Everyone knows that you should not kiss a person who has the flu, acute respiratory infections or ARVI. Yes, it would be unreasonable to kiss someone who sneezes and coughs. However, these are not all the diseases that can be contracted through a kiss.
There are many other infections that enter the body through saliva. The entry gates are microcracks and microdamages in the oral cavity, as a result of which the infection can end up in the bloodstream.
What diseases can you get through a kiss?
How is stomatitis transmitted, is it contagious or not?
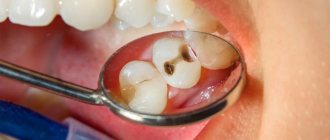
Changes in the mucous membrane of the oral cavity in a person, whether ulcers or scratches, cause discomfort and interfere with normal life. When such changes are detected, many immediately believe that it is stomatitis. How to distinguish characteristic rashes from other diseases of an inflammatory nature and what it is, whether it poses a threat to others and the victim’s body as a whole are questions that plague those who are faced with this problem.
What is stomatitis: causes and symptoms
Stomatitis is an inflammatory disease that affects the oral mucosa, which is caused by various infectious and non-infectious factors.
Over time, the usual form of the sore can become complicated, when ulcers and hemorrhages appear at the site of inflammation, causing even greater discomfort for the patient at the time of eating. Against this background, body temperature rises, malaise and drowsiness appear.
Based on the etiological factor, you can understand whether stomatitis is contagious or not for surrounding people.
For non-infectious stomatitis, the trigger is often a weakened immune system. Young children often face this problem, since their immunity is still defective.
The most common causes of the disease are:
- oral care;
- cleaning your mouth with someone else's personal hygiene devices;
- reduced immune system due to concomitant diseases;
- infectious nature;
- allergic reactions to the active components of toothpastes or rinses;
- mechanical damage from a toothbrush with rough bristles or dental sticks.
Types of stomatitis and routes of infection
In order to figure out whether the patient is contagious to others or not, it is important to distinguish between the types of stomatitis.
- Infectious etiology:
- viruses;
- bacteria;
- fungal flora.
- Non-infectious nature:
- traumatic;
- aphthous.
An examination of the patient’s oral cavity and a survey will help you understand which type is present in the patient. It is important to know with whom this person communicated the day before and what complaints he had. Knowledge of the distinctive features of each listed species will be able to correctly guide the doctor as to whether there is a risk of becoming infectious or not.
Is stomatitis in adults contagious or not?
Due to the fact that there are many etiological factors, not all of them are dangerous. Infectious stomatitis is contagious in adults and children, non-infectious diseases (traumatic and aphthous) are not contagious.
Viral lesions of the mouth, regardless of the pathogen, are transmitted to others through any contact (domestic, hematogenous, etc.) with an infectious person. This species is contagious.
In children, the main cause of stomatitis is the proliferation of bacterial pathogenic flora, due to their curiosity and mania for putting everything in their mouth.
Is stomatitis transmitted through a kiss or not?
Some types of stomatitis can be transmitted through saliva (kissing). Any pimple of infectious etiology poses a certain threat to the health of the person in contact with the patient.
How can stomatitis be transmitted?
- airborne droplets (at the time of communication);
- hematogenous route (through blood);
- contact or household route (unwashed hands, use of shared utensils or other personal hygiene devices);
- from mother to child (breastfeeding);
- interaction with other biological fluids (saliva during kissing, the entry of amniotic fluid into the baby’s oral cavity, sexual intercourse).
Since stomatitis of infectious etiology is contagious for any person, you should familiarize yourself with each type in detail and learn to distinguish them from non-infectious inflammation.
Viral
The viral form is one of the most contagious among other types. This disease is characterized by the presence of a specific pathogen that causes this condition. In this regard, the following are highlighted:
- herpetic;
- enterovirus;
- influenza and parainfluenza;
- associated with the causative agent of chickenpox;
- adenoviral.
Depending on the incubation period, which lasts 5–14 days, characteristic symptomatic manifestations appear. During this period of time, the patient is contagious to others, but danger threatens when symptoms appear (presence of ulcers with blisters, soreness, elevated body temperature). More often, stomatitis is transmitted by airborne droplets.
When kissing an infected person, there is an increased risk of stomatitis (contact with infectious biological fluid).
It is important not to confuse the clinical manifestations of infectious stomatitis with signs of tonsillitis (during examination, the mucous membrane of the tonsils is affected).
Bacterial
Bacterial stomatitis - manifests itself in children. This is due to a weak immune system and frequent injuries to the oral mucosa. Damaged tissue is an entry point for bacteria. In the area of implantation, local inflammation, swelling, and pain appear. There is an unpleasant odor from the mouth. When foreign microorganisms enter the blood, intoxication syndrome increases (body temperature rises, malaise, drowsiness, loss of appetite).
This species is as contagious as a viral one, and is most often transmitted through the air and through household contact.
Fungal
Fungal stomatitis in the mouth is contagious for healthy people if they use shared, poorly washed dishes, etc. The household route of transmission predominates here.
A characteristic feature of this type of stomatitis will be a white coating over the inflamed area of the mucous membrane. Intoxication syndrome is unlikely, since the fungal infection occurs only in the mucous (mucosal) layer.
Aphthous
Aphthous stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa that is not associated with an infectious nature. It occurs most often against a background of stress or as a manifestation of a local allergic reaction.
Upon examination, there will be a white or yellow sore - aphtha, which brings discomfort while eating. Don't worry about your loved ones - it's not contagious!
Traumatic prosthetic stomatitis
Sores or ulcers often appear in the oral cavity due to damage from foreign bodies (solid food, dentures, toothbrush with coarse bristles, etc.). Since the dentures are not tightly fixed, their movement causes irritation and injury to the mucous membrane. At the site of unstable fixation, the tissue becomes inflamed.
Despite the safe form of the disease in this category of people, the question arises whether it is possible to become infected with traumatic stomatitis in general or not.
With ordinary prosthetic stomatitis, there is no danger to others, but if complications are detected after infection, the patient becomes infected.
Preventive measures. How to protect yourself when communicating with a sick person
In order to prevent the development of stomatitis and not become contagious, you need to learn a few points:
- oral hygiene (using your own toothbrush);
- thoroughly wash shared utensils (it is advisable to have your own cup, plate, fork, etc.);
- interrupt contact with an infectious person (wearing a medical mask, keeping a distance at the time of conversation);
- the use of vitamin complexes with reduced immunity;
- proper nutrition;
- visit the dentist once a year.
If signs of illness are detected and in order to avoid possible infection of relatives, you should immediately seek medical help from a dentist.
As a result, it should be remembered that stomatitis that has an infectious etiology is contagious. It is not difficult to distinguish this species from a non-infectious one. Knowledge of the clinical picture of the disease can preserve not only the health of the infected person, but also the health of the people around him.
Cytomegalovirus
This is another member of the herpes virus family. It is very common and in most cases is in an inactive state in the body. Its activation occurs when the immune system is weakened, as well as during stressful situations. The virus is contained in all biological fluids of the infected person, and therefore can easily be transmitted through saliva during a kiss. Cytomegalovirus is especially dangerous for pregnant women, since when infected with it, the child often dies in utero. Surviving children who were infected in utero subsequently develop various abnormalities.
Is stomatitis transmitted through kissing?
Summary: [show]
There are different forms of the disease, each with its own mode of transmission. The causative agent of the disease is transmitted through contaminated objects or by airborne droplets from person to person. Even completely healthy people can get stomatitis if they are in prolonged contact with someone who is sick. This infection is quite contagious and even with an ordinary kiss you can catch it.
Is it allowed to kiss with stomatitis?
The nature and manifestations of the pathology are diverse, and, despite the fact that the disease has been sufficiently well studied, experts cannot accurately determine the mechanism of its formation. According to one version, the disease begins due to the response of the immune system to unknown irritants that have penetrated the oral cavity.
Various microorganisms moving through the air (for example, herpes virus or staphylococcus) can act as such irritants. In this case, when kissing a person who has stomatitis, the partner is almost guaranteed to receive pathogenic viruses or bacteria. To prevent unnecessary risk, it is better not to kiss until you have fully recovered.
During the development of the disease, it is absolutely forbidden to kiss young children, since their immune system has not yet developed ways to fight certain infectious agents. Stomatitis can also be caused by fungi that have settled in the oral cavity, so in such cases it is also worth temporarily limiting kissing so as not to transmit pathogens to your partner.
What to do if stomatitis is not contagious
In some cases, the disease is provoked not by infectious agents, but by other factors. These may be pathologies of the gastrointestinal system, poor oral hygiene, or incorrectly selected dentures. In such cases, you should also not kiss, since due to an imbalance of microflora in the oral cavity and the development of inflammatory processes during illness, bad breath is often observed. The partner in such a situation will receive only unpleasant sensations from the kiss, and not positive emotions.
If hygiene measures are observed and appropriate medications are taken, stomatitis is cured in 10 days, after which you can safely kiss your loved ones.
The likelihood of contracting aphthous stomatitis
People with serious chronic diseases are susceptible to aphthous stomatitis. Most often these are diseases:
- Oral cavity.
- Throat.
- Upper respiratory tract.
The presence of a focus of infection weakens local immunity. The consequence is the appearance of blisters, ulcers, and plaque. A yellow-white coating is characteristic. Erosive changes become pronounced if left untreated.
The disease may not cause concern for a long time. In any disease, with exacerbation of chronic diseases, the eroded surfaces become painful.
The risk of developing aphthous stomatitis increases:
- Poor nutrition .
- The presence of long-term non-healing wounds in the mouth.
- Presence of untreated teeth.
- Gum diseases .
- Incorrectly fitted dentures .
- Oral injuries
Diet for stomatitis
Stomatitis often worries children, becoming a consequence of insufficient immune forces of the body, weakened by some disease.
Aphthous stomatitis is typical for those suffering from diabetes.
Aphthous stomatitis itself is not contagious. Communication with a person who has signs of the disease is not dangerous. The risk of infection arises when a patient with aphthous stomatitis “adds” a viral infection to the underlying disease.
Redness of the throat may indicate pharyngitis, purulent discharge from the tonsils may indicate tonsillitis. In these cases, the pathogen is transmitted to a healthy person through contact with a sick person.
Is it possible to kiss with stomatitis?
- Is it possible to kiss with stomatitis?
- How to treat stomatitis in an adult
- What diseases are transmitted through a kiss?
Can stomatitis be transmitted by kissing?
Stomatitis is diverse in origin and symptoms. Oddly enough, despite the fact that the disease has been thoroughly studied, experts still do not know exactly the mechanism of its occurrence. The most common version is that stomatitis occurs as a response of the human immune system to unfamiliar irritant substances found in the oral cavity.
As a result of the “attack” of lymphocytes of the immune system on the molecules of these substances, numerous small ulcers arise - the main symptom of stomatitis.
Such substances can be pathogenic microorganisms transmitted by airborne droplets, for example, the herpes virus or staphylococci. In this case, if a person with stomatitis wants to kiss his partner, he will almost certainly “give” him these pathogenic viruses or bacteria. Therefore, it is better not to take risks and refrain from kissing until complete recovery. Never kiss young children when they are sick, because their immune system cannot resist some viruses and bacteria that can be passed on to them.
Stomatitis can also be caused by fungi that have entered the oral cavity. In this case, kissing is also undesirable, because you can transmit these fungi to your partner.
If stomatitis is herpetic, it can even be transmitted through dishes. Therefore, during illness, use personal cutlery and rinse it with boiling water. After recovery, be sure to change your toothbrush.
Why you shouldn't kiss, even if stomatitis is not contagious
There are a number of cases when kissing with stomatitis cannot lead to infection of the partner. For example, if this disease is caused by problems in the gastrointestinal tract or arose as a result of poor oral hygiene, as well as insufficiently accurate selection of dentures. But even then, kissing is still undesirable.
The thing is that due to disturbances in the microflora in the oral cavity and inflammatory processes, stomatitis is often accompanied by the appearance of bad breath. Therefore, when you kiss, you can give your partner not pleasure, but very uncomfortable sensations. It’s better to get cured first, and then kiss your loved one for good health. Stomatitis often goes away within 10 days if you maintain good oral hygiene, take medications, or use medicated ointments.
How to treat stomatitis?
As we have already written, the treatment of stomatitis will depend on its type, and it will be prescribed by a dentist. It will include painkillers, drugs to speed up the healing of the mucous membrane, and drugs to prevent the disease in the future.
The doctor prescribes painkillers mainly for severe forms of stomatitis - if painful ulcers seriously interfere with eating, drinking and speaking.
Anti-inflammatory antibacterial agents can be represented by both tinctures and rinses (chamomile, sage, calendula), and disinfecting sprays and gels (Ingalipt, Lugol, Cholisal, Stomatidin, etc.).
If we are talking about contagious stomatitis (viral, fungal), then the course of treatment will consist, among other things, of antiviral and antifungal drugs.
The most difficult thing is to prescribe treatment for allergic stomatitis - first of all, it is necessary to identify and exclude the allergen and include a course of antihistamines.
In addition, immunomodulatory agents may be among the medications prescribed by the doctor. A healthy immune system will suppress the manifestations of herpes or aphthous stomatitis.
Rinses, sprays, tablets... the list of medications and preparations is really extensive, and choosing the right one is quite difficult. Sometimes it happens that the patient will eliminate the symptoms of stomatitis with home treatment, but the source of the disease will not be found, and after some time the problem will emerge again. That is why it is better not to self-medicate, but, if possible, immediately consult a doctor. The specialist will identify the real cause of the disease and select a medicine based on the patient’s age, other symptoms, possible side effects, etc.
You can make an appointment with a specialist at the As-Stom clinic by phone 597-05-05
or using
the online application form
on the website.
Is it possible to get stomatitis through a kiss?
Young people often don’t think about whether stomatitis is transmitted through kissing, and carefreely kiss their other halves. At the same time, they do not take any measures for treatment, considering this disease to be trivial. Is stomatitis so dangerous that you can’t contact other people?
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa, which in most cases is accompanied by the formation of ulcers. Along with this, swelling of the mucous membrane is observed, and a white or yellow-white coating forms. When communicating, a person feels discomfort, and pain occurs while eating. Increased salivation, gums often bleed, and bad breath appears.
Infection with stomatitis through kissing
The symptoms of the disease are quite different, as are the pathogens. Despite the seemingly complete study of stomatitis, scientists to this day do not know the exact method of its appearance; one version is inclined to believe that stomatitis is a reaction of the immune system to irritating substances unfamiliar to the body that have entered the oral cavity. As a result, the body sends lymphocytes to fight them, and so ulcers are obtained, which clearly indicate the presence of the disease.
In addition, a fungal infection in the mouth can also play the role of a pathogen. In such a situation, kissing is also best avoided.
If we are talking about herpes, it is very easy to catch it by using the patient’s dishes, so during the period of illness it is strongly recommended to maintain personal hygiene and scald the dishes with boiling water. Upon completion of treatment, you should change your toothbrush.
There is an excellent remedy against the herpes (aphthous) form of the disease. The use of acyclovir for stomatitis helps get rid of inflammation and pain.
What if stomatitis cannot infect a partner?
There are situations when kissing does not transmit stomatitis to a partner - for example, if the cause of stomatitis is a gastrointestinal disease, poor personal hygiene, or poor-quality fitting of dentures. But even in this case, it is better to refrain from kissing. After all, the altered microflora of the mouth during stomatitis creates a bad odor from the oral cavity, which is unlikely to please your partner . To eliminate the bad odor, you can use Metrogyl Denta. Plus, Metrogyl Denta helps with stomatitis.
You should first undergo a course of treatment, and then you can move on to kissing. As a rule, the illness does not last longer than 10 days if patients adhere to good personal hygiene and take medications responsibly for topical or internal use.
General tips for the prevention and treatment of stomatitis
To prevent stomatitis, it is recommended to follow several rules:
- strengthen the immune system by taking vitamins, eating vegetables and fruits;
- avoid contact with the patient, give him separate dishes, do not use his personal belongings;
- brush your teeth carefully , avoiding injury to the gums;
- avoid stress;
- infections, hormonal diseases are recommended to be treated immediately.
Attention! Stomatitis is treated strictly under the supervision of a doctor who prescribes medications and monitors the patient’s condition . Ulcers and wounds are regularly lubricated with prescribed ointments and gels, and the mouth is rinsed with healing decoctions and solutions.
A kiss that tastes like “stomatitis”: is the disease contagious and how is it transmitted?
Stomatitis is a disease that is a lesion of the oral mucosa.
Often occurs as a result of an immune response to the appearance of molecules that are difficult to recognize by the body.
The appearance of such elements causes an attack on lymphocytes, forming ulcers. The body reacts in a similar way to a human organ transplant.
Stomatitis is transmitted through kissing or any other type of contact . The cause of the disease can be a simple lack of oral hygiene.
Ulcers heal within 7-14 days. People who have had stomatitis are susceptible to recurrent illness, however, with a fairly variable frequency. Sometimes the disease appears several times throughout the year, which indicates a chronic form of the disease.
Is stomatitis contagious?
The question of whether stomatitis is contagious should be considered at the level of the root cause of the outbreak of the disease.
Of course, there are contagious types - herpes and candidal stomatitis are especially dangerous. However, each disease is considered by specialists individually.
The following types of stomatitis exist:
- Viral. Generated by viruses caused by diseases such as chickenpox, herpes or influenza. Symptoms include pain in the oral cavity and fever. It manifests itself in the form of the appearance of purulent blisters, which, bursting, form wounds. This type of disease is contagious;
- Bacterial. It affects not only the mucous membrane, but also the gums, palate or sublingual area with the appearance of cracks and bad breath, as well as nausea, dizziness, increased heart rate and general weakness. In most cases, it poses a danger to newborns who do not have a sufficiently developed immune system due to their age. For adults, viral stomatitis is dangerous only through airborne droplets or in the case of sharing cutlery with a patient;
- It is known that about 20% of the population suffers from this disease, of which pregnant women predominate.
Transmission routes
As mentioned earlier, the routes of transmission of stomatitis can be completely different - from airborne droplets to traumatic.
Children often suffer from stomatitis due to poorly developed immunity, which is not yet able to fully cope with surrounding viruses.
Is stomatitis transmitted through kissing?
Prolonged contact with a sick person can also lead to infection with stomatitis.Constant exposure of the oral mucosa to foreign pathogenic microorganisms causes a decrease in the immune system and a reduction in the protective mechanisms of the oral cavity itself.
That is why the transmission of stomatitis through kissing is quite common.
How to protect yourself?
In order to protect yourself from stomatitis, first of all, you must adhere to the rules of hygiene of the gums and teeth.One of the main protective measures is strengthening the immune system through a healthy diet.
Often stomatitis can be caused by a deficiency of B vitamins, zinc or iron in the body.
A preventive examination by a dentist and timely dental treatment are mandatory.
If the infection with stomatitis is permanent, then it is necessary that all family members living with the patient be examined by a doctor.
The cause of frequent stomatitis may unexpectedly be someone from your close circle, without even knowing it.
Mononucleosis
This disease is also caused by the herpes virus, but not the first type, but the fourth. This virus is also called the Epstein-Barr virus. The virus enters the body through saliva and begins to multiply in the mouth and throat. For this reason, it is very easy to become infected with mononucleosis through a kiss. This disease even has a third name - “kissing disease.” Symptoms of mononucleosis are high fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph nodes. Symptoms do not begin to appear immediately, but after a couple of weeks.
Is it possible to cure periodontal disease forever?
Treatment of the disease is carried out comprehensively with the involvement of specialists in the field of dentistry, immunology, endocrinology, gastroenterology, and therapy. The essence of treatment is to eliminate symptoms, strengthen teeth and prevent relapses. Additionally, restoration of lost tissue is carried out.
It is problematic to cure periodontal disease in the last stage, but contacting competent doctors will help get rid of unpleasant sensations and stop the further development of the disease, preserving your teeth.
Splinting
A treatment method used to strengthen loose teeth. Splinting involves combining individual teeth into a single orthopedic structure in the form of a block to reduce their mobility.
Prosthetics
Prosthetics for periodontal disease are carried out in combination with other treatment methods; it is possible to install several types of dentures, depending on the condition of the gums. Removable prosthetics helps reduce the load on areas affected by periodontal disease: installing clasp, nylon dentures that do not rub the mucous membranes and have a fastening system that does not damage the supporting teeth.
In some cases, permanent bridge structures are used to strengthen a number of teeth located one behind the other.
Prosthetics does not eliminate the cause of the disease. Without an integrated approach, tissue reduction will continue, and after 3-5 years the patient will need replacement prostheses.
Signs of periodontal disease
The disease has an asymptomatic period of development, the symptoms become pronounced after the transition to moderate severity, when the periodontal tissues become very thin. Visual detection of symptoms is complicated by the presence of tartar, which hides the necks of the teeth and does not allow assessing their condition. A diagnosis can only be made after professional cleaning by a dentist.
The number and severity of symptoms depend on the stage. Signs of the disease include:
- exposure of tooth roots;
- the appearance of a pale tint in the gum tissue;
- increased sensitivity of the patient’s teeth to cold and hot foods;
- darkening of tooth enamel;
- development of sclerotic changes in bone tissue;
- the appearance of gaps between teeth;
- discomfort and itching in the gum area;
- loss of stability, loosening of teeth.
Inflammation and bleeding of the gums during periodontal disease are rare and are present in advanced stages of the disease.
To make a diagnosis, the dentist prescribes an x-ray examination, which allows you to determine the presence of sclerosis of bone tissue, the degree of development of gum atrophy and identify foci of osteoporosis.
Treatment
The treatment procedure depends on the stage of the disease and includes the following steps:
- Diagnostics at the dentist, making a diagnosis and taking an x-ray of the jaw;
- In-office dental cleaning to remove hard deposits, antibacterial therapy of the oral cavity;
- Orthopedic treatment of loose teeth to strengthen them. Splinting and prosthetic techniques are used to reduce the load on damaged teeth;
- Physiotherapeutic treatment - procedures to restore blood circulation to the gums and prevent relapses of the disease;
- Gum tissue augmentation is carried out when the necks of the teeth are severely exposed.
Self-treatment is impossible. Home remedies are not able to get rid of the causes of the disease. If you notice the first symptoms, contact your dentist.