and carrots are especially useful for the expectant mother. These vegetables (in any form - raw or cooked) contain the most calcium, vitamins B, C and folic acid.
- Berries and fruits
– vitamin support for pregnant women and the key to the normal development of the child.
- Legumes
contain iron, folic acid and vitamin B-6, necessary for mother and baby.
- Cereals
rich in B vitamins, fiber and iron. Milk porridge will be very useful.
- Spinach.
The plant contains a lot of folic acid, calcium and vitamin A. In addition, the leaves are not at all difficult to grow at home on the balcony, and then enjoy them in the form of soups, purees and side dishes.
And, of course, the expectant mother should avoid taking antibiotics: such drugs can destroy the child’s health.
Game process
The child needs to be interested. A game story for eating is the absolute norm. During the process, you can tell your baby an interesting story in which he will be involved. The well-known “airplane” flying to the “hangar” is a real way to feed a child without nerves and hysterics. However, it is important to understand that if the baby begins to turn away, it means that he has already eaten. There is no need to feed him with the rest of the puree, even if it is only a spoon. Teaching a baby to eat “adult” solid food is a really difficult task that requires attention and patience from parents. Remember that you are helping your child develop one of the most important skills! On this path you need to become an ally to the baby. Force feeding will cause rejection. It is simply impossible to teach by feeding tasteless purees or forcing the child to finish eating porridge when the child is already full.
(2 ratings; article rating 5.0)
Share Share Share
Oral care
Caries in children aged 2-3 years can also develop due to the inattentive attitude of parents. Let's look at the main mistakes that moms and dads make:
- Pacifiers and bottles in a dream.
To teach a child to sleep alone, parents give him a pacifier or even a bottle of milk at night. As a result, the child enjoys the sweet taste of the drink all night, and the teeth are slowly but surely destroyed. Such a habit, of course, will give mom and dad healthy sleep, but in the baby it can lead to bottle caries and malocclusion.
- Sweet life.
Of course, most kids are unfamiliar with the problem of excess weight. Therefore, grandparents strive to treat the child with additional cake or candy. And, as you know, bacteria on enamel love sugar with a tender love, and very soon children under 3 years old develop caries, which requires treatment.
- Insufficient dental care
. Many parents believe that there is no need to care for baby teeth at 2-3 years of age. As a result, plaque accumulates, and carious monsters spread over both grown and still growing teeth.
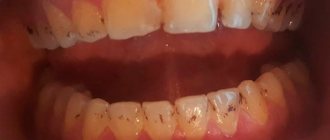
Symptoms of caries in babies
It can be difficult for parents to notice that their child’s teeth are affected by caries. Dentists distinguish several stages of the development of the disease:
- Initial.
Subtle white spots appear on the baby's teeth. These spots can be large or very small, round or rectangular. The child does not experience any unpleasant sensations at the initial stage. Therefore, parents who do not examine their children's teeth skip this stage, and the enamel continues to deteriorate.
- Superficial
. At this stage of caries, teeth change more noticeably: dark spots appear on the top layer of enamel. Some children complain of pain when eating irritating foods (sour, salty and sweet). The enamel is damaged, the tooth cavity opens to bacteria.
- Average
. Caries bacteria reach the dentin (the tissue located inside the tooth). The baby complains of pain when eating foods that are too cold or too hot.
- Deep.
In children, deep caries is much more difficult than in adults. Most of the internal tissue of the tooth is damaged, and pulpitis develops sharply.
Unfortunately, in children under 3 years of age, unlike adults, caries often affects all teeth at once. Several holes may appear on one crown from different sides at once. Therefore, parents need to be extremely attentive to their children and devote time to oral care even before the first tooth appears.
Obsessive neuroses
In most cases, the problem of obsessive-compulsive neurosis and tics is solved by play psychotherapy or a course of medical treatment, and most often by a combination of drug treatment and psychological work with suppressed nervous tension in the child.
Obsessive neuroses in children manifest themselves in the form of obsessive movements and thoughts. Obsessive states (obsessions) manifest themselves as irresistible and involuntarily arising thoughts, fears, and, as a result, obsessive movements.
Intrusive thoughts
- when a child fears for the health and safety of himself and his family
- constantly thinks or imagines that something bad might happen to them
- always remembers negative events that happened to him or his family in the past
Typical obsessive mental actions
- reading license plates, signs, operations with numbers and letters from license plates and signs
- counting lamp posts, houses, lawn fences, etc.
- constant search for “favorite” and “unfavorite” letters and numbers
Obsessive movements and actions.
The scope of their manifestations is very extensive. This could be a nervous tic in a child, or obsessive movements. The most typical obsessive movements and actions in children:
- biting nails and lips
- hair pulling
- thumb sucking, sucking or biting a pencil, pen, button, edge of clothing
- coughing, grunting, or making noises
- twitching of limbs
- blinking and/or stereotypic eye movements
- circling
- tapping, clapping
- rocking
- squatting, limping when walking
- rubbing the body or objects
- shaking and shaking hands and objects
- jumping and skipping for no reason
- muscle contractions of the arms and legs, as well as the face.
Typical complex ritual actions
- Children can walk on certain floor tiles
- walk around, twist, stroke the object a certain number of times
- jump up and clap your hands, pronounce phrases, etc.
Also, neuroses can have a different course:
- episodic
- chronic
- progressive
Neurosis in a child can have different causes
. The most common is the presence of any mental trauma in the child, as well as the presence of emotional factors. Such as: a tense and conflictual situation in the family, incorrect and too harsh and authoritarian upbringing of children.
Often this list also includes physiological reasons: heredity and genetics, previous diseases, physical overload of the child, lack of sleep.
One way or another, all this is due to the fact that the child has increased arousal in certain areas of the brain. Basically we are talking about dysfunction of the subcortical nuclei of the brain, which are responsible for posture and facial expressions, muscle tone and global motor acts. The child is forced to somehow relieve this excitement. Thus, this discharge occurs precisely through actions.
These may be: tics (the child twitches or jerks with some part of the body), fast stereotypical movements, there may be obsessive postures, obsessive movements; the child may sit down, jump, make some sounds, pronounce words or even swear words (with Tourette syndrome). Very often such manifestations are not taken seriously in the initial stages.
Tourette's syndrome is a genetically determined condition associated with obsessive-compulsive disorder and tics, or stereotypical tic-like movements.
Also, neurosis-like obsessive states are largely provoked by chronic streptococcal infection with an increase in antistreptolysin O (ASLO) in chronic tonsillitis, the so-called PANDAS syndrome, ongoing neuroinflammation with an increase in markers such as NSE and S100 protein. We also often see such manifestations in children who are carriers of neuroinfections, that is, infections that have a toxic effect on the nervous system.
EEG (electroencephalography) for children at the Echinacea clinic
We advise you to contact a child neurologist, child psychiatrist and allergist-immunologist. For convenience and coordination of assistance to the child, we practice a consultation of all three specialists. Thanks to this, the appointments are more informative, and the effect of the prescribed therapy occurs faster.
Obsessive neurosis responds well to treatment in the early stages, especially in preschool age.
As for Tourette's syndrome, even if there is a genetic predisposition, this syndrome can become silent. After all, until the debut of Tourette syndrome, the child lives with the same genetic makeup, but there are no tics or vocalisms. This is not only a matter of genetic predisposition to Tourette's syndrome, but also related problems and the current state of the child's health. Working with provoking factors (obsessive-compulsive disorder, infections, concomitant inflammatory diseases, sleep disturbances, high levels of anxiety, etc.) usually leads to gradual improvement, often until the complete cessation of tics and vocalisms.
We widely practice play therapy for the treatment of obsessive neuroses in children
Treatment of caries in children under 3 years of age
The method of treating caries in children under 3 years of age depends on the stage of the disease, the individual characteristics of the child and, of course, his attitude towards dentists.
- At the stain stage, the doctor removes plaque and remineralizes the enamel using solutions or silvers the teeth.
- Superficial, medium and deep caries in children 1-3 years old (and older) are treated using a drill. If necessary, the doctor uses anesthesia. If a child suffers from aching toothache, canal depulpation is performed.
Remineralization
Remineralization is the restoration of damaged tooth enamel. To carry it out, the doctor cleans the surface of the affected area, and then covers the rows with a special composition with fluorine and calcium. The procedure is absolutely painless, most children tolerate it easily.
To avoid the development of caries in children, dentists recommend repeating remineralization every six months.
Silvering
This method enhances the protective abilities of enamel and is recommended for children who are afraid of dentists. The surface of the teeth is coated with silver nitrate. The substance provides a reliable antiseptic effect, but parents should be mentally prepared that after treatment the child’s teeth will turn black.
Sealing
For children over 1 year old, the dentist can fill damaged teeth. This treatment does not necessarily require the use of a drill. If the caries is shallow, the doctor applies a special solution with acid to the tooth. The substance corrodes the affected tooth surface, disinfects the carious cavity and applies photopolymer material.
If a child comes to the doctor with deep caries, it will not be possible to do without drilling. Before starting treatment, the doctor gives the baby anesthesia, since baby teeth have nerve endings.
Treatment of caries in children 2-3 years of age and older can be supplemented with procedures such as
- preparation or opening of a cleaned carious cavity;
- depophoresis – introduction of an electric current of copper-calcium hydroxide ions;
- ozone therapy - treatment of carious cavities using a jet of ozone gas;
- photodynamic therapy – application of a special medicinal paste to a carious tooth and subsequent laser treatment of the area.
What if you don’t treat caries in a child?
Not treating caries on baby teeth means providing your child with a painful childhood. Firstly, caries suddenly “infects” other teeth, and secondly, it almost instantly turns into pulpitis and brings excruciating pain to the baby.
Untreated teeth in children can in the future provoke such serious diseases as:
- chronic allergic processes;
- inflammation in the oral cavity;
- periodontitis;
- chronic inflammation in the mouth.
What are the difficulties?
For adults, the process of chewing food seems completely natural. But the child only has a sucking reflex, and even liquid puree becomes unusual and unfamiliar food for him. In addition, the same period is characterized by other reflex reactions, due to which solid pieces of food that enter the mouth are rejected. They weaken by 4 months, but there is no need to wean the baby from the breast at this age: mother’s milk “adjusts” to the baby’s needs, its composition changes over time.
How to prepare a child for treatment?
Children intuitively feel the fear of adults and begin to be afraid of dentists even before their first glance at the dental chair. In order for the treatment of caries in a baby under 3 years old to go as smoothly as possible, it is necessary to prepare him for a visit to the doctor in advance.
- Find a trusted, good dentist who can establish contact with your child.
- Take your child for preventive examinations to the dentist, do not wait until the tooth hurts. Believe me, pain will greatly increase children's fear.
- Be calm at your doctor's appointment. Remember, all the fears of the parents are transmitted to the baby. There is no need to tell the child “don’t be afraid”, “it won’t hurt”, “like a mosquito will bite” even before he approaches the doctor.
- If your baby is already playing on his own, rehearse your visit to the dentist at home. Treat caries for a bear, bunny, or cat. Let your child get used to the atmosphere of the dental office a little.
- Tell your child that everyone goes to the dentist - mom, dad, and grandparents. And, most importantly, emphasize that visits to the doctor bring joy and relief to everyone.
- Choose a time to visit the doctor when your child is alert and cheerful. Believe me, the baby will not be happy to be in the doctor’s chair during the daytime nap or in the evening when he is already tired. By the way, during the visit the baby should be well-fed.
- If you nevertheless went to the dentist for the first time because of a toothache, convince your child that the doctor will definitely help him. Remember, the baby is already very scared, so there is no need to use the words “drill” or “acute pain”. Better tell a story about how a good doctor will save a child from carious monsters, and his teeth will become white and healthy.
We hope our tips for treating caries in children under 3 years of age will be useful to you. Teach your child not to be afraid of dentists and to take care of their teeth. May you and your children always have beautiful snow-white smiles.
And in order for a child to love brushing his teeth from a very early age, it is important to choose a tasty, high-quality toothpaste for him. ASEPTA baby toothpaste gel-paste is created specifically for children aged 0 to 3 years. The soft, sweet gel carefully cares for the child’s teeth and gums without damaging them, and the natural components of the paste provide protection against caries and inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
The paste does not contain abrasives, fluorine, parabens, or sodium lauryl sulfate, so it is absolutely safe for crumbs. And the bright taste of “tutti-fruiti” will make brushing your teeth very pleasant for your baby.
How and what to feed a baby when teething
The reaction to teeth depends on the individual characteristics of the child, his sensitivity to pain, nutrition and even the climate. Teething is often painful, causing children to refuse to drink or eat for a while. What to feed your baby when teething, as well as what are the first noticeable signs of teething and simple remedies that will help ensure more comfortable feeding and return to normal sleep, we will find out in a conversation with pediatrician Anastasia Anatolyevna Nikulina.
— Anastasia Anatolyevna, when babies start teething, how long does teething last?
— Children can “show off” their first central incisors at about six months. However, the first symptoms of teething in infants may appear a couple of months before the tooth appears. And it is advisable to see the beginning of the process in time to help the baby survive the pain. In most babies, symptoms of discomfort are detected three to four days before teething and usually disappear on the fourth day after the tooth comes out.
Obvious signs of teething in a baby:
- increased salivation, rash on the face and chest from constant wetting;
- swelling of the gums, their increased sensitivity when sucking;
- The toddler is irritable and whiny, capricious, does not accept the breast/bottle;
- the baby gnaws, bites objects, trying to relieve soreness in the mouth;
- The baby's sleep is disturbed and wakefulness appears at night.
— Teething discomfort is often mistaken for a cold or allergy. How to distinguish one condition from another?
— Teeth growth is a physiological stage, and, as a rule, it does not have negative consequences for the child’s health, despite frequent crying, fever, and excessive anxiety. It is possible to differentiate childhood illnesses based on knowledge of their characteristic signs.
Table. How to tell if your baby is teething
| Frequent manifestations | A tooth appears through the gum | The disease develops |
| Cough |
|
|
| Nasal discharge |
A saline solution is recommended for rinsing the spout. |
|
| Increase in body temperature to 38 °C |
|
|
| Rashes |
|
|
| Immunity weakens |
|
| Cough | A tooth appears through the gum
| The disease develops
|
| Nasal discharge | A tooth appears through the gum
A saline solution is recommended for rinsing the spout. | The disease develops
|
| Increase in body temperature to 38 °C | A tooth appears through the gum
| The disease develops
|
| Rashes | A tooth appears through the gum
| The disease develops
|
| Immunity weakens | The disease develops
|
— Parents are often concerned that their children are not eating enough. Are a baby's first teeth and decreased weight gain related?
— Poor appetite is an alarming symptom that occurs against the background of teeth moving and pressure on aching gums during feeding. The baby does not attach well to the breast, pushes out the nipple and receives less nutrition, which leads to a cessation of weight gain. It is better to simply temporarily switch to a free feeding regime, but not to force feed the baby.
Poor appetite in an infant may be accompanied by the following behavioral changes:
- complete or partial refusal of breast/bottle;
- constant whims when feeding with body writhing;
- increased desire to put something in the mouth followed by refusal to eat due to increased discomfort and itching in the gums;
- loss of interest in solid foods, especially in children on a mixed diet.
After the tooth breaks through the gum, the inflammation goes away and the appetite is completely restored. Therefore, you should not worry about your child’s reluctance to eat. The baby can get the required amount of vitamins through breast milk or formula. The main thing is not to skip two meals in a row.
— What if the child often refuses to suck the breast or pacifier?
“Parents need to be patient. An inflammatory process in the mouth - which means nights without sleep and a moody mood - reduces appetite. Any touching of the gums is accompanied by discomfort, so the baby does not want to suck. In such a situation, force feeding is useless. But even if the child misses two or three feedings per day, nothing bad will happen, everything will get better soon. When he gets very hungry, he will still take the breast or bottle and will definitely eat.
— A restless baby is waiting for support - how to soothe itching and inflammation of the gums?
— Teeth do not appear before three months, and sometimes a “dental holiday” in the family is celebrated closer to a year. The parents' task is not to miss the moment the tooth comes out in order to facilitate the process.
Teether-pacifier
- Given with the appearance of the first incisor for scratching the outside of the jaw. The itching subsides as teeth grow along the edges of the mouth. It is better to look for a wide pacifier (it is so convenient to reach hard-to-reach places in the oral cavity) with a narrow handle-limiter (does not interfere with the grip and prevents the pacifier from being swallowed too deeply).
Materials:
|
|
|
Sippy cup
— Teething is accompanied by a strong secretion of saliva, therefore, in order to normalize the water balance, plenty of drinking is often given from a convenient sippy cup. Its spout is made of rubber, and the valve does not allow liquid to leak. In addition, convenient holders prevent the bottle from slipping out of the baby's hands. Children are delighted with this “toy” and drink from a beautiful bottle with great diligence.
Pain reliever, gum gel
- Your doctor will advise you on the best solution. A number of medications to relieve inflammation and soothe gums include lidocaine. But there is no clear dosage for them, and the baby may swallow the medicine. Therefore, when treating gums when a tooth is cutting, lidocaine can lead to intoxication of a small organism and cause serious undesirable consequences.
| Spray/gel with lidocaine dangerous, limited use | Homeopathy inappropriate, safety and effectiveness of drugs have not been proven | Pharmaceutical preparations with belladonna especially dangerous, contraindicated | Non-steroidal drugs for fever are allowed, but their abuse is unsafe for the gastrointestinal tract | Gels based on medicinal plant extracts most safe and effective |
Rules for using gels for pain in teething syndrome:
- at the first concern of the child, a teether and a sippy cup are first given, a circular massage of the gums is done from the wings of the nose to the corners of the mouth;
- the product is used only in case of severe discomfort;
- apply a thin layer up to 3-4 times a day, strictly following the instructions;
- manipulation is performed with a clean finger, accompanied by a circular massage;
- It is preferable to lubricate the gums after feeding and at night;
- Under no circumstances should you allow your baby to chew on a tube of gel.
— Anastasia Anatolyevna, what to feed and how to feed the child when teeth are being cut - do you need to follow a schedule, give the baby something to drink, heat up food? And what is better to give to a child: baby formula/puree soup/vegetable puree? Should I continue breastfeeding?
— When teeth are being cut, it is important to temporarily move away from a clearly planned feeding regimen. It is better to offer your baby breast or formula milk on demand. Everything will soon return to normal and return to the order that developed during life without teeth.
It is preferable not to force the baby to eat thick foods. It is better to prepare liquid, pureed, light meals, and also not to introduce new complementary foods, do not give stale bread or cookies, in order to eliminate the risk of choking on crumbs. The temperature of the food should correspond to the temperature of the child’s body, so as not to worsen the baby’s condition and he does not lose the desire to eat. In case of hyperthermia and drooling, it is advisable to give the baby water.
— Do breastfed and bottle-fed babies experience the same painful condition when a tooth comes out?
— It has been observed that breastfed children tolerate the appearance of teeth more easily. Mother’s breasts are not only a source of complete and healthy food, but also a bioregulator of the emotional state, a way to calm down. Mothers whose babies literally “hang on their chest” observe that periods of prolonged feeding coincide with the appearance of dental cusps.
You need to show extra attention to a bottle-fed baby - hold him in your arms more often, fall asleep with him, spend sleepless nights next to him - fortunately, the tooth comes out completely in just 3-4 days (in the worst case, in a week).
— Do baby formulas have any effect on the baby when teeth are being cut?
— The best food for a newborn is, of course, breast milk. But there is no tragedy in transferring a child to artificial or mixed feeding if it is really necessary. This decision is made by the mother together with the pediatrician.
Fortunately, now there are alternatives to breast milk, and among them are MAMAKO® Premium infant formulas. They have an excellent composition and pleasant taste. One of their main advantages is the base of goat’s milk, which is closer in composition to breast milk than cow’s milk. The peculiarities of the protein component of goat mixtures make them easier to digest.
The eruption of the first teeth through soft, tender gums can cause the child to be whimsical when feeding. But the basic milk nutrition is preserved, and pureed complementary foods will make it easier to eat when there is soreness in the mouth. Also, the growth of teeth will bring less trouble if you pay more attention to the baby, communicate gently with him, distract him by singing or playing. It is important to massage the gums and offer the baby teethers. On the recommendation of a doctor, in case of intense pain, ointments and gels can be used to calm the baby and help teeth break through.
Pediatrician Anastasia Anatolyevna Nikulina
*The ideal food for an infant is mother's milk. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months. MAMAKO® supports this recommendation. Before introducing new foods into your baby’s diet, consult a specialist.
Experts' opinion
The complex composition of ASEPTA Baby toothpaste allows you to simultaneously care for your gums and teeth. The product has:
- Certificate of state registration;
- Certificate of conformity No. ROSS RU. AG81.H01070.
The paste does not contain fluoride and does not require consultation with a doctor before use. The product is safe if swallowed, as it does not contain components harmful to the health of the baby.
Sources:
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of toothpaste “ASEPTA PLUS” GENTLE WHITENING” Author: doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical experience in using the Asepta series of products Fuchs Elena Ivanovna Assistant of the Department of Therapeutic and Pediatric Dentistry State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education Ryazan State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation (GBOU VPO RyazSMU Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia)