From this article you will learn:
- why the gum moves away from the tooth,
- what disease does this indicate?
- what to do if the gum on a tooth has receded.
The article was written by a dentist with more than 19 years of experience.
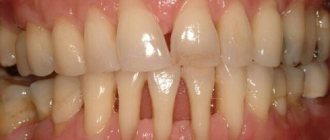
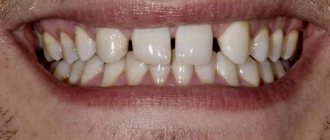
If the gum has moved away from the tooth, this indicates destruction of the attachment of the gum to the necks of the teeth. In this case, the destruction of the periodontal attachment is inflammatory in nature and is one of the symptoms of the development of chronic periodontitis. Such patients usually have additional complaints - bleeding, redness or cyanosis of the gums, and sometimes tooth mobility (Fig. 1).
But, if your gums are receding and your teeth are exposed, this condition, firstly, may also be associated with inflammation of the gums during periodontitis (since inflammatory resorption of the bone around the teeth leads to the fact that the gums sink down). Secondly, there are a number of non-inflammatory reasons, for example, receding gums can occur - 1) due to a traumatic bite, i.e. occlusal trauma, 2) after correcting the bite with braces, 3) due to the thin biotype of the gum, 4) due to the peculiarities of attachment of the lip frenulum to the gum, as well as other reasons.
In Fig. 1 you can see that the patient’s gums have moved away from the teeth (due to the destruction of the dentogingival attachment and the formation of periodontal pockets between the gums and the roots of the teeth) - against the background of gum inflammation.
In Fig. 2 you can see “gum recession” (in the area of the central lower incisors) - this is the term dentists use to describe the condition when the gums recede and the surface of the tooth root is exposed.
Why do gums recede?
Gum loss, or recession (in scientific terms), is very rarely an independent disease. Usually this is a consequence of other diseases and pathological processes in the body, which in one way or another affect the condition of the oral mucosa. The main reasons that provoke poor circulation, atrophy and gum loss are:
- inflammation of periodontal tissues with accumulation of pus and plaque in periodontal pockets;
- poor hygiene, accompanied by the formation of tartar. Gradually, this leads to drooping of the moving part of the gum;
- mechanical, thermal and chemical injuries;
- errors during orthopedic and orthodontic treatment, due to which the gums are injured;
- improper hygiene;
- malocclusion;
- pathologies of the structure of the mucous membrane (the gums are initially thin and weakened) and/or the cortical layer of the bone is too thin, which impairs blood circulation;
- general diseases of the body that affect blood circulation and the functioning of the immune system;
- old age, when gum atrophy may occur.
The neck of the tooth under the crown is exposed
Crowns must be replaced periodically; they cannot last for decades. A properly made crown extends a short distance under the gum (from 0.5 to 1 millimeter). This seals the tooth, so that nothing from the oral cavity gets under the crown onto the tooth.
Over time, the gum atrophies, that is, it begins to slide off the crown. When the intensity of this process increases, when the gum is exposed by approximately 1-2 millimeters, the tooth is exposed. It begins to get affected by various infections contained in the oral cavity. This is the cause of the development of various diseases, caries, which provoke exposure of the neck of the tooth.
If the tooth under the crown is alive, the person complains of an irritable reaction when eating hot or cold. As the inflammatory process develops, severe aching pain begins to bother you. In such a situation, it is possible to save the tooth root. To do this, remove the crown. There are also treatment methods in which there is no need to remove it. More detailed advice can be obtained from the clinic doctor.
Symptoms and forms of the disease
Today, when diagnosing the severity of the disease, the Miller classification is used, which involves 4 stages of gum recession.
- Visually, gum loss is hardly noticeable (or completely unnoticeable) and appears only in the area of contact between the tooth and gum.
- The defect appears slightly in the area of contact between the gum and the neck of the tooth (the level of the attached gum decreases by 1-2 mm). The gums between the teeth remain at the same level.
- The gums recede by 3 mm or more. The necks of the teeth are slightly exposed, but the bone level does not decrease. At this stage, the gums often recede and bleed.
- The most severe stage, when the gums recede by 5 mm or more, the roots of the teeth become visible. Mobility of the teeth is observed, which at this stage of the pathology is often generalized and involves several teeth.
At advanced stages, pathology can be noticed visually, especially when the gums on the front teeth recede. If the pathology is at the beginning of its development, a number of additional symptoms help to detect it.
- Inflammatory process, bleeding.
- Formation of periodontal pockets.
- The sensitivity of the enamel has increased.
- The presence of a thick layer of dental plaque.
- Unhealthy whitish tint of gums.
Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis (using modern technologies), so if you have at least one symptom, you should not postpone your visit to the clinic. Of course, everyone is interested in the question of what to do if the gums on a tooth have receded and what treatment should be chosen. There are two directions: therapeutic and surgical. The choice depends on the severity of the pathology and the underlying disease that led to soft tissue atrophy.
The gum has moved away from the tooth: treatment
If the gum has moved away from the tooth, treatment will largely depend on the severity of the inflammation. For example, if a patient seeks help at a fairly early stage of inflammation (when the depth of periodontal pockets does not yet reach 3 mm and there is no tooth mobility), significant success can be achieved in the treatment of periodontitis and the process can be completely stopped. Advanced cases of gum inflammation will require much more complex treatment and serious financial costs. Next we list the main stages of treatment.
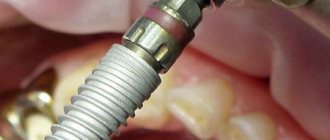
1) Consultation and x-ray diagnostics –
It is necessary to begin treatment with a consultation with a periodontist and a panoramic photograph of the teeth, which will allow you to create an optimal treatment plan taking into account the condition of your teeth and gums. The image will allow you to determine the amount of destruction of bone tissue around each tooth, the location and depth of periodontal pockets, and will help guide the patient in the need for splinting of mobile teeth, the need for prosthetic replacement of missing teeth, and make the correct diagnosis.
An example of a panoramic image of a patient with periodontitis –
Looking closely at the image, you may notice that the level of bone tissue (the bone looks in the image as fine-mesh looped tissue and normally should reach the necks of the teeth) is reduced in different teeth by 1/4 to 4/5 of the length of their roots. The patient has decayed teeth that need to be removed, as well as carious teeth that require treatment (24stoma.ru). The level of bone tissue is most reduced in the front teeth of the upper and lower jaw, which in this case was the result of not only inflammation of the gums, but also the absence of the chewing group of teeth.
To treat gums, it is best to contact not ordinary dental therapists or hygienists, but periodontists. These are the dentists who specialize in gum treatment. The first and most important stage of treatment will be ultrasonic teeth cleaning. Next, a course of anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out, which in most cases can be successfully carried out at home.
2) Removal of dental plaque –
First of all, it is necessary to remove the cause of inflammation - microbial plaque and dental deposits. They are removed from the teeth using an ultrasonic scaler (Fig. 15), usually over several visits. It is simply impossible to remove all dental deposits in just 1 visit in a patient with periodontitis, because... It takes a lot of time to remove subgingival dental plaque, which is localized in periodontal pockets below the gum level.
It is subgingival dental plaque that poses the main danger for further progression of inflammation, so sometimes it is necessary to prescribe the patient even 3-5 times. Learn that without professional cleaning, all other stages (for example, anti-inflammatory therapy, splinting) will be completely meaningless.
Most dentists and hygienists won't bother with finding and removing subgingival calculus...as experience has shown. Therefore, it is very important to find a competent specialist. Anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed immediately after 1 session of removing tartar, and within the first 24 hours you will be able to notice changes in the appearance of the gums. In parallel with the reduction in gum swelling, their volume will also decrease, which will allow you to see new portions of dental plaque and remove them during subsequent visits.
Removing dental plaque with ultrasound: video
You can see in the following photos what happens when subgingival tartar is removed poorly. The first photograph shows that the gums are visually in good condition, although a periodontal probe revealed the presence of a periodontal pocket about 5 mm deep. The second photograph was taken after the gums were detached from the teeth, and it shows a very large amount of destruction of bone tissue, which arose due to the presence of small subgingival tartar on the surface of the tooth root.
3) Anti-inflammatory therapy –
The course of anti-inflammatory therapy usually lasts 10 days. In most cases, it is carried out by the patient himself at home, after doctor’s prescriptions and patient education. However, if the patient has deep periodontal pockets with purulent discharge, the doctor may additionally prescribe washing the periodontal pockets, which is done using a syringe and antiseptic solutions. In some cases, antibiotic therapy may also be prescribed for periodontitis.
Anti-inflammatory treatment regimen - usually a complex is prescribed, consisting of an antiseptic mouth rinse and application of gel to the gums. The procedures are carried out 2 times a day (morning and evening, after meals and subsequent oral hygiene), for 10 days. Most often, a complex of the following drugs is prescribed:
- rinsing with Chlorhexidine (instructions)
- “Cholisal-gel” applications (instructions)
In patients with periodontitis, the correct choice of treatment agents is very important. For example, a standard 0.05% solution of chlorhexidine, sold in pharmacies for 40 rubles, is advisable to use only for superficial inflammation of the gums (gingivitis), but for periodontitis it is better to use a 0.2-0.25% concentration of this antiseptic. It is a big plus when such a solution contains not only a good concentration of chlorhexidine, but also other active ingredients (for example, aluminum lactate for bleeding gums or extracts of medicinal plants).
Antiseptic mouth rinse is carried out after breakfast and oral hygiene, rinse your mouth for 1 minute. After this, the gums need to be dried with a dry gauze pad to remove excess saliva, and an anti-inflammatory gel should be applied to the gum edge. The gel is applied in front of a mirror using a finger, and usually only on the front side of the teeth. After such treatment, it is not recommended to eat for 2-3 hours, and also not to drink for 30 minutes. There are a lot of remedies for treating gums, and we hope that our next articles will help you understand their diversity -
→ The best antiseptics for mouth rinsing, → Rating of the best gels for treating gums.
4) Oral hygiene training –
If you have not yet forgotten the beginning of the article, then remember that the cause of periodontitis and destruction of the dental-gingival attachment is unsatisfactory oral hygiene, which leads to the accumulation of microbial plaque and tartar on the teeth. Therefore, in addition to the basic treatment that we described above, it is very important to constantly maintain high-quality oral hygiene.
Good hygiene doesn't mean just brushing your teeth twice a day, that's not enough. Good oral hygiene includes brushing your teeth after every meal, not snacking on cookies or candy between meals, and regularly using dental floss. You can read about absolutely all the recommendations in the article at the link above. Below, you can watch the video on how to properly use a toothbrush and dental floss.
How to use dental floss and brush correctly -
In the presence of periodontal pockets and mobile gingival margins, it is important to carry out hygiene below the gum level. This can be done using special devices - home irrigators. Special attachments allow you to rinse at home not only areas of the oral cavity that are difficult to reach for hygiene, but also periodontal pockets below the level of the gingival margin. Irrigators can use both ordinary boiled water and special medicinal solutions.
Therapeutic treatment
Conservative treatment is prescribed in the mildest cases, when it is necessary to stop the inflammatory process and potential gum loss due to periodontal diseases (periodontitis or periodontal disease). Usually, the matter is not limited to one procedure: the doctor prescribes a complex treatment, which may include several techniques.
- Professional cleaning.
Removal of hard dental plaque is a basic procedure that precedes the main treatment. - Cleaning periodontal pockets.
To remove pathogenic microorganisms, the closed curettage technique is used. It can be carried out with standard instruments, as well as with the help of a laser and the Vector device (and its analogues). - Rehabilitation physiotherapy.
Used to improve cell health and better restore blood circulation in soft tissues (laser therapy, electrophoresis, current therapy, etc.). - Taking vitamins
, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and preventive therapy.
Summary -
In this article, we briefly listed the main stages of treatment necessary to quickly relieve inflammation. Removing dental deposits from teeth and anti-inflammatory therapy will relieve redness, swelling, bleeding of the gums, the gums will become denser, pale pink in color, and bad breath will disappear. However, the treatment of a disease such as periodontitis does not end there.
In the case of deep periodontal pockets, and when the gums move away from the teeth, it can be assumed with a high degree of probability that splinting of mobile teeth will be required, as well as one of the surgical methods for treating periodontitis (for example, flap surgery or open curettage of the gums). During flap surgery, a thin strip of marginal gum is removed, which is loose and not attached to the teeth and, accordingly, this reduces the depth of periodontal pockets, as well as the rate of progression of periodontitis.
Sources:
1. Dental education of the author of the article, 2. Based on personal experience as a periodontist, 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. American Academy of Periodontology (USA), 5. “Therapeutic dentistry. Textbook" (Borovsky E.V.).
Surgery
In case of severe gum loss, the only effective way to restore it is soft tissue surgery. Today, several surgical techniques are actively used.
| Methodology | Description |
| Flap reconstruction | Gum plastic surgery, when its deficiency is compensated with the help of a donor flap, which is taken from neighboring areas. If the patient’s gums have dropped slightly (by 2-3 mm), this method can be used to quickly restore its previous level. Disadvantages of the technique are traumatic and aesthetic defects (there may be a discrepancy in color between the donor and native areas) |
| Tissue regeneration using plasma lifting and PRF membranes | A more modern technique that does not require taking donor tissue. Injections of plasma and/or installation of fibrin membranes are made into the affected area. This starts the process of tissue regeneration. The treatment is longer compared to the first method, but it is effective and less traumatic |
| Installation of a collagen implant | A minimally invasive technique that is effective for tissue restoration after periodontal disease or age-related gum atrophy. Such implants contain an analogue of connective tissue, which helps restore gums |
| Classic implantation | What to do if the gums have receded, the tooth root is exposed, and the doctor says that tooth extraction is no longer possible? The best solution in this case would be bone grafting and the installation of dental implants. This is the only way to effectively replace lost teeth. In some situations, additional soft tissue plastic surgery may be required. |
In case of mechanical damage, receding gums can be raised using classic surgery with sutures. This is only possible if there are no serious injuries that require additional measures. It is important that surgical treatment is also aimed at eliminating visual defects. To deal with the root cause, comprehensive treatment is required, especially in cases where periodontal diseases develop against the background of problems with the functioning of other body systems.
Miller classification
Today, the generally accepted classification of gum recession is the Miller classification, which is divided into 4 classes
.
First and second classes
according to Miller - root closure is 100 percent possible.
Third class
according to Miller, 100 percent root closure is impossible.
And fourth grade
according to Miller, he is not even being treated.
What treatments are available for each stage of gum recession?
For the first, second and third classes according to Miller - only surgical closure of the exposed necks of the roots of the teeth. The fourth class according to Miller is not treatable, that is, it cannot be treated.
Is there an age limit for treating gum recession?
No.
There is no age limit for treating gum recession.
The gums are receding - what can I rinse with and what ointments should I use?
Unfortunately, it is impossible to cure gum recession (recession) with home remedies or conservative methods, i.e. with the use of medications. To correct the situation, procedures in a dental clinic are always necessary.
But, since one of the reasons for receding gums is an inflammatory process, the dentist can select anti-inflammatory home care products for the patient. These include medicinal pastes, which can only be used as prescribed by a doctor, as well as gels, ointments, rinses, etc.
Quite often, the following are used to treat inflammation in the oral cavity:
- Cholisal
is a gel based on choline salicylate, which has an analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect that lasts 3-8 hours, - Metrogyl Denta
- includes the antibiotic metronidazole and the antiseptic chlorhexidine, especially effective at the initial stage of inflammation, - Solcoseryl
- ointment heals wounds, improves nutrition of injured tissues, and is often used after operations in the oral cavity.
Anti-inflammatory rinses work due to chlorhexidine, herbal components (extracts of geranium, sea buckthorn, hawthorn, sage and chamomile) or a combination thereof. There are a lot of such products on the market, and it is best to consult a dentist before purchasing. It is also important to remember that you should not prescribe any medications to yourself - this may not improve the situation, but rather make it worse.
Surgery to close gum recession
The gum itself, as you understand, will not rise, it will not “bounce into place”, it needs to be put back in its original place, and this is called closing the gum recession.
But I repeat once again: there are also indications and contraindications for the operation, in accordance with certain classes of gum recession according to Miller.
If this is a class one recession, then one forecast. If this is class II gum recession, the prognosis is different. There are many contributing factors to both successful gum recession and failure. That is, at the very beginning of the treatment path, the doctor must determine all the factors for successful closure of gum recession.
Complications
Hyperplasia is dangerous because without treatment it provokes inflammatory processes in the periodontium: gingivitis and periodontitis. This leads to loosening of teeth and their loss.
Due to the fact that it is impossible to clean teeth well, caries often develops. Enamel demineralization occurs. Metabolic processes are disrupted.
Due to increased sensitivity, patients try not to chew on the side where the gum has grown. The chewing load is distributed unevenly, and the risk of losing teeth increases.
Clinical picture during the development of recession
As the disease develops, the gums on the lower teeth recede and those on the upper teeth rise. The roots are gradually exposed. They are not covered with enamel, as a result of which they lack protection. Because of this, tooth sensitivity increases. Visually they look elongated, their color changes at the gums. Interdental gaps form, in which food constantly gets stuck, which brings a lot of inconvenience. In advanced cases, bleeding appears and the gums become inflamed.
The pathology can be localized, that is, affect 1-2 teeth, or generalized, when the entire dentition is involved in the painful process.
Prevention
Simple measures will help prevent gum overgrowth. Dentists recommend brushing your teeth with a soft brush, using dental floss or interdental brushes. Using a rinse aid reduces the number of bacteria settling on the enamel. But all these measures will not help if there is plaque on the teeth. Therefore, professional teeth cleaning in dentistry is where the prevention of hyperplasia begins.
Author of the article Voznyuk Vladimir Aleksandrovich Maxillofacial surgeon-implantologist of the highest category
Work experience: 28 years.
How to Avoid Gum Recession
In order not to expose the neck of the tooth, it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle, maintain proper nutrition, and carry out prophylaxis with a vitamin and mineral complex (with the doctor’s permission). In addition, regular dental care is recommended. This means not only hygiene, but also timely treatment.
If the neck of the tooth is exposed, you need to contact a qualified specialist at Dr. Sadov’s clinic, who will conduct an examination, prescribe an examination, on the basis of which a treatment plan will be drawn up. Self-medication is strictly prohibited. Use traditional methods only after consulting a doctor. Otherwise, the condition may only get worse.
What is the problem?
Because the part of the tooth that is not covered by enamel is exposed, the risk of developing root caries increases. In this case, it is difficult to cure, since ensuring a high-quality fit of the filling material to the root tissues is very problematic due to their hydrophilicity. Over time, teeth can become loose because there is not enough tissue available to hold them in place.
In addition, gum recession is an aesthetic problem, especially when the disease is advanced. People suffering from the disease develop complexes, which leads to social isolation.
Lack of flush hole: consequences
In the absence of a flushing space, the consequences may be as follows:
- inflammatory processes caused by constant contact of mucous membranes with the prosthesis;
- tissue damage with subsequent exposure to pathogens;
- tissue hypertrophy in the affected areas of soft tissue.
If you look at it from a different angle, the rinsing space provokes the penetration of food into the area between the prosthesis and the mucous membrane. But without this gap, the patient will not be able to provide proper oral care. Plaque can accumulate under the bridge, so this area needs more thorough cleaning.
If the patient notes that food debris has entered the resulting space, this may be caused by incorrect installation of the prosthesis, poor quality of construction, or the development of pathologies of the oral cavity. Normally, this situation should not exist.
The neck of the tooth is exposed, how to treat it
After the doctor has diagnosed the cause of the exposed cervix, he recommends the patient one of the following treatment methods:
- Filling the exposed area. This procedure is indicated at the initial stage of the pathological process. When a wedge-shaped defect has formed, there is nothing to attach the filling material to, so filling is irrelevant.
- Remineralization of enamel. A product containing calcium is used. The patient will not feel pain during the procedure. The process lasts about 10 minutes. A drug is applied to the affected tooth to help strengthen the enamel, protect the roots from exposure, and prevent tooth loss. In addition, the advantage of remineralization is the return of the enamel to its former shine. How many sessions a person needs is determined by the doctor.
- The enamel is coated with fluoride (fluoridation). Special varnishes or gels that contain fluoride are used. Fluoridation can be simple or deep. With the help of such methods, the dental neck is restored and tooth sensitivity is reduced. With deep fluoridation, the drug strengthens the enamel as it penetrates inside it.
- Installation of veneers. This is a thin ceramic plate. It is applied to a previously ground tooth. This technique is indicated for advanced cases. With the help of veneers, it is possible to completely eliminate the disease and minimize the risk of its recurrence.
- Crowns. Before installing crowns, the tooth is ground down. It is a radical way to protect the tooth root and prevent further progression of the pathology.
- Gum plastic surgery.
Drug and surgical treatment
If the cause of exposure of the neck of the tooth is a lesion or pathology of the mucous membrane, the patient is consulted by an implant surgeon. During the operation, tissue taken from the palate of the mouth is implanted under the tooth root. This helps to increase the volume of gum tissue and cover exposed areas of the tooth. At the end of the surgical intervention, sutures are placed on the gums. After this, the patient is scheduled to regularly visit the attending physician, who will monitor the healing process.
Use an antiseptic solution to rinse your mouth. You can eliminate swelling and redness of the gums with the help of medicinal gels. If pus is present, an antibacterial drug is prescribed. The choice of medication is made only by the attending physician; self-medication is prohibited.