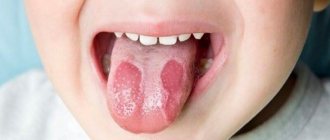
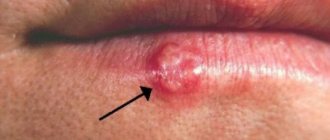
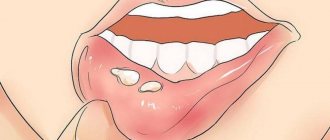
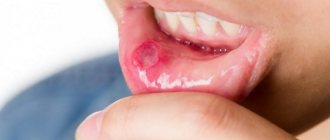
Stomatitis, which occurs in the human oral cavity, is considered primarily a childhood disease, but in fact, more than 20% of adults periodically face a similar problem. This disease manifests itself in the form of yellowish-gray ulcers on the upper or lower palate, throat or tongue of a person.
Stomatitis ulcers that form in the throat cause significant discomfort to an adult or child. Therefore, it is necessary to begin treatment for this disease as soon as possible and take measures to eliminate the symptoms of stomatitis in the mouth. LeaderStom dentistry will tell you about the causes of stomatitis ulcers in the throat and how to cure this disease and avoid possible complications.
Symptoms of stomatitis in the throat
The first signs of the development of stomatitis in the throat can initially be confused with signs of a sore throat, but upon careful examination of the surface of the human oral mucosa, one can notice the characteristic signs of this disease.
Stomatitis in children manifests itself as follows:
- The child's throat turns red and tissue swelling appears.
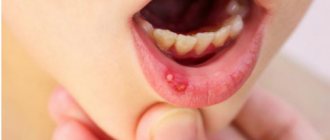
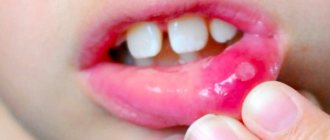
- Stomatitis ulcers appear on the surface of the mucosa. They come in different sizes and are located singly or in groups.
- The baby's temperature rises to 38-39 degrees.
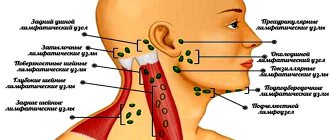
- The submandibular lymph nodes swell.
- The appearance of ulcers in the throat with stomatitis in this case is accompanied by pain, increased salivation, and decreased appetite.
- The child behaves restlessly, cries and is capricious.
The symptoms of stomatitis in children are more pronounced than in adults, and the disease causes children a lot of suffering. To relieve pain, relieve swelling and get rid of stomatitis ulcers in your child’s throat, you need to take your son or daughter to the doctor. The doctor will conduct an examination and diagnosis, and then prescribe appropriate treatment for your child, depending on the form of stomatitis and the reasons that triggered the development of the disease.
Types of aphthous stomatitis
Aphthous inflammation of the oral mucosa occurs:
- sharp;
- chronic recurrent1.
Acute inflammation of the mucous membrane in 70% of cases is observed in children under the age of 3, less often up to 6 years. More often it occurs as an acute infectious disease, with its characteristic sudden onset and symptoms of intoxication1.
Chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis is more common in adults, and is equally common in men and women1. Despite treatment, aphthae appear from 1-2 to 6-8 times a year, more often in spring or autumn8, and no symptoms are observed between these episodes2,3.
Up to contents
Symptoms of stomatitis in adults:
- The disease is accompanied by general malaise, but a person’s temperature rarely rises above 37.5 degrees.
- An adult's throat, just like a child's, with stomatitis becomes red, swollen, and painful ulcers appear on the surface of the mucous membrane.
- Lymph nodes do not always enlarge.
An adult who experiences stomatitis ulcers in the mouth should consult a physician or dentist. Only a doctor will be able to correctly diagnose the disease and prescribe effective treatment for stomatitis formations in the patient’s throat.
Course of the disease
Acute aphthous stomatitis often begins acutely and often against the background of an acute respiratory infection or sore throat1. Body temperature rises, lethargy, weakness, headache, and muscle aches appear8. Against this background, single or multiple aphthae appear on the oral mucosa8, salivation sharply increases, and bad breath appears1. The number of aphthae and their depth and healing time depend on the severity of the disease1.
Chronic aphthous stomatitis can occur in mild or severe forms1,3,4, which can be determined by a dentist.
Up to contents
Causes of stomatitis in the throat
Stomatitis is a disease whose mechanism of occurrence is that the human immune system reacts to irritants in an atypical way, resulting in ulcers in the mouth and throat. This reaction of the immune system can be triggered by bacteria, viruses, fungi and other microorganisms. Therefore, stomatitis in the throat is often a concomitant disease that occurs against the background of another infection.
Based on this, we will name the following causes of stomatitis ulcers in the throat:
- Bacterial infection of the oral mucosa
. Most often, the causative agents of infection are various strains of microorganisms such as streptococci or staphylococci. If a person neglects oral hygiene, or if, for example, he gets a bacterial sore throat, this can trigger the development of stomatitis in the throat. - Viral infections.
In most cases, the formation of stomatitis ulcers in the mouth is provoked by the herpes virus, which penetrates the human body and develops as a separate infection. In this case, small bubbles appear in the throat, which are located in groups. The occurrence of herpetic ulcers is accompanied by itching, pain and redness. - Fungal infection of the oral mucosa.
A fungus of the genus Candida most often develops in the human mouth. Normally, it is always present on the mucous membrane, but weakened immunity, stress, long-term use of antibiotics and hormonal drugs can provoke its growth. As a result, a white coating appears in the throat, palate or tongue of a person, which indicates a fungal infection. The development of stomatitis against the background of a fungal infection is also quite common.
Weakening of the human immune system. The immune system of an adult is weakened by stress and somatic diseases. The child’s immunity is weakened in principle, since it is not yet fully formed and is just learning to fight infections. Stomatitis in this case either occurs as a separate disease or becomes a consequence of some current illness. Avitaminosis. A lack of various vitamins and microelements in the human body can also provoke the formation of stomatitis ulcers in the throat.
Allergic reaction. Allergies to certain foods (chocolate, citrus fruits, peanuts) or the substances they contain (for example, gluten, which is rich in cereals) provoke the appearance of stomatitis ulcers in the throat and on the oral mucosa of a person.
Classification
Depending on the etiology, stomatitis of the throat can be of several types:
- The catarrhal form is more common than other types and is considered the easiest to treat. The main reason for the appearance of inflammation on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity is the unsatisfactory hygienic condition of the teeth and gums.
- The aphthous form is manifested by the formation of blisters on the throat and tonsils. After they burst, the mucous membrane ulcerates. This type of disease is most often localized in the throat.
- Candidal stomatitis is caused by fungi, popularly called thrush. The pathology is characterized by the appearance of a white, thick coating on the affected areas of the mucous membrane. Most often found in the area of the tongue, palate, inner cheeks, and lips. Sometimes candidiasis can also be in the throat.
Necrotic, herpetic, and ulcerative stomatitis are extremely rare. Regardless of the form of the pathology, it can occur in acute and chronic stages.
How to treat stomatitis in adults and children?
The question of how to treat stomatitis in the throat worries people who have had to deal with this disease in the first place. Because the appearance of stomatitis ulcers in the mouth is accompanied by severe unpleasant symptoms, and you want to get rid of them as soon as possible.
Only an experienced doctor - dentist or therapist - can draw up a competent treatment regimen for stomatitis in a patient’s throat. You can seek help from specialists from the LeaderStom network of dental clinics to solve problems associated with the occurrence of stomatitis ulcers.
The method of treating stomatitis in the human throat involves an integrated approach and the use of local and general therapy. In addition, there are prescriptions for the patient’s diet and lifestyle.
The treatment regimen for stomatitis in the human throat includes:
- Gargling with antiseptic solutions or infusions of medicinal herbs.
- Taking antipyretic and painkillers to relieve symptoms of stomatitis.
- Internal administration of antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal, antihistamine or other drugs. Such medications are prescribed by a doctor who first diagnoses the causes of the disease. In accordance with the reason, the choice of drug against stomatitis that occurs in the human oral cavity occurs.
- Taking immunomodulatory drugs and vitamin complexes. It is necessary to support the body, help a person cope with infection, and restore strength. If the causes of stomatitis lie in vitamin deficiency and a weakened immune system, then this is the best way to cope with this disease.
- Compliance with dietary recommendations. In order not to injure the inflamed mucous membrane and ulcers on it, only soft food should be taken, preferably pureed. In this case, puree soups are ideal for a sick person.
- It is necessary to temporarily give up bad habits, such as drinking alcohol and smoking, as this causes an exacerbation of the symptoms of stomatitis localized in the person’s throat.
A timely visit to a doctor, accurate diagnosis and a competent treatment regimen will help save you and your loved ones from oral stomatitis in 7-14 days. The rehabilitation period depends on the severity of the disease and on the reasons that provoked the appearance of stomatitis ulcers in a person’s throat.
The choice of clinic and specialist is of great importance in this situation. As mentioned above, treatment of stomatitis in the mouth is carried out either by a dentist or a therapist. In order to diagnose the disease, you need to come to an appointment with one of these specialists. The doors of the LeaderStom clinic are always open to new patients of any age. Our doctors have been successfully treating oral stomatitis for many years and are happy to offer you their help in solving your health problems.
Literature
- Aphthous stomatitis // Nurse/ No. 5. – 2015. – P. 21.
- Bulkina N.V. Chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis: features of the clinical course and complex treatment // Saratov Medical Scientific Journal / Volume 7. - No. 1. - P. 281-282.
- Strakhova S. Yu., Drobotko L. N. Chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis (lecture) // Regular issues of “RMZh” / No. 29. - dated December 27, 2006. — P. 2096.
- Volkov E. A., Butova V. G., Pozdnyakova T. I., Dzugaeva I. I. Clinical recommendations (treatment protocol) for chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis // Russian Dental Journal / No. 5. – 2014. – P. 35-49.
- Galizina O. A. Main aspects of the occurrence, clinical manifestations, treatment and prevention of chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis // Russian Dental Journal / No. 18(6). – 2014. – P. 39-42.
- Chemicosova T. S. On the prevention of exacerbations of recurrent aphthous stomatitis // Kazan Medical Journal / volume 84. - No. 4. - 2003. - P. 267-269.
- Association of General Practitioners (Family Doctors) of the Russian Federation Clinical recommendations for general practitioners Stomatitis // 2014.
- N. N. Bazhanov Dentistry // ed. Moscow GEOTAR-MED / 2002. – P. 99-100.
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® aerosol // Reg. number P N014010/01 //
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® solution // Reg. number P N014010/02 //
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS // Reg. number LSR-002626/07 //
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS CLASSIC // Reg. number P N015976/01 //
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS EXTRA // Reg. number LSR-004122/09 //
Diagnosis of the disease and its differences from other pathologies
The doctor receives the first data after examining the patient’s mouth. Next, the doctor collects an anamnesis of the disease and the patient must answer when the first symptoms appeared, how quickly the disease developed, whether there were injuries (including burns) to the oral cavity, allergies to foods and medications, whether close relatives suffered from stomatitis.
To identify the causative agent of the disease, you will need to take a smear on the flora and exclude manifestations of herpes and candidiasis. For this purpose, laboratory tests are used - bacterial culture and PCR smear.
For persistent stomatitis, you should check your blood glucose level.
Causes
Stomatitis on the tonsils can be caused by various reasons. Let's conditionally divide them into 3 groups:
- The pathology is provoked by an allergic reaction to food and personal hygiene products. Aggressive environmental influences also cause the development of the disease.
- Infection of the mouth and throat (flu, ARVI, sore throat, purulent diseases of the teeth and gums). The herpes virus, which lives in the body of almost every person, is capable of becoming more active at some point, infecting the oral cavity.
- Injuries to the mucous membrane of the throat, tonsils of various origins (cuts, burns).
Stomatitis on the tonsils mainly occurs due to a weakening of the body's protective functions. Immunity is significantly reduced in cases of oncology, fungal infections, pathologies of the digestive system, and HIV.
Prices
| Name of service | Price, rub.) * |
| Initial consultation with a dentist-therapist | 1,500 rub. |
| Repeated consultation with a dentist-therapist | 800 rub. |
| Treatment of caries (imaging, anesthesia, isolation of the oral cavity, installation of an insulating lining and filling made of composite light-curing imported material) | from 4,350 rub. |
| Comprehensive oral hygiene (OptraGate oral cavity isolation, AirFlow removal of colored plaque, ultrasonic removal of dental plaque, polishing with paste, preventive fluoridation of teeth) | 7,000 rub. |
We accept VISA, MASTERCARD, MAESTRO bank cards for payment.
Would you like us to call you back?
Treatment of herpetic sore throat
Treatment of herpes sore throat in adults should be comprehensive. Typically, the treatment regimen includes the following measures:
- the patient is isolated and placed on bed rest
- you need to drink plenty of fluids and gargle with herbal decoctions
- strict adherence to taking medications prescribed by the doctor for treatment.
First, antihistamines are prescribed to relieve swelling, for example, Suprastin or Claritin. Sore throats are effectively relieved by gargling with decoctions of chamomile, sage, oak bark, tincture of calendula, eucalyptus, and irrigating the throat with antiseptics (Hexoral, Tantum-Verde, Miramistin, Ingalipt, etc.). You can dissolve lozenges for pain in throat. It is recommended to gargle every hour. If you have a severe runny nose, you should rinse your nasal cavity with saline solution.
With herpetic sore throat, you cannot do inhalations, warm up or apply compresses - the thermal effect will only provoke the spread of infection throughout the body.
At temperatures above 38°C, you need to take antipyretic drugs, for example, Ibuprofen. Antibacterial agents are not prescribed for the normal course of the disease. Antibiotics are administered when bacterial complications, such as bronchitis or tracheitis, are added.
It is important to follow a special diet: nothing hot, spicy, or hard that could irritate the mucous membrane of an already sore throat. Food should ideally be liquid-like. It is better to grind the prepared food into puree.
If you adhere to a clear treatment regimen and follow the doctor’s prescriptions, recovery will not take long, and all unpleasant symptoms will quickly disappear.
Prevention
In the oral cavity of any person there is a conditionally pathogenic microflora, which can be activated when immunity decreases. For this reason, it is important to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat well, and treat illnesses.
Hygiene rules must be observed. Do not eat dirty vegetables, wash your hands before eating, and replace your toothbrushes regularly.
For persons predisposed to the disease, any trauma to the oral mucosa should be excluded. Do not eat scalding, hard foods or spicy seasonings. If a wound appears, you should immediately treat it with an antiseptic.
It is imperative to carry out timely treatment of dental and ENT diseases. Chronic diseases and advanced caries are sources of infection.