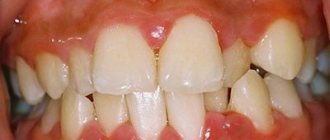
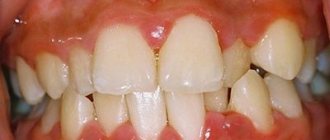
Granulating periodontitis is an inflammatory process in the periodontium, which has a chronic form and periodically worsens. This type of disease is characterized by the formation of granulation tissue. The main symptom is severe pain when chewing food. Acute pain occurs when eating hot food and drinks. Gradually, the gums in the affected area swell, fistulas form, from which pus enters the oral cavity.
Fact: Granulomatous, fibrous and granulating forms of periodontitis often occur when deep caries is left untreated. Therefore, specialists cannot save the tooth and must be removed if treatment began too late and did not lead to a positive result.
Filling made of light-curing material for classes I and V - 2,000 rubles.
Filling made of light-curing material in classes II, III, IV - 3,000 rubles.
Placing a temporary filling - 400 rubles.
Resection of the root apex (frontal group) - 6,500 rubles.
Resection of the root apex (chewing group) - RUB 9,000.
Mechanical and medicinal treatment of canals for periodontitis (1 canal) - 1,100 rubles.
Closing perforations (MTA) - RUB 6,500.
At CELT you can get advice from a dental specialist.
- The cost of a dental consultation is 1,000
- The cost of an orthodontist consultation is 2,000
Make an appointment
Clinical manifestations
The disease progresses dynamically, and its short periods of remission alternate with exacerbations. Clinical manifestations include the following:
- mild pain;
- sensation of fullness in the diseased tooth;
- swelling of the gums.
During periods of exacerbation of granulating periodontitis, localized paroxysmal pain occurs, which intensifies under the influence of irritants (both mechanical and thermal). Slight tooth mobility may be observed, as well as sensitivity of the lymph nodes in the lower jaw.
The appearance of a fistula is accompanied by the growth of granulation tissue around its mouth. Due to the fact that the pus is removed through the fistula canal, the pain subsides and a period of remission begins again.
It is very important not to delay treatment of granulating periodontitis, since its complications can include diseases such as dental granuloma, cyst, osteomyelitis of the jaw, and sepsis.
The pathology occurs in a chronic form and periodically becomes aggravated, which often goes away on its own and the person feels relief. A visual examination reveals pastiness, hyperemia and swelling of the gums. During an exacerbation, upon palpation, the dentist discovers an infiltrate in the root area, touching which causes severe pain. If treatment is not started, the infiltrate will increase in size and a fistula will appear. A fistulous tract with the release of pus can form even on the neck or face, so the symptoms of granulating periodontitis resemble subcutaneous actinomycosis. Further, after the fistula ruptures and the pus comes out, relief occurs, but the person still experiences pain when chewing food or when exposed to heat.
Exacerbation of pathology can be determined by the following clinical manifestations:
- In the area of the inflamed tooth, the lymph nodes increase in size.
- The gums become soft and swollen.
- Touching the affected area causes severe pain.
- Eating hot food or drinks causes burning and pain.
- The periodontal ligament weakens, which leads to loosening of the tooth.
Indications
There are 5 indications for starting treatment for granulating periodontitis:
- Pain on tooth percussion.
- Deformation, destruction, darkening of the tooth.
- Damage to nerves by carious tissue.
- Formation of pale depressions when pressing on the gums.
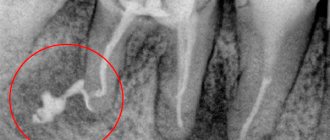
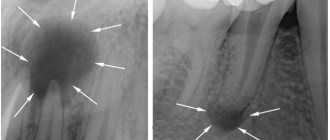
- Destruction of dentin and bone tissue (detected by x-ray).
Contraindications
Contraindications to the operation are:
- Cardiovascular diseases.
- Mental and neurological disorders.
- Allergic reaction to anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics.
- Intolerance to anesthesia.
Symptoms of granulating periodontitis
It is impossible not to notice the appearance of the disease. It is accompanied by:
- sharp acute pain;
- increased temperature in the area of the diseased tooth;
- pain when biting and chewing;
- increased symptoms when eating hot or cold food;
- noticeable enlargement and tenderness of the lymph nodes;
- tooth mobility, looseness and inflammation of the soft tissue of the gums around the diseased tooth;
- swelling of the gums, the presence of purulent discharge.
Additionally, the patient may experience headaches, irritability, loss of appetite, and insomnia. Short-term relief occurs when the abscess naturally opens, and the painful sensations disappear along with the pus. But with a new inflammatory process, the symptoms of the disease return with even greater intensity.
In advanced stages, fistulas form on the mucous membrane in the projection of the root apex from the vestibular surface, in some cases even fistulas form. Localization depends on which tooth the process develops in - fistulas on the chin (from the lower frontal teeth), in the area of the inner corner of the eye (from the upper fangs), in the cheek area (from the upper lateral teeth).
Refusal of treatment leads to the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms, which, together with the blood flow, enter the internal organs, causing septic complications with severe intoxication of the body.
Diagnostics
In order to correctly diagnose and differentiate this type of periodontitis from fibrous or granulomatous, the dentist conducts a visual examination of the oral cavity, which allows us to identify:
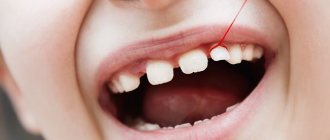
- severely damaged natural tooth crown/large filling/artificial crown;
- change in color of the affected tooth;
- communication between carious and dental cavities;
- insignificant pain reaction to percussion;
- looseness of the gums, on which, after pressing with a dental instrument, a depression is formed.
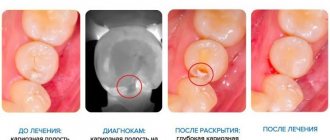
During a visual examination, the specialist sees swelling of the gums, severe tooth decay, and a change in the color of the enamel. Granulating periodontitis is often observed on teeth with large fillings that have not been changed in a timely manner. Probing of pathological carious tissues does not lead to pain. When the probe is pressed on the affected mucous membrane, the gums become pale and indented. The recess is preserved for a long time. Electroodontodiagnosis is used to accurately identify granulating periodontitis. An increase in the sensitivity threshold of the pulp to 100-150 μA is detected. An x-ray is taken which shows the destruction of the jawbone.
In addition to a visual examination, dental x-rays are performed, which reveals destruction of the jaw bone, and electroodontodiagnostics, which determines an increase in the threshold of pulp excitability.
Types of chronic periodontitis
Studies of the clinical picture of the possible course of chronic periodontitis and morphological signs made it possible to identify the following types:
- Granulating
With this form of the disease, under a microscope, a noticeable thickening can be observed in the apical part of the tooth root. There is a change in the surface of the periodontium, it becomes uneven. Over time, granulation tissue grows, which causes resorption of bone tissue in the area of inflammation. This process is often accompanied by the appearance of purulent foci, which provokes the appearance of fistulas. In some cases, soft tissue adjacent to the site of inflammation undergoes granulation. This causes the formation of granulomas of various types (submucosal, subperiosteal, subcutaneous), after opening which, fistulas appear on the face and oral cavity, and unaesthetic scars appear at the site of their healing.
Patients experiencing granulating inflammation report pain when chewing solid food, aggravated by pressure, as well as periodic exacerbations of painful conditions.
- Granulomatous
One of the forms of periapical inflammation, characterized by the formation of granulation tissue in the area of the root apex. The maturation of this tissue along the periphery provokes the appearance of a fibrous capsule that degenerates into a granuloma. Depending on the structural features, simple, epithelial and cystic granulomas are distinguished. Quite often, this form of the disease occurs as a consequence of granulating inflammation.
The course of the disease can occur according to various scenarios. Sometimes the granuloma grows slowly or does not grow at all. In this case, it usually does not cause any discomfort and is discovered by chance during an X-ray examination.
In other patients, the granuloma may enlarge, most often coinciding with exacerbations of chronic periodontitis, provoking changes in the granuloma tissue.
- Fibrous
It is characterized by the formation of a limited focus of inflammation caused by the spread of fibrous tissue. Most often this occurs after treatment of the forms of periodontitis described above, but sometimes the fibrous form occurs independently.
Often, fibrous inflammation is accompanied by excessive formation of cement, and in some cases, sclerosis of adjacent bone tissue.
An X-ray examination allows you to determine the form of chronic periodontitis. It is very important to correctly differentiate different types of disease, since the effectiveness of treatment directly depends on this.
Reviews about our doctors
I would like to express my gratitude to the dentist Elena Nikolaevna Kiseleva and her assistant Svetlana - they are real specialists and at the same time sensitive, not burnt out by years of practice.
Thanks to them, I have been coming back here for many years. Thanks to the management for such doctors! Read full review Svetlana Nikolaevna
13.08.2021
I am very grateful to Evgeniy Borisovich Antiukhin for removing my three eights. Especially considering that the lower tooth was not the simplest (it was located in an embrace with a nerve). The removal took place in 2 stages, one tooth under local anesthesia, two under general anesthesia. I had no idea that wisdom teeth could be... Read full review
Sofia
28.12.2020
Exacerbation of periodontitis: how does it manifest?
The chronic form of the disease may not have any symptoms for a long time, but sometimes exacerbation phases may occur.
At such moments, the disease begins to resemble the acute stage of development: the gums swell, severe pain occurs, and pus appears. When there is no more pus left in the lesion, the pain goes away and the symptoms disappear, but this does not mean that periodontitis has been cured: it has simply entered the chronic stage again. After some time, an exacerbation will occur again, accompanied by the same symptoms.
Factors such as hypothermia, various diseases, or simply a weakened immune system can provoke an exacerbation of the disease.
Treatment
Standard surgery does not always give results, so dental surgeons often have to perform resection of the apical part of the root, hemisection and cystectomy. If this does not lead to a cure, then tooth extraction is performed.
Treatment of chronic granulating periodontitis is carried out comprehensively and is aimed at eliminating the source of infection and preventing its spread, eliminating pathogenic microorganisms in the root canal of the tooth, its high-quality, thorough filling and restoration of the functional and aesthetic characteristics of the crown of the tooth.
Treatment is carried out in several stages; His priority is methods that allow you to save the tooth. As a rule, several visits to the dentist are required, at the first of which he opens the tooth cavity and performs mechanical treatment of the root canals, disinfects and, after applying antiseptic agents, places a temporary filling. During the second visit, the canals are washed and filled with medicinal pastes. If the patient has no complaints and the treatment proceeds according to the planned plan, during the third visit, permanent root canal filling is performed.
Why is chronic periodontitis dangerous?
The anatomical structure of the teeth ensures in most cases the free outflow of serous and purulent masses from the source of inflammation. As a result, the patient may not be aware of the presence of chronic periodontal inflammation for a long time. All this time it is actively developing, exposing tissues to destruction. Sometimes this leads to the fact that it is no longer possible to save the tooth.
In addition to tooth loss, chronic periodontitis leads to the formation of skin or gingival fistulas and various types of granulomas, which require long-term (several months) complex and expensive treatment.
Granulomatous formations pose an additional danger. They can, under the influence of such unfavorable factors as stress or hypothermia, lead to the development of serious inflammatory processes, including sepsis.
Chronic periodontal inflammation can also accelerate the progression of diseases such as nephritis, arthritis and rheumatism, and provoke other health problems.
Recommendations after treatment
After the operation, it is possible to save the affected tooth if it was performed in a timely manner. But you need to take into account that the disease may reappear if you do not follow the dentist’s recommendations and do not monitor the health of your teeth. To avoid relapse of granulating periodontitis after treatment, follow 4 rules:
- Never allow caries and pulpitis to progress. Severe stages of the disease can provoke the development of periodontitis.
- See your healthcare provider every 6 months for a diagnosis and professional cleaning. Professional oral hygiene eliminates soft and hard plaque, as well as all pathogenic bacteria.
- Use dental floss and a toothpick to remove food debris from hard-to-reach areas. Brush your teeth at least 2 times a day.
- Strengthen your immune system, take a vitamin-mineral complex and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Following these recommendations will help you maintain healthy teeth and gums for many years.
Have you encountered this unpleasant disease? Do not delay treatment - contact the dentistry of the CELT clinic!
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Rehabilitation period and prevention
To speed up the healing process, in some situations the patient is prescribed a course of antibiotics and vitamin complexes in order to enhance the natural protective functions of his body. Special medicinal baths and mouth rinses may be prescribed to relieve inflammation.
Following simple preventive measures will help prevent the disease. It is necessary to follow the correct diet - food should be rich in vitamins and minerals. Be sure to brush your teeth with a suitable toothpaste and brush. It is recommended to stop smoking, as well as drinking alcohol, coffee and carbonated drinks. And, of course, even after complete recovery, it is necessary to visit the dentist regularly twice a year.
The dangers of treating periodontitis at home
The desire of some people to avoid visiting the dental office by any means and continue to endure pain cannot be explained. At the same time, patients persistently practice self-medication, search for recipes on the Internet, rinse their mouths with herbs and smear their sore teeth with homemade compounds of dubious content.
Unfortunately, none of the diseases mentioned in the article can be treated at home. Any method that has been proven over the years, which refers to grandmother’s recipes, will not heal, but will only ease the pain and help the outflow of purulent contents. Remember, the use of this or that non-traditional method of treatment must obtain the approval of a doctor.
Painkillers are also only allowed in limited quantities. Many drugs have a strong and negative effect on the liver and gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, it is unacceptable to constantly relieve pain with pills. And heating a sore tooth, trying to reduce the level of discomfort, is strictly prohibited!
Taking self-prescribed antibiotics will not be successful, because the drug is not able to penetrate into the root canals. It will also not be possible to disinfect and eliminate the source of inflammation by rinsing your mouth. In addition to the warnings voiced, let us remind you that the pathogenic microflora of carious tissues is extremely resistant to drugs, so it cannot be destroyed by taking drugs; drilling is required.
It is better to direct all unspent energy to the prevention of dental diseases. Choosing the right toothbrush, getting into the habit of flossing, and getting regular professional teeth cleanings at your doctor's office are the foundations of oral health.
Treatment of tooth enamel erosion, causes, photos, price
Treatment of dental caries using the Icon method without preparation
Retreatment of tooth canals before prosthetics, with granuloma, cyst and aching pain
Repeated endodontic treatment of tooth canals for pulp inflammation
Restoration of tooth enamel, price, drugs
Treat or remove wisdom tooth pulpitis
Dental treatment without pain in Moscow
Third visit
In addition to a visual examination, the doctor will need an x-ray to examine the quality of the therapy and make sure that the abscess is not growing. Having seen a positive result with traces of bone restoration, the doctor either proceeds to install permanent fillings or decides to continue treatment.
If the outcome is favorable, the dentist cleans the tubules from the substrate that temporarily fills them, rinses, disinfects and carefully seals with gutta-percha to the very top.
Finally, an x-ray is taken to show how well the tooth canals are filled. If the filling material extends beyond the apex or does not reach it, the doctor's work was in vain. The channels will have to be redone. In the opposite case, periodontitis recurs with the same force.
A temporary filling is placed for the third time.
Age restrictions
Periodontitis can occur in a person of any age, and there are no age restrictions for its treatment. Pregnant women are treated with special care, since, on the one hand, periodontitis is a dangerous source of infection that reduces immunity and can threaten the adequate course of pregnancy, and on the other hand, highly effective drugs with a strong effect can also threaten the development of the fetus. Therefore, treatment of periodontitis during pregnancy and lactation is carried out using the most gentle methods and drugs. But in order to prevent such situations, it is necessary to carry out routine monitoring, sanitation and medical examination at any age, and even more so during periods of pregnancy planning, as well as the prenatal period.