People who do not have problems with their teeth are very rare. It's all about "universal" human vices. This includes laziness in taking care of your oral cavity, basic ignorance, and, of course, fear of dentists. The classic calculation that “it will pass” has left millions of people without teeth. Any dental disease requires professional treatment. Losing teeth and the dangerous complications associated with this when postponing a visit to the doctor is only a matter of time. Gum problems are no exception. Why gums hurt and why you need to start treating them in a timely manner - we’ll talk about this further.
Causes of pain in the gums
Bacterial inflammation.
A common cause of swelling and pain in the gums is the proliferation in the tissues of pathogenic bacteria that constantly live in the oral cavity. Inflammatory processes on the mucous membrane caused by the proliferation of bacterial flora of the oral cavity are always the result of a weakened immune system. As long as the immune system performs its functions normally, bacteria are not dangerous. As soon as the body's natural defenses are reduced, microorganisms begin to multiply rapidly and cause inflammation.
Lack of hygiene.
Irregular, careless brushing of teeth, leaving plaque on them can provoke the growth of pathogenic microflora. It's all about the acid that microbes produce. It destroys enamel and causes inflammation of the gums.
Tartar
Poor cleaning leads to the formation of deposits - tartar. These deposits damage the bone tissue that anchors the tooth. Because of this, periodontal pockets form, they begin to bleed, and inflammation of the surrounding tissues develops.
Other reasons
Gums hurt in pregnant women, people with a genetic predisposition or with various chronic diseases. Also, pain in the gums can be caused by errors in prosthetics, taking certain medications, allergies, smoking, and injury.
Symptoms
Most often, painful sensations occur during chewing or eating hot or cold food. Some patients complain of almost constant, aching or throbbing pain.
The inflammatory process can develop rapidly. In this case, the pain is usually sharp and severe. May be accompanied by swelling of the gums and swelling of the face. Sometimes the inflammation lasts for years, and since the patient does not experience severe pain, he delays the visit to the dentist, aggravating the situation.
Do your gums hurt? - To the doctor!
Gum pain is often preceded by bleeding, swelling and inflammation. These are all standard symptoms of gingivitis. Standard symptoms of gingivitis and so that gingivitis does not turn into periodontitis and the process of destruction of bone tissue does not begin, leading to mobility and further loss of teeth. To avoid these processes, you must contact your dentist at the slightest manifestation.
Is it possible to treat gums at home using folk remedies? - Can. But, unfortunately, this won't help. And it will even make the problem worse. Prevention could help, but it needs to be done in a timely manner. After all, preventing a disease is easier than treating it.
If your gums are swollen and bleeding, you need a qualified periodontist immediately. He will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
How to relieve pain when pressing on the gums
Remember, only a dentist can help eradicate the pain experienced when pressing on the gums or teeth. It is important to quickly determine the cause of the discomfort and prescribe proper treatment. However, to eliminate discomfort before visiting a doctor, you can try the following methods:
- Take painkillers, such as paracetamol or analgin. The main thing is not to overdo it with such drugs, as they can be addictive and negatively affect the functioning of internal organs.
- Brush your teeth properly, trying to free the inflamed cavity from plaque and food particles.
- Rinse your mouth with a solution of baking soda, furatsilin or potassium permanganate.
Remember, it is strictly forbidden to warm your cheeks and gums or apply warm compresses to the sore spot. Heat can trigger more severe inflammation. Also, you should not take antibacterial or anti-inflammatory drugs without a doctor’s prescription.
It is also prohibited to put analgesics into the cavity of a diseased tooth. This popular method is far from safe: you can not only cause an infection, but also get a serious burn to the mucous membrane.
Gingivitis
The first most common periodontal disease, the symptoms of which are bleeding and swelling of the gum tissue. Develops at any age. Gingivitis is common in pregnant women and teenagers. In this case, the disease begins due to changes in hormonal levels.
The pathological process can be limited to a small area or occur in a generalized manner, involving the gums in the area of all teeth. The initial stage of gingivitis is characterized by pain and bleeding in the gums when brushing your teeth. In the future, the gums may hurt even at rest.
Why does my gum hurt?
Unexpressed aching pain and slight swelling of the gums appear due to injuries to soft tissues, nerves, and jaw bone when removing a tooth from its bed. The gum tissue swells, the nerve endings are compressed, hence the pain. How much your gums hurt after tooth extraction depends on:
- Patient's pain sensitivity;
- degree of complexity of the intervention;
- features of the clinical case;
- location of the dental unit (after extraction of molars, the injury is greater, the pain lasts longer);
- state of immunity.
The body’s normal response from the development of complications is distinguished by the following properties: the pain does not intensify, pathological symptoms are present for no more than 7 days, and no other signs of deterioration in well-being are observed.
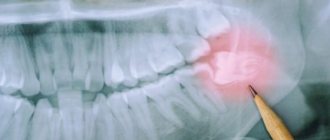
Periodontitis
Bone tissue is involved in inflammation. In the affected area, the teeth begin to seem to be squeezed out of the gums and become mobile.
The onset of the disease is indicated by more pronounced bleeding of the gums, a change in its color, and sensitivity may appear when brushing your teeth and from temperature irritants. The success of this treatment is determined not only by the doctor’s competence, but also by the patient’s active participation in the process and strict adherence to the dentist’s recommendations.
Pain after complex surgery
One of the most common reasons that the gums hurt where the tooth has long been extracted is incorrect or incomplete extraction. Dental defects leading to this:
- crooked roots: it may not be completely removed, part of it remains and eventually begins to rot;
- fragile tooth: if a tooth falls into pieces when touched with a surgical instrument, one of them may remain in the gum and lead to inflammation;
- the tooth has no outer part left: this situation requires complex surgical intervention; simple extraction is not enough;
- The tooth is embedded deep in the gum tissue.
In all these cases, you can get rid of the pain only by extracting the remains of the tooth from the gums. To do this, usually an incision is made in the tissue, and the gums at the site of inflammation are peeled off from the jaw bone. After this, the remaining teeth are cut out using a drill or divided into parts and removed.
Injury
You can injure your gums with an impact, as a result of a burn, even with careless brushing of your teeth. If you have injured the oral mucosa, it is better to carry out antiseptic treatment of the wound surface.
Often, gums are injured chronically. Tissues are subject to constant injury due to:
- broken bite;
- punctures (piercings) of the tongue, lips or cheeks;
- incorrectly selected prosthesis;
- habits of biting off threads with teeth, etc.
Chronic injury entails a serious complication - tissue necrosis, which is treated exclusively surgically.
Pain due to hematoma
If the gums hurt for a long time after removal, the body temperature rises, the gums swell and suppuration begins in the place where the dead tooth was, then this indicates a hematoma. A characteristic sign is the bluish color of the gums in the place where the tooth was.
Why a hematoma occurs: an incorrectly performed operation, during which the doctor damaged a blood vessel, general ailments of the body. For example, a hematoma often appears in people with diabetes or hypertension. A weakened immune system increases the risk of hematoma.
The only way to get rid of toothache due to a hematoma is surgery. During this process, an incision is made in the gum flesh and the accumulated pus is released. After this, the wound is washed and a course of drug treatment is prescribed, which includes rinsing with dental antiseptics and taking antibiotics.
Preventive recommendations
To avoid serious periodontal diseases, the treatment of which will require great effort and material costs, follow these simple rules.
- Contact a periodontist for a consultation.
- Together with your doctor, select the right toothbrush and toothpaste for regular use.
- Follow the classic rules of oral hygiene carefully and regularly. Brush your teeth at least 2 times a day. Use mouthwash after every meal.
- Get additional hygiene products for daily care, for example, dental floss, irrigator.
- Eliminate from your diet foods that are too hot and cold, too sour and salty.
- Reduce the amount of sugar you consume, especially sweets and cookies.
- Eat more foods of plant origin, take vitamin complexes regularly.
Sore and bleeding gums are not the norm. Worsening periodontal problems greatly increases the risk of tooth loss. Therefore, if you find signs of gingivitis, periodontitis, or chronic injury to gum tissue, be sure to make an appointment with your dentist. Specialists of the “Center for Modern Dentistry” are waiting for you!
How long does your gum hurt after tooth extraction?
Normally, after 1-3 days, tissue swelling gradually decreases, pain goes away, and health improves. Already on the 3-4th day, the blood clot is gradually replaced by granulate, and after a week it fills the entire hole. After tooth extraction in the upper jaw, the recovery time is identical to the lower jaw, but bone regeneration in the upper dentition occurs more slowly.
In some clinical cases, the surgeon may cut the gum and drill out the jaw bone. Typically, such manipulations accompany the extraction of the outer eighth molars (wisdom teeth). Then healing takes longer than after a simple operation.
If 5-7 days after the intervention the pain does not decrease, but rather becomes more intense, you should consult a doctor. Acute, nagging, constant pain after tooth extraction can be a symptom of complications.
The tooth socket heals in approximately 2-4 weeks. Recovery time depends on the parameters of the wound and the body’s reaction to the removal procedure. Bone volume is restored approximately 6 months after the intervention.
What to do if alveolitis begins?
As mentioned above, alveolitis is an inflammation of the tooth socket. Here, in addition to normal tissue swelling, you will also experience redness of the mucous membrane, acute pain, and an odor from the socket (as pus and food debris accumulate there). These symptoms are increasing every day.
Alveolitis cannot be treated at home. By taking antibiotics, ointments, rinses and other “home” measures, you can either achieve nothing at all, or transfer the process into a chronic form, when, with minimal symptoms, the bone in the area of removal will dissolve and as a result we will get a huge defect in the bone, which will be difficult to correct. Alveolitis in Samara should be treated only together with a surgeon, strictly adhering to his recommendations.
What does a surgeon do for alveolitis?
- Anesthesia is given;
- When everything has become numb, the surgeon cleans the tooth socket again (removes pus, tooth fragments or bones, if any, rinses the socket with solutions of antiseptics and antibiotics);
- After treating the wound, there are two options: some kind of drug can be put into the hole. Or they can simply fill it with fresh, clean blood and wait for a new clot to form;
- After cleaning, antibiotics, rinses, and epithelializing drugs are prescribed.
After such measures, a noticeable improvement occurs on the second or third day (pain and swelling begin to subside), but healing of the hole takes longer - up to three weeks.
Psychological aspects of tooth loss
Psychological effects range from minimal to neurotic. It gets to the point that people are not able to wear dentures at all, and thinking that they will have to communicate with someone, they do not leave the house at all.
- Fear of an awkward situation if the prosthesis accidentally detaches.
- Losing teeth affects relationships with the opposite sex
- The occlusal (chewing) load is reduced, and the patient cannot afford to eat all the food he would like.
- Inability to eat in public.
- Speech problems. Diction problems in patients can be very serious.
Aesthetic consequences of loss of bone volume due to missing teeth
The facial changes that naturally occur with age can be exacerbated and accelerated by tooth loss. Pronounced aesthetic consequences result from loss of alveolar bone. Patients do not even suspect that all these changes in soft tissues are associated with tooth loss:
- Reduction in facial height occurs due to disturbances in the vertical dimension of the alveolar bone.
- A change in the labiomental angle and deepening of the vertical lines in this area give the face a rougher appearance.
- A malocclusion develops. As a result, the chin turns forward.
- The corners of the lips droop, the patient's face has an unhappy expression.
- Due to poor support of the lip by dentures and loss of muscle tone, the border of the red border of the lips becomes thinner.
- Age-related deepening of the nasolabial philtrum and other vertical lines on the upper lip is more pronounced with loss of bone volume.
- In edentulous patients, the decrease in the tone of the facial muscles that support the upper lip occurs faster, and the lengthening of the lip occurs at an earlier age. As a result, the smile ages.
- Bone atrophy has a negative effect on the attachment of the mental and buccal muscles to the body of the mandible. The fabric sags, creating a double chin. This effect is caused by decreased muscle tone when teeth are lost.
Questions and answers on: tooth hurts under a filling
The most common questions patients ask after tooth filling concern pain.
- Question : “A month ago, I had a tooth healed using paste to kill the nerve and installing a temporary filling, but it hurts when pressed. Also, the gums on the cheek side were swollen. After the temporary filling fell out, I did not install a new one. What to do? Is it related to the root or the nerves?” Answer : “Most likely, the periosteum became inflamed because the canals were not treated in time. It was necessary to treat them and put a permanent filling. In your case, the tooth needs to be removed, but if you consult a doctor urgently, there is a small chance of saving it.”
- Question : “Can a tooth hurt after filling? It’s been 2 hours since the filling was placed, but I feel a little pain.” Answer : “Mild pain in a filled tooth is a natural physiological reaction to surgical intervention in the dental cavity. Periodic painful sensations may be felt for 2 months until complete healing. They will pass unless the pain becomes more severe and increasing.”
- Question : “Yesterday we got a filling, but the tooth still hurts. A small rash and itching appeared near him. I can’t stand it any longer, what should I do?” Answer : “You need to see a doctor to replace the filling. You have developed an allergic reaction to it. This is quite a rare occurrence."
- Question : “A week ago I was treated for caries and a filling was placed at the 6th unit below. But the tooth did not stop hurting. It especially bothers me at night; I can’t sleep due to the throbbing pain. Should a tooth hurt after filling?” Answer : “Most likely, the dentist treated you for deep caries due to periodontitis or chronic pulpitis and made a mistake, guided only by a visual examination of the oral cavity. In any case, it was necessary to take an x-ray of the tooth affected by caries. We urgently need to remove the filling and treat the canals.”
- Question : “2 weeks ago a permanent filling was placed without removing the nerve, but it still hurts me to chew. In addition, the tooth reacts to cold and hot food and at times there is aching pain.” Answer : “Such symptoms may indicate the development of chronic pulpitis or the development of an abscess inside the tooth.”
If various pains appear in the tooth after the filling procedure, then the only recommendation is to contact a qualified specialist. After all, the reasons can be completely different.