A wisdom tooth cyst occurs due to various reasons - the eruption of a wisdom tooth, damage to the “eight”, poorly treated caries or lack of treatment, and some others.
The main danger of a cyst is that its growth is hidden. The patient begins to sound the alarm when the complication has already reached its peak state. In this material we will try to understand what characteristic features are characteristic of a cyst under the “eight”, and whether there is a possibility of its cure with the subsequent preservation of the wisdom tooth.
Make an appointment with a therapist by phone+7(985)532-21-01
Why does a cyst appear at the site of an extracted tooth?
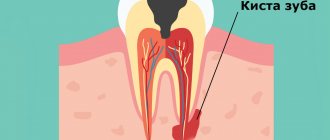
The neoplasm is a hollow capsule of dense tissue filled with serous or purulent contents. It occurs as a response of the body to an infection to limit its spread. Thus, the main reason for its appearance is pathogenic microflora.
Provoking factors:
- Tissue infection during nerve extraction or removal. This may be insufficient antiseptic treatment of the surgical field, unsterile instruments, or other doctor’s shortcomings during the procedure.
- The tooth was removed, but the cyst remained. This option is possible if the necessary diagnostics were not carried out and the doctor simply did not notice the pathological formation.
- Dry hole. After extraction, a blood clot is formed, which protects deep tissues from the penetration of bacteria and food debris. If the blood plug comes off or falls out, the opened cavity becomes the center of an accumulation of pathogenic organisms, which become provocateurs of pathology.
- Medical errors during implantation. If the implant is installed soon after removal, infection and capsule formation may also occur during the procedure.
- Failure to follow the doctor’s recommendations during the rehabilitation period. If the patient is negligent about his health, the risk of developing inflammatory processes increases.
Neglecting antibiotic therapy can ultimately cause a purulent infection. A dry socket is formed due to intensive rinsing of the mouth and licking of a blood clot. If the patient smokes or abuses alcoholic beverages, the wound in the mouth does not heal well, which means the risk of complications increases.
What to do if you find a cyst under a wisdom tooth?
Getting rid of cystic lesions using a conservative method does not bring a positive result, and is practiced in exceptional cases - for example, when surgical intervention is impossible - during pregnancy and breastfeeding, in the postoperative periods and after a serious illness. Physiotherapeutic methods provide temporary relief for the patient, nothing more. The problem requires surgical intervention.
As a rule, when removing a cyst, the specialist does not try to save the figure eight above it. Since this tooth is considered extremely problematic, and at the same time does not play an important role in the process of chewing food. Sooner or later, you will still have to remove the problematic wisdom tooth. And the therapeutic process can be expensive, energy-intensive, and simply complex. The situation is complicated by the fact that the patient seeks help too late, and it is no longer possible to save the molar.
Antibiotics after tooth extraction with a cyst or complex figure eight extraction
After surgery, doctors often prescribe antibacterial and antibiotic drugs. Not in all cases, taking pills is justified, but if there is even the slightest possibility of infection of the wound, then you cannot refuse to take the medication.
Antibiotics are necessary to prevent cyst formation after wisdom tooth removal. It is difficult to remove the figure eight, since the root system is powerful and located deep in the jaw. To extract it, you need to cut the gum, cut off part of the bone, and saw the roots into fragments. With such a complex procedure, tissue is severely damaged and even an experienced surgeon can make a mistake.
Advantages of the classical method
The classic protocol involves 2 stages, separated by time:
Implantation of an artificial rod
The implantologist installs a titanium root into the healed and restored socket and closes it with a plug screw. The implant is not subjected to load until complete engraftment.
Prosthetics
After 4-6 months, the doctor places the gum former for 2 weeks. The orthodontist then installs the crown or denture.
The classic two-stage regimen is preferable for patients with cysts because it allows time for:
- complete drainage of the cystic tumor cavity;
- eliminate infection and inflammation;
- bone tissue growth.
After complete treatment, the risks of complications in the early and late postoperative periods are minimized.
How to recognize a cyst on the gum after tooth extraction
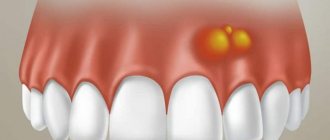
The tumor develops slowly and does not manifest itself for a long time. As the size increases, mild symptoms appear, which worsen during periods of acute respiratory infections, stress and other predisposing factors. You can see what a cyst looks like after tooth extraction in the photo.
Symptoms of the development of cystic formation:
- pain, discomfort when pressing on the gums, when biting;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- swelling of the gums, cheeks;
- increased body temperature;
- development of sinusitis if the neoplasm is located in the maxillary region;
- general malaise, weakness.
If such symptoms appear, you should contact your dentist.
Symptoms of cystic lesions
A characteristic feature of a neoplasm under a wisdom tooth is its latent appearance and development. A person does not even realize that there is a growing cyst until it is accidentally discovered during an X-ray or in the dentist’s chair. Education can also reveal itself during colds, in stressful situations and during periods of winter frost.
As a rule, a trigger is triggered in the form of severe stress or ARVI, which is the catalyst for the purulent process. When the cyst space fills with pus, the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- Painful sensations when touching the affected area;
- Swelling of the face in the area of inflammation;
- Enlarged lymph nodes;
- Body temperature rises;
- Malaise, apathy and lethargy;
If you ignore these symptoms, the disease enters a new phase - flux, osteomyelitis and sinusitis develop. In addition to internal processes, complications can also affect external manifestations - deformation of the dental bite or the appearance of facial asymmetry.
Treatment of a cyst under an extracted tooth
The neoplasm is treated surgically. An x-ray is taken first. The image shows the area where the capsule is localized, its size, complications, for example, bone melting after rupture of the bladder with advanced pathology.
The doctor removes the cystic sac, cleans the cavity of pus, if there is any, and carries out an antiseptic treatment. When using a laser, the operation is performed practically without blood, and wound healing is faster. In any case, you need to take antibiotics to prevent relapse.
How to speed up the time before implant installation
It is impossible to reduce the time from removal to implant installation. However, the patient cannot prolong it. You must follow your doctor's recommendations to prevent the inflammation from spreading. Rules for caring for the oral cavity after removal of a cystic tooth:
- do not drink or eat food for 4 hours;
- do not injure the wound with a toothbrush;
- rinse your mouth regularly with an antiseptic;
- take antibiotics (as prescribed by a doctor);
- use dental gel or paste to accelerate regeneration (as prescribed by a doctor);
- give up smoking and alcohol.
Superficial healing occurs in 10-14 days . It takes 1-6 months to restore bone tissue.
The issue of implantation should not be rushed, since careful and systematic preparation minimizes the risk of early and late complications.
Popular questions
The pathology is dangerous, and the operation and recovery period are painful, so patients are interested in many questions about the tumor:
- How long does swelling last after removal of a dental cyst?
Surgery always leads to soft tissue swelling. A large wound remains at the site of the removed tumor, so the swelling lasts for several days. If the cheek is very swollen, then doctors recommend applying a cold compress to the projection of the operated area several times a day. - What should you do if your tooth hurts after removing a cyst?
The pain spreads to neighboring tissues and can radiate to the temples, throat, and neck. To relieve acute symptoms, you need to take analgesics. After one or two days, the pain will become less intense and the medication can be stopped. - What are the complications after removing a tooth with a cyst?
Possible wound inflammation, bleeding, suture divergence. The most unpleasant consequence is a relapse of the disease. - How long does it take for a wound to heal after removing a tooth with a cyst?
The wound heals in about one week, and complete tissue restoration will take 4 to 6 weeks.
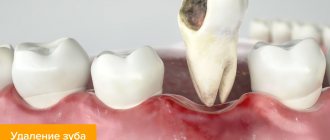
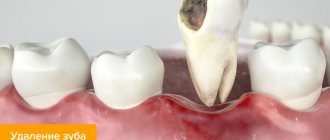
Extraction of a wisdom tooth affected by a cyst
Only surgical intervention, better known as molar tooth extraction, can help get rid of a cyst. A dose of anesthetic is administered to a conscious patient, and general anesthesia is used in exceptional cases. The gum is opened, the flap is moved to the side, and a fragment of bone near the cyst is separated. This makes it possible to remove malignant tumors and infected tissue areas in the area of inflammation.
Removing the “eight” itself is always situational in nature - if the tooth is impacted, then its extraction occurs in parts. Upon completion of the operation, the hole is washed with an antiseptic solution to eliminate the possibility of further inflammation. The bone fragment is placed back, the gum flap is also returned to its place, and the gum is sutured.
After surgery to remove the cyst and tooth, a long recovery period begins. Sometimes it reaches several months: in the case of a large area of tissue damage or during a complex operation. It is important to understand that the quality and time of wound healing further depend on the person himself. At first, a deep hole forms, and it is necessary to carefully monitor oral hygiene - follow the surgeon’s advice, give up bad habits, take antibiotics, and, if prescribed by a doctor, carry out drug therapy.
Make an appointment with a therapist by phone+7(985)532-21-01
Do fissure dental caries need to be treated?
Tooth root caries treated or removed
Removal of a wisdom tooth cyst
Tooth granuloma, what is this disease and how to cure it
Treatment of average dental caries from 6,000 rubles - sign up at the clinic of the Central Administrative District of Moscow
Retrograde pulpitis: diagnosis, causes, treatment, complications
Treatment of wisdom tooth caries if it hurts
X-ray diagnostics –
As we said above, the final diagnosis can only be made using an x-ray, on which a cavity formation in bone tissue will always look like a rounded darkening.
In the x-ray images below we have presented you with 3 options for localizing root cysts. The most common location is root cysts at the apex of the tooth root, but cysts on the lateral surface of the root or located between the roots of multi-rooted teeth are much less common. Radiographs of root cysts of different locations –
What's wrong with a cyst?
- The cyst is prone to growth, and as it grows, it destroys the surrounding bone and disrupts anatomical formations (for example, the lower wall of the maxillary sinus, etc.).
- The cyst can fester, and the inflammatory process spreads into the surrounding spaces, causing serious complications that threaten the patient’s life (abscesses, phlegmon, etc.).
- As the cyst grows, it can push away neighboring teeth and significantly change their position.
- The cyst can lead to a pathological fracture of the jaw if it reaches a very large size.
Cyst on the root of the tooth: causes
As we said above, the formation of a cyst on the root of a tooth is associated with an infection in the root canals. Root canals open at the tops of the roots with small holes, which means that during inflammation, bacteria and their toxins will travel outside the tooth, forming foci of inflammation at the tops of the roots. At the first stage, a so-called apical granuloma (up to 0.5 cm in size) is first formed at the root apex, which is a section of granulation tissue surrounded by a loose fibrous capsule.
Such a granuloma does not yet have a cavity with pus inside, but with a further increase in its size (over 0.5 cm), a cavity is formed inside it, lined from the inside with epithelial cells. Such a cavity formation already corresponds to the concept of “root cyst,” although in dentistry small root cysts ranging in size from 0.5 to 1.0 cm are often also called the transitional term “cystogranulomas.” And the root cyst itself is most often called a formation with a diameter of more than 1.0 cm. Inside the cavity of the cyst there is pus, which is produced by its inner membrane.
Learn more about the reasons for the development of a cyst at the apex of the tooth root -
Infection in the root canals does not occur on its own, and this is not some kind of psychosomatics and related problems, for example, bronchial asthma. Infection in the tooth cavity and root canals occurs in the following two situations:
- Untreated caries, pulpitis and periodontitis - tissues affected by caries contain a large number of cariogenic microorganisms. If caries is not treated, then bacteria gradually enter the dental pulp (neurovascular bundle), causing inflammation in it - pulpitis. If pulpitis is not treated in time, which should consist of removing the infected pulp and filling the root canals, the infection penetrates through the root canals outside the tooth. This leads to the development of a focus of inflammation at the apex of the tooth root, followed by the formation of a root cyst (Fig. 5).
- Poorly sealed root canals - imagine that you have cured your pulpitis in time or the inflammation that has just begun at the apex of the tooth, but after some time you still have a cyst formed at the apex of the root. This happens very often and is due to the fact that the root canals were filled poorly (according to official statistics, dentists fill root canals poorly in 60-70% of cases). The fact is that the infection develops in the unfilled part of the root canal or where the canal was not tightly filled with a filling substance.
Normally, each root canal of a tooth should be filled to the apex of the root. If the canal is not filled to the top of the root, then an infection develops in the unsealed part of the canal, which penetrates beyond the tooth and also causes the formation of a cyst. In Fig. 6-7 you can see radiographs of teeth whose root canals were poorly filled, which in both cases caused the formation of a dental cyst. In Fig. 6, white arrows mark unfilled areas of the root canals. In Fig. 7, only traces of filling material are visible in the root canal, i.e. The root canal is not sealed tightly and not all the way.
Reasons for the development of root cysts in other locations –
The appearance of a root cyst on the side surface of a tooth is usually due to the fact that numerous small branches (opening with holes on the side surface of the root) always extend from the main root canal in the root of the tooth. Therefore, even with high-quality filling of the main root canal, there is a very small risk of a granuloma or cyst appearing on the lateral surface of the root.
A little more often you can find a cyst in another location - between the roots of multi-rooted teeth (in the bifurcation of the roots). Such a cyst usually occurs if the integrity of the hard tissues of the bottom of the tooth cavity is damaged, for example, as a result of a crack or perforation of the bottom of the tooth cavity, or perforation of the upper half of one of the root canals. Such complications are most often the result of dentist mistakes in the treatment of pulpitis and periodontitis.
Is bone grafting necessary after cyst removal?
The decision on the need for bone grafting after treatment of a dental cyst is made by the dentist on an individual basis. If conservative treatment of the disease was carried out, and the affected tooth is preserved, then surgical manipulation is usually not required. When examining the oral cavity, a slight deficiency of bone tissue will be noted, but it will recover on its own within some time after recovery.
If the cystic formation reaches a large size, then the patient will experience a significant lack of his own bone tissue. Indications for osteoplasty do not depend on the preservation or removal of the affected tooth. The only thing that matters is the number of missing jaw bone cells.
In advanced situations, when treatment of a cyst required tooth extraction, and the bone deficiency is so severe that it is dangerous for the patient to apply any physical stress to the jaw, consultation and assistance from an oral maxillofacial surgeon is required. Proper surgical intervention in such a situation becomes especially important, since the future functionality of the jaw as a whole and the possibility of installing implants with crowns depend on it.
How to treat a cyst?
There are 2 ways to treat cysts:
The therapeutic method is carried out by a dentist-therapist, whose main task is to remove the infection from the root canals, that is, to eliminate the factor supporting the cyst. After root canal treatment, temporary medications are left in them, which act on the cyst and contribute to its regression and complete disappearance. At the end of treatment, the root canals are filled with permanent materials and the damaged tooth is restored.
The surgical method - removal of the cyst, is used when the therapeutic method is ineffective. It can be carried out either by removing the “causal” tooth itself along with the cyst, or by trying to preserve it. Saving a tooth is only advisable if, before the cyst removal operation, the infection that caused the inflammatory process has been completely eliminated (the root canals of the “causal” tooth have been properly treated). The cyst is removed by a dental surgeon under local anesthesia.
Both surgical and therapeutic methods of treatment give excellent results, provided they are performed correctly and with high quality.
The choice of treatment method for the cyst is made by the dentist, according to the specific clinical situation.