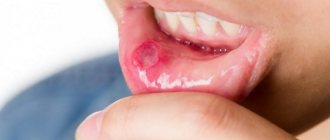
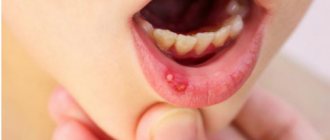
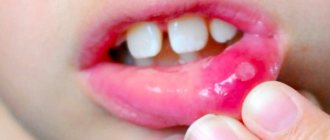
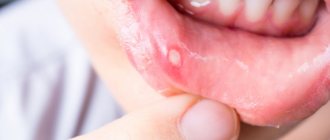
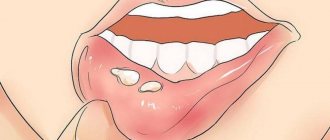
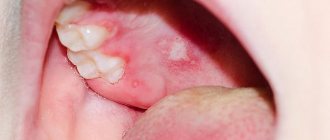
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the mouth (but can also develop on the tongue and lips) that is most often diagnosed in children. Stomatitis in adults is usually a consequence of the introduction of viruses into the oral mucosa. In addition, this disease can occur in the presence of a number of other diseases, due to decreased immunity. For dentists, diagnosing and treating stomatitis in the mouth does not cause any difficulties, while attempts to get rid of the disease on their own can lead to unpleasant consequences
1.What is stomatitis, its types and symptoms
The term stomatitis refers to inflammatory processes in the oral cavity
that cause pain.
Stomatitis can cause discomfort and pain and interfere with eating, sleeping, and other daily activities. Canker sores can occur anywhere in the mouth, including the inside of the cheeks, gums, tongue, lips, and roof of the mouth
.
Types of stomatitis
There are several types of stomatitis, the main ones being:
- Ulcers
, also called aphthous ulcers. They usually appear in the mouth on the cheeks, tongue or lip, and appear as pale or yellowish sores with a red outer border; - Herpes
. Cold sores are fluid-filled sores that are located on or around the lips. Herpes on the gums and upper jaw also occurs, but very rarely. Herpes on the lips first looks like blisters filled with liquid, and then a crust or sore forms on it. Before a cold sore appears, there is often an itching, tingling or burning sensation on the lip. - Irritation of the oral mucosa
. It can be caused by biting the cheeks, tongue or lips, wearing braces, damage to the mucosa from a broken or sharp tooth, burns to the mouth from eating too hot food or liquids, gingivitis and other gum infections, and some autoimmune diseases. For example, systemic lupus, Crohn's disease or Behçet's disease. Mucosal irritation and stomatitis can be a side effect of treatment for other diseases - chemotherapy, antibiotics, drugs used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, epilepsy.
Symptoms of stomatitis
Symptoms of stomatitis depend on what type of stomatitis appears. So, mouth ulcer
usually painful and lasts 5 to 10 days. Often the ulcer appears again. And it is usually not associated with any colds.
Herpes
on the lip is not always painful. Rather, it causes discomfort. Herpes goes away in 7-10 days and its appearance is often a consequence of colds and flu.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Stages of stomatitis
According to the clinical picture, three types of stomatitis are distinguished.
Catarrhal stomatitis
The most common type of stomatitis, caused by poor oral hygiene, tartar and dental diseases. The mucous membranes become inflamed, red and swollen, but there are no ulcers or deep defects. Accompanied by bad breath, increased salivation, dryness and soreness of the mucous membranes.
For catarrhal stomatitis in the mouth in adults, treatment is first of all aimed at relieving inflammation, for which antiseptic solutions, rinses, lozenges, etc. are used. A gentle diet is required to avoid further injury to the mucous membranes.
After eliminating the symptoms of stomatitis, you can treat your teeth and carry out professional hygiene to get rid of tartar and prevent the occurrence of stomatitis in the future.
Ulcerative stomatitis
As a rule, this is the next stage of catarrhal stomatitis. The smell from the mouth intensifies, ulcers with a gray coating appear, eating is accompanied by pain. In some cases, the temperature rises and the lymph nodes become enlarged.
At this stage, only the doctor decides how to treat severe stomatitis and what combination of drugs is suitable in this case: they usually combine painkillers, antihistamines, vitamins, healing agents with antibiotics and treatment of rashes.
Aphthous stomatitis
At this stage, aphthae gradually form - round or oval erosive surfaces 3-5 mm in diameter with a red border and a gray-yellow coating. Aphthae can be single rashes or massively cover the inside of the cheeks and lips, the sides of the tongue, and the palate. Methods for treating stomatitis on the palate in adults depend on the severity of the stage and cause of the disease.
2. Causes of stomatitis
We have already talked above about why irritation of the oral mucosa may begin. Now let's dwell on the question of why ulcers and herpes appear. Ulcers.
In fact, the exact causes of stomatitis in the form of ulcers are not known. But many things can contribute to their development. These include certain medications, oral injuries, poor diet, stress, bacteria and viruses, sudden weight loss and the consumption of certain foods - potatoes, citrus fruits, coffee, chocolate, cheese and nuts.
Stomatitis may be associated with a weakened immune system due to colds, flu, changes in the body's hormonal levels, as well as a lack of vitamin B12 and folic acid. Even accidentally biting the inside of your cheek or chewing on a sharp piece of food can cause an oral ulcer.
Ulcers can occur as a result of a genetic predisposition. In this case, it is considered an autoimmune disease. In general, ulcers appear in about 20% of people, but the disease is not contagious.
Visit our Therapy page
Treatment
Despite the fact that when stomatitis develops in adults, its symptoms and subsequent treatment are interrelated , that is, based on the manifestation of the disease one can roughly get an idea of the cause, in no case should you self-medicate!
Stomatitis can have several causes, and when treating one, a completely different disease can develop.
It may not be stomatitis at all, but, for example, a simple allergy or herpes.
Active substances contained in both medications and medicinal plants may cause allergies or be contraindicated for some people.
3.Herpes
Herpes on the lips
appears due to a virus called herpes simplex virus type 1. Unlike ulcers, herpes is contagious from the moment the herpes blisters rupture until complete recovery. Primary infection often occurs during childhood and can be confused with cold or flu symptoms. Once a person becomes infected with the herpes virus, the virus remains in the body and lies dormant most of the time. But during stress, colds, injuries, hormonal changes, under the influence of sunlight, the virus is activated and herpes appears on the lips.
Herpes tends to appear in the same place. And in addition to infecting other people, the herpes virus can spread to other parts of the infected person's body - the eyes and genitals.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Is stomatitis contagious?
Whether stomatitis is transmitted or not is a question that worries many. Ulcers are not contagious if they are the result of:
– mechanical injuries;
– allergies;
- during intoxication.
If the cause of stomatitis is an infection, then the disease can spread to other people. These types include fungal, herpetic, and infectious stomatitis.
4. Treatment of stomatitis
Stomatitis is treated by dentists.
In general, mouth ulcers usually go away in no longer than two weeks, even without treatment. If the causes of the ulcer are established, the doctor will be able to choose the appropriate treatment. If they are not known, the main therapy will be aimed at alleviating the symptoms of the disease.
The following measures can help relieve pain and inflammation in the mouth:
- You should avoid hot drinks and foods, as well as salty, hot, spicy foods and citrus fruits;
- For severe pain, you can take painkillers;
- Rinsing your mouth with cool water or a small amount of ice can help relieve the burning sensation in your mouth.
To treat an ulcer, which is aimed at eliminating discomfort and protecting against infection, your doctor may recommend drinking more water and rinsing your mouth with salt water. Local anesthesia (such as lidocaine) may relieve pain. But this method for treating stomatitis in children is not recommended. A mixture of hydrogen peroxide and water in a 1:1 ratio or regular baking soda and water can be applied pointwise to the ulcer area. In addition, dentists may prescribe pain-relieving medications and corticosteroid pastes that can protect the affected areas on the lips and gums. Anti-inflammatory pastes, gels and rinses treat ulcers quite effectively and help reduce swelling and pain. They are also effective for severe cases of herpes on days 3-4, when the virus has disappeared but inflammation remains.
In any case, you should consult your doctor before taking medications, as some medications have side effects and are not recommended for people with diabetes and other diseases.
Treatment of herpes
There is no cure for herpes as such. We can only recommend lubricating the area of inflammation with special ointments (usually they contain acyclovir) and applying ice.
Sometimes doctors prescribe antiviral pills for herpes. Some experts believe that they can shorten the healing time of cold sores.
Stomatitis is usually not particularly dangerous, but not all ulcers are harmless. In any case, if stomatitis, inflammation and ulcers do not go away within two weeks, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Symptoms
Symptoms of stomatitis appear depending on the cause. In any case, the first signs are itching and redness of the affected area, the tongue feels uneven. Further, the manifestations are already different from each other.
- Virus - itching intensifies, redness spreads to new areas, rash.
- Bacterial nature - first a rash, then vesicular formations, then blisters, ulcers that become inflamed and or fester.
- Fungi - from the very beginning, a white coating and unbearable itching, accompanied by an unpleasant, sometimes putrid odor from the mouth.
- Increased sugar - the formation of wounds with the release of colorless liquid (ichor), a constant sweetish odor is emitted from the mouth.
- Allergies - a small rash with or without itching, headache, possible weakness, nausea, unfocused attention for a few seconds.
- A sharp increase in temperature to 39 and above, regardless of the time of day, the temperature is not brought down by antipyretics. The skin peels off.
- Immune diseases - the temperature does not rise or drops to 36 and below, weakness, nausea, short-term fainting is possible.
Important! If the symptoms of stomatitis last 5-7 days or longer and no treatment is carried out, the disease goes into an advanced form with possible complications in the form of periodontitis, ulcers in the oral cavity, the development of connective tissue cancer, meningitis, breakthrough of suppuration into the lymphatic system or entry into the blood vessels , and this is blood poisoning, which, if not treated promptly, can be fatal.
How does stomatitis manifest in adults?
Local symptoms include redness, swelling of the mucous membrane, spots, ulcers or wounds in case of mechanical damage1,3. They cause pain or burning5. Plaque may form in the area of inflammation. Sometimes a person complains of bad breath3. The listed symptoms can be severe or minor - it all depends on the depth of the lesion and the duration of the disease3.
In addition to local symptoms, in severe cases there are general ones, similar to those that appear with a cold - increased body temperature, general weakness and lack of appetite2.
to come back to the beginning
How is stomatitis treated in adults?
Complex treatment should be carried out only under the supervision of a doctor. On the one hand, it is important to eliminate the cause of the disease, on the other hand, to alleviate the symptoms and stimulate the restoration of the oral mucosa. The doctor prescribes both local and general therapy, depending on the form of stomatitis.
The following groups of drugs may be used in treatment5:
- antibacterial, antiviral or antifungal (depending on the pathogen);
- antiallergic drugs;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- enzymes;
- agents that stimulate the restoration of the oral mucosa;
- drugs that enhance immunity and improve metabolism.
For some forms of stomatitis, the doctor may prescribe combination medications. For example, Metrogyl Denta®, which is indicated for the treatment of aphthous stomatitis7,8,10.
Metrogyl Denta® is a dental gel that contains metronidazole, which has an antibacterial effect, and the antiseptic chlorhexidine8. This combination can suppress the activity of various types of microorganisms and helps fight infection7,8.
Metrogyl Denta® is widely used in dentistry; it is approved by the Dental Association of Russia (StAR)9. The duration of treatment, dose and frequency of use is determined by the doctor, depending on the degree of damage and severity of the disease.
The appearance of stomatitis may mean that a person has a weakened immune system or that the mucous membrane has been affected by some damaging factor. And sometimes redness and painful sores in the mouth are symptoms of a chronic disease1. A dentist helps to understand the causes and cope with inflammation, and if stomatitis has “deeper roots,” specialized specialists are involved in the treatment. After therapy, it is important to do everything to prevent the disease from occurring again. You need to regularly visit the dentist, replace dentures if they cause mechanical injury, monitor oral hygiene and give up bad habits1,5.
The information in this article is for reference only and does not replace professional advice from a doctor. To make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment, consult a qualified specialist.
to come back to the beginning