Of course, you need to take care of your teeth from a young age! Of course, they need to be treated immediately and in no case should you delay this, albeit not always pleasant, activity. We know this, understand it, and promise ourselves to do just that. But in practice, unfortunately, it turns out completely differently. Some people don’t go to the doctor because of lack of time, others because of lack of funds. As a result, a visit to the doctor is postponed for an indefinite period of time, and then completely forgotten about. But many severe forms of disease and tooth loss could have been avoided simply by visiting a dentist in time.
Human teeth, of course, are not the most convenient organ. They are designed for a short human lifespan - 20 or 30 years. Today, people live much longer, and it is almost impossible to preserve all of their permanent teeth for the rest of their lives, but medicine offers few worthy alternatives to natural teeth.
Acrylic or nylon removable dentures are affordable, but not very comfortable and physiological. Sometimes it is possible to restore a defect in the dentition with a bridge, but this will require damaging completely healthy neighboring teeth. Intramaxillary implants best solve the problem of missing teeth, but they are quite expensive and the recovery period after surgery is long. There is only one conclusion - nothing can be better than your own teeth, so we all need to take care of them.
What causes dental caries?
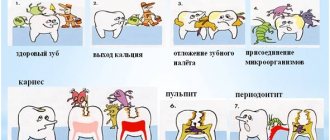
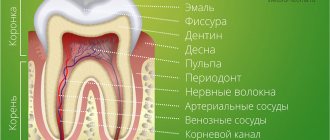
Caries is a progressive disease that destroys the hard tissues of the tooth. Cariogenic bacteria live in the oral cavity; they form a biological film on the surface of the teeth - dental plaque. They feed on carbohydrates that enter our bodies through food and drinks. Bacteria process sugars and produce organic acids. Those, in turn, corrode tooth enamel and deep tooth tissues. This is how caries develops.
In this article
- What causes dental caries?
- How does caries progress?
- A dangerous complication of caries is pulpitis.
- How is pulpitis treated?
- Periodontitis as a dangerous consequence of caries
- How is periodontitis treated?
- What is the danger of caries for the gastrointestinal tract?
- ENT diseases as consequences of caries
- Why is caries dangerous for the heart and blood vessels?
- Risk of death from dental caries
- Conclusion
Although bacteria living in the oral cavity play an important role in the development of carious lesions, a complex of unfavorable factors is important for tooth decay:
- an abundance of “fast” carbohydrates in the diet (sweets, flour);
- poor dental and oral hygiene;
- lack of calcium, fluorine, phosphorus, vitamin D in the body;
- weakened immunity.
Prevention of caries
Many pediatric dentists offer painless and fun treatment. But it is easier to prevent than to treat. Simple preventive measures will help preserve the integrity of baby teeth for as long as possible:
- Daily oral hygiene. As soon as the first tooth appears, you need to purchase children's toothpaste and a brush. Grooming should be done twice a day - morning and evening, and gradually become a healthy habit for the child.
- Proper nutrition. It is necessary to include foods high in calcium (kefir, cottage cheese, cheese, etc.), as well as vegetables and fruits, in the child’s diet. Harmful sweets and fast carbohydrates, on the contrary, should be excluded or reduced as much as possible in the daily menu.
- Preventative examinations with a doctor. A pediatric dentist should be visited 2-4 times a year. This will allow you to monitor dental health and reduce the risk of caries in your child.
It is recommended that a child’s first meeting with a dentist take place after the incisors appear – at 1-1.5 years. This will be a preventive examination, during which parents will be told the principles of caring for children’s teeth and advised on the optimal scheme for monitoring the growth of temporary units.
Watch an informational video on this topic
How does caries progress?
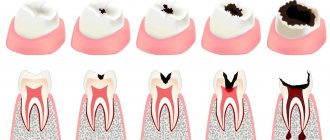
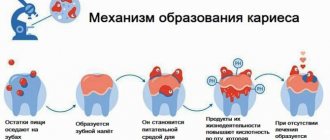
There is a myth that caries is necessarily a hole in the tooth, but in reality, dental disease begins with the loss of mineral substances in the tooth enamel and gradually progresses. Caries goes through four stages in its development. Let's look at them below.
- Spot stage.
There is no hole in the tooth yet, but a whitish spot is noticeable on the surface. A change in the color and structure of the enamel means that it is losing minerals in this area. At an early stage there is no pain or discomfort, so patients rarely go to the dentist, not even suspecting the presence of caries. But it is at the spot stage that caries is easiest to cure. The progression of the disease can be stopped using conservative methods without drilling or installing a filling. At this stage, remineralization, simple and deep fluoridation, and the infiltration method are effective.
- Superficial caries.
At this stage of development of the disease, a small carious cavity forms within the enamel. The patient may have the first complaints: the tooth reacts to cold and hot, sour and sweet, food gets stuck in the resulting hole.
- Average caries.
The carious cavity becomes larger and affects the dentin - the bone tissue of the tooth under the enamel. At this stage, acute toothache most often appears; food stuck in the hole causes severe discomfort, and the patient complains to the dentist. It will not be possible to cure average caries without preparing the tooth, so an operative approach is used in treatment - using a drill, the affected tissue is removed and the cavity is filled with special composite materials.
- Deep caries.
The carious lesion affects the deepest layers of dentin and approaches the dental nerve. All the symptoms that were there before intensify, sometimes becoming chronic. Frequent complications of deep caries are pulpitis and periodontitis (inflammation of the pulp and tissues surrounding the tooth root).
It is better to treat caries in the early stages, while there is no carious cavity in the tooth. Conservative methods will help stop the pathological process without drilling and filling. If a hole has already formed in the tooth, then you cannot do without a drill. What if you don't treat it? Many people have been afraid of dentists since childhood and put off visiting the doctor as much as possible. This should not be done under any circumstances, because caries is dangerous for the body due to its consequences. With an advanced form of the disease, you can lose a tooth or develop purulent inflammation. There are even cases of death from complications of deep caries. Therefore, it is imperative to treat the disease!
Why is treatment of caries, if the tooth does not hurt, still necessary?
When teeth are affected by caries, they can make themselves felt at the most inopportune moment. Imagine the situation: you are on vacation, and you are going to visit another country or are already there, or went to another city or wanted to relax in nature, and the nearest dental clinic is several hours away from you, and your tooth hurts a lot, your cheek is swollen, and No drugs relieve the symptom. What should I do? Of course, it would be better to treat teeth at the initial stage of caries development, before they begin to become inflamed, before acute pain or even a cyst appears. The current situation requires an urgent search for a dentist. Naturally, if you are staying in a foreign country or city, the cost of services will be much higher, and one can only guess how high-quality and durable the result you will get.
One of the important reasons why it is very necessary to treat caries when teeth do not hurt is the possible consequences of untimely treatment.
A dangerous complication of caries is pulpitis.
The most common consequence of untreated caries is pulpitis. It occurs when the infection extends beyond the tooth and spreads to the pulp - the neurovascular bundle, or dental nerve.
The pulp contains nerves and blood vessels and provides nutrition to the dental tissues. Therefore, with pulpitis, the tooth may lose vitality. In severe cases, inflammation spreads to neighboring tissues.
A characteristic symptom of pulpitis is acute, prolonged pain that is difficult to tolerate. It often has a pulsating nature and can radiate to the temple, ear, or throat. The peculiarity is that attacks of pain appear at certain intervals, last about 5 minutes, and can intensify when lying down. It is necessary to begin treatment of pulpitis as quickly as possible.
How is pulpitis treated?
Pulpitis can be treated biologically or surgically. The first is applicable if the disease is in its early stages. The dentist strives to preserve the pulp by eliminating only the inflammation. If possible, pulpitis of primary teeth is treated using a biological method, when it is especially important to preserve the tooth root. Treatment is carried out in several stages. First, the dentist prepares the carious cavity, opening it as wide as possible. Then he treats it with an antiseptic, puts a swab with an antibacterial agent and covers the tooth with a bandage. During the next appointment, if the patient has no complaints, the cavity is treated with medication, filled with a special composition that stimulates dentin production, and a temporary filling is placed for a period of 5 to 7 days. During the third appointment, the dental crown is filled.
When the biological method of treating pulpitis is ineffective, surgical treatment is used. In this case, the inflamed neurovascular bundle is removed completely or partially. Without a nerve, a tooth becomes unviable and its service life is reduced.
Surgical treatment is performed with local anesthesia. First, the carious cavity is prepared, the pulp is removed, the affected area is treated with an antiseptic, medication is injected, and first the root canals are filled, and then the dental crown. As with the biological method, surgical treatment is carried out over several visits to the dentist.
If pulpitis is not treated, it will progress and can lead to very serious complications:
- flux - inflammatory process in the periosteum;
- periodontitis - inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth;
- pulp necrosis - death of its cells;
- sepsis is a blood infection that can develop when an infection enters the bloodstream.
You can avoid such complications if you do not delay your visit to the dentist and begin treatment for the disease at the first symptoms.
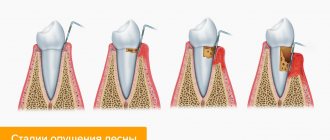
Periodontitis as a dangerous consequence of caries
Against the background of untreated caries and dental pulpitis, the infection penetrates even deeper. As a result, periodontitis develops. This is a disease in which the tissue around the tooth root becomes inflamed - periodontium. Essentially, it is a ligamentous apparatus that holds the tooth in the jaw and provides shock absorption. With periodontitis, an abscess may form near the diseased tooth, and in this case, treatment will require opening the tooth and cutting the gum.
Periodontitis can occur in acute and chronic forms. Acute is characterized by a rapidly developing inflammatory process. The tooth darkens, becomes loose, the patient complains of acute pain, inflammation of the cheek may occur, and swelling appears in the area of the affected tissue. In a chronic course, pronounced symptoms may be absent, and pain occurs only during periods of exacerbation. Chronic periodontitis requires long-term complex therapy, which can take several months. The disease greatly weakens the immune defense and generally negatively affects the condition of the body.
How is periodontitis treated?
The approach to treating periodontitis may vary depending on its type, severity, patient history and other factors.
The chronic form of the disease is treated according to the following scheme:
- The area of the diseased tooth is numbed with anesthetics.
- First, the affected tissue and old fillings are removed from the root canal, the tooth is depulped, and, if necessary, the root canal is expanded using dental drills or a microscopic incision.
- At the second stage, the root canal is cleaned and washed with antiseptic solutions. An antibacterial drug is placed into the canal cavity, which relieves the inflammatory process and fights infection.
- The tooth is covered with a temporary filling, and antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
- The patient is sent home, where he must strictly follow all the dentist’s recommendations. The next appointment is usually scheduled after three or four days.
- At the second stage of treatment, a control photograph is taken. If the inflammation is stopped, the dentist removes the temporary filling and medicine from the root canals, rinses the cavities with an antiseptic, and fills the canals with a special composite material. It contains substances that help restore dental tissues and destroy pathogenic microorganisms. This filling of the canals is temporary and is needed in order to completely stop the inflammation and reduce the risk of re-developing periodontitis in the future. It is done for several months, and the tooth is again covered with a temporary filling.
- A few months later, the patient comes for a follow-up appointment with the dentist, where a tooth photograph is taken again to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment. If the inflammation has completely stopped, the final stage of treatment begins - replacing temporary fillings with permanent ones and restoring the dental crown with a permanent light-curing filling. After this, the process of treating chronic periodontitis is considered complete.
- Unfortunately, it is not always possible to carry out conservative treatment of this disease. In advanced forms, the dentist is forced to resort to surgical treatment, when part of the root or the entire tooth is removed.
Treatment of periodontitis is long, complex and expensive, and the disease itself is a source of chronic infection, negatively affects the entire body, and weakens the immune system. It is easier and safer to contact the dentist on time and treat early caries. The consequences of an advanced disease are dangerous for the body.
Methods for treating caries in children - without pain and fear
There are many methods available for the treatment of caries in primary teeth. All of them are adapted for children and do not cause pain, discomfort or anxiety to the child. Depending on the complexity of the situation, dentists offer the following solutions:
- Remineralization of tooth enamel – restoration of a balanced structure of the tooth surface using special pastes. Formulas with a high content of calcium and sodium should be applied to baby teeth for some time, which will stop the spread of bacteria and the deepening of carious cavities.
- The ICON method is an ideal treatment option for superficial caries. The doctor applies a composition to the carious spot to remove the affected area of enamel, and then closes the cavity with a safe, quick-hardening polymer. The treatment takes place without a drill - quickly and painlessly.
- Ozone therapy is an effective method of combating caries. The damaged area is subjected to targeted exposure to ozone to disinfect the enamel and eliminate carious bacteria. Children tolerate the procedure very well, as it does not cause any discomfort.
- Filling. Cleaning carious cavities is done using a drill or manually without drilling. Next, the doctor treats the tooth with antiseptics and places a filling - white or colored. Treatment of caries of a baby tooth is carried out with anesthesia with local anesthetics or under sedation.
- Laser dental treatment. Advanced technology in which laser beams remove carious lesions quickly and accurately. A filling is placed on the cleaned and disinfected cavity.
A method for treating caries is suggested by the doctor after assessing the degree of damage to the baby tooth.
What is the danger of caries for the gastrointestinal tract?
Caries and its complications have a harmful effect not only on teeth, but also on other organs and systems of the body. In particular, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract - pancreatitis, gastritis, duodenal and stomach ulcers - often occur against the background of dental caries.
The fact is that with caries and any other dental diseases, pathogenic microflora is activated in the oral cavity. Together with food and saliva, it can easily penetrate the esophagus into the stomach and intestines, causing an inflammatory process. As microbes multiply, they crowd out beneficial microorganisms and lead to the development of gastrointestinal diseases. On the other hand, the state of the digestive organs directly depends on the quality of chewing food. Caries negatively affects this function, because with damaged chewing teeth a person cannot efficiently process food to such a state that the gastrointestinal tract can easily absorb and digest it. As a result, there is an excess load on the stomach, intestines, and duodenum, which leads to pathologies of the digestive organs. In addition, poorly chewed food makes it worse for nutrients to be absorbed.
Modern research shows that even deposits on healthy teeth can threaten the health of the stomach and intestines. Thus, the bacteria Helicobacter pylori accumulate in tartar, which contributes to the development of peptic ulcers. Therefore, not only timely treatment of caries, but also its prevention, in particular proper and regular oral hygiene, helps reduce the risk of gastrointestinal diseases.
What happens if childhood caries is not treated?
Treatment of caries of primary teeth, as well as prevention of dental diseases are very important.
And waiting for your teeth to change is wrong and unreasonable. Arguments in favor of monitoring children's health and timely treatment will be:
- High probability of infection of permanent units. Under the milk teeth are the rudiments of the molars. Untreated caries can easily spread to permanent teeth and cause more serious problems.
- Early removal of milk units. In children, caries spreads quickly, and if the crown is severely damaged, doctors remove the tooth. But if the molar is not yet ready to grow, the incisors, canines and molars in the mouth begin to shift. The child’s bite deteriorates, which then has to be corrected with braces, aligners or other orthodontic systems.
- Serious problems with diction. Extracted and damaged teeth make it difficult to clearly pronounce sounds, which complicates communication with peers and often negatively affects school performance.
- Vulnerability to infections. A bad tooth threatens not only the dental health of neighboring units, but can also cause frequent throat diseases and provoke problems with the gastrointestinal tract and heart.
- The appearance of complexes. Decayed teeth look unsightly, which is why the child smiles less and grows aloof and uncommunicative.
- Delayed bite change. After suffering from pulpitis or periodontitis, the resorption of the roots of temporary teeth often stops. This means that baby teeth stop falling out on their own, and they have to be removed by a surgeon.
It is also worth remembering that the process of updating the bite is extended over time and can take up to 6-8 years. Does a child really have to suffer with bad teeth all this time?
Rodikova Tatyana
Unfortunately, parents still have to be convinced to treat caries of baby teeth in children. Many people do not see the danger in this disease and believe that the problem will disappear in the process of changing teeth. After explaining the harm of a carious infection in the oral cavity, many, however, agree with the doctor’s opinion. And every such case makes me very happy!
Why is caries dangerous for the heart and blood vessels?
When brushing your teeth, there is a risk of injury to your gums. This can happen due to a brush that is too hard, careless use of dental floss, or sensitivity of the gums themselves. One way or another, cariogenic bacteria enter the resulting wounds, which can be carried throughout the body by the bloodstream. If they get into the tissue of the heart, inflammation of its valves may develop - infective endocarditis.
Studies show that with advanced caries, the risk of developing cardiovascular pathologies increases by 70%. When bacteria enter the blood, they settle on the vascular walls next to atherosclerotic plaques. As a result, the plaque begins to actively grow and can clog the vessel, disrupting normal blood flow. The most dangerous consequences can be thrombosis, stroke, heart attack, atherosclerosis.
Signs of caries in children
After solving the question “does caries of baby teeth need to be treated,” a new one appears. Namely: how to understand that a child has caries?
The symptoms of dental diseases are simple:
- Complaints of pain - at night, during meals or during the day.
- The appearance of yellow or brown spots on the enamel of the teeth.
- Bad breath.
- Excessively careful chewing of food - with teeth on only one side.
Unfortunately, caries can occur without visible signs. For this reason, dentists advise periodically examining the child’s oral cavity and monitoring the quality of teeth cleaning.
Risk of death from dental caries
Many people underestimate the danger of caries, considering this disease to be frivolous. However, there are known cases of death from complications of untreated caries. How is this possible?
For example, if the inflammatory process from the roots of the teeth of the upper jaw spreads to the maxillary sinuses, sinusitis may occur, which can spread greatly without treatment. When the infection extends beyond the jaws, there is a possibility of a brain abscess, purulent inflammation, sepsis - all these complications can be fatal.
Another danger is the so-called pathological fracture of the jaw. This condition is associated with a cyst in the jaw, which occurs as a complication of advanced caries.
All of these dangers are real and can occur against the background of dental caries. But it is important to understand: only an advanced carious process that has not been treated for many months or even years leads to such serious complications. With regular visits to the dentist, timely treatment of caries at the first symptoms, as well as compliance with the rules of dental hygiene and other preventive measures, the risk of serious consequences for the body is almost zero.
Reason four: financial
In the initial stages, caries treatment is relatively inexpensive and absolutely affordable for everyone. However, with the development of complications up to the loss of a tooth, treatment becomes increasingly more expensive: treating pulpitis is already noticeably more expensive than caries, since the volume of manipulations and materials consumed are greater. As for the loss of a tooth that has not been treated in time, prosthetics will cost quite a hefty sum. Therefore, those people who do not care too much about their health may benefit from the financial argument.