Causes
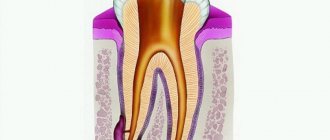
Unlike ordinary sore throat, herpetic sore throat is caused by viruses. Among the main provocateurs, it is worth highlighting the Coxsackie virus type A or B, serovars, and ESNO viruses. They can be infected by droplets, fecal-oral routes, through bodily contact, and unprocessed food.
The pathogen, entering the body, multiplies in the intestines and lymph nodes. The pathogen spreads through the lymph and blood and intensively accumulates in the pharyngeal ring and tonsils. On the third day, the condition of the infected person deteriorates sharply.
Stomatitis and tonsillitis: how to distinguish between pathologies?
How to distinguish a patient's sore throat from stomatitis? To do this, you need to pay attention to the location of the foci of the inflammatory process.
- With angina, ulcers, hyperemic areas and/or ulcers form exclusively on the surface of the tonsils. The mucous membrane of the larynx and palatine arch are red, nasal discharge may appear - transparent or yellowish.
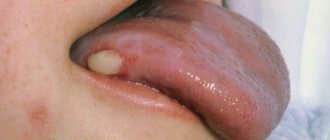
- Stomatitis differs from tonsillitis in that when it develops, aphthae or ulcers appear on the surface of the mucous membranes of the palate, the inside of the cheeks and lips. Possible formation of bubbles filled with cloudy or clear liquid. In this case, they speak of the presence of herpetic stomatitis.
Knowing how to independently distinguish stomatitis from a sore throat, you can promptly identify the pathological process and prevent its spread.
Symptoms
The following clinical picture appears sharply, acutely and violently:
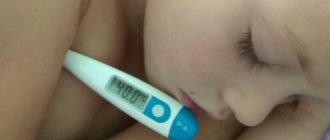
- Within a few hours the temperature rises to 40°C.
- Chills and general weakness of the body appear.
- My head starts to hurt.
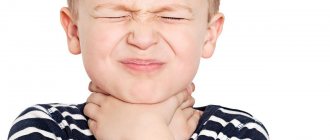
- When swallowing saliva or liquid, an unbearable sore throat develops.
- The color of the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx changes. After a few hours, the throat turns red, and the next day it becomes covered with many reddish blisters.
Acute symptoms last for 2-3 days, and then their intensity decreases.
Stomatitis and sore throat: causes of development
Often stomatitis with sore throat in children develops against the background of a bacterial infection - staphylococcal, streptococcal, etc. But sometimes the onset of the disease occurs against the background of uncontrolled use of antimicrobial agents for tonsillitis.
Factors predisposing to the development of stomatitis with angina in children and adults may include:
- failure to comply with oral hygiene rules,
- hypothermia,
- burn of the oropharyngeal mucosa,
- abuse of spicy and salty foods,
- injuries to the mucous membranes of the mouth or tonsils.
Sore throat and stomatitis at the same time in a child often occur due to the habit of putting fingers, toys and other foreign objects in the mouth. Moreover, stomatitis develops first, and already against its background a catarrhal or even purulent sore throat occurs.
Symptoms of herpetic sore throat in children
Children attending nurseries or kindergartens, as well as schoolchildren, get sick most often. In children in the first three years of life, herpetic sore throat is extremely difficult, since the first signs of the disease are similar to the flu.
In addition to the general signs of intoxication, children appear:
- Temperatures up to 41°C.
- Pronounced hyperemia of the mucous membranes of the mouth and pharynx. During examination, the tissues appear to be filled with blood.
- A day later, 1-2 mm papules in the mouth, surrounded by a red rim. The next day they open, forming ulcers with crusts.
- Runny nose.
- Decreased appetite due to impossible pain.
- Enlarged lymph nodes located in the neck and ears.
If children have weak immunity, then sore throat occurs in waves, i.e. The deterioration of the condition is recorded after a few days, then it improves noticeably.
In addition, children experience stomach upset due to the fact that viruses irritate the mucous membrane of the digestive tract. The child complains of diarrhea and nausea.
Diagnostic features
When tonsillitis develops along with stomatitis, a child, like an adult, requires qualified medical care. For diagnosis, it is often sufficient to conduct a thorough examination of the oral cavity and the mucous membrane of the tonsils.
A mandatory step is to conduct a general clinical blood test. With stomatitis tonsillitis, there is an increase in the number of leukocytes in the biomaterial.
Purulent tonsillitis and stomatitis in a child require special attention from the attending physician. In this case, a smear is performed for bacterial culture. Using bacteriological examination, the type of pathogenic microflora that caused the development of tonsillitis is determined.
Diagnosis and treatment
At the appointment, the ENT doctor will examine the patient and conduct an examination. Based on the diagnostic results, drug therapy is prescribed, including:
- Taking antipyretics based on paracetamol or ibuprofen.
- Taking antiviral drugs prescribed after identifying the exact pathogen.
- Taking antihistamines. The active substance helps relieve swelling and ease breathing.
- Resorption of lozenges, lozenges, use of local sprays. Their antiseptic and bactericidal properties reduce sore throat.
- Local use of antiviral ointments based on interferon.
- Taking immunostimulants to activate the body's defenses to fight the pathogen.
It must be emphasized that antibiotics are powerless for this type of tonsillitis, because they do not affect the reproduction of viruses.
Important to remember! Do not apply heat compresses to the throat. Heating promotes the further spread of viruses throughout the body.
In addition to taking medications, the patient must be isolated from others and observe strict quarantine. The infectious period lasts two weeks. You need to follow a diet and eat pureed liquid food, drink more liquid. Water not only prevents dehydration, but also relieves symptoms of intoxication. If you are sick, you should not smoke, drink boiling water or water from the refrigerator.
Since the throat is constantly injured, healing occurs within 10-14 days. Crusts and sores are washed off with saliva without any residue.
It is important to know! Do not touch the bubbles with your hands or try to squeeze them out.
Stomatitis and sore throat: treatment features
Treatment of stomatitis with tonsillitis in a child should be comprehensive. It is strictly forbidden to resort to antibiotic therapy on your own, as this can lead to side effects or significantly worsen the course of the disease.
So, for these pathologies it is shown:
- Rinse or treat the oropharynx with antiseptic solutions three times. For this purpose, the drug Miramistin has been successfully used.
- Rinsing the mouth and throat with herbal decoctions - chamomile, sage, marigold (prepared from calendula flowers).
- Taking vitamins aimed at speedy recovery of the body: Supradin, Revit, Multitabs.
Symptomatic treatment includes the use of painkillers (ibuprofen) and antipyretics (paracetamol, Panadol, Nurofen). Many drugs have both properties at once, that is, they relieve pain and reduce body temperature at the same time.
Purulent tonsillitis, occurring with signs of stomatitis, is treated with antibiotics of the penicillin group (Ampicillin, Penicillin, Amoxiclav) or cephalosporins (Ceftriaxone). Children are often prescribed the drug Cefixime, available in powder form for the preparation of an oral suspension. The course of therapy is 5–7 days.
Specific features of herpetic sore throat
Herpetic tonsillitis can be distinguished from other types of sore throat by the following characteristics:
- A rash appears on the upper and lower extremities and face if not treated in a timely manner.
- Numerous red blisters appear on the pharynx, adenoids, tongue, and palate. Gradually they develop into ulcers and open. A light transparent exudate emerges from the bubbles. Typically there are from 5 to 20 ulcers in the mouth. If treatment is not started in time, the ulcers merge with each other, forming large areas of damage to the mucous membrane of the throat and mouth. In this case, there is a high risk of complications.
Often, parents mistake herpangina for another disease and try to cure it on their own. Herpetic sore throat should not be confused with:
- Thrush. Candidiasis in the mouth appears as a cheesy coating.
- Herpetic stomatitis. Papules are similar, but with stomatitis they are localized on the gums and tongue.
- Purulent sore throat. Formations accumulate only on the tonsils and lacunae, and with herpetic disease they cover the entire nasopharynx. In addition, a runny nose is a distinctive symptom. With purulent tonsillitis there is no runny nose.
Causes of stomatitis
The main cause of stomatitis is infection: viral, bacterial or fungal. But viruses and bacteria themselves are not dangerous to the body; the disease develops only under certain conditions:
- damage to the mucous membranes: biting the inside of the cheek, burns, injuries from the sharp edge of a chipped tooth or hard dry food, etc. A small wound that gets infected is enough for the disease to develop;
- poor oral hygiene, hard plaque;
- deficiency of vitamins B, zinc, folic acid, iron;
- smoking: causes an imbalance in the microflora of the oral cavity and a constant negative effect of hot smoke on the mucous membranes, which over time can lead to the so-called “smoker’s stomatitis”;
- decreased salivation: occurs due to the use of certain medications, dehydration, stress and a number of diseases;
- Using toothpastes with sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) and brushing your teeth too often;
- incorrectly installed dentures or their low quality;
- hormonal changes during pregnancy, menopause, and adolescence.
At the PROPRICUS clinic in Moscow, treatment for stomatitis is prescribed only after a thorough diagnosis and identification of the cause of the disease.
This allows you to select the most effective therapy depending on the type of stomatitis. Need diagnostics?
Enter your phone number and we will give you a free consultation on your problem
Make an appointment
*By making an appointment you consent to the processing of your data
Complications
Unfortunately, this type of tonsillitis has dangerous negative consequences if the disease is started and left to chance. The greatest danger is from complications of the kidneys, brain and heart. Since the sore throat virus spreads through the flow of lymph and blood, inflammation can overtake certain parts of the brain, causing meningitis and encephalitis. Convulsions, persistent headache, increasing temperature are reasons to seek medical help again.
At the ENT CLINIC in Chertanovo, ENT doctors with extensive experience will carefully examine an adult and a small patient and immediately perform a serological and virological analysis to determine the causative agent. The technical equipment of our medical center allows us to obtain diagnostic results within a couple of hours. Thanks to this, therapeutic therapy is prescribed in a timely manner, with positive dynamics occurring the very next day.
Can pathologies develop simultaneously?
As already noted, stomatitis and tonsillitis are diseases that often accompany each other. This may be due not only to previous viral or bacterial infections of the oropharynx, but also to an incorrect approach to the issue of therapy.
Sore throat and stomatitis at the same time are common occurrences in people who self-medicate. Often, patients cannot correctly determine which pathology they are suffering from, so they resort to very dubious, and therefore dangerous, methods of therapy.
But the worst thing is that some young mothers do not consider it advisable to take their children to the doctor, but use antibiotics at their own discretion. For this reason, sore throat, combined with stomatitis, develops more often in children than in adults.
Classification of the disease
Before starting treatment for herpes stomatitis, it is necessary to determine the form and degree of its progression. At the same time, acute herpetic stomatitis in children is diagnosed already when the virus first enters the body.
The severity of the disease is divided into:
- Light. Small blisters form on the oral mucosa - they quickly disappear after they rupture;
- Average. The rashes are more extensive, body temperature rises (up to 38º);
- Heavy. The patient has an abundance of ulcers in his mouth, and after they disappear, new ones appear. Symptoms are supplemented by fever, headache and chills, sometimes the patient feels sick and has diarrhea.
In the absence of proper treatment, chronic recurrent herpetic stomatitis develops. This form of the disease is already characterized by group rashes (on the inside of the cheeks, tongue and palate). The formations combine and form painful erosions. In the recurrent stage, except for rashes, no other symptoms of the disease are noted. The disease may return 2-6 months after treatment.
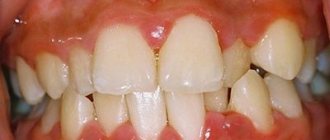
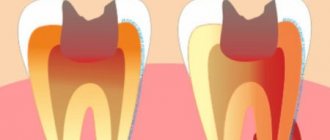
What does stomatitis look like in the mouth?
Initially, during stomatitis, the soft tissues located in the oral cavity swell greatly and swell. The mucous membrane may itch and hurt when fingers press on it. In those places where the rash occurs, the skin may become pale or red. Sometimes tissue hyperemia is noted, so the patient may claim that the mouth is on fire. Later, rashes are observed. Their shade, shape, type depends on stomatitis and its type.
Usually the rashes look like oval or round lesions on the skin, there may be plaque, but the disease is always accompanied by pain. There may be a different number of formations.
Treatment of stomatitis
It is important to contact your dentist in a timely manner. Everything will depend on the disease and the causes of its occurrence. To cure infectious sources, you will need a complex of vitamins, immunomodulators, antibacterial, antifungal, and antiviral medications. They may also use products to help relieve pain and promote rapid healing.
If the inflammatory process appears due to an injury, then all you have to do is treat it and disinfect it. If the nature of the disease is toxic or allergic, then you need to eliminate the cause, and then cleanse the body.
When treating stomatitis, it is important not to consume hot drinks, food, sweet, salty, sour, spicy foods, and you need to follow a diet. If you have thrush, it is recommended to remove fermented milk products.
Stages
There are three forms of the disease:
- Easy. Almost no one here has any rashes. Treatment is quick and easy. This stage is called catarrhal stomatitis. In the absence of timely treatment, it moves to the next stage;
- Average. This is the aphthous stage of stomatitis;
- Heavy. This stage is called ulcerative. During this type of disease, necrotic tissue damage may occur.
After some time, all wounds heal, after which only scars and tissue damage remain. But there are certain consequences of stomatitis; it can become chronic. Treatment is possible here, but it takes longer.