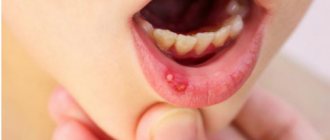
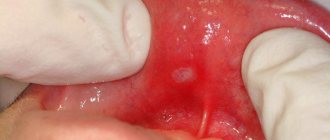
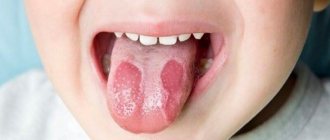
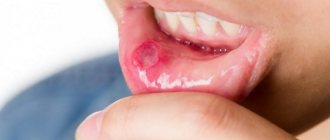
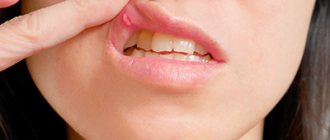
One of the most common diseases of the oral cavity is aphthous stomatitis; it is especially common in children. The disease manifests itself as a rash of gray-yellow ulcers (ulcers), which can be found on the inner surfaces of the lips and cheeks, on the tongue, palate and at the base of the gums. In most cases, the rash is represented by one or two ulcers, but massive accumulations of them are also possible.
Other symptoms of aphthous stomatitis in children include:
- bad breath;
- inflammation of the cervical and occipital lymph nodes;
- elevated temperature;
- loss of appetite;
- general lethargy.
Aphthous stomatitis in children is not contagious. The disease can be caused by various pathogens, so before starting treatment, the doctor must determine through tests what caused it. It is usually associated with viral bacteria and occurs as a complication after suffering from influenza, measles, diphtheria and some other diseases.
There are a number of factors that contribute to the development of aphthous stomatitis in children. This:
- decreased immunity due to frequent colds;
- deficiency in the body of iron, zinc, vitamins A, B, C;
- allergic reactions;
- diseases of teeth and gums;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- damage to the oral mucosa;
- genetic predisposition.
What is aphthous stomatitis
Often, infection of the oral mucosa is accompanied by the formation of ulcers (ulcers). Therefore, the disease is called aphthous, i.e. ulcerative stomatitis. The formation of ulcers begins with slight local redness of some areas of the mucosa, which then ulcerate with the formation of necrotic areas. Aphthae are painful, so the child becomes restless and irritable. The disease most often develops in childhood - 80% of all diagnosed cases. This type of stomatitis is not infectious and is not transmitted by contact.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are usually used during follow-up treatment, when acute manifestations are eliminated.
For the treatment of stomatitis the following is used:
- infusion of chamomile flowers;
- paste from ground burdock seeds with salt and butter;
- decoction of oak bark;
- aloe juice;
- a decoction of the rhizome of snakeweed;
- yarrow decoction;
- infusion of ground rhizome of bergenia;
- infusion of pomegranate peel.
Physiotherapeutic agents include treatment of lesions with ultraviolet rays.
Causes
- Malfunctions of the immune system
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
- Hereditary factor
- Allergies to certain foods and medications
- Avitaminosis
- Unbalanced diet (lack of vitamin B12, folic acid, iron in the diet)
- Tonsillitis, sore throat, pharyngitis
- Local infection with pathogenic microflora (from diseased teeth and gums or from external sources)
- Injury to the mucous membrane (burns, biting, injuries from sharp edges of fillings or braces, etc.)
Features of treatment in children under 3 years of age
Their stomatitis can only be treated by a specialized specialist. The main task of parents of a sick child is to follow the doctor’s recommendations.
For the treatment of stomatitis the following are used:
- local anesthetic ointments, gels (Lidochlor gel and others);
- antiviral drugs (Acicovir, Ganciclovir);
- antifungal agents;
- antibacterial drugs for local and systemic therapy with mandatory sensitivity testing;
- antihistamines;
- in severe cases, steroid drugs are added;
- local treatment with antiseptics (Methylene blue, Iodinol, Miramistin, Rotokan, Hexoral).
It is important to follow a diet during therapy. Do not give your child irritating foods. After eating, be sure to rinse your mouth with herbal decoctions. It is necessary to monitor oral hygiene. And also wash and treat toys with antiseptics.
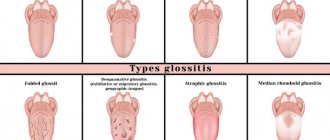
Types of aphthous stomatitis
Depending on the causes of occurrence and the nature of the disease, it is customary to distinguish several subtypes of aphthous stomatitis. The disease can occur in acute or chronic form. The acute course is characterized by the sudden appearance of ulcers with a grayish coating and a red border around the edges. It is usually provoked by a viral infection. If treatment is started in a timely manner, it goes away in about 10 days. The chronic form of the disease is manifested by frequent relapses. In addition to the appearance of aphthae, the child’s lymph nodes increase in size and body temperature rises.
Classification of aphthous stomatitis:
- fibrous - accompanied by the appearance of ulcers and an increase in temperature. The symptoms are similar to herpes, only aphthae are located on the mucous membrane, and not on the skin. The most common type of stomatitis;
- grandular - provoked by a malfunction of the salivary glands, ulcers are localized precisely in this area. The trigger for the onset of the disease may be a respiratory disease or hypothermia;
- necrotic - can manifest itself during any illness when a person’s immunity is weakened. Characterized by necrosis of areas of the epithelium;
- cicatrizing - this form involves the formation of scars (connective tissue) at the site of aft. Features a long treatment time;
- deforming – leads to deformation of the soft tissues of the oral cavity.
- Itching, burning, tingling on the mucous membrane in the initial stage of the disease
- Increase in temperature to 38-39 ° and enlargement of lymph nodes (not always)
- The appearance of ulcers on the inner surface of the mouth (except gums)
- Painful swallowing (in the presence of aphthae on the soft palate and the back of the pharynx)
- Discomfort when chewing food
- Sleep disturbance due to severe pain
- Fatigue, lethargy, irritability
Treatment of the disease depends on the type of stomatitis, so diagnosis before starting treatment is of great importance. The doctor conducts a visual examination and, if necessary, sends for tests: a smear of the epithelium from the ulcer, a blood test. The treatment algorithm is aimed at local treatment of ulcers and eliminating the causes that caused their appearance. As a rule, the doctor prescribes the local use of antiseptics (rinsing and applying gels), antihistamines (for allergic causes of stomatitis), medications to improve immunity, vitamins C and B12, anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics (if necessary).
Important: it is not easy to determine for yourself what type of aphthous stomatitis your child has. But it depends on what medications you need to take. You should not self-medicate, as this may result in a worsening of the baby’s condition. Only a specialist can recognize the form of the disease and prescribe adequate treatment.
Clinical picture
The main symptoms of stomatitis are pain, inability to eat, temperature up to 39º C, swollen lymph nodes, pale mucous membrane. Babies constantly put their fingers in their mouths, trying to soothe the itching. Therefore, this disease first occurs in children aged 1-3 years.
A characteristic symptom is the presence of erosions on the oral mucosa. They are called aphthae, hence the name of the disease.
The disease has five forms:
- Acute and chronic herpetic stomatitis. An infectious disease caused by the herpes simplex virus. Frequent localization: lip, side of the tongue, mucous membrane and folds.
- Chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Characterized by periodic remissions and exacerbations with aphthae rashes.
- Contact allergic stomatitis. Caused by various allergic factors.
- Drug-induced stomatitis. Appears due to medications.
- Traumatic stomatitis. Caused by trauma: sharp crown edge, sharp tooth edge and so on.
Chronicity of the process is associated with untimely consultation with a doctor, attempts at self-medication and individual characteristics of the course of the disease.
Recommendations from home care specialists
In addition to drug therapy, experts recommend:
- increase immunity by taking echinacea, ginseng, eleutherococcus and a course of vitamins;
- maintain oral hygiene;
- relieve local inflammation by rinsing with decoctions of chamomile and oak bark;
- lubricate ulcers with sea buckthorn oil;
- provide the child with a complete balanced diet in finely chopped or pureed form;
- exclude hot, cold, hot, sour and spicy foods from the diet.
Note: the use of traditional medicine in home care is justified only as a supplement to treatment prescribed by a doctor.
The network of dental clinics “Smile” offers services for the diagnosis and treatment of aphthous stomatitis in children. Our specialists are highly qualified and regularly improve their skills in leading centers in Russia and abroad. We have a system of family and cumulative discounts.
You can contact any of the branches of our clinic in Moscow, located within walking distance from the metro:
- Art. Alekseevskaya (VDNKh district, etc. Mira), address: st. 3rd Mytishchiskaya house 3, building 2;
- Art. Shelepikha, address: Shelepikhinskaya embankment, address: building 34, building 1.
Do not delay the start of treatment for stomatitis in children! The sooner therapy is started, the faster the disease will be cured. A comprehensive approach to each clinical case allows our specialists to provide effective assistance, regardless of the severity of the disease. We are waiting for you every day!
Symptoms of the disease and its complications
Aphthous stomatitis does not begin with the formation of ulcers. The stages of the disease are:
- The lymph nodes become inflamed, the temperature rises and general weakness occurs.
- Small blisters form in the mouth, which spontaneously open and turn into aphthae.
- Salivation increases.
- At first, it is unpleasant for the patient to eat food with a pronounced taste, and then chewing any food causes pain.
- With a persistent form of aphthous stomatitis, the lymph nodes become inflamed and become painful on palpation.
- The mucous membranes of the mouth are loose and inflamed.
- A white coating appears on the tongue.
- At the final stage of the disease, aphthae scar, and soreness in the mouth disappears.
If the patient has not received adequate treatment, aphthous stomatitis becomes chronic. Wherein:
- The mucous membranes swell and turn pale.
- Aphthae grow and cover the inner surface of the cheeks, palate and back of the tongue. In advanced forms, the ulcers rise above the surface of the oral mucosa.
- Without receiving proper treatment, the growth of ulcers resumes every two weeks. The wounds bleed and penetrate deeper into the tissues of the mouth.
- When healing, erosions leave deep scars.
Forms of the disease
Aphthous stomatitis can occur in two forms: chronic and acute. Each form of pathology has its own characteristics of symptoms, which help establish the clinical picture during diagnosis.
Acute form of aphthous stomatitis
The pathological condition is accompanied by puffiness and swelling of the mucous membrane, on which aphthae of gray or white color and round shape are formed. With timely initiation of treatment, acute stomatitis lasts up to 10 days. After therapy, the mucous membrane is completely restored.
Chronic form of aphthous stomatitis
It develops in the absence of treatment for acute stomatitis, hereditary predisposition or the presence of chronic diseases that affect the immune system. The peculiarity of the pathology is the occurrence of periodic relapses. The duration of the disease is up to 14–30 days.
Features of formations
The infection affects not only the mucous membrane, but also soft tissues, as well as blood vessels that enlarge and dilate. The result is edema and hypothermia.
Aphthae have characteristic signs:
- clear edges;
- round or oval shape;
- size 3–5 mm;
- yellow, white or gray;
- red edges;
- plurality;
- large distribution area;
- elevation above the surface;
- severe pain.
Aphthous stomatitis occurs in three stages.
- Premonitory. The initial stage, in which the mucous membrane is inflamed, but dry. The child may feel discomfort and pain. The temperature rises. The general condition is deteriorating.
- Rashes. The second stage, at which the child already has rashes. To the deterioration of the general condition, refusal to eat due to pain when eating is added.
- Fading. The disease resolves on its own after 10–14 days, but becomes chronic.
With therapy, complete recovery occurs no earlier than after 7 days. The symptoms are gradually eliminated, and the mucous membrane is covered with a new healthy layer.