Tartar in humans is a mineralized soft plaque that was not removed in a timely manner. Hard dental deposits are formed as a result of an increase in the mass of soft ones if they are not cleaned off. The hardening process occurs due to impregnation with mineral salts in saliva. As a rule, 10–16 hours from the moment of appearance are sufficient for partial mineralization of soft plaque, but the time may vary depending on the individual characteristics of each person.
Stones consist of organic (leukocytes, pathogenic bacteria, protein-polysaccharide components, epithelial cells from mucous membranes) and inorganic (calcium salts) components.
Types of Tartar
Tartars on teeth are classified according to where they are located:
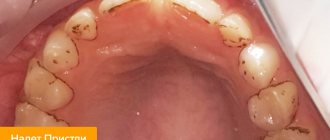
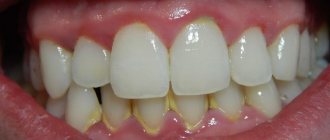
- supragingival - they are visible to the naked eye during a routine examination. They look like dark or yellowish deposits above the gum level. This type of stone is easier to remove;
- subgingival - what this type of tartar looks like can only be determined by a doctor. This type of deposit is located under the gum, below its level, so it is impossible to see it. However, there are indirect signs of the formation of such stones: redness, swelling or cyanosis of the gums, bleeding, and possible outflow of pus from the periodontal pocket.
The second type of hard deposits is more dangerous because it is indirect evidence of periodontitis and periodontal disease. The stone is formed due to the destruction of the attachment of the gum to the surface of the tooth, its detachment. The next stage may be a structural change in the tissues that hold the tooth, loosening and its loss.
Why is fluoridation needed?
Cleaning the dentition from tartar may be accompanied by exposure of the dentinal tubules, and this, in turn, leads to increased tooth sensitivity. To prevent increased sensitivity, fluoridation is carried out - treating the enamel with a gel with an enamel-sealing substance based on copper hydroxide (applied using a tampon).
Techniques used:
- Simple fluoridation - placing a mold with a special solution on the jaw
- Deep fluoridation - applying F-containing varnish separately to each tooth
To achieve a lasting result, it is recommended to repeat the procedure three times at intervals of 1-2 weeks.
To prevent caries, it is recommended to take a course of 10-14 procedures.
Diagnostic features
If supragingival stones are easy to see on your own, then those located under the gum can only be seen with the help of special tools from a dentist. Diagnosis is carried out as follows: the doctor immerses the probe into the periodontal pocket, which makes it possible to verify the presence of hard deposits, as well as determine the depth of the pocket. This will allow you to choose how to remove the stones.
It is possible to diagnose supragingival calculus even in the early stages of its appearance. There are special tablets on sale that, when bitten, stain areas of the tooth with stone.
When should you not brush your teeth with ultrasound?
Despite the atraumatic and highly safe method, ultrasonic cleaning has its contraindications. You will have to choose another method in the following cases:
- with increased tooth sensitivity;
- in the presence of complex orthopedic structures, including braces;
- in the presence of implants;
- patients with tuberculosis and autoimmune diseases;
- during the period of change of bite in children.
It is not recommended to carry out this procedure in the first trimester of pregnancy, with respiratory diseases, or in a state of acute cold.
Mechanism of formation of tartar
The causes of tartar are as follows: after eating food, particles remain in the mouth. They act as a favorable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. They give greater preference to easily digestible carbohydrates: particles of sweet food, baked goods. Experts have found that even one day of lack of hygiene doubles the amount of bacterial plaque in the mouth.
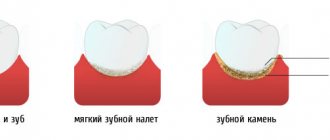
Nutrients are used by microorganisms for more than just reproduction. They also secrete special enzymes - enzymes, which allow them to firmly attach to the surface of the tooth enamel. Lack of hygiene leads to the fact that individual pinpoint colonies quickly merge into one “plaque”, forming an impressive mass of plaque. Before it begins to mineralize, it can be easily brushed off with a toothbrush.
With the gradual mineralization of soft deposits, stone formation occurs. Calcification occurs as follows: calcium salts, which are part of saliva, settle on the soft plaque. Mineralization is accompanied by the process of layering of new and new colonies of bacteria, which leads to an increase in the volume of solid deposits.
The mechanism of tartar formation is accompanied by processes such as the release of toxic substances and inflammatory mediators by plaque. This becomes the cause of inflammatory processes in soft tissues. Symptoms of this complication are:
- bleeding of the gums - due to mechanical stress, and in severe cases, spontaneous;
- redness, cyanosis, swelling of the gums;
- soreness, itching;
- the appearance of pus in periodontal pockets;
- mobility of individual teeth.
Inflammation contributes to an even greater increase in the number of bacteria. In the place where the gums adhere to the surface of the tooth there is a periodontal groove, into which liquid with salts and proteins is produced from the gums. This leads to the growth of bacterial colonies. With inflammation, this fluid becomes larger, resulting in an environment for reproduction that is even more favorable for microorganisms. Calcification occurs even faster.
What are dental deposits?
Such formations on the teeth appear even in those who regularly and conscientiously brush their teeth and take care of their oral cavity. Deposits on teeth are formed under the influence of various factors. They affect not only the crown of the tooth, but also the surface of the gums. Dental deposits often cause the development of diseases of the gums and teeth. They are irritating to the gums and tooth enamel, as they contain a huge amount of bacteria and their metabolic products. Partially, soft plaque is removed when brushing your teeth. But this is only provided that the oral cavity is cleaned correctly and regularly. If personal hygiene rules are not followed, plaque remains on the teeth, between them and gradually leads to the formation of hard deposits.
Causes of tartar
So, we have figured out the mechanism for the appearance of solid deposits. What causes tartar and what contributes to its rapid formation? There are several factors:
- Ignoring hygiene, improper brushing of teeth. An increase in the volume of bacterial plaque leads to rapid mineralization and proliferation of the stone;
- consumption of carbohydrates (sweets, baked goods), preference for soft foods (lack of natural mechanical cleaning with solid foods);
- changes in the composition of saliva, its acidity or increased salivation as a result of metabolic disorders lead to rapid saturation of soft deposits with calcium salts;
- internal diseases, inflammatory, infectious, which causes a large number of pathogenic bacteria;
- rough surface of the teeth - “simplifies” the formation of soft and hard plaque;
- bite defects, which makes it impossible to properly clean some areas (for example, when teeth are crowded);
- taking certain medications that help change the composition of saliva.
The causes of tartar formation can be combined with each other. When visiting a dentist, it is important to find out about them in order to select effective methods of prevention.
Probability and causes of complications
Like any other dental intervention, ultrasonic cleaning can lead to undesirable consequences. Complications may be associated with:
- increased sensitivity of the gums (irritation or bleeding);
- mechanical thinning of tooth enamel as a result of previous procedures using aggressive polishing pastes;
- using an outdated installation (previously less gentle attachments were used);
- low qualification of the dentist.
What is the danger of tartar
Why is it so important to see a dentist? There are several unpleasant and dangerous consequences of tartar:
- halitosis or bad breath - as a result of the constant proliferation of pathogens;
- inflammation of the gums - gingivitis, periodontitis, as well as inflammation of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity (tongue, cheeks, lips, etc.) - microbes release toxins, inflammatory mediators, which causes the inflammatory process;
- spread of inflammation - in the absence of treatment, inflammation covers the tissues that hold the teeth in the jaw, the dentogingival attachment is disrupted, which leads to periodontitis and periodontal disease: loosening, the appearance of periodontal pockets with purulent contents, bone tissue atrophy, exposure of the necks of the teeth, and their loss;
- caries - soft and hard deposits contain microorganisms that provoke the appearance of caries. This occurs due to the release of hydrochloric acid, which destroys the enamel. The resulting defect is populated by pathogenic flora and a carious cavity is formed;
- general deterioration of condition and well-being - toxins released by bacteria are absorbed into the blood, which complicates the course of chronic diseases and can affect the functions of organs and systems.
That is why, regardless of the cause of tartar, it is important to seek professional dental help - removal.
How and why hard plaque forms on teeth
The oral mucosa is simply teeming with all kinds of bacteria, the quantities of which are in a certain ratio to each other. When the bacterial balance is disturbed, some microbes can multiply excessively and provoke all kinds of dental ailments. If for some reason teeth brushing has become poor and irregular, then a concentrate of 200 billion different bacteria will immediately react to this by the appearance of a mineralized film. It actively forms within 15 hours, and within a week it becomes quite noticeable plaque, which will turn into hard tartar in six months.
Tartar removal
Unlike soft deposits, hard deposits cannot be removed on your own: professional dental care will definitely be required. To do this, the doctor can use the following methods for removing tartar in dentistry:
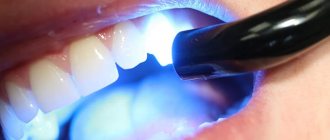
Ultrasonic cleaning. This technique guarantees complete destruction and removal of tartar. It is used for supragingival and subgingival stones. The doctor uses an ultrasonic scaler - a special attachment connected to an ultrasound source machine. By directing the scaler at the tartar, it destroys it, and the supply of water allows you to remove it from the mouth and prevent overheating. Ultrasound does not have a harmful effect on dental tissue.
Air Flow method. The procedure is performed using a device that supplies a water-air mixture with abrasive particles. It is worth noting that this method is combined with ultrasound, but is not used as an independent method of stone removal - the abrasive may not be enough to destroy solid deposits. However, it perfectly fights soft plaque and serves as a way to prevent stones.
Mechanical removal. The doctor, using a special bur, mechanically separates the stone from the tooth and scrapes the enamel surface. This method does not allow impact on subgingival deposits; moreover, it is more traumatic than modern ones and can cause discomfort.
Laser removal. The doctor acts on hard deposits with a special attachment with laser radiation. He removes the stone layer by layer, crushing it. Removal from the oral cavity is carried out using water and a stream of air. The procedure does not cause discomfort and therefore does not require anesthesia.
Chemical removal. It consists of applying special products containing acids and alkalis to the surface of teeth covered with stone. They help soften the hard stone, and then the doctor removes it mechanically. The only disadvantage of this method is its inability to apply to subgingival calculus. This method is used less frequently because acids can damage the enamel and it is important to ensure there are no risks.
Removal of subgingival hard deposits can be performed surgically - using closed or open curettage operations. Such procedures consist of gaining access and mechanical removal of subgingival stone using curettes and special instruments. They are required for diagnosed periodontal disease and involve the simultaneous removal of granulations from periodontal pockets. Curettage is carried out under mandatory anesthesia, since the doctor’s manipulations can be quite painful. It is important to entrust this procedure to a professional, a periodontist.
Treatment
Treatment for stones consists of removing them; there are simply no other methods of treatment. Sometimes it happens that tartar is removed from the surface of the teeth by itself under the influence of solid food, but you should not hope for this. It is better to consult a specialist in a timely manner, a hygienist who will quickly and painlessly remove dental deposits from the surface of the enamel.
If earlier tartar removal was carried out mechanically, that is, it was simply scraped off the surface of the enamel, today there are more modern and painless methods for removing deposits. Among them, the most common is the ultrasonic method of teeth cleaning.
Using the ultrasonic method, the dentist will quickly and effectively remove all dental plaque without injuring either the gums or the enamel surface. The procedure for removing tartar is completed by polishing and grinding the enamel, during which the teeth become shiny and their surface is smooth.
After the removal procedure
After removing hard deposits, the doctor must polish the teeth - plaque accumulates more slowly on a smooth surface. Also, to consolidate the effect and strengthen the enamel, a product containing fluoride can be applied - a solution, gel in drops or fluoride varnish.
It is important to find out the reasons for the formation of tartar in order to take the necessary preventive measures. If one of the factors is a disease or metabolic disorder, consultation with a specialized specialist and correction of the condition is recommended.
Common prevention methods include:
- professional teeth cleaning twice a year - it can be difficult to remove all the plaque that forms on your own, especially if we are talking about an incorrect bite or other structural features of the dental system. It is necessary to visit a hygienist once every 6 months, and for those who wear orthodontic appliances - once every 4-5 months;
- maintaining oral hygiene at home - brushing your teeth twice a day, flossing;
- compliance with certain measures outside the home - use a mouthwash after eating, do not forget about flossing;
- limiting the consumption of foods that contribute to the appearance of a large amount of plaque (tea, coffee, sweet, sticky foods, baked goods);
- choosing a brush with the optimal degree of bristle stiffness (it is better to consult a doctor);
- choosing a paste containing pyrophosphate (in consultation with your doctor) - this component suppresses the formation of tartar;
- preference for solid products as a method of mechanical cleaning of teeth.
Air Flow technology: softer than ultrasound
The technology involves cleaning the dentition (soft and hard deposits) using a water-air jet based on baking soda (sodium bicarbonate). The combination of properties such as the solubility and abrasiveness of sodium bicarbonate makes cleaning very effective, and flavoring agents are added to the mixture to minimize patient discomfort.
The Air Flow method is particularly gentle on the enamel and has a visible result. The cleaning process involves exposing the teeth to a jet under strong pressure at an angle of 30°, during which plaque (not stone) is softened and removed! The dentist’s task is not to touch open areas of dentin and gums during the procedure.
After cleaning using the Air Flow method, smoking and eating/alcohol consumption is prohibited (from 3 to 6 hours).
Air Flow technology is indicated for use in the following cases:
- for cleaning implants, metal-free ceramic structures, ceramic veneers;
- before filling or implantation, during dental restoration;
- if necessary, mineralize tooth enamel (fluoridation);
- for cleaning the bracket system.
Cleaning using this technology involves removing a protective organic film, which temporarily makes the teeth very sensitive. Therefore, it is recommended to use mouth rinses and replace your toothbrush.
Removal at home
It is impossible to remove hardened tartar at home. The only thing you can do is try to remove soft dental plaque. To do this, use special rotating toothbrushes and abrasive toothpastes. You can use such compositions no more than twice a week so as not to damage the enamel.
The use of folk remedies gives a dubious effect, but, if desired, you can try and see for yourself.
- Radish and lemon juice. Grate the radish, add natural lemon juice. Wet the brush and rub your teeth. (The main component of this “elixir” is acids that destroy enamel).
- Eggplant ash. The vegetable should be burned over an open fire, and the most problematic areas should be rubbed with ashes every day. The expected result can be observed after a week and a half.
- Horsetail decoction (for 200 grams of water - 30 grams of dry herb). Boil for half an hour. Rinse your mouth morning and evening with 1/3 cup.
Important. Among the “folk” recipes found online, there is an infusion of celandine, the use of which poses a health hazard.
Causes of plaque formation
- Irregular or improper care, lack of timely removal of food debris;
- Predominance of carbohydrates in food;
- Low chewing activity;
- Pathologies of the digestive system;
- Individual characteristics of saliva composition.
Signs of deposits:
- There is no shine on the enamel;
- The texture of the enamel changes and becomes rough;
- Darkening of the enamel is noticeable in certain areas.
At first the coating is white, but over time it changes color to yellow, then acquires a brownish and even greenish tint. These deposits are noticeable from the outside and do not look aesthetically pleasing.
If you do not take cleansing measures:
- An unpleasant odor appears;
- The area where plaque accumulates is expanding;
- The enamel surface becomes rough.
In people who frequently drink coffee and tea, as well as in smokers, the plaque becomes dark and difficult to remove.