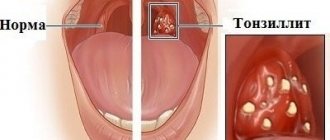
Acute tonsillitis is a sore throat that is well known to all of us. The disease is infectious in nature and affects the lymphoid tissue of the palatine tonsils.
The disease occurs at any age, but tonsillitis is more often diagnosed in children.
The palatine tonsils, or the more familiar name “tonsils” to us, are located in the pharynx and are a kind of barrier to infection. Coping with an infection that enters through the mouth, the tonsils remove dead bacteria and viruses from the body and prevent unpleasant diseases from occurring. But if the body’s defenses are not enough, the tonsils cannot cope with the attack, and the pathogenic microflora firmly settles in the tissues of the tonsils, causing inflammation in them.
Why is tonsillitis called acute? Because a sore throat begins suddenly and occurs with severe symptoms.
Most often, acute inflammation of the tonsils is provoked by streptococcus and staphylococcus bacteria, less often the disease is caused by viruses. The following causes of the disease in children are identified:
- past infectious diseases (in this case we are talking about secondary angina);
- the presence of a focus of infection in the child’s oral cavity and nasopharynx (stomatitis, caries, sinusitis, etc.);
- impaired breathing through the nose due to hypertrophied adenoid vegetations or formed polyps;
- anatomical features of the pharynx;
- allergy;
- hypothermia;
- low immunity.
Sore throat is a highly contagious disease. It spreads by airborne droplets or contact. The development of the disease in a child often begins after close communication with other children. After all, the child is constantly in a group, be it a kindergarten, school or section. Therefore, it is not surprising that the diagnosis of “acute tonsillitis” is often present in the anamnesis of young patients.
During a disease epidemic in a child’s preschool or school, if possible, it is better to stay at home.
Symptoms of tonsillitis in children
The first symptoms of the disease appear suddenly. The child complains of a sharp sore throat. This makes it difficult for him to swallow. There is a lump in the throat. The patient refuses to eat. In this case, enlarged lymph nodes in the neck can be clearly felt.
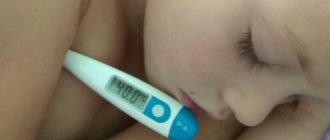
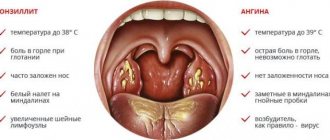
In acute tonsillitis, body temperature rises sharply to 39-40℃. As the disease progresses, symptoms of intoxication become more and more apparent: nausea, vomiting, headaches, dizziness. Possible unpleasant reactions from the gastrointestinal tract.
Another characteristic symptom of angina is the appearance of a white or yellowish coating on the tonsils. It may differ depending on the type of sore throat (for example, in the form of a white film or pustules).
Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
When a child is ill, he does not feel like eating, he quickly gets tired, weak and drowsy.
If you start treating the disease on time, the symptoms of inflammation gradually disappear and recovery occurs.
If treatment is delayed or the acute form of the disease was initially treated incorrectly, without consulting a doctor, the course of a sore throat may be aggravated by severe complications.
Signs of tonsillitis, photo of the disease
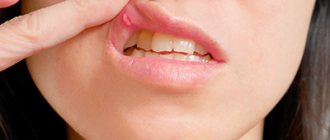
Acute tonsillitis is a very insidious disease, so parents should be wary if a child complains of pain when swallowing. Below are photos of a throat with a sore throat:
With a sore throat, a white or greenish coating is visible on the tonsils
The child's throat hurts very much
If you look at a photo of a child’s simply sore throat, the difference will be noticeable immediately:
With a sore throat, there are no white “plaques” in the tonsils
There is no plaque, which is how chronic tonsillitis is actually diagnosed.
If you try to clean the gaps from white accumulations, they can be easily removed with a spatula. In this case, the opened mucous membrane will not begin to bleed. But the patient will experience severe pain.
Pediatricians include other symptoms of acute damage to the palatine tonsils:
- increase in body temperature (for several days it can remain above 38.5-39 ° C);
- general weakness;
- headache;
- aching joints;
- enlargement of the tonsils (their surface becomes loose);
- inability to swallow food and water normally due to severe pain;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
But sore throat does not always look the same. Having established the presence of a sore throat, the pediatrician will have to determine its shape.
Forms of sore throat in children
Children have all types of tonsillitis that adults suffer from. It all depends on the age of the child. In children under 3 years of age, sore throat most often develops due to a herpetic infection. In children from 3 to 7 years old, sore throat is most often caused by bacterial flora (but the proportion of streptococcal infection is small), in school and adolescence it is also bacterial (in half of the cases it is caused by streptococcus).
Sore throats are divided into:
- primary - inflammation immediately begins in the tonsils (tonsils);
- secondary - sore throat occurs against the background of other infectious diseases (scarlet fever, diphtheria, measles, etc.);
- specific - when the palatine tonsils are affected by specific microflora (fungi, chlamydia, etc.).
Based on the nature of the changes occurring in the tonsils, the following forms of angina are distinguished:
- Catarrhal is the mildest type of disease, which affects only the surface of the tonsils. The inflammatory process is indicated by enlargement and redness of the glands. If the disease is not treated, within 3-5 days catarrhal tonsillitis changes to another form.
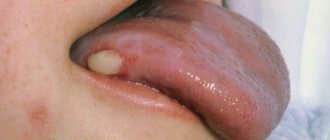
- Follicular - pustules appear on the surface of the palatine tonsils - purulent follicles. The patient feels better when these pustules open. Recovery occurs in approximately a week.
- Lacunar tonsillitis is similar in symptoms to follicular tonsillitis, but is more severe. Purulent plaque appears in the lacunae of the tonsils. This form of sore throat is easily confused with diphtheria. The disease lasts about a week, but if not properly treated it can lead to complications.
- Phlegmonous tonsillitis is a fairly rare but severe form of tonsillitis, in which a purulent abscess forms on one side. The abscess must be opened. After this, the patient feels better. Phlegmonous tonsillitis often occurs as a complication of the follicular and lacunar forms.
- Necrotizing tonsillitis - a gray coating forms on the tonsils. When the plaque is rejected, bleeding ulcers form in its place. This is a severe form of sore throat.
According to the severity of the course, angina is classified into mild, moderate and severe. With a mild form of sore throat, the temperature does not exceed 38°C and lasts up to 5 days. There is soreness in the throat and a slight enlargement of the lymph nodes. But there is no strong weakness.
With a moderate angina, the temperature reaches 38.5°C. There is a feeling of weakness, aching in the muscles and joints. Lymph nodes are enlarged. Symptoms last up to 8 days. A purulent coating is noticeable on the tonsils, which disappears within a week. There are no complications.
Severe sore throats occur with pronounced symptoms of intoxication: a temperature of 40°C that lasts for more than a week, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. There is a coating on the tonsils that does not disappear for more than a week. Lymph nodes are painful and greatly enlarged. Convulsions are possible.
Based on the presence of complications, angina can be either without complications or with complications.
Treatment of tonsillitis
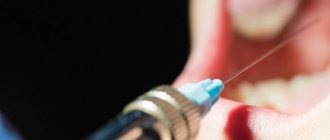
Complex treatment of tonsillitis is carried out under the supervision of an otolaryngologist; self-medication in this case is unacceptable. During the treatment period, the patient is prescribed bed rest, a gentle diet, and plenty of warm drinks. It is necessary to gargle with antiseptic solutions, carry out antibacterial therapy, and take antihistamines to reduce swelling of the throat. At temperatures above 38°C, it is recommended to take antipyretic drugs. Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs are used to treat tonsils. To free the tonsils from accumulated pus, lacunae are washed using the Tonsilor apparatus. Injections into the tonsils, injection of medicinal substances into the lacunae, and lubrication of the tonsils with antiseptics are also used.
For severe pain, it is recommended to use painkillers. To treat tonsillitis, various physiotherapeutic procedures are used: ultraviolet irradiation on the tonsil area, laser and magnetic laser therapy, electrophoresis, UHF, ultrasound, oil and alkaline inhalations.
When treating chronic tonsillitis, treatment can be either conservative or surgical. surgical treatment is used in the absence of positive dynamics in treatment, or the pathology has led to serious complications. During the operation, the tonsil is removed completely or only part of it. New methods of surgery are being used - laser lacunotomy or tonsillectomy using a surgical laser.
If you have symptoms of a sore throat or if you have a long-term, indolent sore throat, contact a medical professional. Modern equipment and the latest treatment methods allow us to provide the most effective care to patients with chronic and acute tonsillitis. Complex treatment of tonsillitis allows you to achieve excellent results and avoid surgical treatment or complications of the disease. You can make an appointment by calling the center or leaving a request on the website.
Possible consequences of sore throat in children
Angina is one of those diagnoses that, with adequate and timely treatment, have a favorable prognosis for recovery. But if the treatment was incorrect, it is possible that complications will develop, which may appear immediately during the course of acute tonsillitis, or may become delayed and appear after recovery. Complications are also divided into local, which negatively affect the pharynx, and general, which affect other organs and systems of the body.
Local consequences of sore throat in children include:
- purulent lymphadenitis - inflammation of the lymph nodes that occurs with the formation of purulent accumulations, the disease is treated surgically;
- swelling of the larynx - the greater the swelling, the higher the risk of suffocation;
- otitis - the nasopharynx is connected to the ear through the auditory (Eustachian) tube, through which the infection easily penetrates into the middle part of the ear during coughing or sharp blowing of the nose, triggering an inflammatory process in it;
- peritonsillar abscess - a condition in which the cavity located in the tissues around the tonsils fills with pus;
- bleeding from the tonsils;
- the likelihood of transition to the chronic form of acute tonsillitis, that is, the development of chronic tonsillitis, when the symptoms of the disease will return throughout the year, subsiding only during remission.
Common complications include heart, kidney, and joint complications.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
All these dangers can certainly be avoided if the disease is diagnosed and treated in a timely manner.
Causes of viral sore throat
As a rule, the virus enters the body when the body’s protective functions are reduced. Immunity may decrease after recently suffering from influenza, acute respiratory viral infections, as well as nutritional disorders (exhaustion). The following factors reduce the body's resistance to viruses:
- Poor nutrition and ignoring vegetables and fruits.
- Staying in an unventilated area. It is for this reason that preschoolers get sick.
- Stress.
The virus can enter by airborne droplets, contact, household and waterborne routes. Children often become infected with viral sore throat when visiting a swimming pool, kindergarten, or school. In close contact with a sick person, the likelihood of getting sick doubles.
Diagnostics
A consultation with an otorhinolaryngologist begins with collecting the patient’s medical history and complaints. The ENT doctor finds out how long the symptoms of inflammation have been appearing and whether any treatment has already been carried out. Direct examination includes palpation of the neck, parotid and occipital areas. Then the ENT doctor examines the oral cavity and pharynx. If necessary, an endoscopic examination of the pharynx is performed. He assesses the condition of the mucous membranes, palatine tonsils (their size, the presence of plaque on them or purulent plugs in them).
The patient may also be prescribed laboratory tests: a general blood test, a throat smear. If complications are suspected, serological blood tests, X-rays, electrocardiography, etc. are additionally performed.
After suffering a sore throat, a child may be diagnosed with myocarditis, arrhythmia, heart murmurs, pyelonephritis, renal failure, and rheumatism. If an infection from the tonsils enters the bloodstream and spreads throughout the body, sepsis may develop.
General recommendations for the treatment of sore throat
Regardless of what medications the ENT prescribes for the child, it is necessary to rinse with antiseptic solutions and treat the tonsils with special sprays. A good effect can be achieved if you give the patient lozenges for resorption, selected according to age (Faringosept, Falimint).
Throughout the illness, the child must remain in bed. His diet should be varied. At the same time, parents should exclude everything hot, cold, spicy, and very sweet from the menu. It is also better to avoid solid foods. The ideal option is broths, non-viscous porridges, pureed soups.
To avoid manifestations of toxic damage to the body, you need to persuade the child to drink as much as possible. Pure water, fruit drinks, dried fruit compotes, teas, decoctions of medicinal herbs are suitable (cannot be used if the baby is prone to allergic reactions).
Acute tonsillitis: treatment of sore throat in children
Therapy for chronic tonsillitis includes medications and physiotherapeutic procedures. The following are prescribed as drug therapy:
- antibiotics;
- antipyretic drugs;
- antiseptic solutions for gargling;
- antiseptic sprays for treating tonsils and pharyngeal mucosa;
- tablets and lozenges for sore throat.
It is very important for the patient to adhere to a diet, excluding too hot or cold liquids, spicy or solid foods. If the child has no appetite, do not insist, but more often give him warm tea, fruit drinks or compotes. The patient's room must be frequently ventilated and wet cleaned.
Traditional medicine recipes should be used with caution, after consulting with your ENT doctor.
Firstly, they can provoke an allergic reaction, and secondly, traditional medicine should not be used as the only method of treatment - only as an additional method. When treating a sore throat in children, you can gargle with herbal decoctions (chamomile, sage), consume honey and other bee products.
If you follow all the recommendations of the otorhinolaryngologist, the symptoms gradually subside, and the baby is on the mend.
Specific features of viral sore throat
Viral tonsillitis differs from other types of tonsillitis in the milder course of the disease, as well as in the following:
- Signs of the disease increase gradually, not abruptly.
- The temperature rises slightly.
- Does not require antibiotics.
- Local symptoms are not very disturbing.
- The clinical picture is aggravated by diarrhea and nausea.
- A sore throat is accompanied by a cough.
- There are no purulent plugs on the tonsils.
At the ENT CLINIC in Chertanovo, otolaryngologists will successfully diagnose the disease and individually select an adequate treatment regimen. The clinic has modern physiotherapeutic treatment methods in its arsenal, which make it possible to effectively and quickly cure a sick child.
Consequences of untreated sore throat
Sore throat must be treated. If parents are negligent about the fact that their child has become infected with this disease, the baby may subsequently experience the following complications:
- inflammatory damage to the lymph nodes, purulent lymphadenitis;
- phlegmon of the neck;
- myocarditis;
- polyarthritis (infectious form);
- rheumatism;
- meningitis;
- sepsis;
- pyelonephritis.
After treatment, the patient must undergo laboratory tests and, if necessary, have an ultrasound of the heart and an ECG. This is necessary so that the pediatrician can make sure that there are no complications.