Tooth abscess: what is it - symptoms and treatment
A dental abscess is an acute infectious pathology characterized by a clearly limited accumulation of pus in the root area. The purulent process is often a dangerous complication of periodontitis, periostitis, and other dental diseases. The lack of timely treatment threatens with adverse consequences not only for the affected segment, but also for the entire body. In Moscow, dental services are provided by the Center for Aesthetic Dentistry near the Otradnoye metro station. Our doctors will quickly and efficiently help eliminate any problem with sore teeth and gums.
What is a tooth abscess
An abscess in dentistry is an inflammatory process accompanied by the formation of a cavity with pus near a segment or its root. The abscess on the root of the tooth is surrounded by a dense connective tissue capsule, separating it from healthy tissue. Pyogenic bacteria penetrate into the unit through chips, cracks, and carious cavities.
During their life, microbes produce toxins that irritate the pulpal nerve receptors, which causes pain. In addition, toxic products of pathogenic flora increase vascular permeability, resulting in soft tissue swelling.
There are three main types of abscess:
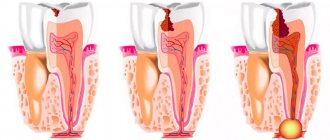
- Periapical - pus accumulates at the root of the tooth (near its apex). A hilar abscess is formed due to an infectious lesion of the pulp. The etiological factor is untreated caries or periodontitis. The progressive inflammatory process spreads to the periosteum and surrounding soft tissue with the formation of a fistula and purulent lump on the gum.
- Periodontal - the focus is located inside the periodontal pockets. The cause is periodontitis. The pulp remains intact, and the infection is localized between the gum and the alveolar ridge.
- Desnevoy. Gum abscess is a purulent formation in the area of the gingival papillae between the segments.
Classification of abscess in dentistry
Doctors say there are three types of tooth abscess:
- Desnev. Only the soft tissues of the mouth are damaged. But, if the disease is started, the periodontal ligaments and periosteum will be drawn into the inflammatory process. Then flux develops.
- Periapical. The pulp is affected. If treatment is not carried out in a timely manner, you will have to perform depulpation or, even worse, tear out the affected unit. More often, this type of disease is diagnosed in children with primary occlusion, which is why dentists have to remove a preschooler’s incisors, canines and molars without waiting for their natural replacement by molars.
- Periodontal. The abscess has a destructive effect on the root, so the tooth becomes loose and falls out prematurely.
The main danger of a purulent tooth abscess is that the pus that has accumulated inside the tumor can penetrate into the blood. Then a general intoxication of the human body will occur. Internal organs, bones, and brain come under attack. A person who ignores the presence of an abscess may develop meningitis, sepsis, and even die.
Why does a tooth fester?
Let's look at why pus forms in teeth. The causes of the pathology can be:
- mechanical damage to the oral mucosa;
- dental diseases of an infectious nature (caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, periodontitis, gingivitis, etc.);
- hematogenous spread of microbes from other foci of infection in the body (sinusitis, pneumonia, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, adnexitis, etc.);
- maxillofacial injuries accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the segment;
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- Iatrogenic causes associated with the introduction of bacteria during dental treatment.
There are risk factors, the presence of which increases the likelihood of pathology: smoking, decreased body defenses, hypothermia, chronic stress. Timely treatment of tooth root periodontitis and other dental diseases reduces the likelihood of an abscess.
Symptoms of gum abscess
The main symptom of the disease is pain. It has a different character (aching, pulsating, acute), is constant or occurs periodically under the influence of stress factors (cold, heat, sour, sweet foods). The pain is often worse when chewing. It can be local or spread to neighboring teeth, ears, eyes. In addition, with an abscess there are other clinical manifestations:
- hyperemia of soft tissues around the affected segment;
- swelling of the inflammation zone;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- foul odor;
- mobility and change in the natural color of the segment;
- the presence of an ulcer on the gum with purulent discharge;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes;
- facial deformation due to swelling;
- hyperthermia, lethargy, sleep disturbance.
Signs of illness
It is almost impossible not to notice the presence of pathology - the symptoms are always very clear. Anyone, even those far from the medical field, can understand that something is wrong with their gums.
- First there is an acute toothache. It becomes more pronounced if you press on the unit, touch it, or knock on it. It intensifies if the patient drinks or eats something hot or cold.
- Soon the gums swell. Even the cheek may swell. This indicates that the inflammation is spreading quickly.
- A bulge forms on the gum. At first it is red or with a bluish tint. But it also happens that it is not there, and pus simply begins to ooze from the gums.
Due to the purulent masses, the patient has an unpleasant taste and a foul odor appears from the mouth. It is not possible to remove it using standard hygiene products - a toothbrush and toothpaste, since pus continues to actively form after brushing your teeth.
An advanced abscess contributes to an increase in body temperature, decreased appetite, and decreased performance. In many patients, the cervical lymph nodes become enlarged.
What to do when you have an abscess
What to do if a tooth breaks: immediately seek help from a dentist. When a fistula forms and the purulent contents drain, the person’s well-being improves and the intensity of pain decreases. However, the pathological process, when the lesion is opened independently, continues to progress and can lead to complications: mediastinitis, thrombophlebitis, sepsis, meningitis, etc.
Therefore, it is important to promptly treat inflammatory diseases of teeth and periodontium. How much it costs to treat pulpitis and other pathologies at North-Eastern Dental Center No. 1 can be found on the corresponding page of the official website.
Breakthrough of purulent masses with an abscess
Often the “bump” grows, swells, and then bursts. Then the pus inside it flows out. After this, the pain goes away and the patient’s well-being improves significantly. But this does not mean that the problem is a thing of the past. It should be remembered that with an abscess, fistula tracts often form. They serve as a protective reaction of the body - they ensure the unhindered outflow of pus and prevent the inflammatory process from further progressing.
The disease may recur. Purulent exudate is able to penetrate into the tissue surrounding the tooth. Therefore, even if the “bump” has burst, you still need to make an appointment with the dentist so that the doctor can conduct an examination and tell you what to do to prevent the disease from returning.
How to treat a tooth abscess
Treatment of a tooth abscess is aimed at eliminating the infectious process and relieving pain. A comprehensive program may include the following activities:
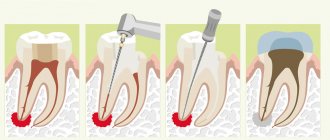
- Opening and draining the lesion. An incision is made on the gum, a drainage is installed through which the pus can freely come out. The drainage system is installed for several days. During this period, the patient is prescribed rinses with antiseptics and saline solutions.
- Endodontic treatment. It involves removing the pulp, treating the root canals with medications and filling them.
- Excision of the root apex. Surgical intervention is performed when the source of infection is located in the periapical area. The surgeon cuts the gum and removes the abscess along with the affected part of the root. The segment itself is preserved.
- Removing a unit. The need for tooth extraction occurs when there is significant destruction of the tooth.
- Therapy with broad-spectrum antibiotics.
- Restoration of the coronal part with a filling or orthopedic construction.
Causes
The main reasons for the development of a tooth abscess:
- exacerbation of chronic periodontitis;
- accumulation of bacterial infection in the tooth pulp;
- violation of sterility conditions during root canal treatment;
- root cyst;
- vertical fracture of the tooth root.
The bacterial microflora of the oral cavity is represented not only by beneficial bacteria. It is also inhabited by streptococci, staphylococci, cocci, lactobacilli, bacteroides, and spirochetes. The inflammatory process begins with the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms beyond the root apex. Hypothermia, colds and infectious diseases predispose them to increased reproduction.
Who treats an abscess
Only a dentist can cure a tooth abscess. If you suspect an abscess, you should contact your general practitioner. He will conduct an examination and, if necessary, schedule a consultation with a dental surgeon.
Preventing a tooth abscess is easier than curing it. To do this, it is necessary to carefully observe oral hygiene, promptly eliminate inflammatory processes in the body, and visit the dentist twice a year. A balanced diet and vitamin-mineral complex products will help compensate for the lack of vitamins and minerals necessary for dental health.
Treatment methods
Pathology sometimes does not cause pain at the initial stage, so not everyone goes to the doctor on time. But usually the inflammatory process develops quickly, and within a day a noticeable tumor forms. You definitely need to see a dentist. Only a doctor after an examination can determine how to treat a tooth abscess.
Home remedies such as rinsing the mouth with saline solution or herbal decoctions, as well as taking painkillers, may provide temporary relief, but will not eliminate the cause of the pathology. They can be used if it is not possible to immediately get to the dentist.
Treatment prescribed by a doctor must be comprehensive. Its purpose is to remove pus and destroy infection. The following methods can be used for this:
- drainage of pus;
- cleaning dental canals or sockets after extraction;
- treatment of caries, pulpitis and filling;
- use of local antiseptic and anti-inflammatory drugs;
- taking antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and painkillers.
Opening a tooth abscess is often performed surgically. Some clinics use low-intensity laser. It allows you to painlessly clean the cavity from pus and disinfect it.
If inflammation has developed on a healthy tooth, it can be saved if you consult a doctor in a timely manner. Removal is a last resort; doctors resort to it only in advanced cases. But this is the main method of treatment if an abscess has developed in a baby tooth or wisdom tooth in an adult, as well as in cases where the dental tissue is severely destroyed.