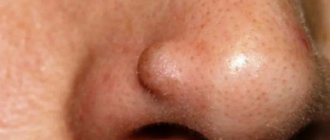
Milium (horny cyst, whitehead, “millet”) is an epidermal cystic formation at the mouth of the hair follicle, looking like a small white grain. Typically, milia are localized on the face in areas with relatively thin skin, very rarely on the body, and exist for a long period without any changes. Milia are a fairly common cosmetic problem and can occur at any age. Whiteheads appear especially often during puberty; also often found in newborn babies (neonatal acne). Female representatives are more susceptible to the appearance of milia.
How is it formed
Every person from birth has a genetically determined skin color - the so-called permanent pigment.
When exposed to external and internal factors, an additional one is produced, which can be either a temporary physiological phenomenon (natural tanning) or a pathological one, difficult to remove even with special lasers (lentigo, vitiligo, etc.). The formation mechanism itself occurs in the epidermal layer. Here are located keratinocytes - epidermal cells. Their life cycle is up to 60 days, so they are constantly updated. To protect young and vulnerable cellular structures from sun exposure, melanocytes exist. They belong to the nervous system and are called upon to produce melanin, which absorbs ultraviolet radiation.
If the body is healthy, there is no overdose of solar radiation, melanocytes will produce a sufficient amount of protection. However, if there are failures, the “protectors” begin to be distributed unevenly, which leads to the formation of hyperpigmented areas.
Causes of hyperpigmentation
An increase in melanin production can be associated both with physiological changes occurring in the body and as a result of pathologies. The most well-known factors influencing the occurrence of stains are:
- endocrine diseases;
- hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and adrenal glands;
- metabolic disorder;
- vitamin deficiency or hypervitaminosis;
- helminthic infestations;
- severe intoxication of the body;
- trauma or inflammatory processes;
- prolonged exposure to the sun;
- taking medications - antibiotics of the tetracycline group, gentamicins, erythromycins, as well as some NSAIDs, salicylic acid, antidepressants, diuretics, sleeping pills and sedatives, antihistamines, St. John's wort extract, etc.;
- heredity.
Changes can also appear due to prolonged stress. Since melanocytes belong to the nervous system, any fluctuations and unstable conditions lead to serious pigmentation disorders.
Causes of age spots on the face
Cosmetic flaw occurs in women, men and even newborn children. There are several reasons for pigmentation:
- frequent and intense exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the skin - disrupts cell structure, inhibits regeneration, destroys collagen fibers;
- trauma - scratches, abrasions, cuts, hematomas can activate the production of melanin in a certain area;
- hormonal imbalance - during puberty, during pregnancy, menstruation, menopause;
- pathologies of internal organs - most often the adrenal glands, liver, gall and thyroid glands;
- skin diseases, especially acne;
- taking certain medications with photosensitivity effects;
- poor circulation in the extremities;
- diseases of the reproductive system;
- infections, viruses, bacteria, fungal pathologies;
- heredity.
In newborns, pigment spots may appear due to the difficulties of the mother's delivery. Most of them go away on their own in the first year of life, but all formations require monitoring.
Localization of spots
They can have different sizes, both with clear contours and blurry ones, merge together or not grow at all. Depending on the differential diagnosis and the type of hypermelanosis, they can be located both in certain areas and without specific boundaries, covering absolutely any area of the body.
On the face
One of the most common sites of localization of many hyperpigmentations. This is due to the fact that the skin here is thin enough so that negative factors can attack them faster. Among the common phenomena are freckles, which can decorate the face all year round and also appear and disappear after exposure to the sun. They are also localized over the entire surface or located pointwise in the area of the cheeks, eyes, and forehead.
Anti-age drugs
Bb Laboratories – Delicate oil for deep cleansing
Laennec – solution for injection
Bb Laboratories – Two-phase serum concentrate
Two-phase placental serum concentrate
On the body
Namely on the arms, shoulders, chest, back, groin area. For each individual disease, there are areas where pigment accumulation is observed. For example, senile hyperpigmentation is typically located on the hands, forearms, and upper back.
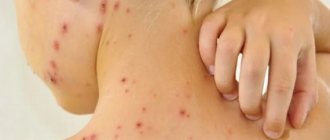
What is post-acne
Acne can appear on the face and neck, in the interscapular area, on the back and in the upper chest. Acne or acne is the formation of inflammatory elements on the skin - compacted reddened tubercles (papules) and blackheads, purulent white heads with redness around them. If elements are injured, squeezed out or heal poorly, post-inflammatory, scarring, and pigmentary changes form on the skin - this is post-acne.
This is what post-acne looks like
Types and symptoms of age spots
Let's consider the most characteristic signs of hypermelanosis, as well as control methods that are relevant for each specific type of pathology.
Freckles
The most common type of melanin accumulation. They are mainly located on the face, in the cheek area. In advanced cases, they can completely cover the entire surface of the skin with small distances between the spots. And also have a round or oval shape, small diameter, clear contours.
Genetic predisposition plays a major role, so freckles can appear in childhood. People with red and blond hair are most susceptible to them. This is due to the need for high melanin production to protect the skin.
Freckles can be easily distinguished from other types of spots by the complete disappearance of pigmentation in cold weather, and the appearance of a whole scattering on the face with the arrival of warmth. Therefore, to combat them, creams with maximum sun filters are used throughout the year, as well as lightening cosmetics.
Melasma
Spots without clear boundaries and endings, varying in shade from bronze to dark brown. They have the ability to stretch, grow, and merge with each other into huge pigmented areas that occupy a large surface of the body. The main provoking factor is considered to be hormonal disorders caused by menopause, pregnancy, and the use of oral contraceptives. Treatments include peeling methods and procedures that promote cell renewal. When the root causes are eliminated, the stains quickly disappear.
Melasma
The second name is melanosis. It can be acquired or hereditary, manifests itself in the form of an accumulation of melanin with uneven but clear boundaries and localization in open areas of the body. May occur as a result of Addison's disease, hemochromatosis, due to sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation, anthracene or acridine substances, diseases of the pituitary gland, ovaries, adrenal glands, syphilis, tuberculosis, malaria, treatment with hormones. Pigmentation is accompanied by redness, itching, peeling, and roughening of the skin.
To prevent progress, sunscreens are used, drug therapy is prescribed with steroid groups, retinoids, hydroacids, and vitamins B (1.6) and C are additionally used.
Becker's nevus
A characteristic defect in men, it is much less common in women. The first manifestations can be as early as 10 years of age. It is a hyperpigmented area protruding above the surface of the skin, on which dark long hairs grow. It occurs both as a result of genetic factors and can appear after sun exposure, changes in hormonal levels, in particular androgens. The location most often is the upper back and chest; it is not often found on the legs, groin, or head. It has a warty surface on which acne or comedones can be seen. Does not respond well to any cosmetic procedures or medications. An argon laser is used to minimize the aesthetic defect.
Secondary
Occurs at the site of mechanical damage. They can be either deep cuts, scratches, or acne, comedones, ulcers and other superficial causes that trigger the inflammatory process in the skin cells. There is an excess of melanin, resulting in staining. They are localized where the damage was and go away after the area returns to normal and the inflammation disappears. To speed up the lightening process, you can use special lightening creams or cosmetic procedures aimed at renewing the epidermal layer.
Age
As we age, the negative effects of ultraviolet radiation lead to increased melanin production in certain areas of the body. These are usually open areas that have been exposed to a lot of sunlight during their lifetime. With age, spots appear with a diameter of 1 to 5 cm, which are darker in color than the entire surface of the skin.
Berlocc's dermatitis
Refers to contact types of immune response to irritants. Usually due to contact with perfumes, colognes, and deodorants. It is located where the skin came into contact with the substance. Symptoms may include not only a change in the color of the dermal layer, but also itching, peeling, and swelling. It disappears quickly, just stop using perfume and in a few days everything will return to normal.
Chloasma
Large spots can merge into one large skin defect. They do not have a clear contour or boundaries and can grow and increase in size throughout life. Among the provoking factors are pregnancy and lactation, menopause, changes in hormonal levels due to diseases, stress, taking oral contraceptives, steroids, the use of hormone-containing ointments and some cosmetics.
How to prevent the appearance of age spots?
If the cause of pigmentation does not lie in a hereditary factor, a cosmetic defect can be avoided. Preventive measures:
- do not develop diseases of internal organs - be sure to undergo routine examinations with doctors twice a year;
- do not get carried away with tanning - both in the sun and in the solarium;
- take care of skin protection - go outside in winter, after applying cream with SPF 30, in summer the indicator should be 50;
- choose wisely skincare products to maintain a beautiful and even skin tone;
- maintain a drinking regime - do not let the skin dry out;
- monitor hygiene, prevent the development of acne and the formation of comedones;
- control hormonal levels.
It is also important to take care of prevention long before the period of wilting. The sooner sufficient attention is paid to care and protection, the later the skin will undergo age-related changes. Pigment spots are a phenomenon that can and should be combated. Don’t give up if home treatments don’t bring results; you can always turn to a cosmetologist for help.
What causes pigment spots to appear on the face after sunbathing?
Most manifestations of hyperpigmentation occur after the negative effects of ultraviolet rays. Among those that immediately appear are freckles, various melasma and chloasma. There are also those that have a cumulative effect, for example, lentigo.
Also, if during the summer vacation there were inflammatory processes in open areas of the body, most likely after they heal, a change in shade can be clearly observed.
Prolonged exposure to the hot sun with the presence of existing tumors and increased pigmentation can be fraught with the degeneration of harmless spots into aggressive cancer - melanoma. Therefore, you should limit your tanning time and use special cosmetics for protection.
How to remove pigmentation on the face at home using cosmetics
If the spots are not intense and do not occupy large areas, you can make them lighter yourself. Pharmaceutical products and skincare products are suitable for this:
- Hydroquinone, lavender oil, hydrogen peroxide, and resorcinol have an exfoliating and keratolytic effect.
- Weak fruit acids, which can be used at home, work well to whiten stains. This is citric, ascorbic, and lactic acid of low concentration. These products are also suitable for preparing for salon chemical peels.
- Lightening cosmetic compositions marked Anti-Pigment. Creams, lotions and serums containing azelaine, kojic acid, vitamin C.
Any product can be used only after testing for possible allergies. If the body accepts the composition calmly, without a negative reaction, you can begin the procedures according to the instructions for the drug.
Age spots and peeling
Melanin accumulation occurs in the upper layers of the epidermis. In order to remove unaesthetic problems, products that stimulate the renewal of the dermis are used. The most effective peelings are: chemical, mechanical, laser. They promote the regeneration of epidermal cells, forcing keratinocytes to produce new ones as quickly as possible, which will not have a large accumulation of coloring pigment. When eliminating the root causes of hyperpigmentation, there is a chance that you will forget about various spots for a long time.
Causeless manifestations
It happens that people try to protect their skin, use special sunscreens, but hyperpigmented areas still appear. It's like it happens for no apparent reason. However, for melanocytes to malfunction, even a small but prolonged stress or temporary hormonal imbalance is enough.
It is also worth noting the cumulative negative effect of ultraviolet radiation, which can manifest itself over the years on areas of the body that received sunburn in early childhood. Therefore, only at first glance it seems that hypermelanosis arose without provoking factors. In fact, he has hidden reasons.
Liver pigment spots
Deterioration in the functionality of internal organs can also lead to the formation of aesthetic defects. The liver plays the role of a filter, retaining and processing all dangerous substances, and then removing them from the body. In cases where she fails to cope with her duties, slow but sure intoxication occurs, which is manifested not only by internal, but also by external pathologies.
Metabolic processes in tissues are disrupted, including the normal distribution of melanin; it accumulates in certain areas. Most often it appears on the face. The contours of such spots are not uniform, they do not have a clear boundary. The color can also vary from light to dark brown.
Lentigo
The phenomenon is popularly known as “senile ripples.” Appears in older people in areas of the body that have been exposed to intense ultraviolet rays throughout their lives. The pigment usually appears on the arms from the hands to the top of the shoulders, upper back, décolleté, and face. It is distinguished by its small size, different diameters and chaotic arrangement of spots.
The first manifestations can be noticed after 40 years; they noticeably age the appearance, so many people at this stage turn to cosmetologists to eliminate the defect. During menopause, hormonal changes lead to an increase in the amount of pigment. Chemical, mechanical and laser peels are used for treatment. Cosmetics and whitening creams will not cope with the problem.
There are various causes of hypopigmented spots on a child's face, ranging from conditions that resolve on their own within a few weeks to conditions that can last a lifetime.
Causes of white spots on a child's face
White spots can be caused by the following skin conditions:
Milia
Milia are also called milk spots. These tiny white bumps usually appear on the face and rarely on the upper torso or limbs. Although milia can be seen at any age, it is common in newborns.
Causes and diagnosis of milia
Milia occurs due to entrapment of keratin (skin scales) beneath the surface of the skin. If there is no improvement after a couple of weeks, you should consult a doctor. Diagnosis is made by visual examination and no tests are required.
Prevention and treatment of milia
There is no cure for milia and it often goes away within a few weeks or months. There is no need to treat milia in children.
How can you reduce milia at home?
- Wash your child's face daily with mild soap and water.
- Pat your face dry after washing.
- Be careful not to scratch the milia to prevent skin damage and infection.
- Do not apply lotions or oils to your baby's face.
Note: Some may confuse baby pimples or Epstein pearls with milia. However, acne can cause red bumps and pustules on the face. Epstein's pearls are small, white-yellow cysts that often resemble milia, but they appear on the roof of the mouth and gums.
Pityriasis alba (lichen alba)
Pityriasis alba is a self-limiting skin condition that causes dry, thin, scaly and pale patches on the face. It is common in children and adolescents and is considered a type of eczema or dermatitis.
The name of this condition comes from the characteristic appearance of the skin.
Causes of white ptyriasis
The causes of white ptyriasis have not yet been clarified. However, atopic dermatitis and dry skin often coexist with it. Exposure to the sun can make it more visible by tanning the surrounding skin.
Suspected causes such as under- or over-bathing, low serum copper levels, ultraviolet radiation, or Malassezia yeast have not yet been proven to cause hypopigmentation.
Symptoms and signs of ptyriasis alba
One or more white spots, varying from 0.5 to 5 cm in diameter, are a characteristic sign of pityriasis alba. It may also cause mild itching in some children.
Diagnosis of pityriasis versicolor
The condition can be diagnosed through a physical examination by a doctor. A skin biopsy may show mild spongiotic (fluid accumulation between cells) dermatitis with decreased melanin pigment. A skin scraping may also be taken to rule out a yeast infection.
Treatment of white lichen
Treatment is not recommended in asymptomatic cases. Moisturizers are helpful for dry skin, and mild hydrocortisone (topical steroid) creams can help reduce itching and redness in the area.
Tacrolimus ointment, pimecrolimus cream, and calcineurin inhibitors have been shown to be effective in the treatment of pityriasis alba.
The appearance of the skin may gradually return to normal over several months or two to three years.
Prevention of white deprivation
Limited sun exposure may help reduce your risk of developing this disease.
Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a depigmentation of the skin due to the loss of melanocytes, which are the cells that produce the skin pigment called melanin. Vitiligo can affect both sun-exposed and unprotected areas of the body. Also, with the disease, depigmentation of the lips and gray hair are often observed.
Causes of vitiligo
The exact causes of vitiligo are unknown. The disease may be associated with dysfunction or loss of melanocytes (the cells that produce the pigment melanin), which give the skin its color. This may be due to genetic factors or an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks the melanocytes.
Vitiligo can occur at any age, but the onset of the disease is typical in children and adolescents.
Diagnosis of vitiligo
Vitiligo can be diagnosed through a physical examination. Rarely, a skin biopsy is performed to help confirm the diagnosis by the absence of melanocytes (pigment cells) on the skin. Thyroid disease and diabetes are checked as these may increase the risk of vitiligo in many people.
Treatment of vitiligo
Mild vitiligo may not require treatment: the spots will disappear over time. However, there are several treatments available to make your skin tone even.
Corticosteroid creams, photochemotherapy (PUVA), narrow band ultraviolet B (UVB) therapy, and depigmentation are a few treatment options. Using sunscreen can reduce tanning of the skin around vitiligo patches, and concealers can hide white spots on the skin.
Although vitiligo can be distressing to many people due to its appearance, it is not a medically dangerous condition. Vitiligo is not an infection, skin cancer, or a contagious disease.
Shingles
Shingles is a fungal skin infection that causes lighter or darker patches on the skin. The disease occurs at any age, but is most often seen in adolescents and young adults.
Causes of herpes zoster
Shingles is caused by a yeast that is usually present on the skin. Their excessive growth under the influence of environmental factors can lead to the appearance of spots on the skin. Malnutrition and excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis) can also lead to yeast growth.
Note: Shingles cannot be passed from one person to another (not contagious) since most people have Malassezia yeast on their skin. This condition is not caused by poor hygiene.
A weak immune system, oily and moist skin, or hot and humid climates may increase the risk of contracting shingles. Children taking corticosteroid medications may also be susceptible to this condition.
Signs and symptoms of shingles
Although white patches can appear on the face, they are often found on the chest, back, and forearms. The spots may be pink or light brown and have scales. Skin changes are usually limited to the outer layer of the skin and often do not cause any pain or itching.
Diagnosis of herpes zoster
A physical examination is sufficient to diagnose shingles. In rare cases, doctors may collect a skin scraping to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment of herpes zoster
Shampoo containing selenium sulfide is the main treatment method. If the condition does not go away, then you can use antifungal or anti-dandruff shampoos. The skin may improve over a short period of time in many children. However, it may take several months to achieve an even skin tone. To prevent relapse of the disease, monthly use of shampoo is recommended.
Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis
Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis (IGH) is a skin condition with small, white, oval patches.
IGH is more common in older, fair-skinned people than in children and often goes undetected.
Causes of idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis
The exact cause of hypomelanosis is unknown. Although this has not yet been proven, it is believed that it may be related to sun exposure.
Diagnosis of idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis
A physical examination is sufficient to determine the condition. Rarely are biopsy samples taken. There is usually a decrease in the number of melanocytes in the affected areas, although they are not completely absent as in vitiligo.
Treatment of idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis
IGH spots are benign and do not require medical treatment. Most procedures are aimed at improving the cosmetic appearance of the skin.
Home remedies may include regular use of sunscreen and physical barriers to prevent sun exposure, as it can promote or accelerate hypomelanosis.
References:
- Milia; Healthychildren; The American Academy of Pediatrics
- Milia; MedlinePlus; The United States National Library of Medicine
- Pityriasis alba; DermNet NZ; The New Zealand Dermatological Society
- Donald N. Givler, et al.; Pityriasis Alba; The United States National Library of Medicine
- Pityriasis alba; C. S. Mott Children's Hospital; The University of Michigan 6. Pityriasis alba; The Australasian College of Dermatologists (ACD)
- Vitiligo; The mission of the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases
- Vitiligo; National Health Service
- Diagnosing Vitiligo; NYU Langone Medical Center
- Vitiligo: Diagnosis and Treatment; The American Academy of Pediatrics
- Tinea Versicolor; Harvard Medical School
- Pityriasis Versicolor; National Health Service
- Falon Brown and Jonathan S. Crane; Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis; The United States National Library of Medicine
- Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis; DermNet NZ; The New Zealand Dermatological Society
Solarium - is it harmful?
It is also a mistake to think that sun tanning is harmful, and nothing will happen in specialized salons in a few minutes. On the beach, the skin gets a lot of heat, but this happens gradually. In the booths, a loading dose of ultraviolet radiation is given in a few minutes, which is difficult to obtain outdoors even in a whole day.
People with a fair skin type, with the presence of moles and nevi, freckles, existing aesthetic defects in the form of increased melanin production, need to get rid of the habit of visiting a solarium. The consequences can be expressed both in the progression of unsightly changes in the epidermal layer, and in their degeneration into malignant neoplasms.
Diagnostics
To accurately determine the type of hypermelanosis, as well as to identify effective means of control, you need to contact a dermatologist. At the initial visit, the doctor will collect the patient's medical history to determine the most likely internal and external factors that will indicate a certain type of disorder. He will examine the skin and also prescribe a number of tests:
- AOK and OAM;
- blood biochemistry;
- Wood's lamp tests;
- scraping;
- biopsy.
If a malignant neoplasm or fungal infection is suspected, referrals will be given for the last two procedures on the list. As a result, the specialist will be able to accurately determine the type of illness and prescribe therapeutic or cosmetic procedures.
Anti-age drugs
Bb Laboratories – Hyaluron-elastin-collagen extract
Laennec – solution for injection
Curacen Essence (20 fl x 2 ml)
Two-phase placental serum concentrate
How to fight
Among the modern and effective methods of struggle, it is worth highlighting:
- cosmetic preparations;
- laser peeling;
- phototherapy.
Depending on the variety, medications may be prescribed to address the underlying causes. However, to remove an aesthetic defect, it will be necessary to wait for the cell surface to renew itself, or to help it renew itself faster with the help of additional deep peeling and cosmetic photorejuvenation procedures.
Cosmetic preparations
Among the popular drugs that give noticeable results in the fight against hyperpigmentation are placental products with a high content of natural peptides, amino acids and hyaluronic acid, as well as vitamins, micro- and macroelements. Injection product Curacen (Curasen) and non-injection drug Curacen Essence (Curasen Essence) are the ideal choice of cosmetologists for triple action: brightening, moisturizing and eliminating wrinkles. You can also use specialized cosmetics from the Laennec Skincare brand - LNC. This line offers to transform the skin at the cellular level, eliminating and preventing hyperpigmentation.
Now you know about the main causes of pigmentation, as well as what causes the appearance of age spots on the face, and you can easily answer the question - what to do when pigments have already appeared. Dermatologists recommend not only limiting time spent on the beach and using sunscreen in summer, but also year-round use of skin protection from the negative effects of ultraviolet radiation. It is this that becomes the main catalyst, and in combination with internal disorders of the body can lead to serious changes in the epidermal layer.
Treatment of milia
Milia do not go away on their own; it is almost impossible to get rid of them with the help of cosmetics. Under no circumstances should you squeeze out milia yourself, as this will damage the hair follicle and sebaceous gland. Such self-medication often leads to the subsequent formation of a larger acne or the addition of an infection, which can cause the formation of a rough scar.
Treatment of milia is carried out by a dermatologist and consists of opening and removing the cyst capsule with its contents. The choice of removal method depends on the location, number, size and depth of the milia. For single milia, mechanical removal is carried out (using a sterile needle and curettage) with preliminary and subsequent antiseptic treatment of the skin. Small wounds left after such a procedure heal on their own without leaving a trace.
For multiple whiteheads, modern methods are used - removal of milia with a laser, radio wave method or electrocoagulation. The crusts formed at the cauterization site disappear on their own within 10-14 days. Removing more than 10 elements at one time is not recommended to avoid significant trauma to the skin and disruption of the sebaceous glands.