Science knows that caries develops due to bacteria that are found in plaque. Almost all types of germs can be transmitted from one person to another. In this regard, the question arises whether caries is contagious. This can be answered in the affirmative. However, everything is much more complicated than it seems.
In this article
- The problem of caries development
- Is tooth decay contagious?
- Why is tooth decay contagious in children?
- Is caries inherited?
- Does caries transfer from one tooth to another?
There are many myths surrounding caries, as one of the most common dental diseases. Most people believe that carious lesions are a consequence of poor hygiene. Some people believe that caries is transmitted through saliva, so you can get it during a kiss. Scientists claim that the main cause of this pathology is cariogenic microbes from the Streptococcus group. Moreover, each of these statements is partially or completely true. Let's try to figure out whether caries is transmitted from person to person or not. First, let's find out what causes this disease.
The problem of caries development
Caries is the slow process of destruction of enamel and dentin - the hard tissues of the tooth. It is caused by harmful bacteria of the Streptococcus mutans group.
These microbes live off the carbohydrates that a person eats and multiply in the oral cavity if he does not follow the rules of hygiene. At the same time, they release acid, which eats away the enamel and destroys dentin. This is the main cause of tooth decay. There are a number of factors predisposing to this disease:
- Insufficient hygiene. If a person does not brush his teeth or does it rarely and incorrectly, the risk of developing caries increases many times over. Bacteria and their metabolic products are washed off with a toothbrush and toothpaste. Lack of hygiene leads to the rapid spread of germs in the oral cavity.
- Poor nutrition. Streptococcus mutans feed mainly on sucrose, so carious lesions are observed more often in people who abuse sweets.
- Bad habits. Smoking contributes to the formation of plaque and tartar on teeth, which are a favorable environment for cariogenic microbes.
- Weak immunity. The body can resist germs if it has good protection in the form of a strong immune system. Otherwise, a person becomes more vulnerable to any diseases, including caries.
- Taking certain medications. They can cause problems with metabolism or saliva production. It contains substances that neutralize acids left behind by bacteria. In addition, due to insufficient secretion, microbes are not washed away from the oral cavity.
- Hormonal imbalances. Impaired hormone production causes metabolic problems, which causes weakening of the enamel.
- Lack of vitamins and minerals. If the body receives little magnesium, fluorine, phosphorus, and calcium, tooth enamel becomes more vulnerable to cariogenic microbes.
There are other causes of caries, for example, childhood, pregnancy, wearing orthopedic structures, etc. As a rule, carious lesions occur as a result of the influence of not just one factor on the body, but a whole group.
Is tooth decay transmitted from person to person?
Many dentists share the opinion that a cariogenic microorganism can be transmitted from person to person. Most often this happens in childhood, when complementary foods “tested” by parents are given to the baby. Bacteria left on the spoon is a common cause of the problem. Caries is contagious if the simplest hygienic conditions are not observed:
- The baby should have separate utensils;
- Do not lick your baby's pacifier or spoon;
- The little one must have a balanced diet so that his immunity is strong;
- Reduce the amount of sweet foods so as not to provoke the growth of pathological bacteria;
- Be sure to follow all hygiene rules;
- You need to choose the right brushes, pastes, rinses;
- Avoid fluoride and calcium deficiency in the body;
Parents need to strictly monitor the condition of their oral cavity. Sanitation and treatment of superficial caries should be carried out in a timely manner. Pathology often develops in hard-to-reach areas. Little saliva gets into these areas, so the acidity there increases. Therefore, at the first signs of illness, you should immediately contact a dentist. Prevention plays an important role.
Is tooth decay contagious?
Since caries is a direct consequence of exposure to microbes on teeth, the question of the contagiousness of this disease is fair. However, these microorganisms are not as highly contagious as influenza, ARVI, tuberculosis and other viruses and bacteria to be transmitted by airborne droplets. Moreover, these microbes, being part of our microflora, are found in the oral cavity of all older people, except newborns.
But it is worth understanding that their presence does not always lead to the development of caries. There must be the predisposing factors discussed earlier. Some people never get tooth decay, while others cannot get rid of it for years. At the same time, cariogenic microbes are found in the oral cavity of both. Only with weak immunity, poor hygiene and the presence of other factors, the microbes that cause caries become dangerous.
Thus, it is impossible to become infected with caries through a kiss, someone else’s spoon, fork, toothbrush and other personal items. However, there is a category of people for whom cariogenic microbes from the oral cavity of another person are dangerous. We are talking about small children.
How can you become infected with caries?
The bacteria Streptococcus mutans enters our mouths during childhood, and the main source of infection in this case is almost always adults. Moms and dads lick the spoons with which they feed their children, older brothers and sisters give the younger ones a bite of their apple. Parents often make another mistake - they buy their kids one toothbrush between them. This happens in families with twins or triplets. Parents think that they are saving the family budget in this way, but in fact they contribute to the transmission of infection from one child to another.
There is one consolation: adults have nothing to worry about. He is not at risk of becoming infected with Streptococcus mutans because these microorganisms have been living in his mouth for a long time.
Why is tooth decay contagious in children?
They are more susceptible to tooth decay than adults. There is an explanation for this: children eat more sweets, take care of their hygiene worse, and have a weaker immune system. If there are cariogenic microbes in the oral cavity, the risk of developing caries in a child is higher than in an adult. This especially applies to very young children under the age of 3 years.
Let us describe several typical cases that can lead to infection of a child with bacteria of the Streptococcus group. So, a baby can become infected with tooth decay when the mother tries his food to check her temperature. This cannot be done, and not only because of cariogenic microbes. An adult’s mouth contains many bacteria that a child’s immune system cannot cope with. There is a risk of infection with microbes that will cause an infection. Some mothers, if their baby drops the pacifier, suck on it and put it back in the baby's mouth. In such situations, women risk both their health and the health of their children.
Caries in baby teeth develops quickly, destroying hard tissue and damaging the gums. The baby constantly cries and refuses to eat. Many parents turn a blind eye to this problem, believing that caries of primary teeth is not dangerous. However, it can cause complications, including: oral infections, systemic diseases, gastrointestinal problems and caries of molars.
How to protect a child from carious bacteria?
First of all, you must follow one rule - do not put anything in the child's mouth that was previously in the parent's mouth. You can always moisten the pacifier with water, not saliva. The child should try food with a separate spoon or fork. If your child drops cutlery, do not lick it, as this is not the way to clean it. In the first months of a child’s life, you should also avoid kissing on the lips, especially if the parents have pronounced caries.
Be careful who and when you kiss But the problem applies not only to children, but also to people who like to kiss. Cause? The touching of tongues and the exchange of saliva that occurs during a long and passionate kiss are also an exchange of bacterial flora between partners. Bacteria literally move from mouth to mouth.
The saliva of a person who does not have cavities contains a balanced amount of "good" and "bad" bacteria, which are natural oral flora. However, at the moment of contact with the saliva of a person with caries and developed bacterial plaque, the balance may be upset. More caries bacteria appear and the risk of developing caries increases even with healthy teeth.
Moreover, the pH of the mouth may also change during a kiss, especially if one of the kissers previously ate a large portion of sweets, drank a sweet drink or wine. In this situation, the oral environment is acidified by acids produced by sugar-feeding bacteria.
Is caries inherited?
This is another common question related to the nature of the origin of caries. Incorrect metabolism, weak immunity, abrasion of enamel and anatomical structures of the jaw can be inherited from parents to children. Oral bacteria do not pass from mother to child during pregnancy or delivery. A child may have a genetic predisposition to diseases and conditions that increase the risk of developing tooth decay. There is no gene for caries pathology as such.
How to find out if you have dental caries
Absolutely all people are carriers of the bacteria Streptococcus mutans, but being a carrier does not mean getting sick. If the body’s immune response is strong enough, if tooth enamel receives a sufficient amount of microelements, if a person takes proper care of his oral cavity every day, then the risk of caries is reduced several times.
For comparison! In countries where preventive medicine is properly structured, this disease occurs several times less frequently. For example, in Finland, 175-200 cases of caries are diagnosed per 1000 children aged 7-12 years, while in Russia for the same number of children there are 1000-1200 cases of caries, i.e. and sick children, and the number of affected teeth in our country is much higher.
Does caries transfer from one tooth to another?
Can a tooth affected by caries lead to infection of the tissue of neighboring teeth with carious bacteria? This happens in the absence of treatment and insufficient hygiene. The number of bacteria in the mouth increases, they spread throughout the entire cavity, forming pathological foci in different places of the jaw. The patient may be diagnosed with multiple caries with localization of carious lesions on several teeth.
So, it is possible to become infected with caries, but carious bacteria alone are not enough for the development of the disease. Only in the presence of several factors does a person begin the process of demineralization of enamel and destruction of dentin. Dentists recommend not to worry about this and not be afraid of contracting caries through a kiss. It is better to pay more attention to hygiene. However, brushing your teeth alone is not enough. As additional hygiene products, it is necessary to use dental floss, rinses and irrigators. Doctors also advise eating right, exercising, and visiting the dentist twice a year. If you follow preventive measures, you can live your whole life without caries.
Sources:
- tvoidantist.ru
- stoma.click
- mnogozubov-ru.turbopages.org
Do adjacent teeth become infected with caries?
The development of pathogenic microbes occurs in hard-to-reach places where the proper amount of saliva, which reduces acidity, or the bristles of a toothbrush, which remove plaque, do not reach. Such a place may be the closure of the walls of two crowns. If you do not use dental floss or an irrigator - special devices for cleaning the interdental space, then bacteria will actively multiply in this cramped corner - and caries will affect both crowns. Thus, the disease does not spread to neighboring units, but develops between them.
Signs that can help identify a tendency to caries
The first symptoms, which may indicate a predisposition to carious lesions, appear in a child at a very young age:
- saliva is too viscous;
- delay in the eruption of baby teeth or incompletely erupted teeth;
- improperly formed dental units;
- numerous plaque on tooth enamel, which accumulates very quickly.
As a child gets older, he or she may begin to complain of a sour taste in the mouth that gets worse after eating.
How to identify caries?
Many dental diseases begin asymptomatically and also develop asymptomatically to serious stages. Pain occurs when the tooth is already completely destroyed. The earlier caries is detected, the easier and cheaper it is to treat, and there is a chance that you will forget about it for a long time.
Caries develops gradually, and its symptoms gradually appear. If you are attentive to your health, you will not miss the onset of the disease.
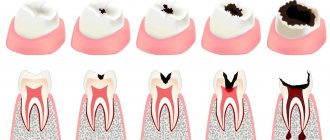
- Caries at the spot stage.
This is the beginning of the carious process, while demineralization of the enamel is just beginning. It loses a critical amount of minerals and becomes porous. At this stage, dull spots appear on the surface of the tooth. There are no indentations yet - only the color of the enamel changes: it becomes whiter or turns yellow. In the future, caries will progress, and the color of the spot will darken. A change in the color of an area of enamel is the only sign of incipient tooth disease.
- Initial caries.
At this stage, the enamel has already lost its original structure and begins to deteriorate. You can notice a depression, but the carious process has not yet gone beyond the tooth enamel. From time to time a person notices increased tooth sensitivity to irritants: cold or hot. If you haven’t noticed this before, this is a reason to make an appointment with a dentist.
- Average caries.
A carious cavity has formed in the tooth, but it is located within the dental dentin - the tooth tissue located under the enamel. The tooth reacts to cold, hot, sour. Food gets into the tooth cavity, causing discomfort.
- Deep caries.
The carious cavity occupies a significant part of the dental crown. The tooth reacts to irritants; food entering the carious cavity causes pain. Moreover, you can accurately identify the problem tooth. This is a serious condition because... Often at this stage, changes may appear in the pulp - the neurovascular bundle that nourishes the tooth. Further progression of the process in the absence of treatment will cause a complication in the form of pulpitis.
Caries can affect both the front incisors and chewing teeth. It can be located anywhere in the tooth, including between the teeth – on the proximal, i.e. lateral surface. There are frequent cases of gingival lesions, this is the so-called cervical caries. The most difficult to treat is tooth root caries.
Sometimes caries may not be noticeable during a routine examination if the cavity develops under a thin layer of enamel. In this case, dentists talk about hidden caries, which requires additional diagnostics and must be identified especially carefully.
Infection in adults
Teeth affected by caries
It is not true to believe that tooth decay is transmitted through a kiss. It is caused by bacteria under certain factors (listed below).
But it is important to understand that every adult already has a full set of these same bacteria, so you can kiss calmly and not be afraid that this will certainly cause caries. If there is no caries, this means that a person has strong protective mechanisms and genetically determined factors that prevent the formation of pathogenesis. A significant part in this is due to hygiene and human lifestyle.
The following factors contribute to the development of caries:
- weak immunity;
- poor-quality and unbalanced nutrition: deficiency of microelements and vitamins, excessive passion for sweets, carbonated drinks such as forfeit or cola;
- poor oral hygiene, the use of toothpaste and toothbrushes, the price of which is the lowest, so a person thinks that his teeth are safe after two brushings, but this is not entirely true, since hard-to-reach places remain uncleaned;
- the presence of bad habits, for example, older women who smoke are much more likely to visit dentists and lose teeth than men of the same age;
- prolonged drug therapy, self-medication, which leads to disruption of the integrity of enamel and dentin;
- endocrine pathologies;
- wearing orthopedic or orthodontic structures, which, firstly, cause damage to the tooth, and secondly, make it difficult to clean the teeth.
What to do if you are prone to illness
Caries develops slowly and gradually destroys teeth. Pathology can be cured at any stage of its development. Of course, doing this at the initial stage of the onset of the disease is much easier. Therefore, even at a young age, you need to visit the dentist regularly. If you have a predisposition to the disease, you must:
- undergo orthodontic treatment if you have problems with your bite and crowded teeth;
- strengthen the enamel with special pastes and gels, which a specialist will help you choose;
- enrich your diet with foods rich in calcium and fluoride;
- minimize the consumption of sweets;
- if necessary, seal the fissures;
- brush your teeth twice a day for three minutes;
- change your toothbrush at least once every two to three months;
- rinse your mouth after eating;
- clean interdental and hard-to-reach areas of the oral cavity with floss and irrigator;
- immediately treat identified carious formations, whether they are on molars or baby teeth.
How to prevent caries: preventive measures
The most effective and, importantly, cheapest way to combat carious lesions is its prevention. Since it is impossible to completely get rid of harmful bacteria, you can slow down or completely stop their reproduction and spread.
- daily oral hygiene (it is important to brush your teeth in the morning after breakfast and in the evening before bed, in the afternoon after lunch and afternoon snack, you need to rinse your mouth with a special solution or just water and remove food particles with dental floss),
- balanced diet (limit the consumption of sugar-containing dishes, increase the consumption of vegetables and fruits, fish and fiber),
- giving up bad habits (tobacco smoke destroys enamel and negatively affects the condition of the gums, reducing their protective function and slowing down metabolism),
- refusal of uncontrolled use of medications, especially antibiotics,
- giving up the habit of licking spoons, pacifiers, toys of small children,
- maintain overall immunity in good shape.
Thus, carious lesions can be avoided, even when infected with the bacteria that cause them.
Treatment of caries
Placement of fillings
Filling a carious cavity is the main method of treating caries. Before this, the dentist carefully removes the affected tooth tissue so that caries does not develop further.
Filling materials come in different types, but the most common and popular option at the moment is heliocomposite. They are the most durable, durable and aesthetically pleasing: you can choose a material that will be as close in color as possible to the tooth tissue and therefore unnoticeable. Of course, material manufacturers are also very important. GUTA CLINIC uses products from Japanese companies GC and Tokuyama Dental C, and French Septodont (including materials that have special permission for use in pediatric dentistry).
Unfortunately, absolutely all fillings are placed only temporarily. Their service life is on average 5 years (although it can be longer if the mineral density of the tooth tissue is high enough). Over time, the material shrinks, which can result in thin tooth walls breaking off or secondary caries developing. The color also changes over time, so that the filling becomes noticeable.
The filling needs to be changed if:
- it is destroyed;
- the filling material does not adhere tightly to the tooth, this increases the likelihood of recurrent caries;
- the filling hangs over the gum - this causes inflammation, pain and bleeding;
- the filling does not restore the anatomical shape of the tooth (in particular, the surface of the filling is heavily erased), which leads to a change in the bite;
- Root canal treatment of a filled tooth is necessary.
Complications of caries
If you delay treatment of caries, this will inevitably lead to unpleasant consequences, sometimes even tooth loss.
Typical complications of caries:
- Pulpitis
is an inflammation of the neurovascular bundle of the tooth, which causes severe pain. If you miss the moment, the pulp dies (necrotizes), and the tooth tissues stop receiving the necessary nutrition from the inside. - Periodontitis
– inflammation around the roots of the tooth (periodontal); - Periodontal abscess
- the formation of a purulent cavity at the roots of the tooth. - A cyst
is another consequence of periodontitis. Destruction of bone tissue with the formation of a cavity where a cyst is formed, usually filled with pus. - Flux
is the detachment of the periosteum and the filling of the resulting space with pus.