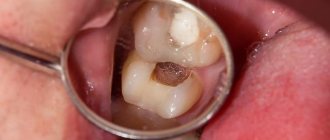
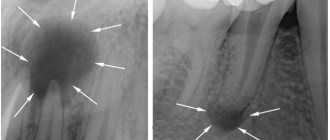
Chronic periodontitis is one of the forms of the disease that occurs due to the fact that pathogenic microorganisms penetrate into the periodontal tissue through the openings of the root canals located at the tops of the dental roots. Chronic periodontitis of the roots is accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the ligaments that provide fixation and stability of the tooth, destructive processes of bone tissue and can lead to the formation of granulomas and large cysts.
Chronic periodontitis is a pathological process in the periodontal tissues. This is associated with the development of inflammation in the periodontium and the formation of fibrous, granulating, granulomatous tissue. In the chronic form of the disease, exacerbations periodically occur, during which swelling of the gums, loosening of teeth, the appearance of fistulas with the release of pus, etc. are observed. Specialists identify this pathology and distinguish it from similar diseases using electroodontometry, X-rays and visual examination. Lack of proper treatment leads to tooth loss due to weakening of the ligamentous apparatus and the growth of large capsules with pus.
Filling made of light-curing material for classes I and V - 2,000 rubles.
Filling made of light-curing material in classes II, III, IV - 3,000 rubles.
Placing a temporary filling - 400 rubles.
Resection of the root apex (frontal group) - 6,500 rubles.
Resection of the root apex (chewing group) - RUB 9,000.
Mechanical and medicinal treatment of canals for periodontitis (1 canal) - 1,100 rubles.
Closing perforations (MTA) - RUB 6,500.
At CELT you can get advice from a dental specialist.
- The cost of a dental consultation is 1,000
- The cost of an orthodontist consultation is 2,000
Make an appointment
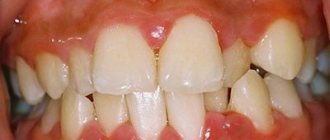
Symptoms of the disease
General symptoms depend on the form of the pathology. When granulomas form, attacks of pain are observed when exposed to hot food. Pressure on the affected tooth and gum is accompanied by pain. The size and density of the mucosa in the affected area changes, and a granuloma forms under the bone or mucosa.
An exacerbation is accompanied by the appearance of fistulas, which grow and gradually release their contents into the oral cavity. In this case, purulent fistulas can appear not only on the gums, but also on the cheekbones, cheeks, neck, and chin. Isolation of pus may be performed along with the isolation of granulosa tissue. Then the fistula goes away, and a scar appears in its place.
The granulomatous form occurs for a long time without pronounced symptoms. Only after the granuloma grows to a large size and cysts form, the main symptoms appear: discoloration and severe pain in the tooth, development of gumboil and swelling of the gums in the affected area. Cysts that are too large can cause a jaw fracture and long-term rehabilitation.
Fibrous periodontitis is the most hidden form of pathology. There is no pain when chewing food or drinking hot drinks. Severe symptoms are observed only during exacerbation. There is general poisoning of the body due to the penetration of pus into the blood, the tooth becomes loose, and the lymph nodes in this area become larger.
Clinical researches
Clinical studies have shown that for the treatment of chronic localized periodontal disease of traumatic etiology in young patients, a complex of therapeutic and preventive measures is required, which includes domestic gum balm and gum gel with propolis (JSC VERTEX, Russia), as well as personal hygiene products oral cavity in the form of therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste "ASEPTA PARODONTAL SENSITIVE" (JSC "VERTEX", Russia) and mouth rinses "ASEPTA PARODONTAL ACTIVE" and "ASEPTA PARODONTAL FRESH", (JSC "VERTEX", Russia), which allows within 6 months after completion of complex treatment, not only improve oral hygiene and reduce inflammatory processes in the gums by 55.37%, but also reduce the number of relapses of localized periodontitis by 21.36%.
To increase the effectiveness of treatment of chronic localized periodontitis of traumatic etiology in young people, it is advisable to include a gum balm in the complex of treatment and preventive measures, which should be used after completion of the surgical stage (curettage) as a gingival dressing, and subsequently used to optimize gum regeneration, gum gel with propolis, should be used against the background of adequate individual oral hygiene.
Sources:
- Prevention of recurrence of localized periodontitis in young A.K. YORDANISHVILI, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, North-Western State Medical University named after. I.I. Mechnikov, Military Medical Academy named after. CM. Kirov, International Academy of Sciences of Ecology, Human Safety and Nature.
- Report on clinical trials to determine/confirm the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: mouth rinse "ASEPTA PARODONTAL" - Solution for irrigator." Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Head. Department of Preventive Dentistry S.B. Ulitovsky, doctor-researcher A.A. Leontiev First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after academician I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry.
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
Causes of chronic periodontitis
Chronic periodontitis appears in the absence of treatment of the acute form. The disease develops due to traumatic, toxic, infectious, mechanical effects on tissue.
The infectious form develops due to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the oral cavity. This is due to damage to soft tissues by staphylococci, diphtheroids, and streptococci. The penetration of bacteria into tissues occurs through the openings of the root canals or through the hematogenous route. Often the infection progresses against the background of osteomyelitis, sinusitis, periodontitis, and tonsillitis.
The fibrous form often progresses after severe trauma. For example, after tissue destruction with a pin, filling, or crown. Pathology can also develop due to a strong blow.
Drug-induced periodontitis occurs due to the use of drugs that provoke coagulative necrosis of the periodontal ligament. These include resorcinol-formalin and arsenic paste. Tissue poisoning is provoked by local anesthesia, iodine, acids, etc.
Indications
The lack of a positive result after conservative and surgical treatment is the main indication for removal of affected teeth. Extraction is performed for the following symptoms:
- Significant damage to the crown.
- Severe loosening of the tooth.
- Formation of large cysts and granulomas.
- Impossibility of performing the operation due to obstruction of the canals.
- Lack of results with surgical and conservative treatment.
Contraindications
- Oral infections.
- Allergy to anesthesia.
- Intolerance to antibiotics and antimicrobial agents.
- Acute diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Poor blood clotting.
Causes of inflammation
Periodontitis is an acquired disease; it is caused by both health problems and mechanical damage.
The most common reasons include:
- untreated pulpitis (inflammation of the internal tissues of the tooth due to an infection brought inside);
- caries;
- fillings and dentures installed poorly (not in size or not accurately).
In addition, periodontitis occurs in smokers, people with diseases (heart, digestive) and those who are susceptible to hormonal imbalances.
Age is not a barrier for the onset of periodontitis. In children, it occurs after injuries or bruises to the oral cavity. In adults, the formation of ulcers is caused, among other things, by trauma to the canals with surgical instruments and excessively large fillings that violate the integrity of the tooth.
In addition, in some cases, periodontitis is a consequence of the body’s individual reaction to certain medications or chemicals entering the tissue during treatment.
Do not heat the sore spot or use traditional medicine. The best thing is to see a doctor
Types of chronic periodontitis and their clinical manifestations
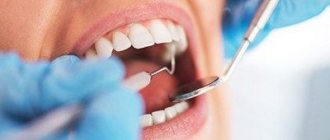
It is customary to distinguish several forms of the disease, the diagnosis of which is necessary in order to correctly prescribe treatment for chronic periodontitis. To do this, the dentist conducts a visual examination of the oral cavity, prescribes electroodontic diagnostics and x-rays.
Chronic fibrous periodontitis
Self-diagnosis of this type of chronic periodontitis is very difficult due to the almost complete absence of clinical manifestations.
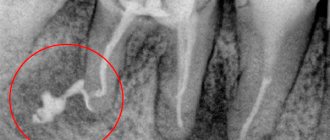
The patient does not experience pain, and there is no reaction to temperature stimuli. During the examination, the dentist notes a change in the color of the tooth, the presence of a reaction to percussion and painful probing. The tooth cavity is filled with dead pulp, which emits a putrid odor. The X-ray image clearly shows the increase in the periodontal fissure at the root apex; there is no destruction of bone tissue and cement.
Chronic granulating periodontitis
The painful sensations characteristic of this type of chronic periodontitis are not significant.
There are sensations of heaviness and fullness, and minor pain may be present when exposed to mechanical stimuli. Exacerbation of chronic granulating periodontitis is accompanied by the formation of a fistula through which pus comes out or granulation tissue grows. With this disease, the gums become loose. When pressing on the inflamed area with the blunt end of a dental instrument, a small depression appears, which disappears only after some time. The x-ray image shows the focus of the destructive processes of bone, dentin and cement.
Chronic granulomatous periodontitis
The symptoms of chronic periodontitis of this type are also practically invisible to the patient. Sometimes minor discomfort and pain may occur when biting on the affected tooth.
An examination by a dentist can reveal a change in the color of the crown of the tooth, but a carious cavity is not necessarily present. Remnants of dead pulp are found in the root canals. If the canals were previously sealed, then the quality of the filling is not good enough.
An X-ray image allows you to determine the destruction of bone tissue, which has a round shape. Often this process can be found on dental tissues or the root apex area.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made by a dentist-therapist based on the patient’s complaints and characteristic symptoms. Carrying out X-ray diagnostics in the initial stages of the disease is difficult, since changes are noted already in the presence of periodontal pockets.
Marginal periodontitis is differentiated from the apical form of the disease, in which the inflammatory focus is in contact with the apex of the tooth root, and does not form at the gingival margin. The pathology must be distinguished from gingivitis and periodontitis, in which periodontal tissue is not damaged.
Treatment of the chronic form
Good patency of the canals allows for therapeutic treatment:
- Opening a tooth.
- Antiseptic treatment.
- Cleaning the channels.
- Use of anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Installation of a temporary filling.
After the procedure, antibiotics are prescribed and re-appointed after 3 months. If the x-ray shows a cure for the disease, then the canals are treated with an antiseptic and a permanent filling is installed. Surgical intervention involves cystectomy, resection of the upper part of the root, hemisection, and root removal. Lack of results after treatment is a reason for extraction of the diseased tooth.
Surgical treatment of periodontitis
Surgical intervention is prescribed when conservative methods are ineffective. Surgical treatment of periodontitis in the clinic is prescribed if:
- The patient is diagnosed with root canal obstruction;
- Multiple cysts and granulomas have formed around several teeth;
- inside the crown there is a pin that is too firmly fixed, which makes it difficult to “get close” to the root canals;
- the dimensions of the lesion in periodontitis exceed 10 mm;
- None of the types of treatment proposed by the specialist brought the desired result, as evidenced by the results of radiography.
Surgical treatment of periodontitis involves:
- removal of a certain part of the root or the entire root;
- removal of a pathological unit with the prospect of implantation and prosthetics.
When resection of the root apex, the part that was subjected to the inflammatory process is removed. With this treatment, it is possible to preserve the “living” part of the root and the tooth itself, restoring it with a filling or a ceramic crown.
Exacerbation of chronic periodontitis
Often patients seek treatment for acute chronic periodontitis, which manifests itself quite clearly. This mainly applies to granulomatous and granulating types, exacerbations of which occur much more often than fibrous types. Clinical manifestations during this period include:
- constant localized pain;
- swelling of soft tissues;
- the presence of a reaction to mechanical stimuli;
- painful reaction of the lymph nodes.
Forms of apical periodontitis
Depending on how the disease progresses, it is customary to distinguish two main forms. Treatment of apical periodontitis is prescribed after its cause has been identified and an accurate diagnosis has been made.
Acute apical periodontitis
Acute apical periodontitis lasts from two days to two weeks and is characterized by pronounced pain symptoms. It comes in two types:
- Serous periodontitis occurs at the very beginning of intoxication and the development of inflammatory processes. Clinically, it manifests itself in incessant aching pain, accompanied by sensitivity when biting on an inflamed tooth;
- Purulent periodontitis also manifests itself in constant pain, which intensifies when touching the tooth or lightly tapping it. Added to this is the feeling that the tooth does not fit into the dental arch. The formation of pus and increased acidity lead to swelling of periodontal fibers, causing the tooth to become mobile. Soft tissues swell, and lymph nodes enlarge due to the spread of cellular elements mixed with lymph and blood.
Chronic apical periodontitis
Chronic apical periodontitis comes in different types:
- Fibrous - occurs almost without symptoms. To properly diagnose it, the dentist must perform a visual examination and x-rays. They will reveal a change in the color of the tooth, a painful reaction to tapping on it, the presence of a carious cavity, as well as an abnormal expansion of the periodontal gap at the root apex;
- Granulating - characterized by mild nagging pain, sensations of tooth expansion, and the appearance of a fistula from which pus flows. The gums around the diseased tooth swell, and when pressed with a dental instrument, a depression appears. An X-ray examination can reveal bone loss at the root apex, which has unclear contours, destruction of cement and dentin;
- Granulomatous - characterized by almost asymptomatic course. There is an unpleasant pain when biting. A diseased tooth changes color and tapping on it is painful. When palpating the gums, the dentist detects a bulging granuloma. An X-ray examination allows you to see the destruction of dental tissue at the root apex.
Recommendations after treatment
After conservative or surgical treatment, you should not eat food for 2-3 hours due to the effects of anesthesia. Pain may be experienced for 7 days after surgery. It is recommended to rinse your mouth with antiseptics and a decoction of medicinal herbs. For severe pain, it is recommended to take painkillers. If pain persists and severe swelling is observed, contact your doctor immediately.
At the same time, the crown of the tooth changes its color, the presence of a carious cavity and tooth mobility are noted. Dentists at the CELT clinic successfully treat even the most advanced and severe forms of chronic periodontitis!
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
What absolutely cannot be done when treating periodontitis?
- In no case are patients recommended to heat the side where periodontitis develops - heat, on the contrary, activates the spread of infection, and the pain will intensify;
- Do not “dampen” the pain with painkillers or rinses. Treatment by applying cold at home will also not bring results. Especially when a tubercle with purulent contents has already formed on the gum, which indicates the transition of periodontitis from the acute to the chronic stage;
- Do not delay going to the doctor and dental treatment in a clinic. There is no need to wait for the disease to go away on its own. Periodontitis does not go away on its own and without treatment! All the symptoms indicate that inflammation is developing inside the tooth, which cannot be stopped without dental care.
Our prices
| Code no. | Name of procedures | Unit of measurement | Cost, rub. |
| 300 | Application anesthesia | 100,00 | |
| 301 | Infiltration anesthesia, conduction | 450,00 | |
| 401 | Mechanical treatment of the canal with hand tools | 800,00 | |
| 403 | Drug and ultrasound treatment of the canal (repeated) | 500,00 | |
| 404 | Filling with temporary (therapeutic) material. | 500,00 | |
| 405 | Canal filling using lateral condensation method | 1000,00 | |
| 305 | Placement of a light-composite filling (Esthet-X, Filtek) | 2 800,00 |
* The prices indicated on the website are not a public offer. The exact cost of treatment can only be determined at an appointment with a doctor.
Prices for treatment in Korolev full price list
Share on social media networks:
Article Expert:
Konoplya Larisa Mikhailovna
Orthopedic dentist - general practitioner. Education: Minsk State Medical Institute. Regularly improves his professional level at international seminars and conferences.
Work experience 30 years