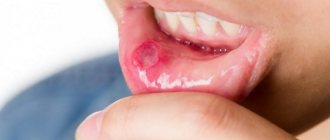
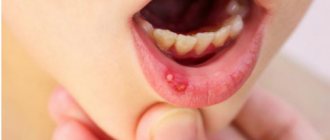
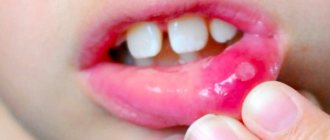
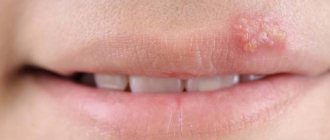
September 9, 2022 Stomatitis is rarely perceived as a serious disease. But the symptoms of this disease indicate otherwise. Pain that worsens with every movement of the lips and tongue, the inability to chew food and sleep disturbances caused by burning and discomfort in the mouth make stomatitis more than a serious problem for those who experience it. But the complications of this disease are no less dangerous. Infection and inflammation left untreated can quickly spread to the mucous membrane of the tonsils, pharynx, and larynx and lead to even more serious illnesses. The listed circumstances are enough to understand: at the first signs of stomatitis, treatment should begin, which should be comprehensive and take into account all aspects of the disease and the patient’s needs.
The importance of the complex action of the drug
A specific type of pathogen is often responsible for the occurrence of stomatitis. But, as the disease develops, the primary infection, for example, viral, may be joined by a secondary one - bacterial or fungal. This requires the use of drugs that have antimicrobial activity against a wide range of pathogens and the ability to relieve inflammation caused by infection. But we should not forget about treating symptoms that cause severe discomfort and generally worsen well-being.
So, to summarize, treatment of stomatitis should include the following areas:
- elimination of symptoms;
- relieving inflammation;
- treatment of bacterial and fungal infections;
- elimination of swelling of the oral mucosa and gums.
Such a drug, which has a complex effect, is Tantum® Verde spray for stomatitis in adults and children over 3 years of age. There is also a Tantum® Verde Forte spray with double concentration of the active ingredient for adults over 18 years of age.
What is stomatitis? Causes, symptoms, treatment of the disease
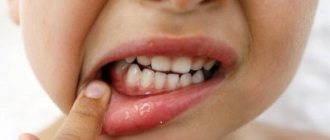
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane in the oral cavity. In one form or another, almost every person, starting with infants, has suffered from this disease at least once in their life. The disease can last from 4 days to 2 weeks, depending on the severity and effectiveness of treatment. Effective treatment of stomatitis at home is also possible, but not every form of this disease. If the disease is left to take its course, complications are likely.
Causes of stomatitis and its types
There are certain types of stomatitis, which differ precisely in the causes of the disease:
- fungal - caused by a special fungus Candida albicans and is considered a contagious disease; accordingly, the cause of the disease may be contact with an already sick person or poor oral hygiene;
- aphthous - caused by a lack of essential vitamins and minerals in the body, especially iron and vitamin B 12;
- herpetic - it is provoked by the herpes virus, it is also contagious, the cause is contact with the skin or lips of the patient;
- occurring after external influences - inflammation of the oral mucosa, like stomatitis in adults, often appears due to improperly selected dentures, as a result of frequent alcohol consumption and smoking.
- allergic - this type of stomatitis often occurs after taking certain medications, especially in large quantities;
- which is a reaction to prolonged administration or use of antibiotics that destroy beneficial microorganisms in the oral cavity, it becomes unprotected from any type of bacteria and viruses.
Sometimes the cause of stomatitis can even be low-quality toothpaste, some components of which can irritate the mucous membrane.
Stomatitis
Symptoms
Each type of stomatitis has common symptoms, but may differ in some ways:
- usually the disease begins with slight redness;
- later, the affected areas begin to itch and hurt;
- in advanced cases, bubbles form that can burst;
- fungal stomatitis has a characteristic white coating, especially in infants;
- herpetic stomatitis is expressed in characteristic rashes on the lips, sometimes large and painful;
- if the disease is not treated, it can progress to inflammation in the facial area.
Sometimes stomatitis can be one of the signs of other diseases, such as diabetes.
IMPORTANT! Stomatitis never causes fever, blood pressure, or stomach upset. These symptoms already indicate another concomitant disease, often more serious.
In infants, a symptom of stomatitis may be refusal to feed or unreasonable crying and general anxiety.
Treatment
If the disease is detected at an early stage, you can use proven home remedies. For example, rinse your mouth with a solution of hydrogen peroxide for several days; it is sold in every pharmacy. Only the peroxide itself should be diluted with water in a ratio of 1:5. Regular consumption of fresh yogurt, but without dyes, helps well - this procedure restores healthy microflora. Interestingly, regular consumption of garlic also helps healthy microflora and kills fungi and viruses.
Before deciding how to treat stomatitis, you need to determine what causes it. If antibiotics are used, success can be achieved by limiting their use. If this is an allergic reaction, remove the allergen and take antihistamines.
In cases where you have to deal with a viral or fungal infection, medications are used to treat stomatitis: antiviral ointments and antifungal agents: miramistin or hexoral.
Traditional medicine recommends rinsing the mouth with decoctions of calendula, St. John's wort or chamomile. As a protective agent for the mucous membrane, you can use sea buckthorn oil or ordinary petroleum jelly. Aloe juice is a good disinfectant for the oral cavity.
Prevention
To prevent the occurrence of this disease, you should follow certain simple rules:
- Maintain regular oral hygiene;
- do not abuse sweets and foods containing yeast;
- do not use antibiotics without a doctor’s prescription;
- Smoking and drinking less.
Do not forget about regular visits to the dentist; this often allows you to identify and prevent almost all possible diseases of the teeth and oral cavity.
Features of using the spray for stomatitis
In addition to the complex action, Tantum® Verde spray for the treatment of stomatitis provides the following advantages:
Uniform spraying of the drug over the entire mucosal area
The droplet type of spraying of the drug is optimal for uniform application of the product to the surface of the mucous membrane. The spray also provides a wide spray angle - this allows you to cover the maximum area of the mucous membrane with a minimum number of injections1,2.
Frequency of use for stomatitis
Benzidamine in the aerosol provides a long-lasting effect, which reduces the frequency of use of Tantum® Verde while maintaining its symptomatic and therapeutic effect.
Be sure to take into account the need for proper use of the spray:
- the drug should be used only in accordance with the instructions and without exceeding the specified dosage;
- It is not recommended to use the spray for more than 7 days without consulting a doctor3;
- After using the spray, you should refrain from eating or drinking for some time.
Principles of treatment of aphthous stomatitis for adults and children
- Combined (local and general) - aimed at all stages of pathogenesis (inflammation, restoration of the integrity of the mucous membrane).
- The diet is as gentle as possible chemically and mechanically with the exception of fried, sour, salty, spicy foods. Small meals 5-6 times a day, pureed food, small portions, warm.
- Antiseptics are used as rinses to prevent further infection of the oral cavity and the development of aphthous stomatitis, and to remove remnants of epithelial decay.
- Furacillin is a nitrofuran derivative, effective against most gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. Recipe for preparing the solution: dissolve a tablet (0.02) of furacillin in 100 ml of warm water.
- Chlorhexidine in the form of 0.1% or 0.05% solution for rinsing and irrigation.
In addition, antiseptics are used in the form of finished dosage forms: miramistin, stomatidine, ingalipt. Painkillers or anesthetics relieve pain from stomatitis, especially severe during eating. Therefore, they are prescribed before meals.
Lidocaine is convenient for use in the form of a gel or aerosol. The mechanism of analgesic action is based on blocking pain impulses in nerve endings. The aerosol is used in 2 doses every 1.5-2 hours, no more than 20 doses per day.
Hexoral spray is indicated for the treatment of aphthous stomatitis in adults. The action lasts up to 12 hours. Apply 2 times a day, morning and evening after meals.
Treatment of stomatitis in children
Children are the most vulnerable category, since they are most often susceptible to the development of stomatitis. Tantum® Verde spray can be used for stomatitis in children starting from 3 years of age. It has a pleasant minty taste that kids like. The design features of the dispenser allow not only to spray the drug over the entire surface of the mucous membrane, but also to apply it pointwise - only to areas of inflammation, without pain or discomfort. The onset of the analgesic effect within a minute4 after spraying and the duration of local anesthesia can help normalize the child’s sleep and appetite.
Reasons contributing to the development of aphthous stomatitis
- Injuries to the oral cavity (mechanical, thermal, chemical).
- Inflammatory diseases of the teeth and nasopharynx: caries, periodontitis, gingivitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis.
- Treatment with cytostatics and radiation therapy for cancer.
- Low quality dentures.
- Neglect of oral hygiene standards.
- AIDS.
- Pregnancy period and menopause in women due to hormonal imbalance.
- Diseases of the digestive system.
- Allergies of various origins (food, medication, microbial).
- Lack of complete proteins, vitamins B, C, folic acid, macroelements selenium, zinc in the diet.
- Diseases that cause depletion of the body (tuberculosis).
- Abuse of strong alcoholic drinks, smoking.
The symptoms of aphthous stomatitis in adults are determined by the pathogen, the general state of local and general immunity, and concomitant diseases.
- Acute aphthous stomatitis begins with fever, weakness, and headache. Regional lymph nodes are enlarged. Hyperemic round or oval spots appear on the oral mucosa, slightly rising above the surface. Then the areas of hyperemia become ulcerated. Erosions are painful, pain not only when chewing, but also at rest. Some erosions are covered with fibrin films. The plaque is tightly fused to the underlying tissues; when you try to remove it, the surface bleeds. Erosions are located singly on the mucous membrane of the lips, cheeks, and lateral surfaces of the tongue.
- Chronic aphthous stomatitis is formed either with inadequate treatment of the acute form of aphthous stomatitis, or with a significant decrease in general immunity. It is characterized by a cyclical course: periods of exacerbation are replaced by remission.
- Necrotic form of aphthous stomatitis. Not only the mucous membrane is affected, but also the submucosal layer. Tissue necrobiosis occurs. Aphthae are deep and their characteristic feature is painlessness. It is observed in debilitated patients with a sharp decrease in general immunity (AIDS, tuberculosis, cancer, blood diseases, severe infectious diseases). The healing period extends from 2 weeks to a month.
- Grandular - aphthae lie at the mouths of the minor salivary glands. Salivation is impaired. Relapse can occur after acute respiratory viral infections, with exacerbation of foci of chronic infection.
- The scarring form of aphthous stomatitis affects young people. The genetic factor of insufficiency of the secretory apparatus of the salivary glands plays a role. Aphthae capture not only the mucous membrane in the area of the terminal salivary sections, but also the underlying connective tissue. The ulcers are painful and reach 1.5 cm in diameter. Dissipated throughout the mucous membrane of the pharynx and anterior palatine arches. The healing process continues for up to 3 months, leaving scars.
- Deforming form of aphthous stomatitis. Due to the destruction of connective tissue and subsequent scar healing, the architecture of the oral cavity is disrupted.
Antibacterial agents for the treatment of aphthous stomatitis
— After bacteriological analysis of the contents of aphthous stomatitis with determination of the causative agent of stomatitis, antibacterial ointments and gels are used.
- Actovegin;
- Holisal;
- Metrogil Denta;
- Wound healing;
— Sea buckthorn oil, rosehip oil, carotoline - these products contribute to better epithelization of defects in the oral mucosa.
— General treatment of aphthous stomatitis is aimed at relieving symptoms of intoxication, boosting immunity, and preventing complications.
— In the acute course of aphthous stomatitis at high temperatures, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed - ibuprofen, paracetamol.
— If stomatitis occurs against the background of a chronic disease, treat the underlying disease.
— In case of reduced immunity, the prescription of immunomodulators: immudol, ribomunil, thymalin.