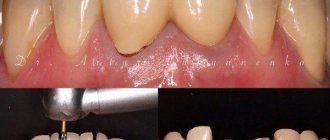
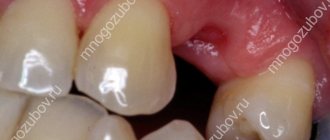
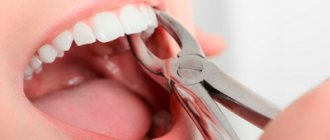
It may take one minute or an hour, using a drill and a scalpel, but there is no way to avoid it.
Tooth extraction is a surgical operation to remove a tooth from its socket. A basic dental procedure that can scare anyone. Fear of removal is due to the idea of ancient times, when they did not think much about the patient’s comfort, much less about good anesthesia.
The fear has not gone away, but approaches to dentistry have changed dramatically. Let's look at when it is necessary to be examined by a dental surgeon, what options are available for tooth extraction, and how to quickly recover after surgery. We will also consider frequently asked questions to the dentist.
Indications and contraindications for removal
The removal operation leads to complete loss of the crown and deformation of the jaw, so dentists recommend installing a prosthesis to avoid complications and cosmetic defects.
The decision on removal is made by the dentist after examination and x-ray examination on an individual basis. The following conditions are indications for urgent surgery:
- acute inflammatory process, tissue suppuration and swelling, spread of infection to soft tissues and bones;
- abscess, cyst suppuration;
- severe swelling and the impossibility of therapeutic treatment;
- tooth decay and impossibility of restoration.
Extirpation is prescribed routinely for the following pathologies:
- Chronic periodontitis. Advanced sluggish inflammation of connective tissue.
- Advanced periodontitis. Inflammation of the gums causes teeth to become loose and fall out.
- Malocclusion associated with abnormal positioning of incisors and molars. In this case, the operation is performed to restore the correct structure of the dentition.
- Fracture of the jaw along with the tooth.
- With the development of neoplasms in the jaw area, especially malignant ones.
You cannot perform surgery during an exacerbation of respiratory diseases or stomatitis, since the postoperative socket is highly likely to become infected and fester.
A contraindication to extirpation is the serious condition of the patient - the development of renal failure, cancer, acute circulatory and cardiac disorders, etc. In this case, it is recommended to stop the underlying disease, and only then proceed with dental surgery.
The relative indication for surgery is the first trimester of pregnancy, since anesthesia cannot be used. Surgery is not recommended for the 9th month of gestation, as well as for women during menstruation, since the woman’s body undergoes a heavy load during this period.
Recovery after deletion
In the postoperative period, additional care for the socket is indicated to prevent complications. Possible complications are associated with the wrong choice of technique, an error during removal, systemic diseases, and improper care after surgery.
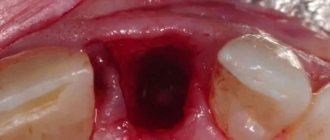
Bleeding very often occurs after surgery, which the dentist can treat with hydrogen peroxide and socket tamponade. If bleeding continues, the dentist uses hemostatic drugs to stop bleeding from the socket.
At home, after removal, you need to treat the hole with antiseptic drugs - this means rinsing the mouth with weak antiseptic solutions. To relieve pain, you need to take medications prescribed by your doctor. Swelling, inflammation, and itching may occur near the hole of the extracted tooth - you should contact your dentist with these complaints, as this is a sign of infection or the development of periodontal inflammation.
Hygienic procedures after removal remain unchanged, but direct contact of the toothbrush bristles with the socket should be avoided. While eating, you need to cover the hole with cotton wool and then rinse your mouth with warm water and soda.
Surgical dentistry has moved forward in many ways in terms of the technologies, drugs and techniques used. Today, the risk of inadequate surgery is practically absent, and the dentition can be restored in many ways. Surgical dentistry is directly related to orthopedics, orthodontics, and aesthetic dentistry, so the patient does not have to worry about an aesthetic defect after treatment.
Is it painful to remove without pain relief?
Treatment without anesthesia is carried out quite often at the request of the patient. Treatment of shallow caries and extraction of baby teeth are almost painless. In such cases, anesthesia may not be used, or only a local anesthetic may be used.
Removal is definitely a painful procedure. How severe the pain will be depends on the condition of the crown and root, and its location. Very excruciating pain awaits a patient who is indicated for the removal of a wisdom tooth and entire, firmly seated molars.
Modern dentistry allows the use of anesthesia even in cases of intolerance to certain drugs. It is recommended to tell the doctor which medications cause negative reactions, and the dentist will select a safe remedy.
What does the sensation of pain depend on?
How painful it is to pull teeth, according to research, depends on several factors. In the same patient, the intensity of pain during extraction may vary depending on the following signs:
- a molar or baby tooth needs to be pulled out - removal of a baby molar is almost painless, since it does not have powerful long roots, like those of a permanent one;
- location on the jaw arch - frontal molars are removed with a feeling of much less intense pain, since they are smaller in size, their root system is not as developed as that of the lateral teeth. The same can be said about trauma to the surrounding soft tissues - they suffer less, especially in comparison with wisdom tooth extraction;
- tooth shape and number of roots - by nature, human molars can have 1-2 or 3-4 branches of a stabilizing root system. So, tooth extraction will be more uncomfortable the more root branches the molar has.
It is necessary to clarify that whether it is painful to pull out a tooth depends not only on the listed factors, but also on the perception of the procedure by the person himself. If you experience a feeling of panic and intense fear before the extraction, this psychological state can directly affect the procedure and actually provoke intense pain. There are many stories among patients not only about how much pain is felt during extraction, but also that there is a big difference whether a molar is removed from above or below, supposedly this affects the intensity of the discomfort.
We need to figure out whether these rumors have a scientific basis. Dentists claim that, regardless of the location of the tooth, it can be removed completely painlessly if high-quality anesthesia is administered, but the jaw may begin to hurt after the end of the freezing period. The severity of the pain syndrome will depend on several points:
- how much bone and soft tissue was destroyed;
- is there an acute inflammatory process at the time of removal;
- a frontal or lateral tooth is subjected to extraction;
- the lower or upper molar is removed;
- whether there is an accumulation of pus in the area of the unit being removed.
The fact that lower units are more difficult to remove from the bed is also due to the density of the bone tissue. All these factors directly affect the degree of destruction and recovery time after the molar has been removed. Therefore, it makes no sense to say that it is painful to remove the lower teeth, but not the upper ones; the location will only affect the adaptation period after extraction.
Tooth extraction with anesthesia injection
Dentists recommend carrying out the procedure with an injection of anesthesia, then the question is, does it hurt?
remove the tooth, it will fall off on its own. The drug reduces the conductivity of nerve endings, and pain impulses are temporarily not transmitted, the patient does not feel anything. The effectiveness of anesthesia depends on the drug. If a weak remedy is used, the patient feels mild pain.
The anesthesia lasts for a limited amount of time. The drug is gradually absorbed and eliminated from the body, and the sensitivity of the nerve endings is completely restored.
Anesthesia injections are performed differently in the upper and lower jaws due to the difference in structure. Less medication is required to treat the upper jaw because it has a porous structure. The medicine easily penetrates the tissue and acts quickly. When treating the lower jaw, it is necessary to inject the drug deeply. There are strong muscles and tight ligaments that interfere with the distribution of anesthesia.
Patient reviews
Review 1
Before describing the procedure, I want to talk about my pain threshold. I can NOT stand pain. At all! I LOVE IT!!! For example, before treating caries, I ask you to give me 2 painkiller injections. And then one day my wisdom tooth began to hurt. I endured it steadfastly! But patience has come to an end! I had to go to the clinic.
Sitting down in a chair, I, as usual, asked for 2 injections and mentally prepared myself for torture :) Instead of somehow supporting and encouraging me, the doctor said: - Nahhh... but the tooth is in an inaccessible place! You can’t even get close to him!!!
Then she asked me to open it wider, then even wider, then again and again... It seemed to me that the corners of my mouth were already torn, and the doctor kept asking me to make my “mouth wider”! At the same time, she said, “What can I do here...” and tried to pick up the tooth with pliers.. These attempts lasted about 5 minutes. There was no particular pain, it was just unpleasant that the doctor could not pick up the tooth and was scared from waiting for the outcome. In the end, I asked: - Maybe I’ll go already?!!! If she can’t pick up a tooth, then WHAT will happen next?! To my deep surprise, the doctor did not even try to persuade me to stay and complete the procedure. She simply said: “Go!”
Well, wow :) This has never happened to me before. Usually doctors persuade: - Well, be patient... If you came, then you need to be patient. And here on you - go... I ask: - And what to do now? The answer was: “Nothing!” Rinse! And don't eat anything for 2 hours. And don't drink anything hot all day. - Why??? - Because the wound should heal. - So you REMOVED my tooth??? - Yes!
Just like that! While I was preparing for “medieval torture” and many hours of torment, the specialist did her job! BRAVO!!! I was delighted! After a couple of hours, the freezing sensation began to subside and the pain returned. She was tolerable, rinsing helped. After a few days the pain went away, but the wound healed for probably a whole month! The pain was weak and dull... The gums ached a little and as if something was pulling. But everything ended well! Everything is overgrown evenly.
Review 2
One of the four teeth had grown into the gum and began to rot there. Therefore, when I came to my favorite dentist, there was only one diagnosis - the wisdom tooth needed to be removed. I honestly couldn’t even get scared when I was already given anesthesia and the fragile dentist started pulling my tooth.
From the sensations, I can’t say that it hurt, no, the anesthesia worked well, but there was a feeling, I felt the tooth being taken with forceps, how it was being pulled, and I was even surprised how my fragile doctor pulled out this chunky tooth. He fought hard to get out, but for professionals there are no problems.
After this, of course, my gums bled a little, I was prescribed mouth rinses so that everything would heal faster. My gums healed within a day. I did not feel any discomfort due to the missing wisdom tooth.
Therefore, I can say for sure that the devil is not as scary as he is painted. Yes, it was unpleasant, but not painful and it could be tolerated. And if I have to remove the rest of my wisdom teeth, I won’t be the least bit upset or scared. Since there is nothing scary in this procedure.
Anesthesia methods
There are three methods of anesthesia:
- local using a spray;
- local injection into the gum;
- general anesthesia or anesthesia.
Local is used if the patient can remain motionless during manipulation. General anesthesia is indicated for people with severe mental illness, children, and sometimes adults who have a strong fear of the dentist.
Most patients are recommended to have local anesthesia injected into the gums around the affected area. If the patient is afraid of surgery, it is recommended that he take a sedative first. It is important to note that alcohol is contraindicated before removal.
Local anesthesia with a spray is carried out in cases where the tooth is loose, or for therapeutic purposes. Dental spray is often used to remove baby teeth in young children.
Possible consequences and complications
Extraction, like any operation, can cause a negative reaction from the body. If your cheek is swollen, your throat hurts, or there is a sharp throbbing pain in the socket, there is a high probability of an inflammatory process.
Early complications:
- fainting, shock, collapse;
- fracture, dislocation of the jaw;
- perforation of the maxillary sinus (when removing an upper molar or premolar), falling of root fragments into the gum;
- trauma, dislocation, fracture of an adjacent or opposite tooth;
- severe bleeding, hematoma formation.
Late complications:
- inflammation of the alveoli (alveolitis);
- inflammation of peripheral nerves (neuritis);
- restriction of jaw movement (muscle contracture).
By contacting a specialist in a timely manner, the consequences of removal can be minimized.
How does deletion work?
Removal surgery can be simple or complex. The doctor grabs the crown with forceps and swings it from side to side, spinning it around its axis to free it from ligaments and bone tissue. As a result, the surgeon removes the crown along with the root and places a gauze tampon in the hole to stop the bleeding.
If the crown has collapsed almost completely and there is no way to grab it with forceps and remove it along with the root, the operation is considered difficult. If the root is not affected, it can be left and a prosthesis installed on top. The damaged root is removed by cutting the gum. This operation is more traumatic and painful for the patient.
After surgery, it is recommended to stop drinking and eating for 2-3 hours, and then not chew on the injured side for several days. A blood clot forms in the hole, which protects the wound from infection, so you should not touch the gum with your tongue and try to rinse out the clot.
After the procedure, the gums hurt for another 1-3 days, depending on the degree of injury. Painkillers are prescribed to relieve pain. If the unpleasant sensations do not go away within 2-3 days, but only intensify, you should urgently consult a doctor.
Experts' opinion
Question: Is it possible to rinse your mouth after tooth extraction? If yes, then with what?
Answer : During the first 24 hours after a molar tooth has been removed, doctors at the Optimal Choice clinics do not recommend rinsing your mouth at all. Active rinsing of the mouth, even if its goal is to cleanse food debris, can lead to a number of negative consequences. The main danger is the destruction and washing out of the formed blood clot in the socket, which interferes with rapid healing. This can also lead to the development of alveolitis. In the first few days, instead of rinsing, it is better to use baths with a decoction of medicinal plants (sage, chamomile, oak bark), a weak solution of salt or baking soda (or a mixture of them in equal proportions), furatsilin, miramistin, chlorhexidine, if prescribed by a doctor.
Question: After tooth extraction, the gums hurt and swelling is noticeable. What to do?
Answer: Slight tissue swelling and pain are very often consequences of the removal of molars. For relatively tolerable pain, it is recommended to take analgesics prescribed by your doctor. If the pain is severe, then you urgently need to visit the dentist again for a check. A cold compress applied to the cheek on the side of the extracted tooth for 15-20 minutes will help relieve swelling.
Molar tooth extraction
It is recommended to begin removing molars or molars after examining an x-ray, since the doctor needs to assess the location of the roots. A blind operation is fraught with complications.
If the molar has no abnormalities, it is removed with forceps. For maxillary molars, bayonet forceps are used. To remove teeth from the lower jaw, forceps with spikes are used that reach under the gum.
If the molar has a structural anomaly, for example, the root is located deeper than usual or the presence of bone tissue in the wrong place, then the situation becomes more complicated. A complex operation is performed with dissection of the gums or jaw tissue. If you try to remove such a molar in the usual way, nothing will work. Part of the tooth root may remain inside, increasing the risk of infection.
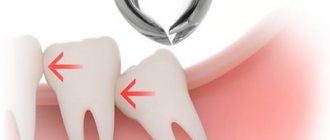
Wisdom tooth removal
Removing an upper wisdom tooth is no different from a similar operation on a regular molar and is carried out in the following order:
- anesthesia is performed;
- the doctor separates the tooth from the gum;
- the doctor grabs the tooth with forceps;
- shaking it from side to side, removes it.
The lower ones have tortuous roots; they are difficult to remove; the crown will need to be divided into parts. Sometimes wisdom teeth do not grow in completely; they are called impacted. Often this situation is accompanied by inflammation and suppuration of the gums, the patient complains of pain and the doctor decides to remove it. The impacted tooth is removed after making an incision in the gum, freeing the crown.
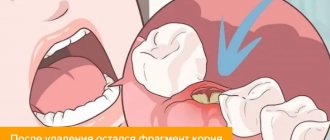
Is it painful to remove the root?
If the patient does not treat caries for a long time, the crown will completely crumble, but the root will remain inside the gum. This condition is fraught with the development of inflammation and suppuration, so it is recommended to cure the root and install a prosthesis, or remove the root if it cannot be treated.
Removing the root does not hurt if anesthesia is used. But after the operation, when the effect of the drug wears off, aching pain will appear. Its severity depends on the degree of injury to the gums. Unpleasant sensations occur 3 days after surgery.
Tooth extraction during pregnancy
Dentists recommend checking the teeth of a woman who is planning a pregnancy so that treatment can be carried out in advance. If the patient neglects the recommendation and is faced with the need for removal, the procedure is performed in the second trimester. Starting from the 12th week of pregnancy, you can use some anesthetics, but there is still a risk of complications.
Surgery is stressful for the body, especially for women during gestation. The procedure can lead to premature birth, cause high blood pressure, dizziness and fainting. Therefore, dentists recommend avoiding removal in pregnant women and, if possible, carrying out therapeutic treatment.
Sources
- Operative maxillofacial surgery and dentistry. Ed. V.A. Kozlova, I.I. Kagan. Year 2022.
- Delete operation. Tutorial. Author Bazikyan E.A. and others. Dentistry. Chapter 4. Afanasyev V.V. [and etc.]; Ed. V. V. Afanasyeva. Year 2018
- Dentistry. Chapter 4. Afanasyev V.V. [and etc.]; Ed. V. V. Afanasyeva. Year 2018
- Propaedeutic dentistry. Edited by E.A. Bazikyan, chapter 12.
- Biomechanics of removal surgery. St. Petersburg State Medical University named after I. P. Pavlova, Dept. surgical dentistry, Dept. medical and biological physics; [comp. Lisenkov V.V. et al.]
Attention!
This article is posted for informational purposes only and under no circumstances constitutes scientific material or medical advice and should not serve as a substitute for an in-person consultation with a professional physician.
For diagnostics, diagnosis and treatment, contact qualified doctors! Number of reads: 6004 Date of publication: 03/11/2019
Dentists - search service and appointment with dentists in Moscow