A dental cyst is a formation that forms near the apex of the tooth root near the bone tissue of the jaw. The causes of the disease can be many, and at first it is asymptomatic - often the patient learns about the presence of a cyst during preventive examinations or from the results of X-ray images taken for other purposes. However, the cyst tends to grow, even at a slow pace, and sooner or later it will manifest itself with unpleasant symptoms. This forces us to take urgent measures. Treatment for a dental cyst depends on when exactly its presence was diagnosed.
Tooth cyst - what is it?
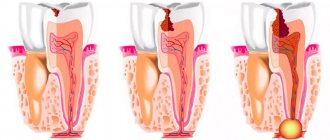
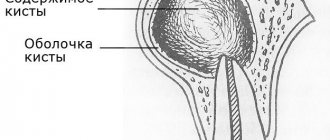
A dental cyst is a cavity formation. What does a dental cyst look like: it is a sac with liquid or a pasty substance. The walls of the cyst are formed by a layer of epithelial tissue. Inside the cyst there is pus, dead cells and bacteria.
The roots of the teeth of the upper jaw have a more porous structure, so the inflammatory process of cysts in the apex of the roots in this case proceeds faster and more intensely.
A cyst on the root of a tooth can be of different sizes - from 5 mm to several cm. The cause of the formation of a “purulent sac” is always an infectious process, and it, in turn, can be provoked by a number of factors.
What does a cyst look like in a photo?
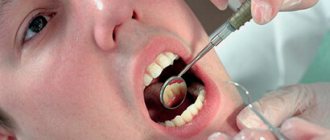
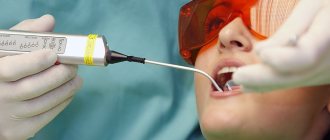
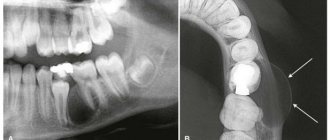
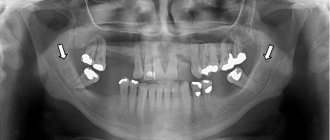
As already mentioned, the only reliable method for diagnosing a cyst is radiographic examination . In the picture it looks like a dark round or oval spot that is clearly defined. Usually located at the apex of the tooth root. It is simply impossible to make a mistake with the diagnosis; even a novice dentist can easily recognize the disease on an x-ray.
The only exception is a dental cyst, which is not visible on an x-ray. This usually happens if not the entire tooth root is within the field of view of the x-ray image, and is located partially outside the image. In this case, if the doctor suspects the presence of a cyst or granuloma, a repeat image should be taken that would completely display the entire root system of the suspicious tooth, as well as neighboring ones.
Reasons for the formation of a dental cyst
Conditionally, the reasons can be divided into two groups:
- Poor oral hygiene - the development of caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, inflammation of the soft tissues of the oral cavity, which results in a cyst.
- Jaw injuries - facial injuries, complicated teething, violation of the technology for installing dental prostheses, filling complex, narrow, curved root canals during endodontic treatment, excessive loads on the teeth as a result of spasms of the masticatory muscles, malocclusion, etc.
These phenomena and diseases can cause inflammation, the focus of which is located at the root of the tooth. Still, the most common cause of a cyst is considered to be a carious lesion - ignoring caries leads to the formation of a cavity in the crown, damage to dentin and the inner soft part - the pulp, and subsequently inflammation of the periodontal tissues. The body strives to “isolate” healthy tissue around the tooth root from the inflammatory process, as a result of which a sac with purulent contents is formed. Why is a dental cyst dangerous? The answer to this question depends in part on the specific type of education.
In what cases is a tooth removed?
The most common reason for removal is the need to sanitize the oral cavity due to exacerbation of chronic periodontitis, if it is impossible to eliminate the inflammatory process in the upper part of the tooth. The cause of odontogenic osteomyelitis is often multi-rooted teeth. The doctor can remove them by selecting a removable denture, but these are already extreme measures when there are necessary direct indications for such a procedure.
To remove it, surgery is necessary. It is produced under painkillers. During the operation, medical instruments are used to remove the tooth from the alveolar socket of the jaw. To remove it, you need to peel off the gum. After this, the ligamentous apparatus that connects the tooth to the alveolus is destroyed and removed.
When a multi-rooted tooth is removed, the patient undergoes an X-ray examination in several projections. The dentist studies its structure, shape, location of the roots and their possible deviation.
Indications:
- periodontitis (when inflammation cannot be eliminated);
- malocclusion;
- major damage to the ligamentous apparatus, thanks to which the tooth is held in the gum;
- when a problematic tooth cannot be restored due to illness, injury or severe caries;
- when orthodontic treatment is necessary;
- formation of cysts, sinusitis, when it is impossible to save;
- if it interferes with the correct fixation of the prosthesis;
- hyperdontia, which leads to deformation in the dentition.
Types of dental cysts
- Retromolar. A common cause of its appearance is chronic tissue inflammation due to complicated teething, most often molars. Wisdom or “eight” teeth are more susceptible to disease than others - they often grow in the wrong direction due to a lack of space in the jaw, which has already formed by adulthood.
- Eruption cyst. These are forms of the retromolar variety, but comparatively softer. It is a small formation that forms during teething. It is believed that the appearance of the disease is “due” to a local decrease in protective forces when baby teeth are replaced by permanent ones.
- Follicular. It is a consequence of the pathology of the development of the molar tooth and appears from the follicles during the formation of dental tissues.
- Radicular. This is the most common type of cyst; in this case, it is the result of a chronic inflammatory process or injury.
- Residual. Occurs after tooth extraction if a root fragment remains in the socket. Its presence provokes inflammation and the formation of a purulent vesicle.
- Keratocyst. The result of pathological formation of periodontium. The cyst in this case appears from the epithelium, which is required for the formation of periodontal tissues. As a rule, it causes difficulty in teething.
- Cyst of “eye” teeth. Appears during inflammatory processes occurring in the maxillary sinuses.
Cyst removal surgery with simultaneous tooth extraction
At the first signs of uncertainty about the success of treatment from your specialist doctor, I strongly recommend that you seriously think about minimizing the unpleasant stages of treatment and minimizing costs by carrying out a psychologically uncomfortable, but tactically correct procedure for removing the causative tooth.
The biggest criticism against specialists performing these procedures is that doctors cannot honestly tell the patient about the low probability of success, while continuing to inspire imaginary hope. Time, money, and traffic congestion when treatment fails add up to the negative perception of failed treatment. Even the most impeccable treatment technology is useless if the tactics are chosen incorrectly. In my opinion, also the narrowest point when discussing the technique of such operations with patients is the lack of understanding of the goals and mechanisms of working with bone materials and stimulators of bone regeneration in the treatment of dental cysts.
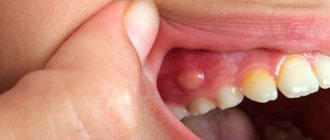
Symptoms of a dental cyst
The formation of a dental cyst occurs slowly. The first stage is the formation of a granuloma - it is difficult to diagnose and does not cause unpleasant symptoms. There may be only slight pain in the gums and teeth during chewing; as a rule, it does not cause inconvenience.
Only X-ray diagnostics can reliably determine the presence of a developing cyst. Since there is no cause for concern, the scan is most often performed for other reasons - for example, before installing braces or a prosthetic for another tooth.
As the cyst grows, the patient begins to feel an increase in symptoms and notes the appearance of new signs:
- pain in the gums and teeth can radiate to the opposite dentition;
- body temperature rises;
- swelling of the soft tissues forms around the tooth, swelling of the cheek on the causal side.
Other symptoms may indicate complications that have already begun.
Indications for cystectomy
Main indications for cyst removal:
- a cyst formed as a result of a malformation of the odontogenic epithelium;
- the presence of a large cyst on the upper or lower jaw in the absence of teeth in its area;
- a small cyst located within 1 or 2 teeth.
- large cysts of the lower and upper jaws in the absence of adjacent teeth and preservation of bone tissue;
- lack of positive dynamics with conservative treatment of dental cysts.
Only a doctor can determine how much this particular operation is necessary for a patient after examination and a detailed study of the problem.
Why is a dental cyst dangerous?
The formation of a cyst itself does not cause serious complications. However, when wondering why cysts on the roots of teeth are dangerous, you should take into account that these formations are prone to growth, and the lack of timely treatment can cause a number of complications:
- flux or periostitis - inflammation of the periosteum, which is fraught with serious consequences for overall health;
- periodontitis - it can be both the cause of a cyst and its consequence; the spread of inflammation to the bone tissue leads to tooth loss and changes in the structure of the jaw bone;
- phlegmon - it is localized in the tissues of the neck and face, can lead to general infection of the body and poses a danger to health and life;
- osteomyelitis of the jaw;
- sinusitis - the answer to the question of why a tooth cyst near the nose is dangerous, this disease can be not only the cause, but also a consequence of the formation;
- tumor malignancy;
- blood poisoning as a result of the formation of large amounts of pus.
Such an impressive list of serious consequences obliges you to be attentive to your oral health and, when the first alarming signs appear, be sure to contact a dentist.
Cyst removal surgery with removal of the causative tooth
- Complex pain relief is carried out.
- The causative tooth is carefully removed according to the pre-implantation preparation protocol. A root extraction mechanism to ensure preservation of the remaining bone architecture surrounding the cyst.
- Ultrasonic cleaning of bone from sprouted cyst membranes.
- Antibacterial and antiseptic treatment of the cellular pattern of the bone, previously in contact with the cyst.
- Introduction of a local antibiotic into the cyst cavity.
- The bone cells are examined using optics. In case of slight impregnation of the cellular pattern of spongy bone with pus, a simultaneous injection of a bone regeneration stimulator is carried out.
- In cases of active suppuration from bone cells, even after removal of the cyst membranes, it is sometimes better to leave the defect open and drained without introducing any medications. By allowing the body to free itself from inflammation for several days, we are guaranteed to reduce the amount of trauma from the necessary deep cuttings of the compromised bone.
Please note that the estimate for the specified treatment case cannot be the same in different clinical situations and is compiled depending on the amount of bone tissue regeneration stimulator administered.
For example: removal of a cyst and simultaneous removal of tooth 16.
- Complex pain relief RUR 3,000
- Tooth extraction - 3,500 rub.
- Removal of a cyst, depending on the complexity, duration and volume of the operation - from 7,000 to 14,000 rubles.
- Optional: installation of bone regeneration stimulators, osteoplastic material Bio-Oss 0.5 - 6,200 rub.
Sincerely, Levin D.V., chief physician
Conservative treatment of dental cysts
A dental cyst can be cured using conservative methods - but this is only relevant for those cases when the disease was diagnosed in the early stages and the size of the formation does not exceed 1 cm. An important condition is the patency of the root canals, since it is through them that drug treatment is carried out. It is worth noting that the conservative method is used more often in young patients.
The main goal of conservative therapy is to eliminate the inflammatory process. It is carried out in several stages:
- Gaining access to the root canals - removing tissue softened by caries or an old filling, studying the patency of the canals, their direction and length. To do this, the dentist inserts small instruments into the canals and takes an x-ray - this allows you to clearly assess the condition of the tissues. Afterwards, the canals are processed mechanically - using tools, and, if necessary, expanded.
- Medicinal treatment of the canals with antiseptic agents - rinsing with Chlorhexidine and sodium hypochlorite.
- Opening of the apical foramen and removal of antibacterial drugs beyond it, into the cyst. To neutralize the acidic environment of the cyst, highly alkaline drugs are used - usually calcium hydroxide. It helps to destroy the walls of the cyst, destroy pathogenic bacteria, protect bone tissue, and accelerate healing.
- If necessary, the application of the drug is repeated - as many times as necessary to stop the inflammatory process.
- Temporary canal filling. It is carried out after the doctor is convinced of the effectiveness of therapy and the absence of disease. The canals are filled temporarily for the purpose of further monitoring the condition of the tooth - if, according to the results of a subsequent assessment of the condition of the tissues, inflammation is not observed, the canals are filled with permanent material.
Next, it is important to visit the doctor according to the schedule, since it is necessary to assess the dynamics of bone tissue restoration.
Physiotherapy can also be added to the main course of therapy. Relatively recently, depophoresis began to be widely used - it allows you to eliminate infectious processes in the canals of the root system. This method consists of using copper-calcium hydroxide - the affected tissue is exposed to a weak electric current, which promotes deep penetration of the drug. Often three sessions are enough to completely eliminate the disease.
Recommendations for speedy healing
After the operation, you must adhere to some rules:
- The first meal should be taken no earlier than 2-3 hours after removal;
- do not visit the sauna or steam room on the day when the operation is to take place;
- do not touch the socket of the extracted tooth with foreign objects or your tongue;
- Hygienic cleaning should be done the next day after the intervention.
Our clinic has created the most favorable conditions for this procedure. The patient will not feel psychological or physical discomfort. Before the operation, our laboratory will check the condition of the body and take the necessary tests. And only after eliminating all contraindications, the dentist will select the optimal anesthesia option. After the operation, the doctor will prescribe the necessary treatment for a speedy recovery and conduct a qualified consultation.
Surgical treatment of dental cyst
What is dangerous about a cyst in the gum above a tooth is that it requires surgical intervention if you do not see a doctor in time.
It is indicated for cysts larger than 1 cm, as well as in other cases:
- obstruction of root canals, their complex structure;
- presence of a tooth crown;
- presence of a pin in the root canal;
- impossibility of saving the tooth due to its severe destruction.
There are several methods of surgical treatment - the doctor chooses one of them, based on information about the patient’s age, individual characteristics of the structure of the patient’s dental system, the size of the cyst, and the degree of tissue damage.
Contraindications for surgery
Despite the fact that the operation is considered quite simple, there are still limitations in its implementation. The main contraindications to cystectomy:
- diseases of the oral mucosa (gingivitis, stomatitis, periodontitis);
- disorders of the cardiovascular system;
- diabetes;
- malignant tumors in the oral cavity.
The operation cystectomy is very similar in name to cystotomy - an easier and simpler operation. Many people confuse them, however, these two procedures are fundamentally different from each other. Cystotomy of a dental cyst involves removing only the anterior wall of the cyst, when cystectomy eliminates the problem completely.
On a note. The cystectomy operation does not take much time, it lasts no more than an hour. It goes quickly and as painlessly as possible for the patient. The rehabilitation period also takes place in the shortest possible time if you follow all your doctor’s prescriptions.
What to do after tooth root resection?
Root resection is well tolerated by patients and does not cause major problems even in the postoperative period, but it is necessary to follow a number of rules that will alleviate the condition and speed up recovery.
Typically, after surgery, patients are prescribed antibiotics and vitamin supplements. They must be taken strictly as prescribed by the doctor.
It is necessary to maintain gentle but regular oral hygiene and use antiseptic rinses.
You can't overwork your body. During the healing period, it is better to limit physical and emotional stress.
Do not eat hot or hard food, it should be warm and soft.